当前位置:网站首页>The use of a semaphore/interprocess communication 】 【 Shared memory
The use of a semaphore/interprocess communication 】 【 Shared memory
2022-08-02 16:02:00 【white U】
信号量:
:特殊的变量 值 > 0 减1 代表获取资源 p操作 (会阻塞)
加1 代表释放资源,v操作 (会阻塞)
作用 : 同步进程 (Program traffic lights,Controls access to a resource by a process)
临界资源:同一时刻,只允许一个进程访问的资源
临界区:访问临界资源的代码段

帮助手册 man semget;(信号量)man semctl(封装)Semaphores are controlled by the kernel.不受A/B进程的控制
semget()创建/获取an existing semaphore
//A Create a semaphore(The semaphore needs to be initializedsemget---semctl()) ,B只需要加入(No need to initialize againsemget()获取信号量)semop()p,v 修改信号量semctl()初始化,删除信号量 (初始值为1,Indicates that the resource is free)
sem_init()// semget—semctl(),emget()
sem_p()// semop() -1
sem_v()// semop() +1
sem_destory() semctl()
引用头文件:
#include <sys/sem.h>
//Create and acquire semaphores
//key Equivalent to the identifier of the semaphore,如果使用同一个key,is using the same semaphore
int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg); / // 整数值 //Number of semaphores to create //如文件的权限
//A set of semaphores can be created,Just created one IPC_CRET|IPC_EXCL|0600
//如果创建失败,两种情况(信号量已存在,(semget()获取即可,或 创建失败)
//如果创建成功,接下来
//初始化信号量
int semctl(int semid, int semnum, int cmd, ...);
//semnum:第几(第一个0)个信号(可以创建一组(多个 )can be initialized separately
//cmd 命令(SETVAL) (IPC_RMID)
// ... 联合体(给SETVAL赋值)
semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,a) //给信号量赋值
semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID) //删除信号量
int val; /Value for SETVAL; (给信号量赋值)
union semun//联合体
{
**int val; /Value for SETVAL; (给信号量赋值)**
struct semid_ds *buf; /* Buffer for IPC_STAT, IPC_SET */
unsigned short *array; /* Array for GETALL, SETALL */
struct seminfo *__buf; /* Buffer for IPC_INFO (Linux-specific) */
};
使用 union semun The union assigns values to the semaphore
union semun a;
a.val = 1;
// Handling of semaphores
int semop(int semid, struct sembuf *sops, size_t nsops);
unsigned short sem_num; /* semaphore number */
short sem_op; /* semaphore operation */
short sem_flg = SEM_UNDO; /* operation flags */ //p操作后,When the program terminates abnormally,可以自动执行V操作
例如:创建a.c / b.c文件
Semaphore file sem.c
头文件:
- sem.h文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
union semun
{
int val;
};
void sem_init();
void sem_p();
void sem_v();
void sem_destroy();
- sem.c文件
#include "sem.h"
static int semid = -1;
void sem_init()
{
semid = semget((key_t)1234,1,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0600);
if ( semid == -1 )//全新创建失败,may already exist
{
semid = semget((key_t)1234,1,0600);
if ( semid == -1 )
{
printf("create sem failed\n");
}
}
else//全新创建成功,初始化
{
union semun a;
a.val = 1;
if ( semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,a) == -1 )
{
printf("semctl setval failed\n");
}
}
}
void sem_p()
{
struct sembuf a;
a.sem_num = 0;
a.sem_op = -1;//p
a.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;
if( semop(semid,&a,1) == -1 )
{
printf("semop p failed\n");
}
}
void sem_v()
{
struct sembuf a; //处理信号量
a.sem_num = 0; //表示第1个信号量
a.sem_op = 1;//给信号量赋值
a.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO; //表示如果p操作后,程序异常结束,可以自动执行v操作,释放资源.
if( semop(semid,&a,1) == -1 ) //判断V操作是否成功
{
printf("semop v failed\n");
}
}
void sem_destroy()
{
if ( semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID) == -1 )
{
printf("destroy failed\n");
}
}
- a.c 文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "sem.h"
int main()
{
sem_init();
for( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ )
{
sem_p();
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
int n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
sem_v();
n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
}
sleep(10);
sem_destroy();
exit(0);
}
- b.c文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "sem.h"
int main()
{
sem_init();
for( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ )
{
sem_p();
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
int n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
sem_v();
n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
}
}
编译命令:
gcc -c sem.c
gcc -o a a.c sem.c
gcc -o b b.c sem.c
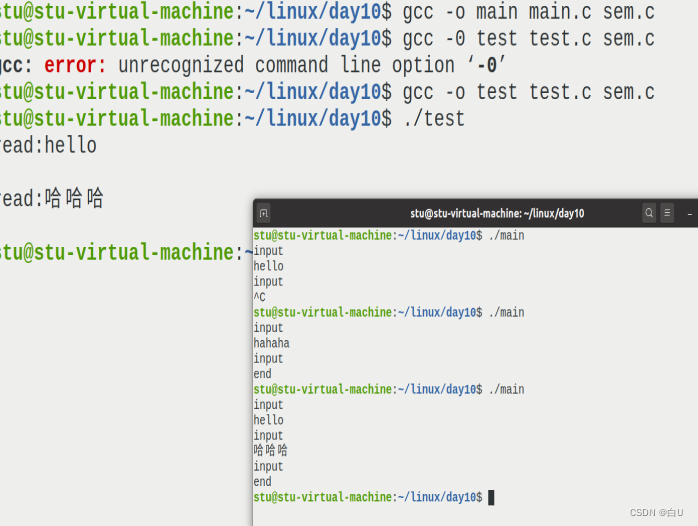
执行: ./a& ./b& (Indicates simultaneous execution in the background)
when ending the process,使用ipcscommand to see if it willa.c 和b.cboth ended
如果没有使用ipcrm手动结束.Prevent an exception from the next execution.(unless restarted,The semaphore responsible for undeleted has been around)
Semaphore learning mainly understands the process of using semaphores,
初始化,
p操作
v操作
删除信号量
共享内存
- Multiple processes share the same piece of physical memory.
(先开辟一块物理内存,Multiple processes map it into their own virtual address space,If a process modifies the content on this memory,Other shared processes will also see it immediately.)
But no synchronization mechanism is provided,A semaphore is required for control进程的同步.
定义两个信号量:
目的:Guaranteed when no data is written on the read side,The write side is only allowed to write data once.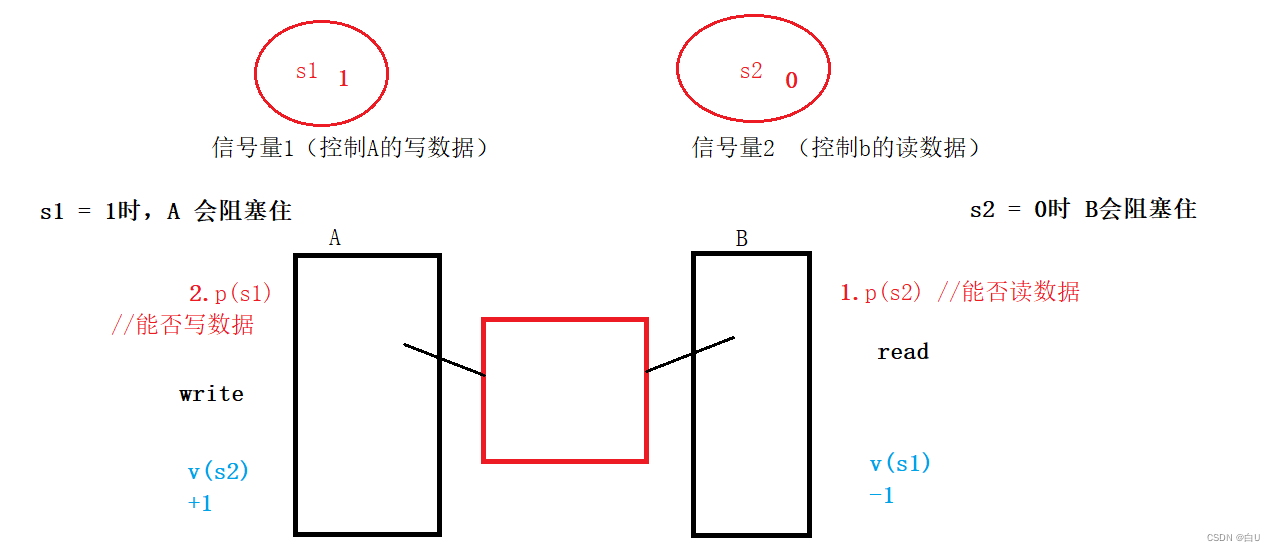
(Implement the function of the pipeline)
- sem.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#define SEM1 0
#define SEM2 1
#define SEM_MAX 2
union semun
{
int val;
};
void sem_init();
void sem_p();
void sem_v();
void sem_destroy();
- sem.c
#include "sem.h"
static int semid = -1;
void sem_init()
{
//创建信号量 //最多创建
semid = semget((key_t)1234,SEM_MAX,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0600);
if ( semid == -1 )//全新创建失败,may already exist
{
//获取信号量
semid = semget((key_t)1234,SEM_MAX,0600);
if ( semid == -1 )
{
printf("create sem failed\n");
}
}
else//全新创建成功,初始化
{
union semun a;
int arr[SEM_MAX] = {
1,0}; //两个信号量,初始值分别为1,0
for( int i = 0; i < SEM_MAX; i++ )
{
a.val = arr[i]; //给信号量赋值,控制信号量,成功返回0
if ( semctl(semid,i,SETVAL,a) == -1 )
{
// i:Which semaphore to assign to
printf("semctl setval failed\n");
}
}
}
}
void sem_p(int index)
{
//用输入的indexto control different semaphores
if ( index < 0 || index >= SEM_MAX )
{
return;
}
struct sembuf a;
a.sem_num = index;
a.sem_op = -1;//p
a.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;
if( semop(semid,&a,1) == -1 )
{
printf("semop p failed\n");
}
}
void sem_v(int index)
{
if ( index < 0 || index >= SEM_MAX )
{
return;
}
struct sembuf a;
a.sem_num = index;
a.sem_op = 1;//v
a.sem_flg = SEM_UNDO;
if( semop(semid,&a,1) == -1 )
{
printf("semop v failed\n");
}
}
void sem_destroy()
{
if ( semctl(semid,0,IPC_RMID) == -1 )
{
printf("destroy failed\n");
}
}
- Handling of two semaphores:(S1 S2)
else//全新创建成功,初始化
{
union semun a;
int arr[SEM_MAX] = {1,0}; //两个信号量,初始值分别为1,0
for( int i = 0; i < SEM_MAX; i++ )
{
a.val = arr[i]; //给信号量赋值,控制信号量,成功返回0
if ( semctl(semid,i,SETVAL,a) == -1 )
{ // i:Which semaphore to assign to
printf(“semctl setval failed\n”);
} - test.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "sem.h"
int main()
{
int shmid = shmget((key_t)1234,128,IPC_CREAT|0600);
if ( shmid == -1 )
{
exit(1);
}
char * s = (char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
if ( s == (char*)-1 )
{
exit(1);
}
sem_init();
while( 1 )
{
sem_p(SEM2);
if ( strncmp(s,"end",3) == 0 )
{
break;
}
printf("read:%s\n",s);
sem_v(SEM1);
}
shmdt(s);
sem_destroy(); //在读操作结束后 销毁信号量
exit(0);
}
//在读操作结束后 销毁信号量
- main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include "sem.h"
int main()
{
//创建共享内存 key:标识 size: 128
int shmid = shmget((key_t)1234,128,IPC_CREAT|0600);
if ( shmid == -1 )
{
exit(1);
}
//Map the requested physical memory into the virtual address space of the process
//If the mapping is successful,返回共享内存的首地址,否则返回空
char* s = (char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);
if ( s == (char*)-1 )
{
exit(1);
}
sem_init();
while( 1 )
{
printf("input\n");
char buff[128] = {
0};
//键盘获取数据
fgets(buff,128,stdin);
sem_p(SEM1);
//(读操作) 将获取的数据,copied to shared memory
strcpy(s,buff);
sem_v(SEM2);
//结束
if ( strncmp(buff,"end",3) == 0 )
{
break;
}
}
//断开映射
shmdt(s);
exit(0);
}
p77《linux平台开发》
作业: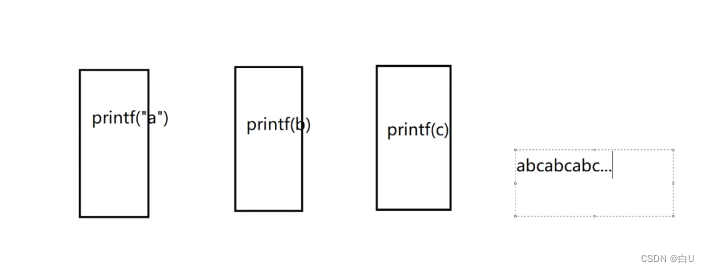
aProcesses only outputa
bProcesses only outputb
cProcesses only outputc
打印结果 abcabcabc…
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
5款最好用的免费3D建模软件(附下载链接)
Test case exercises
VirtualLab Fusion中的可视化设置
永久更改pip源
win10无法识别蓝牙麦克风
富文本编辑
【进程间通信】信号量的使用/共享内存
Oauth2.0 资源服务器搭建
第三十一章:二叉树的概念与性质
字符数组/字符串数组|数组指针/指针数组/
Detailed explanation of MATLAB drawing function fplot
嵌入式学习硬件篇------初识ARM
EastWave:垂直腔表面激光器
剑指offer:删除链表中重复的节点
移动拷贝构造函数
golang内存相关文章-收集
IDEA 单元测试报错:Class not found
Unity Line-Renderer
shader入门精要3
剑指offer:反转链表