当前位置:网站首页>[concurrent programming series 9] priorityblockingqueue, delayqueue principle analysis of blocking queue
[concurrent programming series 9] priorityblockingqueue, delayqueue principle analysis of blocking queue
2022-07-27 06:00:00 【m0_ sixty-seven million five hundred and ninety-five thousand n】
[](() The fourth sinking
The fourth cycle is the subscript 0 The location of , That's the element 8, Finish first 1 and 3 Replacement , Then finish 3 and 8 Replacement :
! 《 A big factory Java Analysis of interview questions + Back end development learning notes + The latest architecture explanation video + Practical project source code handout 》 Free open source Prestige search official account 【 Advanced programming 】 [ Insert picture description here ](()
At this time, because the subscript of the smallest node is 2,2<half, So it will cycle again ( Notice that when you cycle again, you still take the first element 8 To compare with the left and right child nodes ), Then it will 8 and 2 Replace , Put the element 2 Assign to subscript 2 The location of , Then the cycle condition is not satisfied at this time , End of cycle , At this time, the element 8 Assign to subscript 6 The location of :

The two processes in the above figure can be seen , Elements 8 Will sink all the way to the end .
This completes the initialization sorting , The final array consists of :[8,5,2,7,6,4,1,9,3] Turn into [1,3,2,5,6,4,8,9,7].
[](() Additive elements ( producer )
put(E) Method will call offer(E) Method ,[ Last article blocked queues ](() In the article , We know ,offer(E) Method is not blocked , And here is an unbounded array, and it won't block , So call directly offer(E) The method is ok :
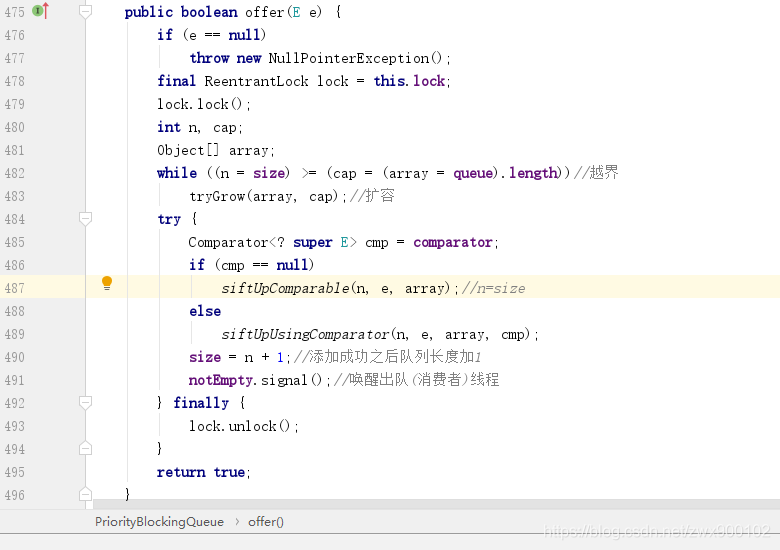
The logic here is simple , First of all, let's see if there is any cross-border , If you cross the boundary, expand the capacity first , Capacity expansion will be discussed later .
Then adding elements is mainly about the floating process , Enter the default collation floating method siftUpComparable:

Or use the binary heap sorted above , Suppose we add an element now 4, You will get the following binary stack :

At this time, in order to ensure that the newly added elements are not smaller than the root node according to the sorting rules , You need to float the newly added element .
[](() For the first time
Find out 4<6, So will 6 At the end of the line , Pay attention to this time 4 It will not be assigned to the queue , because 4 You still need to continue to float to confirm where it is placed

[](() The second rise
The second time you go up, you will find 4<3, Not satisfied, so it will jump out of the loop , Confirm that 4 Placed in the subscript 4 The location of , Complete the operation of inserting elements

[](() Get elements ( consumer )
call take() Method to get the element

It mainly depends on dequeue() Method :

The main logic of this method is :
1、 Get the first element first ( Need to return ) And the last element
2、 Then set the last element to empty
3、 Use the value of the last saved element to sink from scratch
The last step sinking operation is the same as the last step sinking operation of initialization , Until the sinking is completed, a smallest element will be born and put back into the head node
[](() Capacity expansion
Finally, let's analyze the expansion tryGrow Method
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {
lock.unlock(); // Release the lock before capacity expansion ( When expanding the membership fee , Get out of the lock first , Let the dequeued thread operate normally )
Object[] newArray = null;
if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,
0, 1)) {// adopt CAS Operation ensures that only one thread can be expanded
try {
int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?
(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small
(oldCap >> 1));
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {// If it is larger than the current maximum capacity, it may overflow
int minCap = oldCap + 1;
if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)// An exception will be thrown if the expansion of an element also overflows or exceeds the maximum capacity
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;// If the maximum capacity is exceeded after capacity expansion , Only expand to the maximum capacity
}
if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)
newArray = new Object[newCap];// Initialize a new array according to the latest capacity
} finally {
allocationSpinLock = 0;
}
}
if (newArray == null) // If it's empty , Explain the front CAS Failure , There are threads expanding , Give up CPU
Thread.yield();
lock.lock();// Re locking here is to ensure that only one thread can copy the array
if (newArray != null && queue == array) {
queue = newArray;
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);// Copy the old elements to the new array
}
}
[](()DelayQueue
=======================================================================
DelayQueue It's an unbounded blocking queue that supports delay to get elements . Use in queue PriorityQueue To achieve . Elements in the queue must implement Delayed Interface :

Interface defines a getDelay Method to get the current remaining expiration time , In addition, it realizes Comparable Interface , So there will be one compareTo Method .
[](()DelayQueue Examples of use
1、 Create a new object , Realization Delayed , And rewrite getDelay and compareTo
package com.zwx.concurrent.queue.block.model;
import java.sql.Time;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyElement implements Delayed {
private long expireTime;// Expiration time ( millisecond )
private int id;
public long getExpireTime() {
return expireTime;
}
public void setExpireTime(long expireTime) {
this.expireTime = expireTime;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public MyElement(int id, long expireTime) {
this.id = id;
this.expireTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + expireTime;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
// Class receives milliseconds , however getDelay Method in DelayQeue It's nanoseconds , Therefore, a unit conversion is needed here
return unit.convert(expireTime - System.currentTimeMillis(),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
// Be careful , The sorting here should make sure that the one that expires first comes first , Otherwise, it will block the unexpired
return Long.valueOf(expireTime).compareTo(((MyElement) o).expireTime);
}
}
package com.zwx.concurrent.queue.block;
import com.zwx.concurrent.queue.block.model.MyElement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
public class DelayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++){
MyElement myElement = new MyElement(i,i*1000);
list.add(myElement);
}
DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue(list);
while (true){
try {
MyElement myElement = (MyElement) delayQueue.take();
System.out.println(myElement.getId());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
[](()DelayQueue Class diagram
Next, let's look at the class diagram

There are only two constructors , The first is an empty constructor , The second is to initialize a collection by default .
[](() initialization

Call... Through a loop add(e) Method to add , then add Method to call offer(e) Method :

[](() Additive elements ( consumer )
DelayQueue The elements of the queue are maintained internally PriorityQueue On , So the above calls q.offer(e) Method .
leader Indicates the thread that obtains the lock .q.peek()==e Indicates that the current first element is the element just added , So we need to leader Set to null , Wake up and get out of the team ( consumer ) Threads vie for locks again .
q.offer(e) Method is basically the same as the above PriorityBlockingQueue Logical consistency in

[](() Get elements ( consumer )
take Method will get the elements in turn , If the first element does not expire , It's going to keep blocking :
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
for (; {
E first = q.peek();
if (first == null)
available.await();// The queue is empty , The block
else {
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
if (delay <= 0)
return q.poll();// If it's due , Call poll Method takes the element and returns it directly
first = null; // don’t retain ref while waiting
if (leader != null)
available.await();// The header node is not empty , It indicates that a thread holds the lock and is waiting for the expiration time , So block directly
else {//leader==null
Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread();
leader = thisThread;// Set the header node as the current thread , A thread in the table name is waiting for the header node element to expire
try {
available.awaitNanos(delay);// Blocking specified time
} finally {
if (leader == thisThread)
leader = null;
}
}
}
}
} finally {
if (leader == null && q.peek() != null)
available.signal();
lock.unlock();
}
}
[](()Leader-Follower Threading model
stay Leader-follower There are three modes for each thread in the thread model :
leader: Only one thread becomes leader, Such as DelayQueue If there is a thread waiting for the element to expire , Then other threads will block waiting
follower: Will always try to compete leader, Grab leader Then I started working
processing: Threads in process
DelayQueue There's one in the queue leader attribute :private Thread leader = null; What we use is Leader-Follower Threading model .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
How MySQL and redis ensure data consistency
php 定义数组使用逗号,
Day 9. Graduate survey: A love–hurt relationship
数字图像处理 第二章 数字图像基础
10. Gradient, activation function and loss
GBase 8c产品简介
cycleGAN解析
Numpy basic learning
Day 11. Evidence for a mental health crisis in graduate education
Inno setup package jar + H5 + MySQL + redis into exe
MySQL查询操作索引优化实践
golang封装mysql涉及到的包以及sqlx和gorm的区别
14. Example - Multi classification problem
Numpy基础学习
Day 11. Evidence for a mental health crisis in graduate education
pytorch转onnx相关问题
向量和矩阵的范数
个人开发者申请代码签名证书的签发流程
【好文种草】根域名的知识 - 阮一峰的网络日志
Activity之应用进程创建流程简析