当前位置:网站首页>倍增、DFS序
倍增、DFS序
2022-07-31 01:01:00 【xingxg.】
目录
路径最小值

dfs,相当于一个初始化操作;
以及有一个跟ST表类似的预处理操作
query函数的总体思想就是,利用2个节点的深度来不断向上查最近公共祖先。(前提是2个节点处于同一深度,代码中有体现这一点,可能处于同一深度之后,u就是v的祖先,也可能不是,那就继续向上查找)
// problem :
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
const int LOGN = 18;
const int N = 201000;
int n, q;
int dep[N], par[N][LOGN + 1], val[N][LOGN + 1];
std::vector<pair<int, int>> e[N];
int query(int u, int v) {
int ans = 1 << 30;
if(dep[u] > dep[v]) swap(u, v);
int d = dep[v] - dep[u];
for (int j = LOGN; j >= 0; --j) if (d & (1 << j)) {
ans = min(ans, val[v][j]);
v = par[v][j];
}
if (u == v) return ans;
for (int j = LOGN; j >= 0; --j) if (par[u][j] != par[v][j]) {
ans = min(ans, min(val[u][j], val[v][j]));
u = par[u][j];
v = par[v][j];
}
ans = min(ans, min(val[u][0], val[v][0]));
return ans;
}
void dfs(int u, int f) {
dep[u] = dep[f] + 1;
for (auto p : e[u]) {
int v = p.first;
if (v == f) continue;
par[v][0] = u;
val[v][0] = p.second;
dfs(v, u);
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int u, v, w;
scanf("%d %d %d", &u, &v, &w);
e[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w));
e[v].push_back(make_pair(u, w));
}
dfs(1, 0);
for (int j = 1; j <= LOGN; ++j) {
for (int u = 1; u <= n; ++u) {
par[u][j] = par[par[u][j - 1]][j - 1];
val[u][j] = min(val[u][j - 1], val[par[u][j - 1]][j - 1]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
printf("%d\n", query(u, v));
}
return 0;
}DFS序练习1

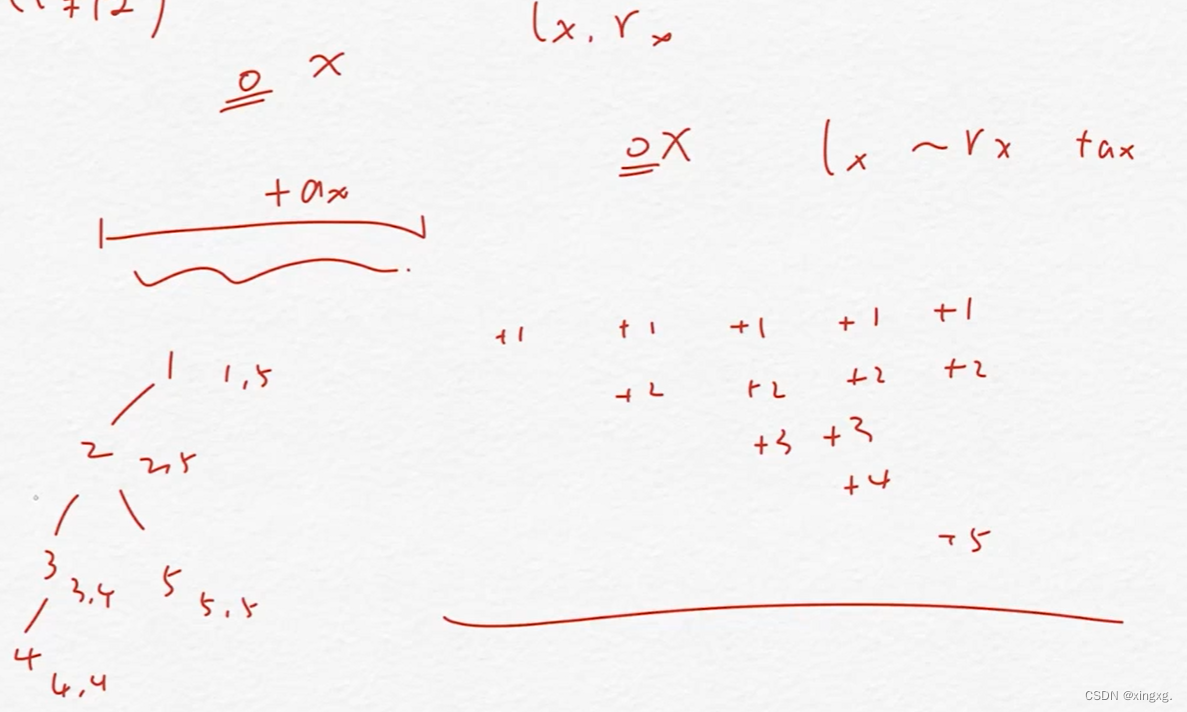
DFS序, 将一棵树有序化,特点是子树的序号是连续的,(子树 相当于 涉及区间问题)
c1 维护区间和
c2 维护点x到根的点权和 (差分)
为什么为想到差分呢? 可以知道,点x的孩子要到根的话,那么一定会经过点x,所以要加上x这个点的点权, 所以是区间加,并且是单点查询,很自然就想到差分树状数组了。
// problem : DFS序
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
const int N = 201000;
int n, q, l[N], r[N], tot, a[N];
std::vector<int> e[N];
template<class T>
struct BIT{
T c[N];
int size;
void init(int n){
size = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) c[i] = 0;
}
inline void modify(int x, T d){
while(x <= size){
c[x] += d;
x += x & -x;
}
}
inline T query(int x){
T res = 0;
while(x){
res += c[x];
x -= x & -x;
}
return res;
}
};
BIT<ll> c1, c2;
void dfs(int u, int f) {
l[u] = ++tot;
for (auto v : e[u]) {
if (v == f) continue;
dfs(v, u);
}
r[u] = tot;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
c1.init(n);
c2.init(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
c1.modify(l[i], a[i]);
c2.modify(l[i], a[i]);
c2.modify(r[i] + 1, -a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if (ty == 1) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
int d = y - a[x];
a[x] = y;
c1.modify(l[x], d);
c2.modify(l[x], d);
c2.modify(r[x] + 1, -d);
} else {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%lld %lld\n", c1.query(r[x]) - c1.query(l[x] - 1), c2.query(l[x]));
}
}
return 0;
}
DFS序练习2

这题跟上一题没有区别,唯一变动的地方就是多了个换根操作,这也是难点之一。
我们一旦换了根,那我们原先的DFS序就会被打乱。这里的解决方法是不进行真正的换根操作,而进行逻辑上的换根。当我们查询x点子树的点权和时,通过x和root之间的关系,来进行模拟换根处理。
这里x和root之间有3种关系:
1、x 就是 root ----> query(n)
2、root是x的子孙 整体减去 x 的包含root区间的那个子区间
3、其他 还是正常的query(r[x]) - query(l[x] - 1)
第1种情况很明显,不画图演示。
第2种情况:

第3种情况: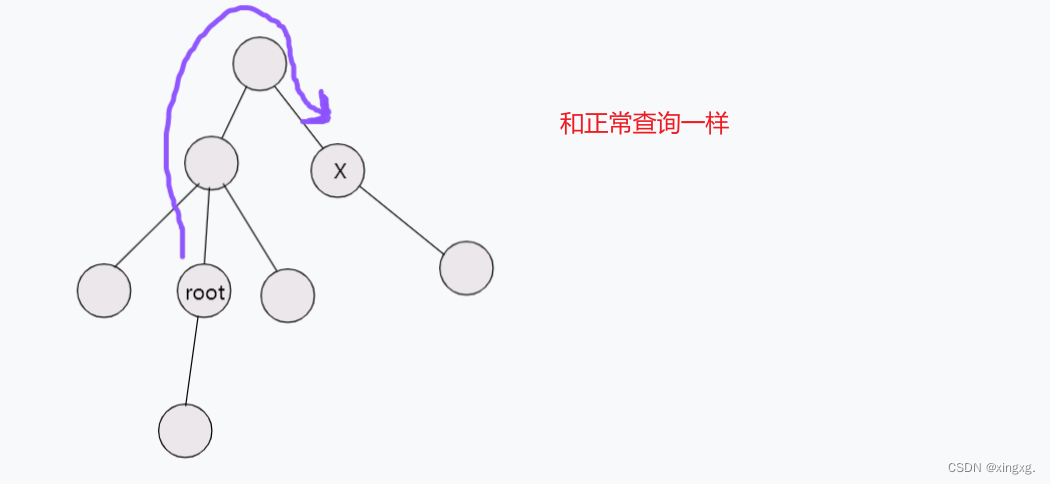
// problem : DFS序
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define pb push_back
const int N = 201000;
int n, q, l[N], r[N], tot, a[N];
std::vector<int> e[N];
vector<PII> son[N];
template<class T>
struct BIT{
T c[N];
int size;
void init(int n){
size = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) c[i] = 0;
}
inline void modify(int x, T d){
while(x <= size){
c[x] += d;
x += x & -x;
}
}
inline T query(int x){
T res = 0;
while(x){
res += c[x];
x -= x & -x;
}
return res;
}
};
BIT<ll> c1;
void dfs(int u, int f) {
l[u] = ++tot;
for (auto v : e[u]) {
if (v == f) continue;
dfs(v, u);
son[u].push_back(make_pair(l[v], r[v]));
}
r[u] = tot;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &q);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int u, v;
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
c1.init(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
c1.modify(l[i], a[i]);
}
int root = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) {
int ty;
scanf("%d", &ty);
if (ty == 1) {
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
int d = y - a[x];
a[x] = y;
c1.modify(l[x], d);
} else if (ty == 3){
scanf("%d", &root);
} else {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x == root) {
printf("%lld\n", c1.query(n));
} else if (l[x] < l[root] && r[x] >= r[root]) {
auto seg = *prev(upper_bound(son[x].begin(), son[x].end(),
PII {l[root], r[root]}));
printf("%lld\n", c1.query(n) - (c1.query(seg.second) - c1.query(seg.first - 1)));
} else {
printf("%lld\n", c1.query(r[x]) - c1.query(l[x] - 1));
}
}
}
return 0;
}边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Typescript14 - (type) of the specified parameters and return values alone

typescript16-void
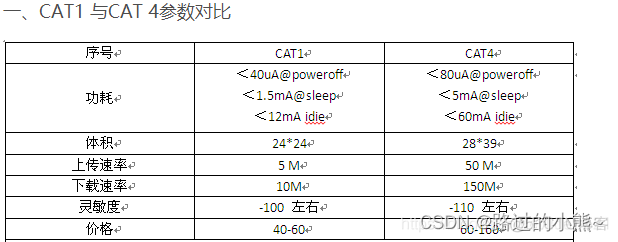
The difference between 4G communication module CAT1 and CAT4
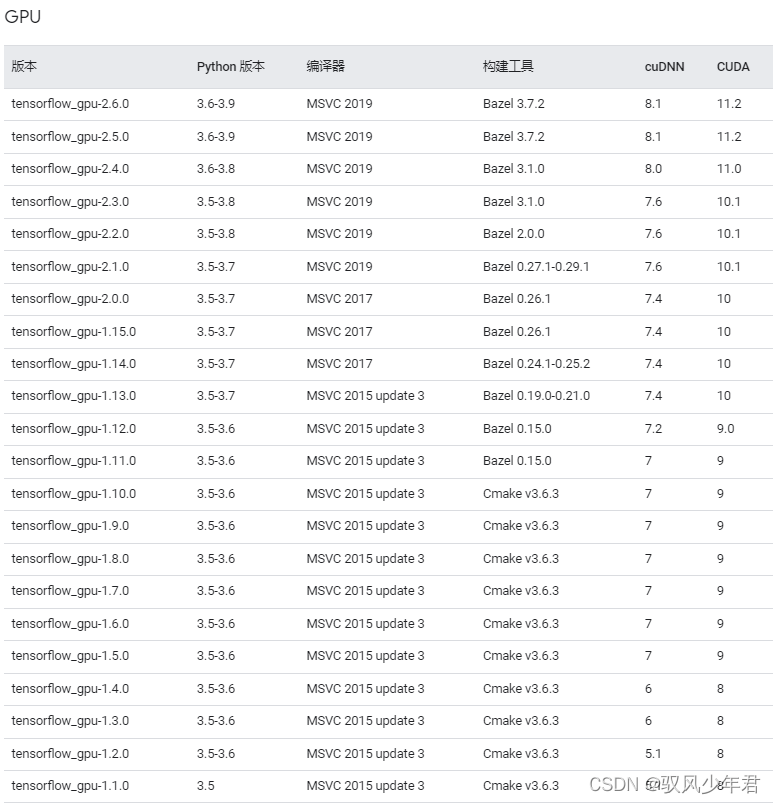
tensorflow与GPU版本对应安装问题

Mysql: Invalid default value for TIMESTAMP

typescript15- (specify both parameter and return value types)
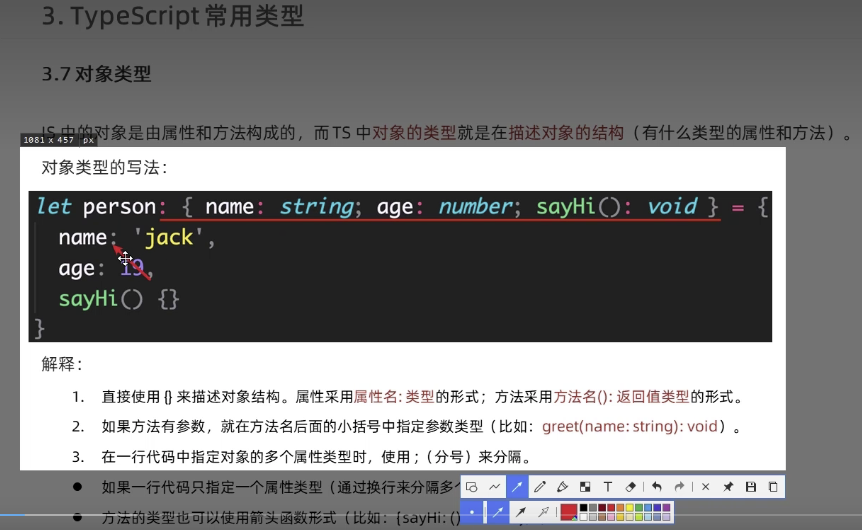
typescript18-对象类型
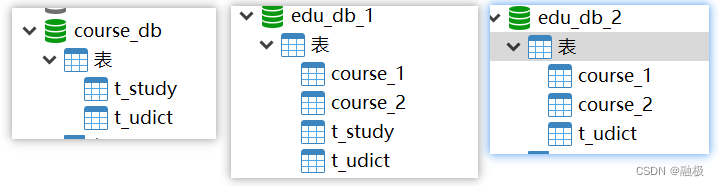
ShardingSphere之公共表实战(七)
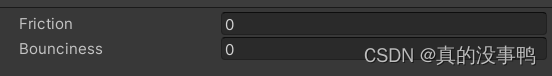
Unity2D horizontal version game tutorial 4 - item collection and physical materials

剑指offer17---打印从1到最大的n位数
随机推荐
Thesis understanding: "Designing and training of a dual CNN for image denoising"
BOM系列之Navigator对象
Sping.事务的传播特性
【952. 按公因数计算最大组件大小】
TypeScript在使用中出现的问题记录
MySQL database advanced articles
【Yugong Series】July 2022 Go Teaching Course 013-Constants, Pointers
ShardingSphere之水平分库实战(四)
The client series of the DOM series
查看zabbix-release-5.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm包内容
[C language course design] C language campus card management system
typescript10-commonly used basic types
Artificial Intelligence and Cloud Security
typescript17-函数可选参数
XSS related knowledge
Huawei's "genius boy" Zhihui Jun has made a new work, creating a "customized" smart keyboard from scratch
场景之多数据源查询及数据下载问题
埃拉托斯特尼筛法
蓝牙mesh系统开发二 mesh节点开发
《实战》基于情感词典的文本情感分析与LDA主题分析