Compile constants 、ClassLoader class 、 Depth analysis of system class loader
Class initialization

- Class initialization steps

- Class initialization time

Example :
/**
* @name: FinalTest
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 21:51
**/
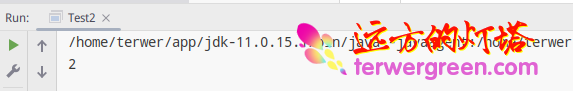
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(FinalTest.x);
}
}
class FinalTest {
public static final int x = 6 / 3;
static {
System.out.println("FinalTest static block");
}
}
Running results
/**
* @name: Test3
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 22:24
**/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(FinalTest2.x);
}
}
class FinalTest2{
public static final int x = new Random().nextInt(100);
static {
System.out.println("FinalTest2 static block");
}
}
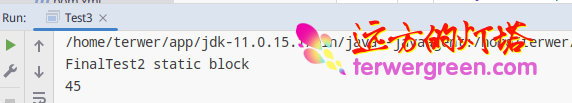
In front of a x Is a constant , It can be determined when compiling , therefore , Class will not be initialized .
Back one x It cannot be determined during compilation , The operation phase can be determined, so , Class will be initialized .

Example
/**
* @name: Test4
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 22:52
**/
public class Test4 {
static {
System.out.println("Test4 static block");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Child.b);
}
}
class Parent {
static int a = 3;
static {
System.out.println("Parent static block");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
static int b = 4;
static {
System.out.println("Child static block");
}
}
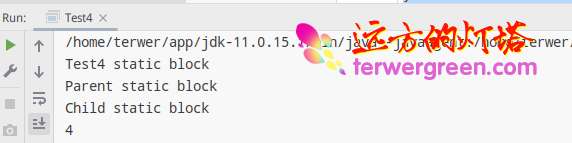
Running results
Example
/**
* @name: Test5
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 23:02
**/
public class Test5 {
static {
System.out.println("Test5 static block");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent2 parent;
System.out.println("-----------------");
parent = new Parent2();
System.out.println(Parent2.a);
System.out.println(Child2.b);
}
}
Running results
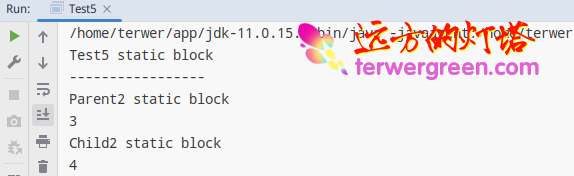
For subclasses in programs “ Active use ” This will cause the parent class to be initialized , however , Active use of the parent class does not result in subclass initialization ( It is impossible to say that a Object Class objects cause all subclasses in the system to be initialized ).

Example
/**
* @name: Test6
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 23:27
**/
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Child3.a);
Child3.dosomething();
}
}
class Parent3 {
static int a = 3;
static {
System.out.println("Parent3 static block");
}
static void dosomething() {
System.out.println("do something");
}
}
class Child3 extends Parent3 {
static {
System.out.println("Child3 static block");
}
}
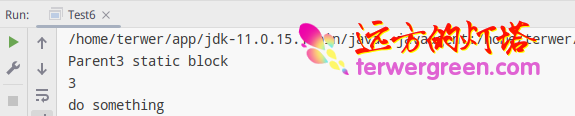
Running results

Example
/**
* @name: Test7
* @author: terwer
* @date: 2022-07-05 23:45
**/
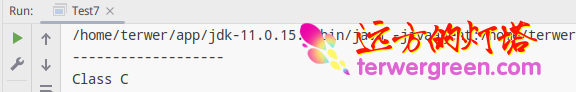
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
Class<?> clazz = classLoader.loadClass("com.terwergreen.classloader.C");
System.out.println("-------------------");
Class.forName("com.terwergreen.classloader.C");
}
}
class C {
static {
System.out.println("Class C");
}
}
Running effect