当前位置:网站首页>SOM Network 1: Principles Explained
SOM Network 1: Principles Explained
2022-08-01 21:47:00 【@BangBang】
SOM 介绍
SOM (Self Organizing Maps):自组织映射神经网络,是一种类似于kmeans``的聚类算法,for finding data聚类中心.它可以将The relationship is complex and nonlinearhigh latitude data,Mapping to have simple geometry and interrelationshipslow-latitude space.(Low-latitude maps can reflect the topological structure between high-latitude features)
- 自组织映射(Self-organizing map, SOM)通过学习输入空间中的数据,生成一个
低维、离散的映射(Map),To some extent, it can also be regarded as one降维算法. SOM是一种无监督的人工神经网络.不同于一般神经网络基于损失函数的反向传递来训练,它运用竞争学习(competitive learning)策略,依靠神经元之间互相竞争逐步优化网络.且使用Neighbor relation function(neighborhood function)to maintain the input space拓扑结构.- 由于基于
无监督学习,这意味着训练阶段不需要人工介入(即不需要样本标签),我们可以在不知道类别的情况下,对数据进行聚类;可以识别针对某问题具有内在关联的特征. Data visualization can be achieved;聚类;分类;特征抽取等任务
特点归纳
- 神经网络,竞争学习策略
- 无监督学习,不需要额外标签
- Great for visualization of high-dimensional data,能够维持输入空间的拓扑结构
- 具有很高的泛化能力,It can even recognize input samples it has never encountered before
网络结构
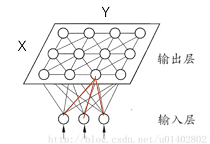
SOMThe network structure has2层:输入层、输出层(Also called the competition layer),.
输入层:包含D个节点,The number of nodes is determined by the dimension of the input features,Same as input feature dimension.输出层:Usually the nodes of the output layer are arranged in layersX行Y列的矩阵形式,输出层有X x Y个节点.
网络的特点
- (1) each node of the output layer,通过
Dright side,with all sample pointsDdimensional eigenvectors are connected.,输出层 i , j i,j i,j A node vector of locations:
W i j = [ w i j 0 , w i j 0 , . . . w i j D ] W_{ij} = [w_{ij0},w_{ij0},...w_{ijD}] Wij=[wij0,wij0,...wijD]
换句话说:输出层 i , j i,j i,j A node for a location can use oneD维矢量 W i j W_{ij} Wij来表征` - (2)
经过训练后,between each node of the output layer,There is a certain correlation according to distance,That is, the closer you are,关联度越高,It can also be expressed as two points that are closer to each other,This is two pointsD维矢量will be closer. - (3)
训练的目的:学习X x Y个D维权重 W W W,All training samples can be used(每个样本D维特征向量)Map to the nodes of the output layer.
High latitude space(输入)距离近的点,The distance is also closer after mapping to the output layer.For example, two sample points are relatively close to each other ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)上,或者映射到 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)和 ( i , j + 1 ) (i,j+1) (i,j+1)上.
模型训练过程
- 1 准备训练数据datas:
N x DN为样本的数量,Dis the dimension of the feature vector for each sample
通常需要正则化:
d a t a s = d a t a s − m e a n ( d a t a s ) s t d ( d a t a s ) datas=\frac{datas-mean(datas)}{std(datas)} datas=std(datas)datas−mean(datas) - 2.确定参数 X , Y X,Y X,Y X = Y = 5 N X=Y=\sqrt{5\sqrt{N}} X=Y=5N , 向上取整
- 3.权重 W W W 初始化: W W W的维度为(X x Y x D)
- 4.迭代训练
1) Read a sample point x x x : [D] # D维
2) 计算样本 x x x respectively with the output layer X ∗ Y X*Y X∗Ynodes to calculate the distance,找到距离最近的点 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)作为激活点,set its weight g g g为1
3) for other nodes in the output layer,Take advantage of it and location ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)node distance at ,Calculate their weights g g g,与 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)The closer the location is,则权重越大. Complete the calculation of the output layerX*Y节点权重 g g g,特点是以 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)where the weight is the largest,The farther away it is, the smaller it is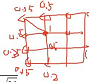
- 4) Update the representation vectors of all nodes in the output layer:
W = W + η ∗ g ∗ ( x − W ) W=W +\eta*g*(x-W) W=W+η∗g∗(x−W)
其中 η \eta η是学习率, x − W x-W x−WRepresents the currently updated output layer node and input samplex的距离,The purpose of updating a node's representation vector is to make the node approximate the input vector x x x
整个SOM映射过程,Equivalent to inputNsamples for cluster mapping,比如输入样本 x 1 x1 x1, x 2 x2 x2, x 3 x3 x3 Maps to output nodesa, 样本 x 4 x4 x4, x 5 x5 x5, x 6 x6 x6Maps to output nodesb,Then you can use the output nodeato characterize the sample x 1 x1 x1, x 2 x2 x2, x 3 x3 x3;Use output nodesbto characterize the sample x 4 x4 x4, x 5 x5 x5, x 6 x6 x6
- 经过多轮迭代,Finished characterizing the output node vector W W W的更新,The representation vectors of these nodes can characterize the input samplesx
(N x D).Equivalent to taking the input sample,映射为(XxYxD)的表征向量 W = w 1 , 1 , w 1 , 2 , , , w x , y W=w_{1,1},w_{1,2} ,,, w_{x,y} W=w1,1,w1,2,,,wx,y
权重初始化 W:[X,Y,D]
Weight initialization mainly includes3种方法:
- 1 随机初始化,然后标准化 W = W ∣ ∣ W ∣ ∣ W=\frac{W}{||W||} W=∣∣W∣∣W
- 2 Picked randomly from the training data X ∗ Y X*Y X∗Y个,来初始化权重
- 3 对训练数据进行
PCA,Take the two eigenvectors with the largest eigenvaluesM:D x 2 Mapping as a basis vector.
距离计算方式
采用欧式距离计算 ,公式如下:
d i s = ∣ ∣ x − y ∣ ∣ dis =|| x-y || dis=∣∣x−y∣∣
Calculate the weights of the output nodesg
Suppose the activation point coordinates are ( c X , c y ) (c_X,c_y) (cX,cy) ,其他位置 i , j i,j i,j处的权重gThere are two main methods of calculation:
高斯法
g ( i , j ) = e − ( c x − i ) 2 2 σ 2 e − ( c y − j ) 2 2 σ 2 g(i,j)= e^{-\frac{(c_x-i)^2}{2\sigma^2}}e^{-\frac{(c_y-j)^2}{2\sigma^2}} g(i,j)=e−2σ2(cx−i)2e−2σ2(cy−j)2
可以看出到 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)is the activation point ( c X , c y ) (c_X,c_y) (cX,cy),计算得到的g=1.The weights exhibit a Gaussian distribution.Among them the Gaussian method σ \sigma σThe value also changes with the number of iteration steps,更新方式跟学习率方式一样,参见后面学习率的更新
Hard threshold method
这种方法比较直接,以 ( c X , c y ) (c_X,c_y) (cX,cy)within a certain range of the centerg为1,其他为0,;Generally, the Gaussian method is selected
学习率更新
η = η 0 1 + t m a x s t e p / 2 \eta=\frac{\eta_0}{1+\frac{t}{max_{step}/2}} η=1+maxstep/2tη0
其中 t t tIndicates the current iterationstep, m a x s t e p max_{step} maxstepThe total number of iterations for network training,学习率 η \eta η随着迭代次数的增加,会越来越小.
边栏推荐
- 树莓派的信息显示小屏幕,显示时间、IP地址、CPU信息、内存信息(c语言),四线的i2c通信,0.96寸oled屏幕
- Appendix A printf, varargs and stdarg A.3 stdarg.h ANSI version of varargs.h
- 0DFS中等 LeetCode6134. 找到离给定两个节点最近的节点
- C Pitfalls and Defects Chapter 7 Portability Defects 7.7 Truncation During Division
- LVS负载均衡群集
- groupByKey和reduceBykey的区别
- Based on php film and television information website management system acquisition (php graduation design)
- Unity Shader 常规光照模型代码整理
- SAP ABAP OData 服务如何支持删除(Delete)操作试读版
- scikit-learn no moudule named six
猜你喜欢

KMP 字符串匹配问题

Based on php online learning platform management system acquisition (php graduation design)
MySQL related knowledge

找工作必备!如何让面试官对你刮目相看,建议收藏尝试!!

HCIP---多生成树协议相关知识点

基于php在线学习平台管理系统获取(php毕业设计)
C Expert Programming Chapter 1 C: Through the Fog of Time and Space 1.4 K&R C
Small program -- subcontracting
树莓派的信息显示小屏幕,显示时间、IP地址、CPU信息、内存信息(c语言),四线的i2c通信,0.96寸oled屏幕

MySQL相关知识
随机推荐
Raspberry Pi information display small screen, display time, IP address, CPU information, memory information (C language), four-wire i2c communication, 0.96-inch oled screen
Appendix A printf, varargs and stdarg A.1 printf family of functions
基于php在线学习平台管理系统获取(php毕业设计)
Shell编程之条件语句
Based on php Xiangxi tourism website management system acquisition (php graduation design)
【Jmeter常用断言组件】
【建议收藏】ヾ(^▽^*)))全网最全输入输出格式符整理
迁移学习——Discriminative Transfer Subspace Learning via Low-Rank and Sparse Representation
多商户商城系统功能拆解19讲-平台端发票管理
shell programming conventions and variables
Based on php film and television information website management system acquisition (php graduation design)
scikit-learn no moudule named six
Day016 类和对象
9. SAP ABAP OData 服务如何支持删除(Delete)操作
统计单词数
C语言必杀技3行代码把运行速度提升4倍
2022-08-01 第五小组 顾祥全 学习笔记 day25-枚举与泛型
0DFS中等 LeetCode6134. 找到离给定两个节点最近的节点
如何优雅的性能调优,分享一线大佬性能调优的心路历程
Uses of Anacoda