当前位置:网站首页>Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)
Hands on deep learning (III) -- Torch Operation (sorting out documents in detail)
2022-07-04 09:42:00 【Stay a little star】
List of articles
- A very detailed document , Study pytorch You can study it in detail :
- Reproduce some important functions and knowledge points :
- One 、 establish tensor tensor
- Two 、tensor And numpy Mutual conversion between
- 3、 ... and 、tensor.function And tensor.function_ The difference between
- Four 、 modify tensor The shape of the
- 5、 ... and 、 Index operation
- 6、 ... and . Operate element by element
- 7、 ... and . Merge operation
- 8、 ... and 、 Comparison operation
A very detailed document , Study pytorch You can study it in detail :
http://www.feiguyunai.com/index.php/2019/09/11/pytorch-char02/#23_Jupyter_Notebook
Reproduce some important functions and knowledge points :
One 、 establish tensor tensor
Example :
# according to list The data generated tensor
torch.Tensor([1,2,3,4,5,6])
# Generates a shape based on the specified shape tensor
torch.Tensor(2,3)
# Generate according to the given shape torch
t = torch.Tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(t)
# tensor Dimension size information of tensor
t.size()
print(t.shape)
# Create based on known size tensor
torch.Tensor(t.size())
Be careful :
- torch.Tensor yes torch.empty and torch.tensor A mixture between , however , When data is passed in ,torch.Tensor Use global default dtype(FloatTensor),torch.tensor Infer data types from data .
- torch.tensor(1) Returns a fixed value 1, and torch.Tensor(1) Return a size of 1 Tensor , It is a randomly initialized value
t1 = torch.Tensor(1)
t2 = torch.tensor(1)
print("t1 Value {},t1 Data type of {}".format(t1,t1.type()))
print("t2 Value {},t2 Data type of {}".format(t2,t2.type()))
# Generate unit matrix
t3 = torch.eye(2,2)
# The generation is all 0 Matrix
t4 = torch.zeros(2,3)
# Generate data according to rules
t5 = torch.linspace(1,10,4)
# Generate random numbers satisfying uniform distribution
t6 = torch.rand(2,3)
# The returned data has the same shape , It's all worth 0 Tensor
t7 = torch.zeros_like(torch.rand(2,3))
print(" Unit matrix :{},/n Zero matrix :{},/n Regular data format “”")
Two 、tensor And numpy Mutual conversion between
# tensor To Numpy
tensor_test = torch.tensor([1,2,3])
print("tensor Format :{}".format(tensor_test))
print("numpy Of list Format :{}".format(tensor_test.numpy()))
# Numpy To Tensor(besides chartensor)
numpy_test = np.ones([3,3])
print("numpy Of list Format :{}".format(numpy_test))
print("tensor Format :{}".format(torch.from_numpy(numpy_test)))
Be careful :
tensor and numpy Most functions of are similar , Many functions with the same operation are also the same , The biggest difference between them is tensor You can call GPU Running and numpy Of ndarray Mainly in the CPU Speed up operations in
3、 ... and 、tensor.function And tensor.function_ The difference between
x = torch.tensor([1,2])
y = torch.tensor([3,4])
z1 = x.add(y)
z2 = y.add_(x)
print(" Do not change its own value x={};z={};".format(x.numpy(),z1.numpy()))
print(" Change your own value y={};z={};".format(y.numpy(),z2.numpy()))
Be careful :
Adding an underscore indicates that the form of the original data will be modified , Use the same memory space
Four 、 modify tensor The shape of the
# size—— return tensor The attribute value , And shape Equivalent
shape_test = torch.randn(2,3)
# shape—— View the properties
print(shape_test.shape)
print(shape_test.size())
# dim—— View dimensions
print(shape_test.dim())
# view—— Change dimensions ( Note that the amount of data does not change )
print(shape_test.view(3,2))
print(shape_test.view(-1)) # Expand to one-dimensional vector
# unsqueeze—— Add dimensions , The following parameters are the dimensions to be added
new_shape_test = torch.unsqueeze(shape_test,0)
print(new_shape_test)
print(" The original dimension :{}".format(shape_test.shape))
print(" Added dimension :{}".format(new_shape_test.shape))
explain :
Adding a dimension above means adding a dimension at the position , for example unsqueeze(shape_test,0) It means that shape_test Add a dimension to the outermost layer of
5、 ... and 、 Index operation
# manual_seed()—— Set random seeds
torch.manual_seed(100)
index_test = torch.rand(2,3)
print(" Raw data :{}".format(index_test))
# []—— Get slice data
print(" The first line of data :{}".format(index_test[0,:]))
print(" The last column of data :{}".format(index_test[:,-1]))
# Indexes
mask =index_test>0 # Index based on raw data
print(torch.masked_select(index_test,mask)) # Get the value according to the index
print(torch.nonzero(mask)) # Get the subscript of a non-zero value
# torch.gather—— In the prescribed form 、 Way to index
#out[i][j] = input[index[i][j]][j] # if dim == 0
#out[i][j] = input[i][index[i][j]] # if dim == 1
index1 = torch.LongTensor([[0,0,0],[1,1,1],[1,1,0]])
a = torch.gather(index_test,0,index1) # index_test Is the data ;dim=0 Represents a row index ,dim=1 Indicates index by column ;index The size of alpha is the size of the output
print(" Index results by row (index The number of columns of corresponds to the number of columns of the original matrix ):{}".format(a))
index2 = torch.LongTensor([[2,2,2,2],[2,1,1,1]])
b = torch.gather(index_test,1,index2)
print(" Index results by column (index The number of rows of corresponds to the number of columns of the original matrix ):{}".format(b))
# torch.scatter_ Is with the gather The opposite operation
out_index = torch.zeros(2,4)
out_index.scatter_(1,index,b) #dim=1,index2 It's the index ,b Is the value obtained by index
print(" Put the index value back to the corresponding position ( Restore raw data ):{}".format(out_index))
explain :
gather The data from input Press index Take out , and scatter_ Is to put the extracted data back . Be careful scatter_ The function is inplace operation .
6、 ... and . Operate element by element
common :
- abs/add—— Absolute value operation and addition operation
- addcdiv(t,v,t1,t2)——t1 And t2 Divide by element , ride v, Add t
- addcmul(t,v,t1,t2)——t1 And t2 Multiply by elements , ride v, Add t
- cell/floor—— Round up and down
- clamp(t,min,max)—— Restrict tensor elements to a specified interval
- exp/log/pow—— Index 、 logarithm 、 power
- mul(*)/neg—— Multiplication by element 、 Take the opposite
- sigmoid/tanh/softmax—— Activation function
- sign/sqrt—— Take the symbol / Square root
t = torch.randn(1,3)
t1 = torch.randn(3,1)
t2 = torch.randn(1,3)
t3 = torch.randn(1,3)
print("t:{}".format(t))
print("t1:{}".format(t1))
print("t2:{}".format(t2))
print("t3:{}".format(t3))
print('#'*50)
# Matrix addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
print(" Add :{}".format(t2+t3))
print(" Subtraction :{}".format(t2-t3))
print(" Multiplication :{}".format(t2*t3))
print(" division :{}".format(t2/t3))
print('#'*50)
#t+0.1*(t1/t2)
print(" Fast calculation :t+0.1*(t1/t2)( among t1/t2 It's matrix division ):\n{}".format(torch.addcdiv(t,0.1,t1,t2)))
print('#'*50)
# Calculation sigmoid
print('sigmoid The result of function calculation :{}'.format(torch.sigmoid(t)))
print('#'*50)
# take t Restriction on [0,1] Between
print(' Limit the area :{}'.format(torch.clamp(t,0,1)))
print('#'*50)
#t+2 Perform local operation
t.add_(2)
7、 ... and . Merge operation
# Generate a system containing 6 The number of vectors
a_test=torch.linspace(0,10,6)
# Use view Method , hold a Turn into 2x3 matrix
a_test=a_test.view((2,3))
# Along the y Axis direction accumulation , namely dim=0
b_test=a_test.sum(dim=0) #b The shape of is [3]
# Along the y Axis direction accumulation , namely dim=0, And keep it containing 1 Dimensions
b_test=a_test.sum(dim=0,keepdim=True) #b The shape of is [1,3]
print(a_test)
print(b_test)
summary :
- cumprod(t,axis)—— stay axis Dimension pair t Accumulate
- cumsum(t,axis)—— stay axis Dimension pair t Add up
- mean/median—— Mean and median
- std/var—— Standard deviation and variance
- norm(t,p=2) —— return t Of p Norm of order
- prod(t)/sum(t)—— For all the t Elements accumulate and accumulate
8、 ... and 、 Comparison operation
x=torch.linspace(0,10,10).view(5,2)
print(x)
# Find the maximum value of all elements
print(" Global maximum :{}".format(torch.max(x)))
# seek y Maximum value in the axis direction
print("y Direction maximum :{}".format(torch.max(x,dim=0)))
# For the biggest 2 Elements
print(" maximal n Element and its relative index ( stay dim Index direction ):\n{}".format(torch.topk(x,2,dim=0)))
# The index returned is the same as dim Relevant ,dim=0 Indicates the index by row ( namely y Index of direction )
# tock Back to value Represents the two largest values in the corresponding column ,index Indicates the number of rows corresponding to the value
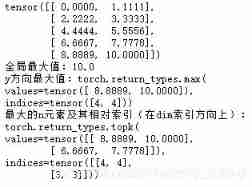
summary :
- eq—— Compare tensor Whether it is equal or not
- equal—— Compare tensor Whether there is the same shape And the value
- ge/le/gt/lt —— Greater than / Less than / Greater than or equal to / Comparison of less than or equal
- max/min(t,axis)—— Along axis The direction of return is maximum 、 After the minimum
- topk(t,k,axis)—— At the designated axis Take the largest in the direction k It's worth
It's over , I'll go after you like it
边栏推荐
- Hands on deep learning (39) -- gating cycle unit Gru
- Pcl:: fromrosmsg alarm failed to find match for field 'intensity'
- Global and Chinese market of bipolar generators 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Hands on deep learning (38) -- realize RNN from scratch
- mmclassification 标注文件生成
- What are the advantages of automation?
- Global and Chinese market of wheel hubs 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Daughter love: frequency spectrum analysis of a piece of music
- Write a jison parser from scratch (6/10): parse, not define syntax
- PHP is used to add, modify and delete movie information, which is divided into foreground management and background management. Foreground users can browse information and post messages, and backgroun
猜你喜欢
Normal vector point cloud rotation
PHP student achievement management system, the database uses mysql, including source code and database SQL files, with the login management function of students and teachers

26. Delete duplicates in the ordered array (fast and slow pointer de duplication)

2022-2028 global tensile strain sensor industry research and trend analysis report
libmysqlclient. so. 20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
回复评论的sql

2022-2028 global gasket plate heat exchanger industry research and trend analysis report

libmysqlclient.so.20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory

C # use gdi+ to add text to the picture and make the text adaptive to the rectangular area

At the age of 30, I changed to Hongmeng with a high salary because I did these three things
随机推荐
mmclassification 标注文件生成
Get the source code in the mask with the help of shims
自动化的优点有哪些?
Golang Modules
技术管理进阶——如何设计并跟进不同层级同学的绩效
Hands on deep learning (35) -- text preprocessing (NLP)
C # use gdi+ to add text to the picture and make the text adaptive to the rectangular area
Are there any principal guaranteed financial products in 2022?
Go context 基本介绍
ArrayBuffer
SSM online examination system source code, database using mysql, online examination system, fully functional, randomly generated question bank, supporting a variety of question types, students, teache
Golang type comparison
26. Delete duplicates in the ordered array (fast and slow pointer de duplication)
Solution to null JSON after serialization in golang
Problems encountered by scan, scanf and scanln in golang
UML sequence diagram [easy to understand]
libmysqlclient. so. 20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
How to write unit test cases
Global and Chinese markets of water heaters in Saudi Arabia 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
JDBC and MySQL database

