当前位置:网站首页>6.824 Lab 3B: Fault-tolerant Key/Value Service
6.824 Lab 3B: Fault-tolerant Key/Value Service
2022-06-13 00:14:00 【Ethan97】
brief introduction
A long-running raft The server will accumulate a large number of logs , These logs will take up a lot of space in memory . In order to compress the space occupied by logs ,raft You can snapshot the current kvserver The state of is stored , And discarded apply Log .
Ideas
After log compression , Because it is contained in snapshot Inside entry All removed ,entry The subscript ≠ entry index - 1, At this time :
entry Subscript = entry index - lastIncludedIndex - 1 or
entry index = entry Subscript + lastIncludedIndex + 1
So we need to reconstruct the original raft from index How to get subscripts .
When to send InstallSnapshotRPC: When leader Find a server Of nextIndex Too small , The index Has been included in snapshot in , At this time leader Hair InstallSnapshotRPC To the server, And put it nextIndex Set as lastIncludedIndex + 1.
Initially considered by kvraft Control when snapshots : namely kvraft call raft Methods provided GetRaftState( Actually called raft.persister.ReadRaftState) obtain raft State data for ,kvraft Then serialize your own state data , Finally save it to persister in . The result is TestSnapshotRecoverManyClients3B There's something about it append Operation missing . The reasons for this are as follows :
Consider one client issue append request , In the... Corresponding to the request entry After submission ,raft Will be entry Of command Submit to kvraft.kvraft Read the request , But before the request is processed ,kvraft The lock on the is takeSnapshot Method take away , And start generating snapshot. At this time raft Of lastApplied The domain has grown by itself , however kvraft Of db This has not been applied yet entry, It's caused raft and kvraft The state does not correspond to ,raft Think that you have apply Of entry More than it really is .
The solution is to generate a snapshot by raft control , When you need to generate snapshot when ,raft adopt applyCh towards kvraft Send a message ( Set up CommandValid = false,CommandType = TakeSnapshot). We will not let kvraft call raft Methods for persistence , Rather let kvraft Pass its serialized data to raft, from raft Make the final persistence . In order to make kvraft Pass the snapshot to raft, Set up channels snapshotCh.
InstallSnapshotRPC The implementation of the :
The paper is described as follows :
because lab There is no requirement to achieve snapshot Fragmentation , Just implement 1.5.6.7.8. Five o'clock . In particular, it needs to be considered clearly commitIndex, lastApplied and lastIncludedIndex The relationship between , Otherwise, it will cause lastApplied < 0 The situation of ; Be careful not to violently lastIncludedIndex The post log is discarded , This may cause the submitted logs to be lost ; We will kvraft The required snapshot is sent to applyCh in .
Summarized below :
- Leave the task of checking when the snapshot is taken to raft,raft In some logs apply Check whether a snapshot is required after ( Submit log to
applyChfromapplyCommittedEntriesbe responsible for ), Avoided raft In a goroutine Commit log updateslastApplied, The other goroutine Concurrent snapshot generation ; - raft Through special
ApplyMsgnotice kvraft Send the snapshot toSnapshotChin , from raft Is responsible for callingraft.persister.SaveSnapshotAndState; - raft In the installation snapshot When will snapshot adopt
applyChSend to kvraft.
Realization
server.go:
package kvraft
import (
"../labgob"
"../labrpc"
"../raft"
"bytes"
"log"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
"time"
)
const Debug = 0
func DPrintf(format string, a ...interface{
}) (n int, err error) {
if Debug > 0 {
log.Printf(format, a...)
}
return
}
const (
Timeout = 800 * time.Millisecond // request timeout duration
)
type Op struct {
Key string
Value string
Type string // type of operation is either get/put/append
ClientId int64
RequestId int
}
type KVServer struct {
mu sync.Mutex
me int
rf *raft.Raft
applyCh chan raft.ApplyMsg
snapshotCh chan []byte
dead int32 // set by Kill()
maxRaftState int // snapshot if log grows this big
Db map[string]string
index2Ch map[int]chan Op // log index -> notification channel, to notify waiting goroutine
LastAppliedRequestId map[int64]int // clientId -> last applied request id, to avoid applying a duplicated command
}
func (kv *KVServer) Get(args *GetArgs, reply *GetReply) {
command := Op{
Key: args.Key,
Value: "",
Type: "Get",
ClientId: args.ClientId,
RequestId: args.RequestId,
}
isLeader := kv.startCommand(command, Timeout)
if !isLeader {
reply.Err = ErrWrongLeader
return
}
kv.mu.Lock()
reply.Value = kv.Db[args.Key]
kv.mu.Unlock()
reply.Err = OK
return
}
func (kv *KVServer) PutAppend(args *PutAppendArgs, reply *PutAppendReply) {
command := Op{
Key: args.Key,
Value: args.Value,
Type: args.Op,
ClientId: args.ClientId,
RequestId: args.RequestId,
}
isLeader := kv.startCommand(command, Timeout)
if !isLeader {
reply.Err = ErrWrongLeader
return
}
reply.Err = OK
return
}
func (kv *KVServer) startCommand(command Op, timeout time.Duration) (isLeader bool) {
kv.mu.Lock()
index, _, isLeader := kv.rf.Start(command)
if !isLeader {
kv.mu.Unlock()
return
}
if _, ok := kv.index2Ch[index]; !ok {
kv.index2Ch[index] = make(chan Op, 1)
}
ch := kv.index2Ch[index]
kv.mu.Unlock()
select {
case op := <-ch:
kv.mu.Lock()
delete(kv.index2Ch, index)
if op.RequestId != command.RequestId || op.ClientId != command.ClientId {
// One way to do this is for the server to detect that it has lost leadership,
// by noticing that a different request has appeared at the index returned by Start()
isLeader = false
}
kv.mu.Unlock()
case <-time.After(timeout):
isLeader = false
}
return
}
// listener is in charge of reading from apply channel
func (kv *KVServer) listener() {
for !kv.killed() {
msg := <-kv.applyCh
if msg.CommandValid == false {
if msg.CommandType == raft.InstallSnapshot {
kv.mu.Lock()
snapshot := msg.Command.([]byte)
kv.installSnapshot(snapshot)
kv.mu.Unlock()
} else if msg.CommandType == raft.TakeSnapshot {
kv.mu.Lock()
snapshot := kv.snapshot()
kv.mu.Unlock()
kv.snapshotCh <- snapshot
}
continue
}
kv.mu.Lock()
op := msg.Command.(Op)
lastAppliedRequestId, ok := kv.LastAppliedRequestId[op.ClientId]
// this is a command not applied before
if !ok || lastAppliedRequestId < op.RequestId {
kv.LastAppliedRequestId[op.ClientId] = op.RequestId
switch op.Type {
case "Put":
kv.Db[op.Key] = op.Value
case "Append":
kv.Db[op.Key] += op.Value
}
}
// although this is a command that applied before
// some client may be waiting for its result, same command but append to log twice
// we should send message to the waiting goroutine anyway
ch, ok := kv.index2Ch[msg.CommandIndex]
kv.mu.Unlock()
if ok {
ch <- op
}
}
}
// the tester calls Kill() when a KVServer instance won't
// be needed again. for your convenience, we supply
// code to set rf.dead (without needing a lock),
// and a killed() method to test rf.dead in
// long-running loops. you can also add your own
// code to Kill(). you're not required to do anything
// about this, but it may be convenient (for example)
// to suppress debug output from a Kill()ed instance.
func (kv *KVServer) Kill() {
atomic.StoreInt32(&kv.dead, 1)
kv.rf.Kill()
// Your code here, if desired.
}
func (kv *KVServer) killed() bool {
z := atomic.LoadInt32(&kv.dead)
return z == 1
}
// servers[] contains the ports of the set of
// servers that will cooperate via Raft to
// form the fault-tolerant key/value service.
// me is the Index of the current server in servers[].
// the k/v server should store snapshots through the underlying Raft
// implementation, which should call persister.SaveStateAndSnapshot() to
// atomically save the Raft state along with the snapshot.
// the k/v server should snapshot when Raft's saved state exceeds maxRaftState bytes,
// in order to allow Raft to garbage-collect its log. if maxRaftState is -1,
// you don't need to snapshot.
// StartKVServer() must return quickly, so it should start goroutines
// for any long-running work.
func StartKVServer(servers []*labrpc.ClientEnd, me int, persister *raft.Persister, maxraftstate int) *KVServer {
// call labgob.Register on structures you want
// Go's RPC library to marshall/unmarshall.
labgob.Register(Op{
})
kv := new(KVServer)
kv.me = me
kv.maxRaftState = maxraftstate
kv.index2Ch = make(map[int]chan Op)
kv.LastAppliedRequestId = make(map[int64]int)
kv.Db = make(map[string]string)
kv.snapshotCh = make(chan []byte)
kv.applyCh = make(chan raft.ApplyMsg)
kv.rf = raft.Make(servers, me, persister, kv.applyCh)
kv.rf.SetSnapshotCh(kv.snapshotCh)
kv.rf.SetMaxRaftState(kv.maxRaftState)
go kv.listener()
return kv
}
// get snapshot data of kvserver
func (kv *KVServer) snapshot() []byte {
w := new(bytes.Buffer)
e := labgob.NewEncoder(w)
err := e.Encode(kv.Db)
err = e.Encode(kv.LastAppliedRequestId)
err = e.Encode(kv.maxRaftState)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("[%d] fails to take snapshot.", kv.me)
}
return w.Bytes()
}
// install a given snapshot
func (kv *KVServer) installSnapshot(snapshot []byte) {
if snapshot == nil || len(snapshot) < 1 {
// bootstrap without any state?
return
}
r := bytes.NewBuffer(snapshot)
d := labgob.NewDecoder(r)
var Db map[string]string
var LastAppliedRequestId map[int64]int
var MaxRaftState int
if d.Decode(&Db) != nil || d.Decode(&LastAppliedRequestId) != nil ||
d.Decode(&MaxRaftState) != nil {
log.Fatalf("[%d] fails to read persistent snapshot", kv.me)
} else {
kv.Db = Db
kv.LastAppliedRequestId = LastAppliedRequestId
kv.maxRaftState = MaxRaftState
}
}
raft.go:
package raft
// this is an outline of the API that raft must expose to
// the service (or tester). see comments below for
// each of these functions for more details.
//
// rf = Make(...)
// create a new Raft server.
// rf.Start(command interface{}) (index, Term, isleader)
// start agreement on a new log entry
// rf.GetState() (Term, isLeader)
// ask a Raft for its current Term, and whether it thinks it is leader
// ApplyMsg
// each time a new entry is committed to the log, each Raft peer
// should send an ApplyMsg to the service (or tester)
// in the same server.
import (
"bytes"
"log"
"math/rand"
"sync"
"time"
)
import "sync/atomic"
import "../labrpc"
import "../labgob"
// as each Raft peer becomes aware that successive log entries are
// committed, the peer should send an ApplyMsg to the service (or
// tester) on the same server, via the applyCh passed to Make(). set
// CommandValid to true to indicate that the ApplyMsg contains a newly
// committed log entry.
//
// in Lab 3 you'll want to send other kinds of messages (e.g.,
// snapshots) on the applyCh; at that point you can add fields to
// ApplyMsg, but set CommandValid to false for these other uses.
type ApplyMsg struct {
CommandValid bool
Command interface{
}
CommandIndex int
CommandTerm int
CommandType int
}
// types of command
const (
InstallSnapshot = iota
TakeSnapshot
)
// states of a raft server
const (
Follower = iota
Leader
Candidate
)
// time-related constants, in millisecond
const (
FixedTimeout = 210
RandomTimeout = 500
CheckTimeoutPeriod = 10
HeartbeatPeriod = 100
)
type Entry struct {
Command interface{
}
Term int
}
// A Go object implementing a single Raft peer.
type Raft struct {
mu sync.Mutex // Lock to protect shared access to this peer's state
peers []*labrpc.ClientEnd // RPC end points of all peers
persister *Persister // Object to hold this peer's persisted state
me int // this peer's index into peers[]
dead int32 // set by Kill()
// persistent state on all servers:
currentTerm int // latest Term server has seen (initialized to 0 on first boot, increases monotonically)
votedFor int // CandidateId that received vote in current Term (or null if none)
log []Entry // log entries; each entry contains command for state machine, and Term when entry was received by leader (first index is 1)
lastIncludedIndex int // last included index of snapshot
lastIncludedTerm int // last included term of snapshot
// volatile state on all servers:
commitIndex int // index of highest log entry known to be committed (initialized to 0, increases monotonically)
lastApplied int // index of highest log entry applied to state machine (initialized to 0, increases monotonically)
state int // each server has three state: Follower/Leader/Candidate
timer Timer // time a server, if time-out, then convert to candidate and kick off an election
applyCh chan ApplyMsg // channel to send message to application
snapshotCh chan []byte // channel used by application to send snapshot to raft
newApplicable *sync.Cond // condition variable used to wake goroutine that apply committed entries
maxRaftState int // maximum raft state size, when is exceeded, raft should take a snapshot
// volatile state on leaders:
nextIndex []int // for each server, index of the next log entry to send to that server (initialized to leader last log index + 1)
matchIndex []int // for each server, index of highest log entry known to be replicated on server (initialized to 0, increases monotonically)
}
type AppendEntriesArgs struct {
Term int // leader’s term
LeaderId int // so follower can redirect clients
PrevLogIndex int // index of log entry immediately preceding new ones
PrevLogTerm int // term of prevLogIndex entry
Entries []Entry // log entries to store (empty for heartbeat; may send more than one for efficiency)
LeaderCommit int // leader’s commitIndex
}
type AppendEntriesReply struct {
Term int // currentTerm, for leader to update itself
Success bool // true if follower contained entry matching prevLogIndex and prevLogTerm
// additional information needed to back up faster
ConflictTerm int // term of the conflicting entry
FirstConflictTermIndex int // index of the first entry of conflicting term
LastLogIndex int // index of the last log entry
}
type RequestVoteArgs struct {
Term int // candidate’s term
CandidateId int // candidate requesting vote
LastLogIndex int // index of candidate’s last log entry
LastLogTerm int // Term of candidate’s last log entry
}
type RequestVoteReply struct {
Term int // currentTerm, for candidate to update itself
VoteGranted bool // true means candidate received vote
}
type InstallSnapshotArgs struct {
Term int // term of RPC caller
LeaderId int // id of this leader
LastIncludedIndex int // last included index of snapshot
LastIncludedTerm int // last included term of snapshot
Snapshot []byte // sole bytes of snapshot
}
type InstallSnapshotReply struct {
Term int
}
type Timer struct {
startTime time.Time
timeout time.Duration
r *rand.Rand
}
// convert from index to position in log
func (rf *Raft) index2Pos(index int) int {
return index - rf.lastIncludedIndex - 1
}
func (t *Timer) isExpired() bool {
return time.Now().Sub(t.startTime) > t.timeout
}
func (t *Timer) reset() {
t.timeout = FixedTimeout*time.Millisecond +
time.Duration(t.r.Int63n(RandomTimeout))*time.Millisecond
t.startTime = time.Now()
}
// return currentTerm and whether this server
// believes it is the leader.
func (rf *Raft) GetState() (term int, isLeader bool) {
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
term = rf.currentTerm
isLeader = rf.state == Leader
return
}
func (rf *Raft) RequestVote(args *RequestVoteArgs, reply *RequestVoteReply) {
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
reply.VoteGranted = false
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
// 1. Reply false if term < currentTerm (§5.1)
if args.Term < rf.currentTerm {
return
}
// If RPC request or response contains term T > currentTerm: set currentTerm = T, convert to follower (§5.1)
// this server MUST NOT immediately convert to follower of this candidate
// we still need to check condition 2. to decide whether we vote for a server
if args.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.convertToFollower(args.Term)
}
// 2. If votedFor is null or candidateId, and candidate’s log is at least as up-to-date as receiver’s log, grant vote (§5.2, §5.4)
// Raft determines which of two logs is more up-to-date by comparing the index and term of the last entries in the logs.
// If the logs have last entries with different terms, then the log with the later term is more up-to-date.
// If the logs end with the same term, then whichever log is longer is more up-to-date.
lastLogTerm, lastLogIndex := rf.lastIncludedTerm, rf.lastIncludedIndex
if len(rf.log) > 0 {
lastLogTerm = rf.log[len(rf.log)-1].Term
lastLogIndex = rf.lastIncludedIndex + len(rf.log)
}
if (rf.votedFor == -1 || rf.votedFor == args.CandidateId) &&
(args.LastLogTerm > lastLogTerm || args.LastLogTerm == lastLogTerm && args.LastLogIndex >= lastLogIndex) {
rf.state = Follower
rf.timer.reset()
rf.votedFor = args.CandidateId
rf.persist()
reply.VoteGranted = true
}
}
func (rf *Raft) AppendEntries(args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) {
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
reply.Success = false
reply.ConflictTerm = -1
reply.LastLogIndex = -1
// 1. Reply false if term < currentTerm (§5.1)
if args.Term < rf.currentTerm {
return
}
// this is a legit leader because term >= currentTerm, therefore we reset timer
rf.timer.reset()
// If RPC request or response contains term T > currentTerm: set currentTerm = T, convert to follower (§5.1)
// if this leader has a higher term, then we should adopt his term and convert to follower.
// we should set votedFor = args.leaderId, since this is a legit leader and we do not expect to vote for anyone else.
// if we set votedFor = -1, and then some server from previous term crashes,
// and then reboot and kick off an election at this term, servers with votedFor = -1
// may vote for them even though they are following this leader.
// this reboot server may become a leader and overwrite committed entries.
if args.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.currentTerm = args.Term
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = args.LeaderId
rf.persist()
} else if rf.state != Follower {
rf.state = Follower
}
DPrintf("[%d] receives AppendEntries RPC from %d, (currentTerm = %d, logLength = %d)", rf.me, args.LeaderId, rf.currentTerm, len(rf.log))
// 2. Reply false if log does not contain an entry at prevLogIndex whose term matches prevLogTerm (§5.3)
// because snapshot only include applied entries, which are also committed, and a leader always has all committed entries
// if pos < 0, it means that log entry is included in the snapshot, we will simply accept it
pos := rf.index2Pos(args.PrevLogIndex)
if pos >= 0 && (pos >= len(rf.log) || rf.log[pos].Term != args.PrevLogTerm) {
lastLogIndex := rf.lastIncludedIndex
if len(rf.log) > 0 {
lastLogIndex = rf.lastIncludedIndex + len(rf.log)
}
reply.LastLogIndex = lastLogIndex
if pos < len(rf.log) {
reply.ConflictTerm = rf.log[pos].Term
reply.FirstConflictTermIndex = rf.firstIndex(reply.ConflictTerm)
}
return
}
// 3. If an existing entry conflicts with a new one (same pos but different terms),
// delete the existing entry and all that follow it (§5.3)
// do not truncate its entries if they have the same term
// check entries until they don't match
cur := 0
for cur < len(args.Entries) && cur+pos+1 < len(rf.log) {
if cur+pos+1 >= 0 && rf.log[cur+pos+1].Term != args.Entries[cur].Term {
break
}
cur++
}
args.Entries = args.Entries[cur:]
// 4. Append any new entries not already in the log
// truncate rf.log only when new entries present, prevent it from truncating valid entries
if len(args.Entries) > 0 {
DPrintf("[%d] truncates its log from len = %d to len = %d", rf.me, len(rf.log), args.PrevLogIndex+pos)
rf.log = rf.log[:cur+pos+1]
rf.log = append(rf.log, args.Entries...)
rf.persist()
}
// 5. If leaderCommit > commitIndex, set commitIndex = min(leaderCommit, index of last new entry)
if args.LeaderCommit > rf.commitIndex {
DPrintf("[%d] updates its commitIndex from %d to %d", rf.me, rf.commitIndex, min(args.LeaderCommit, len(rf.log)))
rf.commitIndex = min(args.LeaderCommit, rf.lastIncludedIndex+len(rf.log))
}
rf.newApplicable.Signal()
reply.Success = true
}
// find first index of the given term
func (rf Raft) firstIndex(term int) int {
left, right, pos := 0, len(rf.log)-1, -1
for left <= right {
mid := left + (right-left)/2
if rf.log[mid].Term < term {
left = mid + 1
} else if rf.log[mid].Term > term {
right = mid - 1
} else {
pos = mid
right = mid - 1
}
}
if pos == -1 {
return -1
}
return pos + rf.lastIncludedIndex + 1
}
// find last index of the given term
func (rf *Raft) lastIndex(term int) int {
left, right, pos := 0, len(rf.log)-1, -1
for left <= right {
mid := left + (right-left)/2
if rf.log[mid].Term < term {
left = mid + 1
} else if rf.log[mid].Term > term {
right = mid - 1
} else {
pos = mid
left = mid + 1
}
}
if pos == -1 {
return -1
}
return pos + rf.lastIncludedIndex + 1
}
// the service using Raft (e.g. a k/v server) wants to start
// agreement on the next command to be appended to Raft's log. if this
// server isn't the leader, returns false. otherwise start the
// agreement and return immediately. there is no guarantee that this
// command will ever be committed to the Raft log, since the leader
// may fail or lose an election. even if the Raft instance has been killed,
// this function should return gracefully.
//
// the first return value is the index that the command will appear at
// if it's ever committed. the second return value is the current
// Term. the third return value is true if this server believes it is
// the leader.
func (rf *Raft) Start(command interface{
}) (index, term int, isLeader bool) {
index = -1
term = -1
isLeader = false
rf.mu.Lock()
// return false if this is not the leader
if rf.state != Leader || rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
isLeader = true
index = rf.lastIncludedIndex + len(rf.log) + 1
term = rf.currentTerm
// append new entry to leader
e := Entry{
Command: command, Term: rf.currentTerm}
rf.log = append(rf.log, e)
DPrintf("[%d] appends new entry to log from start function, command=%v, term=%v", rf.me, e.Command, e.Term)
rf.persist()
rf.mu.Unlock()
rf.callAppendEntries()
return
}
// caller should hold rf.mu while calling this function
func (rf *Raft) maxCommitIndex() int {
maxCommit := rf.commitIndex
next := rf.commitIndex + 1
for rf.canCommit(next) {
// to eliminate problems like figure 8
// Raft never commits log entries from previous terms by counting replicas.
// leader commits an entry from this term to implicitly commit entries from previous term
pos := rf.index2Pos(next)
if rf.log[pos].Term == rf.currentTerm {
maxCommit = next
}
next++
}
return maxCommit
}
// check if entry[index] is allowed to be committed
func (rf *Raft) canCommit(index int) bool {
if index > rf.lastIncludedIndex+len(rf.log) {
return false
}
// count servers that have log[index]
count := 1
for i, n := range rf.matchIndex {
if i == rf.me {
continue
}
if n >= index {
count++
}
}
return count > len(rf.peers)/2
}
// the tester doesn't halt goroutines created by Raft after each test,
// but it does call the Kill() method. your code can use killed() to
// check whether Kill() has been called. the use of atomic avoids the
// need for a lock.
// the issue is that long-running goroutines use memory and may chew
// up CPU time, perhaps causing later tests to fail and generating
// confusing debug output. any goroutine with a long-running loop
// should call killed() to check whether it should stop.
func (rf *Raft) Kill() {
atomic.StoreInt32(&rf.dead, 1)
// Your code here, if desired.
}
func (rf *Raft) killed() bool {
z := atomic.LoadInt32(&rf.dead)
return z == 1
}
// the service or tester wants to create a Raft server. the ports
// of all the Raft servers (including this one) are in peers[]. this
// server's port is peers[me]. all the servers' peers[] arrays
// have the same order. persister is a place for this server to
// save its persistent state, and also initially holds the most
// recent saved state, if any. applyCh is a channel on which the
// tester or service expects Raft to send ApplyMsg messages.
// Make() must return quickly, so it should start goroutines
// for any long-running work.
func Make(peers []*labrpc.ClientEnd, me int,
persister *Persister, applyCh chan ApplyMsg) *Raft {
rf := &Raft{
}
rf.peers = peers
rf.persister = persister
rf.me = me
rf.applyCh = applyCh
rf.log = make([]Entry, 0)
rf.lastIncludedIndex = 0
rf.lastIncludedTerm = 0
rf.commitIndex = 0
rf.lastApplied = 0
rf.maxRaftState = -1
rf.newApplicable = sync.NewCond(&rf.mu)
rf.timer = Timer{
startTime: time.Now(), r: rand.New(rand.NewSource(int64(me + 1)))}
rf.state = Follower
rf.timer.reset()
// initialize from state persisted before a crash
rf.readPersist(persister.ReadRaftState())
// notify kvserver to install snapshot
msg := ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: false,
Command: rf.persister.ReadSnapshot(),
CommandIndex: 0,
CommandTerm: 0,
CommandType: InstallSnapshot,
}
go func(msg ApplyMsg) {
rf.applyCh <- msg
}(msg)
// periodically check if it hits timeout
go rf.periodicTimeout()
// monitor if there's any newly committed entry to apply
go rf.applyCommittedEntries()
return rf
}
func (rf *Raft) sendRequestVote(server int, args *RequestVoteArgs, reply *RequestVoteReply) bool {
ok := rf.peers[server].Call("Raft.RequestVote", args, reply)
return ok
}
func (rf *Raft) sendAppendEntries(server int, args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) bool {
ok := rf.peers[server].Call("Raft.AppendEntries", args, reply)
return ok
}
func (rf *Raft) periodicTimeout() {
for !rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Lock()
// not a leader when timer expires, convert to candidate and kick off an election
if rf.state != Leader && rf.timer.isExpired() {
go rf.kickOffElection()
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
time.Sleep(CheckTimeoutPeriod * time.Millisecond)
}
}
func (rf *Raft) periodicHeartbeat() {
for !rf.killed() {
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.state == Leader {
rf.mu.Unlock()
rf.callAppendEntries()
} else {
// not a leader anymore, exit this goroutine
rf.mu.Unlock()
return
}
time.Sleep(HeartbeatPeriod * time.Millisecond)
}
}
func (rf *Raft) kickOffElection() {
rf.mu.Lock()
rf.timer.reset()
rf.state = Candidate
rf.currentTerm++
rf.votedFor = rf.me
rf.persist()
DPrintf("[%d] kicks off an election at term %d", rf.me, rf.currentTerm)
// record rf.currentTerm because we need to release the lock while calling RequestVote RPC
term := rf.currentTerm
voteCount := 1
done := false
rf.mu.Unlock()
for i := range rf.peers {
if i == rf.me {
continue
}
go func(server int) {
voteGranted := rf.callRequestVote(server, term)
if !voteGranted {
return
}
// receive vote from server
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
voteCount++
DPrintf("[%d] gets vote from %d.", rf.me, server)
// if this goroutine sees there's not enough vote, exits
if done || voteCount <= len(rf.peers)/2 {
return
}
// get enough votes, become a leader
done = true
// double check if it's still in the term when the election started
if rf.currentTerm == term {
DPrintf("[%d] gets enough votes and now becomes the leader (currentTerm = %d, voteCount = %d, numPeer = %d)", rf.me, rf.currentTerm, voteCount, len(rf.peers))
// we should not set votedFor = -1, since a leader should not vote for anyone else in his term
rf.initializeLeader()
// start a go routine to send out heartbeat periodically
go rf.periodicHeartbeat()
}
}(i)
}
}
// caller should hold rf.mu while calling this function
func (rf *Raft) initializeLeader() {
rf.state = Leader
// nextIndex is initialized to the end of the log
rf.nextIndex = make([]int, len(rf.peers))
for i := 0; i < len(rf.nextIndex); i++ {
rf.nextIndex[i] = rf.lastIncludedIndex + len(rf.log) + 1
}
// match index is initialized to 0
rf.matchIndex = make([]int, len(rf.peers))
for i := 0; i < len(rf.matchIndex); i++ {
rf.matchIndex[i] = 0
}
}
// since sending on the applyCh can block, it must be done in a single goroutine.
// this goroutine shouldn't hold any lock while sending message into rf.applyCh
func (rf *Raft) applyCommittedEntries() {
for !rf.killed() {
rf.newApplicable.L.Lock()
// check if there is any new applicable entry
for rf.lastApplied >= rf.commitIndex {
rf.newApplicable.Wait()
}
var messages []ApplyMsg
// apply committed entries
for i := rf.lastApplied + 1; i <= rf.commitIndex; i++ {
pos := rf.index2Pos(i)
msg := ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: true,
Command: rf.log[pos].Command,
CommandIndex: i,
CommandTerm: rf.log[pos].Term,
}
messages = append(messages, msg)
}
rf.newApplicable.L.Unlock()
for _, m := range messages {
rf.applyCh <- m
rf.mu.Lock()
rf.lastApplied++
DPrintf("[%d] applies entry[%d].(Command=%v).", rf.me, m.CommandIndex, m.Command)
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
rf.mu.Lock()
if rf.shouldSnapshot() {
rf.mu.Unlock()
msg := ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: false,
Command: nil,
CommandIndex: 0,
CommandTerm: 0,
CommandType: TakeSnapshot,
}
rf.applyCh <- msg
snapshot := <-rf.snapshotCh
rf.snapshotAndTrim(snapshot)
} else {
rf.mu.Unlock()
}
}
}
func (rf *Raft) callAppendEntries() {
rf.mu.Lock()
// update leader's commitIndex every time before sending heartbeat
rf.commitIndex = rf.maxCommitIndex()
// new committed entry, wake goroutine applyCommittedEntries to apply theses entries
rf.newApplicable.Signal()
me := rf.me
rf.mu.Unlock()
for i := 0; i < len(rf.peers); i++ {
if i == me {
continue
}
rf.mu.Lock()
// nextIndex backs up to a position that leader doesn't have anymore
pos := rf.index2Pos(rf.nextIndex[i])
if pos < 0 {
DPrintf("[%d] sends snapshot to %d.", rf.me, i)
rf.mu.Unlock()
rf.callInstallSnapshot(i)
rf.nextIndex[i] = rf.lastIncludedIndex + 1
continue
}
var prevLogTerm int
if pos == 0 {
prevLogTerm = rf.lastIncludedTerm
} else {
prevLogTerm = rf.log[pos-1].Term
}
args := AppendEntriesArgs{
Term: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
PrevLogIndex: rf.nextIndex[i] - 1,
PrevLogTerm: prevLogTerm,
Entries: rf.log[pos:],
LeaderCommit: rf.commitIndex,
}
reply := AppendEntriesReply{
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
go func(server int, args *AppendEntriesArgs, reply *AppendEntriesReply) {
ok := rf.sendAppendEntries(server, args, reply)
if !ok {
DPrintf("[%d] fails to contact %d.", me, server)
return
}
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
// a reply contains higher term, convert to follower
if reply.Term > rf.currentTerm {
rf.convertToFollower(reply.Term)
} else if !reply.Success && reply.LastLogIndex != -1 {
// back up strategy
// case 1: follower does not have any entry at args.PrevLogIndex,
// back up to follower's end of log
// s1 4
// s2 4 6 6 6
// case 2: leader has entry with the same term of follower's conflicting entry,
// back up to leader's last index of entry with the conflicting term
// s1 4 4 4
// s2 4 6 6 6
// case 3: leader does not have follower's conflicting term at all
// back up to follower's first index of entry with the conflicting term
// s1 4 5 5
// s2 4 6 6 6
if reply.LastLogIndex < args.PrevLogIndex {
rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.LastLogIndex + 1
} else if lastIndex := rf.lastIndex(reply.ConflictTerm); lastIndex != -1 {
rf.nextIndex[server] = lastIndex + 1
} else {
// leader does not have entry with reply's term at all
rf.nextIndex[server] = reply.FirstConflictTermIndex
}
} else {
// AppendEntries RPC is accepted
rf.matchIndex[server] = args.PrevLogIndex + len(args.Entries)
rf.nextIndex[server] = rf.matchIndex[server] + 1
}
}(i, &args, &reply)
}
}
func (rf *Raft) callInstallSnapshot(server int) {
rf.mu.Lock()
args := InstallSnapshotArgs{
Term: rf.currentTerm,
LeaderId: rf.me,
LastIncludedIndex: rf.lastIncludedIndex,
LastIncludedTerm: rf.lastIncludedTerm,
Snapshot: rf.persister.ReadSnapshot(),
}
reply := InstallSnapshotReply{
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
rf.peers[server].Call("Raft.InstallSnapshot", &args, &reply)
}
func (rf *Raft) callRequestVote(server int, term int) bool {
rf.mu.Lock()
DPrintf("[%d] sends request vote to %d.", rf.me, server)
lastLogIndex, lastLogTerm := rf.lastIncludedIndex, rf.lastIncludedTerm
if len(rf.log) > 0 {
lastLogIndex = rf.lastIncludedIndex + len(rf.log)
lastLogTerm = rf.log[len(rf.log)-1].Term
}
args := RequestVoteArgs{
Term: term,
CandidateId: rf.me,
LastLogIndex: lastLogIndex,
LastLogTerm: lastLogTerm,
}
var reply RequestVoteReply
rf.mu.Unlock()
// actually send a RPC
ok := rf.sendRequestVote(server, &args, &reply)
if !ok {
return false
}
rf.mu.Lock()
// a reply contains higher term, convert to follower
if rf.currentTerm < reply.Term {
rf.convertToFollower(reply.Term)
}
rf.mu.Unlock()
return reply.VoteGranted
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
} else {
return b
}
}
func (rf *Raft) convertToFollower(term int) {
rf.currentTerm = term
rf.state = Follower
rf.votedFor = -1
rf.timer.reset()
rf.persist()
}
func (rf *Raft) snapshotAndTrim(snapshot []byte) {
// raft hold the lock while taking snapshot in case of applying new entries
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
pos := rf.index2Pos(rf.lastApplied)
// we need to make sure lastApplied > lastIncludedIndex before we set lastIncludedTerm = rf.log[pos].Term
// otherwise corresponding position in log of lastApplied would be -1.
lastIncludedIndex, lastIncludedTerm := rf.lastApplied, rf.lastIncludedTerm
if rf.lastApplied != rf.lastIncludedIndex {
lastIncludedTerm = rf.log[pos].Term
}
state := rf.getPersistData(pos+1, lastIncludedIndex, lastIncludedTerm)
rf.persister.SaveStateAndSnapshot(state, snapshot)
DPrintf("[%d] takes snapshot.", rf.me)
// trim log
rf.log = rf.log[pos+1:]
rf.lastIncludedIndex = lastIncludedIndex
rf.lastIncludedTerm = lastIncludedTerm
}
// save Raft's persistent state to stable storage,
// where it can later be retrieved after a crash and restart.
// see paper's Figure 2 for a description of what should be persistent.
func (rf *Raft) persist() {
data := rf.getPersistData(0, rf.lastIncludedIndex, rf.lastIncludedTerm)
rf.persister.SaveRaftState(data)
}
func (rf *Raft) getPersistData(startPos, lastIncludedIndex, lastIncludedTerm int) []byte {
w := new(bytes.Buffer)
e := labgob.NewEncoder(w)
err := e.Encode(rf.currentTerm)
err = e.Encode(rf.votedFor)
err = e.Encode(rf.log[startPos:])
err = e.Encode(lastIncludedIndex)
err = e.Encode(lastIncludedTerm)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("[%d] fails to encode raft state.", rf.me)
}
data := w.Bytes()
return data
}
// restore previously persisted state.
func (rf *Raft) readPersist(data []byte) {
if data == nil || len(data) < 1 {
// bootstrap without any state?
return
}
r := bytes.NewBuffer(data)
d := labgob.NewDecoder(r)
var currentTerm, votedFor, lastIncludedIndex, lastIncludedTerm int
var entries []Entry
if d.Decode(¤tTerm) != nil || d.Decode(&votedFor) != nil || d.Decode(&entries) != nil ||
d.Decode(&lastIncludedIndex) != nil || d.Decode(&lastIncludedTerm) != nil {
// fail to read persistent data
log.Fatalf("[%d] fails to read persistent state", rf.me)
} else {
rf.currentTerm = currentTerm
rf.votedFor = votedFor
rf.log = entries
rf.lastIncludedIndex = lastIncludedIndex
rf.lastIncludedTerm = lastIncludedTerm
if rf.lastApplied < lastIncludedIndex {
rf.lastApplied = lastIncludedIndex
}
if rf.commitIndex < lastIncludedIndex {
rf.commitIndex = lastIncludedIndex
}
DPrintf("[%d] read persisted data, lastIncludedIndex = %d, lastIncludedTerm = %d", rf.me, lastIncludedIndex, lastIncludedTerm)
}
}
func (rf *Raft) InstallSnapshot(args *InstallSnapshotArgs, reply *InstallSnapshotReply) {
rf.mu.Lock()
defer rf.mu.Unlock()
reply.Term = rf.currentTerm
// 1. Reply immediately if term < currentTerm
if args.Term < rf.currentTerm {
return
}
// 5. Save snapshot file, discard any existing or partial snapshot with a smaller index
// 6. If existing log entry has same index and term as snapshot’s last included entry,
// retain log entries following it and reply
pos := rf.index2Pos(args.LastIncludedIndex)
if pos < len(rf.log) &&
(pos < 0 || rf.log[pos].Term == args.LastIncludedTerm) {
// whether this server still have entry with LastIncludedIndex
// raft may not yet apply those log entries before they are truncated
// raft need to make sure they are applied before truncate
if pos >= 0 && rf.lastApplied >= args.LastIncludedIndex {
rf.log = rf.log[pos+1:]
rf.lastIncludedTerm = args.LastIncludedTerm
rf.lastIncludedIndex = args.LastIncludedIndex
state := rf.getPersistData(0, args.LastIncludedIndex, args.LastIncludedTerm)
rf.persister.SaveStateAndSnapshot(state, args.Snapshot)
}
return
}
// 7. Discard the entire log
// 8. Reset state machine using snapshot contents (and load snapshot’s cluster configuration)
rf.log = []Entry{
}
state := rf.getPersistData(0, args.LastIncludedIndex, args.LastIncludedTerm)
rf.persister.SaveStateAndSnapshot(state, args.Snapshot)
rf.readPersist(rf.persister.ReadRaftState())
msg := ApplyMsg{
CommandValid: false,
Command: rf.persister.ReadSnapshot(),
CommandIndex: 0,
CommandTerm: 0,
CommandType: InstallSnapshot,
}
go func(msg ApplyMsg) {
rf.applyCh <- msg
}(msg)
}
func (rf *Raft) SetSnapshotCh(snapshotCh chan []byte) {
rf.snapshotCh = snapshotCh
}
func (rf *Raft) SetMaxRaftState(maxRaftState int) {
rf.maxRaftState = maxRaftState
}
func (rf *Raft) shouldSnapshot() bool {
return rf.maxRaftState != -1 && rf.maxRaftState < rf.persister.RaftStateSize()
}
边栏推荐
- Enterprise wechat H5_ Authentication, H5 application web page authorization login to obtain identity
- TypeError: wave.ensureState is not a function
- [vscode]todo tree a to-do plug-in
- C language standard IO, such as printf(), scanf(), etc
- How leaflet gracefully displays the bubble window of overlapping points
- 2022-06-13日报: 图灵奖得主:想要在学术生涯中获得成功,需要注意哪些问题?
- Cherry Blossom powder Dudu
- 新增博客地址
- 【Matlab】符号计算
- How to quickly query the online status of mobile phones
猜你喜欢
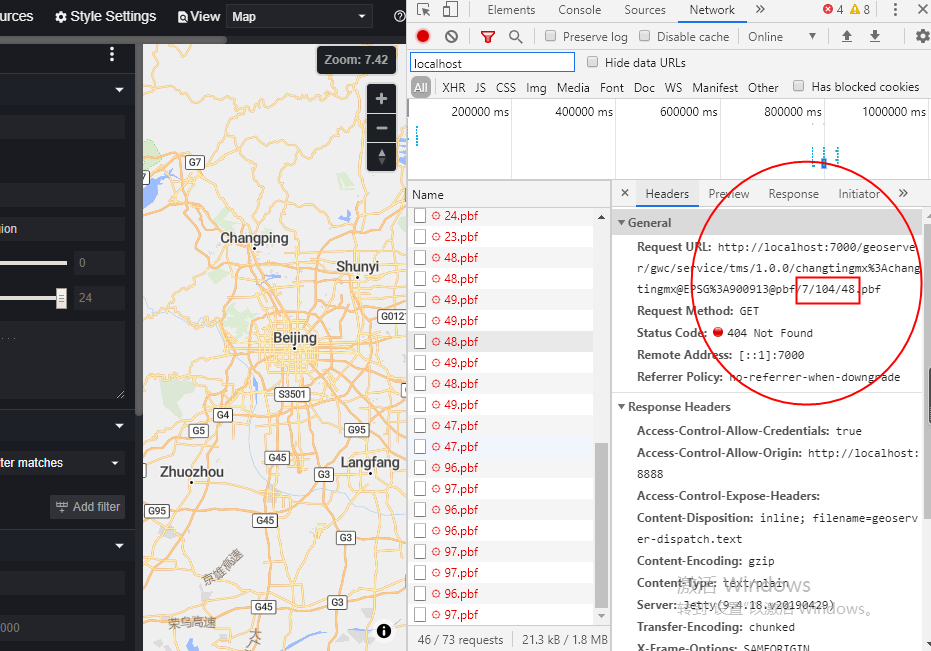
How to make maputnik, a vector tile matching artifact, support GeoServer

Kaust:deyao Zhu | value memory map: a graph structured world model based on off-line reinforcement learning
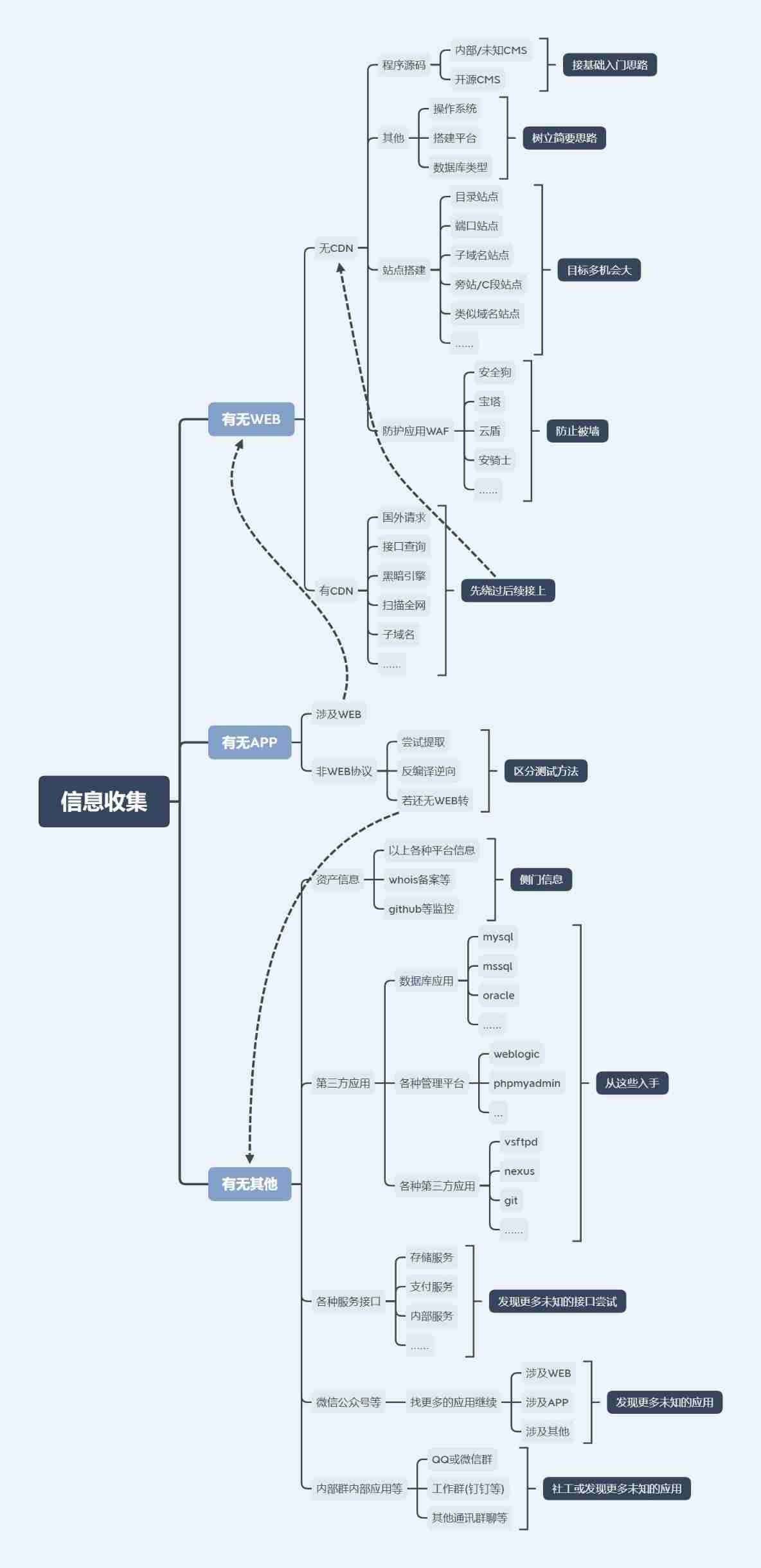
Information collection for network security (2)

What are the levels of safety accidents

Matlab【路径规划】—— 无人机药品配送路线最优化

A detailed explanation of synchronized

Video tracker error troubleshooting
![[vscode]todo tree a to-do plug-in](/img/52/c977bc9cd021ca6fd12bcc22ae9f78.jpg)
[vscode]todo tree a to-do plug-in

On the parameters of main function in C language

Masa auth - overall design from the user's perspective
随机推荐
Basics of network security (1)
PMP test difficulty and pass rate
Can branches sign labor contracts with employees
ik分词器的安装
Accelerating with Dali modules
SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) workflow function introduction
[matlab] matrix operation
Machining Industry MES system Mold Industry MES system CNCl Medium Industry MES System MES code scanning and reporting MES data collection
June 11, 2022 diary: Mr. Wang's spring, mixed in
Information collection for network security (2)
Buuctf-[ciscn 2019 preliminary]love math
The difference between caching and buffering
分公司能与员工签劳动合同么
What are the levels of safety accidents
How to use Huawei cloud disaster tolerance solution to replace disaster recovery all-in-one machine
KAUST:Deyao Zhu | 价值记忆图:基于离线强化学习的图结构世界模型
Is the brokerage account in qiniu business school safe? Is the account opening rate low
Memory address mapping of u-boot
[LeetCode]7. Integer inversion thirty-nine
TypeError: wave.ensureState is not a function