当前位置:网站首页>Solving Poisson equation by tensorflow
Solving Poisson equation by tensorflow
2022-06-27 16:12:00 【Galerkin code farmer】
This code was written two years ago , At that time, the code was very poor , So the code has some bug And the effect of solving Poisson equation is not very good , If you are interested, you can try to modify the code to improve the numerical accuracy
code1
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import time
tic = time.time()
h1 = 0.1
h2 = 0.05
M = int(1/h1) + 1
N = int(1/h2) + 1
x_train = np.linspace(0,1,M)
y_train = np.linspace(0,1,N)
matr = np.zeros([M,N,2])# Store all grid points in the matrix matrix On , Each row represents the coordinates of a grid point
for i in range(M):
for j in range(N):
matr[i,j,0] = x_train[i]
matr[i,j,1] = y_train[j]
ma = matr.reshape(-1,2)
print(ma.shape)
ma_in = matr[1:-1,1:-1].reshape(-1,2)# Store all grid points in the matrix matrix On , Each row represents the coordinates of a grid point
print(ma_in.shape)
ma_b = np.concatenate([matr[0],matr[-1],matr[:,0][1:-1],matr[:,-1][1:-1]],0)
print(ma_b.shape)
def f(x,y):# The right-hand function of a differential equation f
return - (2*np.pi**2)*np.exp(np.pi*(x + y))*np.sin(np.pi*(x + y))
def u_accuracy(x,y):
return np.exp(np.pi*(x + y))*np.sin(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*y)
def u_boundary(x,y):
return 0*x*y
right_in = f(ma_in[:,0],ma_in[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)
right_b = u_boundary(ma_b[:,0],ma_b[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)
print(right_in.shape,right_b.shape)
ma_min = np.array([[0,0]])
ma_max = np.array([[1,1]])
np.random.seed(1234)
tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed(1234)
# Definition tensorflow frame
prob_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32)
x_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])
x_in_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])
x_b_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])
right_in_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,1])
right_b_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,1])
x_min_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [1,2])
x_max_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [1,2])
layers = [2,10,10,1]
H = 2*(x_tf - x_min_tf)/(x_max_tf - x_min_tf + 1e-7) - 1
H_in = 2*(x_in_tf - x_min_tf)/(x_max_tf - x_min_tf + 1e-7) - 1
H_b = 2*(x_b_tf - x_min_tf)/(x_max_tf - x_min_tf + 1e-7) - 1
# Define weights and offsets
def w_init(in_dim,out_dim):
w_std = np.sqrt(2/(in_dim + out_dim))
return tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([in_dim, out_dim], stddev = w_std), dtype=tf.float32)
weights = []
biases = []
num_layers = len(layers)
for i in range(0,num_layers - 1):
w = w_init(in_dim = layers[i],out_dim = layers[i + 1])
b = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1,layers[i + 1]], dtype = tf.float32), dtype=tf.float32)
weights.append(w)
biases.append(b)
# Output approximate solution
num_layers = len(weights)# Than layers Less length 1
for i in range(0,num_layers - 1):
w = weights[i]
b = biases[i]
E = tf.eye(tf.shape(w)[0],tf.shape(w)[1])
tf.nn.dropout(w,rate = prob_tf)
H_in = tf.tanh(tf.add(tf.matmul(H_in,w), b)) + tf.matmul(H_in,E)
H_b = tf.tanh(tf.add(tf.matmul(H_b,w), b)) + tf.matmul(H_b,E)
H = tf.tanh(tf.add(tf.matmul(H,w), b)) + tf.matmul(H,E)
W = weights[-1]
b = biases[-1]
u_in = tf.add(tf.matmul(H_in,W),b)
u_b = tf.add(tf.matmul(H_b,W),b)
u = tf.add(tf.matmul(H,W),b)
# Define the loss function
u_x = tf.gradients(u_in,x_in_tf)[0][:,0]
u_y = tf.gradients(u_in,x_in_tf)[0][:,1]
u_xx = tf.gradients(u_x,x_in_tf)[0][:,0]
u_yy = tf.gradients(u_y,x_in_tf)[0][:,1]
loss_in = 0.5*tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(u_x) + tf.square(u_y) - 2*u_in*right_in_tf)
#loss_in = 0.5*tf.reduce_mean((-u_xx - u_yy - 2*right_in_tf)*u_in)
loss_b = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(u_b - right_b_tf))
belta = 5e3
loss = tf.add(loss_in,belta*loss_b)
# initialization
def plot_curve(data):# Visualization of the loss function training process
fig = plt.figure(num = 1,figsize = (4,3),dpi = None,facecolor = None,edgecolor = None,frameon = True)# Number , Width and height , The resolution of the , The background color , Border color , Show border or not
plt.plot(range(len(data)),data,color = 'blue')
plt.legend(['value'],loc = 'upper right')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
lr = 5*1e-3
optim = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = lr)
trainer = optim.minimize(loss)
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
train_loss = []
step = []
error = []
train_step = 6000
for i in range(train_step):
batch = 19
st = i*batch%len(ma_in)
end = st+ batch
feed = {
prob_tf:0.5,x_tf:ma,x_in_tf:ma_in[st:end],x_b_tf:ma_b,right_in_tf:right_in[st:end],right_b_tf:right_b,x_min_tf:ma_min,x_max_tf:ma_max}
sess.run(trainer,feed_dict = feed)
if i%600 == 0:
print('train_step = {},loss = {}'.format(i,sess.run(loss,feed_dict = feed)))
train_loss.append(sess.run(loss,feed_dict = feed))
feed_val = {
x_tf:ma,x_in_tf:ma_in,x_b_tf:ma_b,right_in_tf:right_in,right_b_tf:right_b,x_min_tf:ma_min,x_max_tf:ma_max}
u_pred = sess.run(u,feed_dict = feed_val).reshape(M,N)
x,y = np.meshgrid(x_train,y_train)
error_square = ((u_pred - u_accuracy(x,y).T)**2).sum()/(u_accuracy(x,y)**2 + 1e-7).sum()
error_step = np.sqrt(error_square)
error.append(error_step)
step.append(i)
print(error_step)
toc = time.time()
plot_curve(train_loss)
print(toc - tic)
feed = {
prob_tf:0.5,x_tf:ma,x_in_tf:ma_in,x_b_tf:ma_b,right_in_tf:right_in,right_b_tf:right_b,x_min_tf:ma_min,x_max_tf:ma_max}
u_pred = sess.run(u,feed_dict = feed).reshape(M,N)
print(type(u_pred),u_pred.shape)
x,y = np.meshgrid(x_train,y_train)
print(type(u_accuracy(x,y)),u_accuracy(x,y).shape)
error_square = ((u_pred - u_accuracy(x,y).T)**2).sum()/(u_accuracy(x,y)**2 + 1e-7).sum()
error = np.sqrt(error_square)
print(error)
plt.subplot(2,1,1)
x,y = np.meshgrid(x_train,y_train)
plt.contourf(x,y,u_accuracy(x,y),40,cmap = 'Blues')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('accuracy solution')
plt.subplot(2,1,2)
x,y = np.meshgrid(x_train,y_train)
plt.contourf(x,y,u_pred.T,40,cmap = 'Blues')
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('numerical solution')
code2
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import time
np.random.seed(1234)
tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed(1234)
def f(x,y):# The right-hand function of a differential equation f
return - (2*np.pi**2)*np.exp(np.pi*(x + y))*np.sin(np.pi*(x + y))
def u_accuracy(x,y):# Define the exact solution
return np.exp(np.pi*(x + y))*np.sin(np.pi*x)*np.sin(np.pi*y)
def u_boundary(x,y):# Define the boundary function
return 0*x*y
# Define internal points
class INSET():# Define the training set , Contains points inside the area
def __init__(self):
self.dim = 2
self.xa,self.xb,self.ya,self.yb = 0,1,0,1
self.area = (self.xb - self.xa)*(self.yb - self.ya)
self.nx,self.ny = 20,30
self.hx = (self.xb - self.xa)/self.nx
self.hy = (self.yb - self.ya)/self.ny
self.size = self.nx*self.ny
self.X = np.zeros([self.size,self.dim])
for i in range(self.nx):
for j in range(self.ny):
self.X[i*self.ny + j,0] = self.xa + (i + 0.5)*self.hx
self.X[i*self.ny + j,1] = self.ya + (j + 0.5)*self.hy
self.u_acc = u_accuracy(self.X[:,0],self.X[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)# Internal point exact solution
self.right = f(self.X[:,0],self.X[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)# To the right of the inner point
# Define boundary points
class BDSET():# Define the training set , Contains area boundary points
def __init__(self):
self.dim = 2
self.xa,self.xb,self.ya,self.yb = 0,1,0,1
self.area = (self.xb - self.xa)*(self.yb - self.ya)
self.length = 2*((self.xb - self.xa) + (self.yb - self.ya))
self.nx,self.ny = 20,30
self.hx = (self.xb - self.xa)/self.nx
self.hy = (self.yb - self.ya)/self.ny
self.size = 2*(self.nx + self.ny)
self.X = np.zeros([self.size,self.dim])
for i in range(self.nx):
for j in range(self.ny):
self.X[i,0] = self.xa + (i + 0.5)*self.hx
self.X[i,1] = self.ya
self.X[self.nx + j,0] = self.xb
self.X[self.nx + j,1] = self.ya + (j + 0.5)*self.hy
self.X[self.nx + self.ny + i,0] = self.xb - self.xa - (i + 0.5)*self.hx
self.X[self.nx + self.ny + i,1] = self.yb
self.X[2*self.nx + self.ny + j,0] = self.xa
self.X[2*self.nx + self.ny + j,1] = self.yb - self.ya - (j + 0.5)*self.hy
self.u_acc = u_boundary(self.X[:,0],self.X[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)# Exact solutions of boundary points
# Define test sets
class TESET():# Define test sets
def __init__(self):
self.dim = 2
self.xa,self.xb,self.ya,self.yb = 0,1,0,1
self.hx = 0.1
self.hy = 0.05
self.nx = int((self.xb - self.xa)/self.hx) + 1
self.ny = int((self.yb - self.ya)/self.hx) + 1
self.size = self.nx*self.ny
self.X = np.zeros([self.size,self.dim])
for j in range(self.ny):
for i in range(self.nx):
self.X[j*self.nx + i,0] = self.xa + i*self.hx
self.X[j*self.nx + i,1] = self.ya + j*self.hy
self.u_acc = u_accuracy(self.X[:,0],self.X[:,1]).reshape(-1,1)# The exact solution
class NN:
def __init__(self,inset,bdset,layers,belta):
self.inset = inset# Prepare to pass in the training set inner point
self.bdset = bdset# Prepare the incoming training set boundary points
self.datamin = np.array([[inset.xa,inset.ya]])
self.datamax = np.array([[inset.xb,inset.yb]])
self.layers = layers# Prepare the afferent neuron layer
self.inset_x_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])# Prepare to pass in the training set inner point
self.bdset_x_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])# Prepare the incoming training set boundary points
self.right_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,1])# Prepare the right item of the internal point of the training set
self.ub_tf = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,1])# Prepare to pass in the training set boundary point function value
self.min = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])# Prepare the lower limit of the two axes of the dataset
self.max = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [None,2])# Prepare the upper limit of the two axes of the dataset
self.feed = {
self.inset_x_tf:inset.X,self.bdset_x_tf:bdset.X,
self.right_tf:inset.right,self.ub_tf:bdset.u_acc,
self.min:datamin,self.max:datamax}# Prepare the feed data set
self.Hin = 2*(self.inset_x_tf - self.min)/(self.max - self.min) - 1# Normalization processing
self.Hbd = 2*(self.bdset_x_tf - self.min)/(self.max - self.min) - 1# Normalization processing
self.weights,self.biases = self.NNinit()# By function NNinit Completion weight , Offset initialization
self.u_in = self.NNU(self.Hin)# By function NNU Complete the calculation , That is, the approximate value of the internal points of the training set
self.u_b = self.NNU(self.Hbd)# By function NNU Complete the calculation , That is, the approximate value of the boundary points of the training set
self.ux,self.uy = self.u_grad(self.inset_x_tf)# adopt u_grad The first order partial derivatives of the interior points of the training set are obtained
self.loss_in = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.ux) + tf.square(self.uy)) -\
tf.reduce_mean(2*self.u_in*self.right_tf)# The loss function for the interior point obtained from the principle of minimum potential energy
self.loss_b = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.u_b - self.ub_tf))# The loss function for the boundary point
self.loss = self.loss_in + belta*self.loss_b# The total loss function
self.optim = tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = 5e-3)# Prepare the optimizer
self.minimizer = self.optim.minimize(self.loss)
''' config=tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=True) self.sess = tf.compat.v1.Session(config) '''
self.sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()# Create a session
init = tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()# Initialize variable
self.sess.run(init)
def w_init(self,in_dim,out_dim):# Initialization weight
w_std = np.sqrt(2/(in_dim + out_dim))
return tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([in_dim, out_dim], stddev = w_std), dtype=tf.float32)
def NNinit(self):# Initialization weight , bias
weights = []
biases = []
num = len(self.layers)
for i in range(0,num - 1):
w = self.w_init(in_dim = self.layers[i],out_dim = self.layers[i + 1])
b = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([1,self.layers[i + 1]], dtype = tf.float32), dtype=tf.float32)
weights.append(w)
biases.append(b)
return weights,biases
def NNU(self,Input):# Calculate the output of neural network
Input = tf.cast(Input,tf.float32)
weights,biases = self.NNinit()
num = len(weights)
for i in range(0,num - 1):
w,b = weights[i],biases[i]
Input = tf.tanh(tf.add(tf.matmul(Input,w),b))
W,B = weights[-1],biases[-1]
return tf.add(tf.matmul(Input,W),B)
def u_grad(self,Input):# Calculate the gradient
Input = tf.cast(Input,tf.float32)
u = self.NNU(Input)
ux = tf.gradients(u,Input)[0][:,0:1]
uy = tf.gradients(u,Input)[0][:,1:2]
return ux,uy
def ERROR(self):# Define the error between the exact solution and the approximate solution of the training set
fenzi_in = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.u_in - self.inset.u_acc))
fenzi_b = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.u_b - self.bdset.u_acc))
fenmu_in = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.u_in))
fenmu_b = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.u_b))
fenzi = fenzi_in + fenzi_b
fenmu = fenmu_in + fenmu_b
return tf.sqrt(fenzi/fenmu)
def train(self,step):# Define the training process
print('train the neural network')
st_time = time.time()
LOSS = self.sess.run(self.loss,feed_dict = self.feed)
loss_best = LOSS
weights_best = self.sess.run(self.weights)
biases_best = self.sess.run(self.biases)
record = 400
for j in range(step):
self.sess.run(self.minimizer,feed_dict = self.feed)# The optimization process
if j%record == 0:
error = self.sess.run(self.ERROR(),feed_dict = self.feed)
LOSS = self.sess.run(self.loss,feed_dict = self.feed)
print('train step:%d,loss:%.2f,error:%.2f'
%(j,LOSS,error))# Print loss function , Training set error
if LOSS < loss_best:
loss_best = LOSS
weights_best = self.sess.run(self.weights)# Ready to save optimal weights
biases_best = self.sess.run(self.biases)# Prepare to save the optimal offset
epo_time = time.time() - st_time
print('one epoch used:%.2f'%(epo_time))
print('------------------------------------------------')
def trainbatch(self,step):# Try to use batch Enter to improve accuracy , Reduce the time
print('train the neural network')
st_time = time.time()
batch = self.inset.nx
LOSS = self.sess.run(self.loss,feed_dict = self.feed)
loss_best = LOSS
weights_best = self.sess.run(self.weights)
biases_best = self.sess.run(self.biases)
record = 100
for j in range(step):
x = i*batch%len(self.inset.X)
y = x + batch
feed = {
self.inset_x_tf:inset.X[x:y],self.bdset_x_tf:bdset.X,
self.right_tf:inset.right[x:y],self.ub_tf:bdset.u_acc,
self.min:datamin,self.max:datamax}
self.sess.run(self.minimizer,feed_dict = feed)
if j%record == 0:
error = self.sess.run(self.ERROR(),feed_dict = self.feed)
LOSS = self.sess.run(self.loss,feed_dict = self.feed)
print('train step:%d,loss:%.2f,error:%.2f'
%(j,LOSS,error))
''' if LOSS < loss_best: loss_best = LOSS weights_best = self.sess.run(self.weights) biases_best = self.sess.run(self.biases) '''
epo_time = time.time() - st_time
print('one epoch used:%.2f'%(epo_time))
print('------------------------------------------------')
inset = INSET()
bdset = BDSET()
teset = TESET()
layers = [2,20,10,1]
belta = 5e3
#datamin = np.array([[teset.xa,teset.ya]])
#datamax = np.array([[teset.xb,teset.yb]])
ne = NN(inset,bdset,layers,belta)# Instantiate the class
epochs = 3
st = time.time()
for i in range(epochs):# Start training
print('epochs:%d'%(i))
#ne.trainbatch(500)
ne.train(2000)
ed = time.time()
print('all used time:%.2f'%(ed - st))
# Prediction function approximation and error
feed = {
ne.inset_x_tf:teset.X,ne.min:datamin,ne.max:datamax}
u_pred = ne.sess.run(ne.u_in,feed_dict = feed)# Utilization class NN Medium u_in To calculate the approximation on the test set
u_acc = np.array(teset.u_acc,dtype = np.float32)# Take out the exact solution in the test set
def LERROR(u_pred,u_acc):
fenzi = np.square(u_pred - u_acc).sum()
fenmu = (np.square(u_acc) + 1e-7).sum()
return np.sqrt(fenzi/fenmu)
print('the test error:%.3f'%(LERROR(u_pred,u_acc)))# Print the error on the test
M = teset.nx
N = teset.ny
x_train = np.linspace(teset.xa,teset.xb,M)
y_train = np.linspace(teset.ya,teset.yb,N)
x,y = np.meshgrid(x_train,y_train)
plt.contourf(x,y,u_pred.reshape(M,N).T,40,cmap = 'Blues')# Draw an image
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('numerical solution')
边栏推荐
- Sigkdd22 | graph generalization framework of graph neural network under the paradigm of "pre training, prompting and fine tuning"
- Bit.Store:熊市漫漫,稳定Staking产品或成主旋律
- 一场分销裂变活动,不止是发发朋友圈这么简单!
- Redis Series 2: data persistence improves availability
- 事务的四大特性
- Regular matching starts with what, ends with what, starts with what, and ends with what
- VS编译遇到的问题
- QT5.5.1桌面版安装配置过程中的疑难杂症处理(配置ARM编译套件)
- Luogu_ P1008 [noip1998 popularization group] triple strike_ enumeration
- 3.1 simple condition judgment
猜你喜欢

PSS:你距离NMS-free+提点只有两个卷积层 | 2021论文
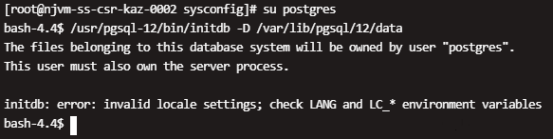
Centos8 PostgreSQL initialization error: initdb: error: invalid locale settings; check LANG and LC_* environment
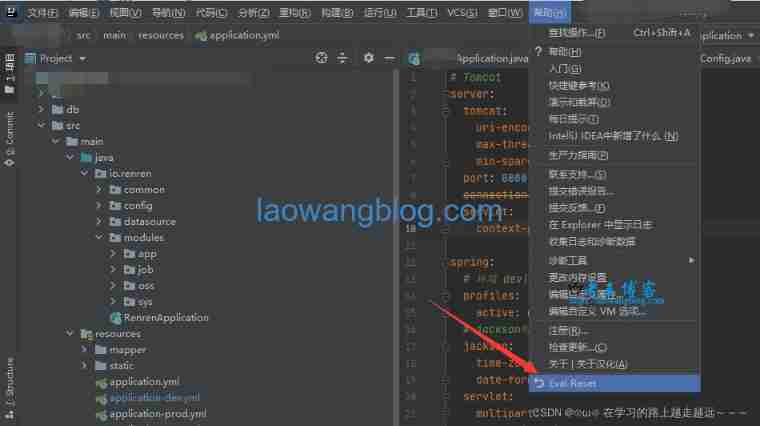
IDE Eval reset unlimited trial reset

ICML 2022 | 阿⾥达摩院最新FEDformer,⻓程时序预测全⾯超越SOTA

Pisa-Proxy 之 SQL 解析实践

【Pygame小遊戲】這款“吃掉一切”遊戲簡直奇葩了?通通都吃掉嘛?(附源碼免費領)

带你认识图数据库性能和场景测试利器LDBC SNB

Jialichuang EDA professional edition all offline client release

A distribution fission activity is more than just a circle of friends!

Open source 23 things shardingsphere and database mesh have to say
随机推荐
List转Table
SIGKDD22|图“预训练、提示、微调”范式下的图神经网络泛化框架
Luogu_ P1007 single log bridge_ thinking
【Pygame小遊戲】這款“吃掉一切”遊戲簡直奇葩了?通通都吃掉嘛?(附源碼免費領)
Sigkdd22 | graph generalization framework of graph neural network under the paradigm of "pre training, prompting and fine tuning"
Realize simple three-D cube automatic rotation
VS编译遇到的问题
Design of electronic calculator system based on FPGA (with code)
SQL parsing practice of Pisa proxy
The role of the symbol @ in MySQL
实现简单的三D立方体自动旋转
Luogu_ P1002 [noip2002 popularization group] crossing the river_ dp
A distribution fission activity is more than just a circle of friends!
树莓派初步使用
鴻蒙發力!HDD杭州站·線下沙龍邀您共建生態
Mode setting of pulseaudio (21)
Logstash excludes specific files or folders from collecting report log data
等保三级密码复杂度是多少?多久更换一次?
Design of vga/lcd display controller based on FPGA (with code)
Hierarchical clustering and case analysis