当前位置:网站首页>[VTK] vtkPolydataToImageStencil 源码解读
[VTK] vtkPolydataToImageStencil 源码解读
2022-07-03 10:04:00 【comedate】
1. 类的作用:
模板类将多边形数据转换为图像模板。
多段数据可以是封闭曲面网格,也可以是一系列多段线轮廓(每个切片一个轮廓)
2. 主要步骤:
Description of algorithm:
- cut the polydata at each z slice to create polylines
沿 Z 切片方向创建折线 - find all “loose ends” and connect them to make polygons
(if the input polydata is closed, there will be no loose ends)
找到所以未了结的部分,并连接成多边形 - go through all line segments, and for each integer y value on a line segment,
store the x value at that point in a bucket
遍历所有线段,对于每个线段上的每个整数y值,存储在该点的x值 - for each z integer index, find all the stored x values and use them to create one z slice of the vtkStencilData
对于每个z整数索引,查找所有存储的x值,并使用它们来创建一个z切片的 vtkstencildata
vtkImageStencilRaster raster(&extent[2]);
此光栅通过记录曲面上每个y整数位置的所有“x”位置来存储所有线段。
3. 代码详解:
源码中,最主要的实现函数是: 线程执行函数:
void vtkPolyDataToImageStencil::ThreadedExecute(
vtkImageStencilData *data,
int extent[6],
int threadId)
{
// the spacing and origin of the generated stencil
double *spacing = data->GetSpacing();
double *origin = data->GetOrigin();
// if we have no data then return
if (!this->GetInput()->GetNumberOfPoints())
{
return;
}
// Only divide once
double invspacing[3];
invspacing[0] = 1.0/spacing[0];
invspacing[1] = 1.0/spacing[1];
invspacing[2] = 1.0/spacing[2];
// get the input data
vtkPolyData *input = this->GetInput();
// the output produced by cutting the polydata with the Z plane
vtkPolyData *slice = vtkPolyData::New();
// This raster stores all line segments by recording all "x"
// positions on the surface for each y integer position.
vtkImageStencilRaster raster(&extent[2]);
raster.SetTolerance(this->Tolerance);
// The extent for one slice of the image
int sliceExtent[6];
sliceExtent[0] = extent[0]; sliceExtent[1] = extent[1];
sliceExtent[2] = extent[2]; sliceExtent[3] = extent[3];
sliceExtent[4] = extent[4]; sliceExtent[5] = extent[4];
// Loop through the slices
for (int idxZ = extent[4]; idxZ <= extent[5]; idxZ++)
{
if (threadId == 0)
{
this->UpdateProgress((idxZ - extent[4])*1.0/(extent[5] - extent[4] + 1));
}
double z = idxZ*spacing[2] + origin[2];
slice->PrepareForNewData();
raster.PrepareForNewData();
// Step 1: Cut the data into slices
if (input->GetNumberOfPolys() > 0 || input->GetNumberOfStrips() > 0)
{
this->PolyDataCutter(input, slice, z);
}
else
{
// if no polys, select polylines instead
this->PolyDataSelector(input, slice, z, spacing[2]);
}
if (!slice->GetNumberOfLines())
{
continue;
}
// convert to structured coords via origin and spacing
vtkPoints *points = slice->GetPoints();
vtkIdType numberOfPoints = points->GetNumberOfPoints();
for (vtkIdType j = 0; j < numberOfPoints; j++)
{
double tempPoint[3];
points->GetPoint(j, tempPoint);
tempPoint[0] = (tempPoint[0] - origin[0])*invspacing[0];
tempPoint[1] = (tempPoint[1] - origin[1])*invspacing[1];
tempPoint[2] = (tempPoint[2] - origin[2])*invspacing[2];
points->SetPoint(j, tempPoint);
}
// Step 2: Find and connect all the loose ends
std::vector<vtkIdType> pointNeighbors(numberOfPoints);
std::vector<vtkIdType> pointNeighborCounts(numberOfPoints);
std::fill(pointNeighborCounts.begin(), pointNeighborCounts.end(), 0);
// get the connectivity count for each point
vtkCellArray *lines = slice->GetLines();
vtkIdType npts = 0;
vtkIdType *pointIds = nullptr;
vtkIdType count = lines->GetNumberOfConnectivityEntries();
for (vtkIdType loc = 0; loc < count; loc += npts + 1)
{
lines->GetCell(loc, npts, pointIds);
if (npts > 0)
{
pointNeighborCounts[pointIds[0]] += 1;
for (vtkIdType j = 1; j < npts-1; j++)
{
pointNeighborCounts[pointIds[j]] += 2;
}
pointNeighborCounts[pointIds[npts-1]] += 1;
if (pointIds[0] != pointIds[npts-1])
{
// store the neighbors for end points, because these are
// potentially loose ends that will have to be dealt with later
pointNeighbors[pointIds[0]] = pointIds[1];
pointNeighbors[pointIds[npts-1]] = pointIds[npts-2];
}
}
}
// use connectivity count to identify loose ends and branch points
std::vector<vtkIdType> looseEndIds;
std::vector<vtkIdType> branchIds;
for (vtkIdType j = 0; j < numberOfPoints; j++)
{
if (pointNeighborCounts[j] == 1)
{
looseEndIds.push_back(j);
}
else if (pointNeighborCounts[j] > 2)
{
branchIds.push_back(j);
}
}
// remove any spurs 删除支线
for (size_t b = 0; b < branchIds.size(); b++)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < looseEndIds.size(); i++)
{
if (pointNeighbors[looseEndIds[i]] == branchIds[b])
{
// mark this pointId as removed
pointNeighborCounts[looseEndIds[i]] = 0;
looseEndIds.erase(looseEndIds.begin() + i);
i--;
if (--pointNeighborCounts[branchIds[b]] <= 2)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
// join any loose ends 连接所以的未了结的点
while (looseEndIds.size() >= 2)
{
size_t n = looseEndIds.size();
// search for the two closest loose ends
double maxval = -VTK_FLOAT_MAX;
vtkIdType firstIndex = 0;
vtkIdType secondIndex = 1;
bool isCoincident = false;
bool isOnHull = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n && !isCoincident; i++)
{
// first loose end
vtkIdType firstLooseEndId = looseEndIds[i];
vtkIdType neighborId = pointNeighbors[firstLooseEndId];
double firstLooseEnd[3];
slice->GetPoint(firstLooseEndId, firstLooseEnd);
double neighbor[3];
slice->GetPoint(neighborId, neighbor);
for (size_t j = i+1; j < n; j++)
{
vtkIdType secondLooseEndId = looseEndIds[j];
if (secondLooseEndId != neighborId)
{
double currentLooseEnd[3];
slice->GetPoint(secondLooseEndId, currentLooseEnd);
// When connecting loose ends, use dot product to favor
// continuing in same direction as the line already
// connected to the loose end, but also favour short
// distances by dividing dotprod by square of distance.
double v1[2], v2[2];
v1[0] = firstLooseEnd[0] - neighbor[0];
v1[1] = firstLooseEnd[1] - neighbor[1];
v2[0] = currentLooseEnd[0] - firstLooseEnd[0];
v2[1] = currentLooseEnd[1] - firstLooseEnd[1];
double dotprod = v1[0]*v2[0] + v1[1]*v2[1];
double distance2 = v2[0]*v2[0] + v2[1]*v2[1];
// check if points are coincident
if (distance2 == 0)
{
firstIndex = static_cast<vtkIdType>(i);
secondIndex = static_cast<vtkIdType>(j);
isCoincident = true;
break;
}
// prefer adding segments that lie on hull
double midpoint[2], normal[2];
midpoint[0] = 0.5*(currentLooseEnd[0] + firstLooseEnd[0]);
midpoint[1] = 0.5*(currentLooseEnd[1] + firstLooseEnd[1]);
normal[0] = currentLooseEnd[1] - firstLooseEnd[1];
normal[1] = -(currentLooseEnd[0] - firstLooseEnd[0]);
double sidecheck = 0.0;
bool checkOnHull = true;
for (size_t k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
if (k != i && k != j)
{
double checkEnd[3];
slice->GetPoint(looseEndIds[k], checkEnd);
double dotprod2 = ((checkEnd[0] - midpoint[0])*normal[0] +
(checkEnd[1] - midpoint[1])*normal[1]);
if (dotprod2*sidecheck < 0)
{
checkOnHull = false;
}
sidecheck = dotprod2;
}
}
// check if new candidate is better than previous one
if ((checkOnHull && !isOnHull) ||
(checkOnHull == isOnHull && dotprod > maxval*distance2))
{
firstIndex = static_cast<vtkIdType>(i);
secondIndex = static_cast<vtkIdType>(j);
isOnHull |= checkOnHull;
maxval = dotprod/distance2;
}
}
}
}
// get info about the two loose ends and their neighbors
vtkIdType firstLooseEndId = looseEndIds[firstIndex];
vtkIdType neighborId = pointNeighbors[firstLooseEndId];
double firstLooseEnd[3];
slice->GetPoint(firstLooseEndId, firstLooseEnd);
double neighbor[3];
slice->GetPoint(neighborId, neighbor);
vtkIdType secondLooseEndId = looseEndIds[secondIndex];
vtkIdType secondNeighborId = pointNeighbors[secondLooseEndId];
double secondLooseEnd[3];
slice->GetPoint(secondLooseEndId, secondLooseEnd);
double secondNeighbor[3];
slice->GetPoint(secondNeighborId, secondNeighbor);
// remove these loose ends from the list
looseEndIds.erase(looseEndIds.begin() + secondIndex);
looseEndIds.erase(looseEndIds.begin() + firstIndex);
if (!isCoincident)
{
// create a new line segment by connecting these two points
lines->InsertNextCell(2);
lines->InsertCellPoint(firstLooseEndId);
lines->InsertCellPoint(secondLooseEndId);
}
}
// Step 3: Go through all the line segments for this slice,
// and for each integer y position on the line segment,
// drop the corresponding x position into the y raster line.
count = lines->GetNumberOfConnectivityEntries();
for (vtkIdType loc = 0; loc < count; loc += npts + 1)
{
lines->GetCell(loc, npts, pointIds);
if (npts > 0)
{
vtkIdType pointId0 = pointIds[0];
double point0[3];
points->GetPoint(pointId0, point0);
for (vtkIdType j = 1; j < npts; j++)
{
vtkIdType pointId1 = pointIds[j];
double point1[3];
points->GetPoint(pointId1, point1);
// make sure points aren't flagged for removal
if (pointNeighborCounts[pointId0] > 0 &&
pointNeighborCounts[pointId1] > 0)
{
raster.InsertLine(point0, point1);
}
pointId0 = pointId1;
point0[0] = point1[0];
point0[1] = point1[1];
point0[2] = point1[2];
}
}
}
// Step 4: Use the x values stored in the xy raster to create
// one z slice of the vtkStencilData
sliceExtent[4] = idxZ;
sliceExtent[5] = idxZ;
raster.FillStencilData(data, sliceExtent);
}
slice->Delete();
}
4. 总结技术点:
- 平面与 polydata 相交得到线段
- 线段根据规则连接成多边形
- 遍历 y, 使用 raster.InsertLine 方法填充直线上的所以的点
- 遍历所有的 z, 得到 Z slice
从而得到所以的点;
边栏推荐
- I have been doing software testing for three years, and my salary is less than 20K. Today, I put forward my resignation
- 程序进程管理工具-go supervisor
- 嵌入式軟件測試怎麼實現自動化測試?
- 如何成为一名高级数字 IC 设计工程师(1-2)Verilog 编码语法篇:Verilog 1995、2001、2005 标准
- Android log system
- How did I grow up in the past eight years as a test engineer of meituan? I hope technicians can gain something after reading it
- Oracle 11g single machine cold standby database
- 【Proteus仿真】74HC154 四线转12线译码器组成的16路流水灯
- 解决undefined reference to `__aeabi_uidivmod‘和undefined reference to `__aeabi_uidiv‘错误
- Qt:qss custom qstatusbar instance
猜你喜欢

T5 attempt

Stack, monotone stack, queue, monotone queue

Summary of interview questions (2) IO model, set, NiO principle, cache penetration, breakdown avalanche
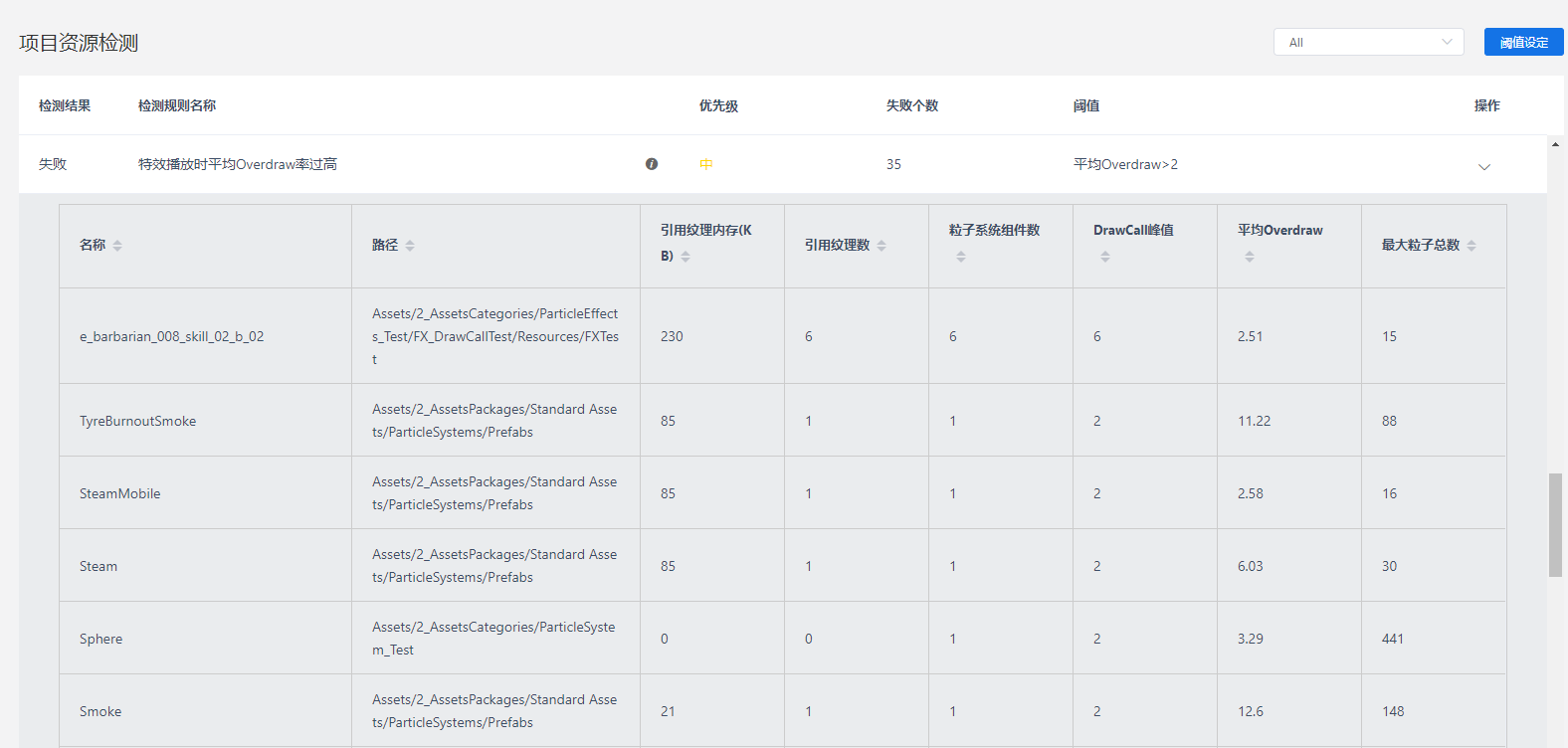
Unity移动端游戏性能优化简谱之 画面表现与GPU压力的权衡

Encapsulation attempt of network request framework of retro + kotlin + MVVM

The testing department of the company came to the king of the Post-00 roll, and the veteran exclaimed that it was really dry, but

2021 reading summary (continuously updating)
8年测试总监的行业思考,看完后测试思维认知更深刻

软件测试工程师的5年之痒,讲述两年突破瓶颈经验
My understanding of testing (summarized by senior testers)
随机推荐
Touch and screen automatic rotation debugging
进程与线程
QT: QSS custom qtoolbar and qtoolbox instances
The testing department of the company came to the king of the Post-00 roll, and the veteran exclaimed that it was really dry, but
I, a tester from a large factory, went to a state-owned enterprise with a 50% pay cut. I regret it
2021 reading summary (continuously updating)
线性表顺序表综合应用题P18
Overview of testing theory
QT: QSS custom qsplitter instance
Google Earth Engine(GEE)——当我们前后影像来弥补插值效果得时候,没有效果怎么办?
[proteus simulation] 16 channel water lamp composed of 74hc154 four wire to 12 wire decoder
Hard goods | write all the codes as soon as you change the test steps? Why not try yaml to realize data-driven?
数据库增量备份 - DB INCR DB FULL
Android log system
Have you learned the new technology to improve sales in 2021?
Unity移动端游戏性能优化简谱之 画面表现与GPU压力的权衡
触摸与屏幕自动旋转调试
面试题总结(2) IO模型,集合,NIO 原理,缓存穿透,击穿雪崩
Test what the leader should do
Ext file system mechanism principle