当前位置:网站首页>How to handle the expired data of redis and what are the elimination mechanisms?
How to handle the expired data of redis and what are the elimination mechanisms?
2022-06-30 07:57:00 【Floating across the sea】
Redis Will the expired data be deleted immediately ?
It will not be deleted immediately .Redis There are two strategies for deleting expired data :
- Periodically delete some data ;
- Lazy deletion ;
from Redis edition 7.0.0 Start :EXPIRE Added options :NX、XX and GT、LT Options .
- NX: When key Set the expiration time only when there is no expiration ;
- XX: Only key Set the expiration time only when it has expired ;
- GT: Only when the New expiration date The expiration time is set only when it is greater than the current expiration time ;
- LT: The expiration time is set only when the new expiration time is less than the current expiration time .
In the master-slave or cluster architecture , The clocks of the two machines are seriously out of sync , Is there going to be a problem ?
key Expired information is in Unix Absolute timestamp It means .
In order for the expiration operation to work properly , The time between machines must ensure stable synchronization , Otherwise, the expiration time will be inaccurate .
For example, two machines whose clocks are seriously out of sync RDB transmission , slave The time of is set to the future 2000 second , If be in, master One of the key Set up 1000 Second survival , When Slave load RDB When key Think it's time to key Be overdue ( because slave The machine time is set to the future 2000 s), Not waiting 1000 s It's overdue .
Lazy deletion
Inert deletion is simple , That is, when there is a request from the client to query the key When , Check key Is it overdue , If expired , Delete the key.
For example, when Redis Received... From client GET movie: Ozawa # m …… Leah .rmvb request , I'll check first key = movie: Ozawa # m …… Leah .rmvb Has it expired , If it expires, delete .
The initiative to delete expired data is given to each access request .
Delete periodically

Just rely on client access to judge key Whether to delete after expiration is certainly not enough , Because there are key Out of date , But no one will visit in the future , How to delete these data ?
You can't let these data 「 It's not shit to occupy the manger 」.
So called periodic deletion , That is to say Redis The default for each 1 Seconds to run 10 Time ( Every time 100 ms Do it once ), Randomly select some with expiration time each time key, Check if it's overdue , If it is found that it has expired, it will be deleted directly . overdue key exceed 25%, Then continue
Be careful : Not all libraries are checked in one run , All the keys , It's a random number of keys .
Whether it's scheduled deletion , Or inert deletion . When the data is deleted ,master Delete instructions will be generated and recorded to AOF and slave node .
If there is too much expired data , Scheduled deletion cannot delete completely ( Every time you delete the expired key Or more than 25%), At the same time these key It will never be requested by the client again , That is, you can't go , What will happen ? Will it lead to Redis Out of memory , How to deal with it ?
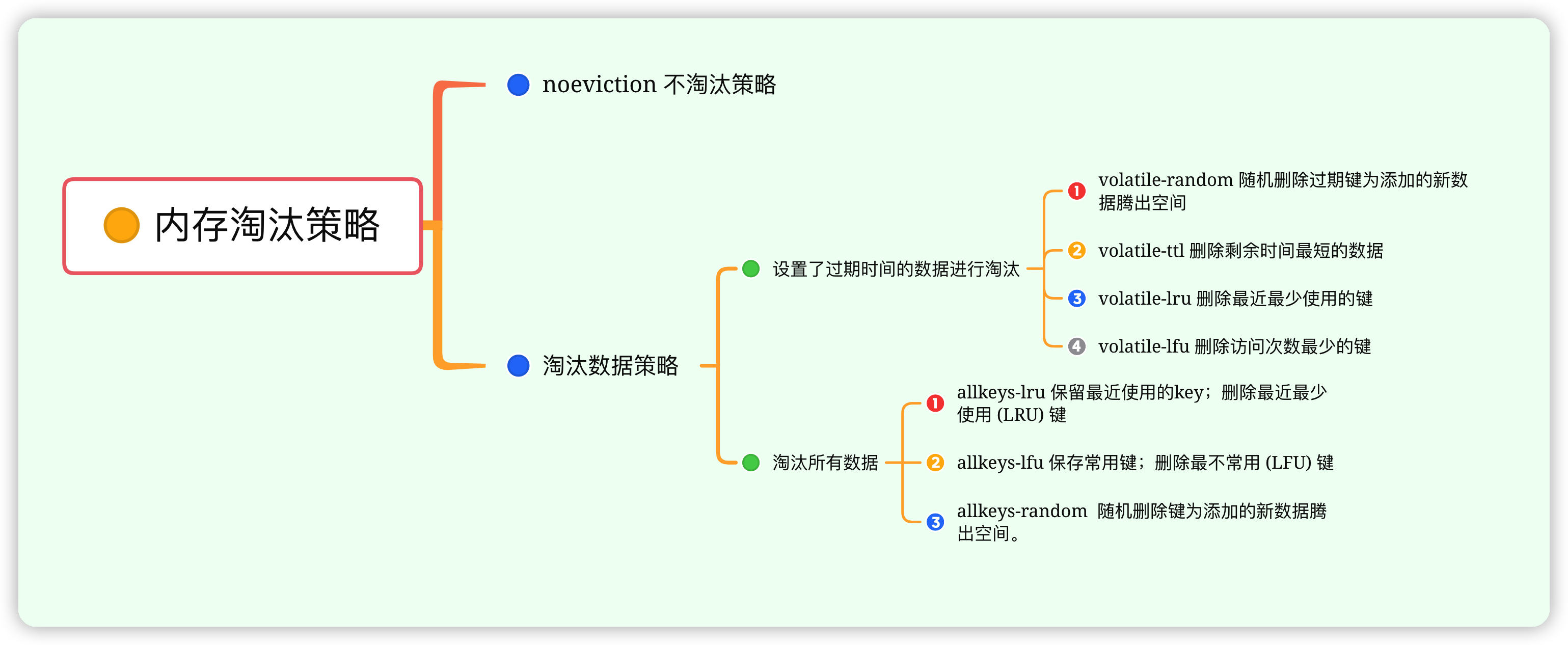
When redis Node allocated memory usage reached maximum ,Redis The memory obsolescence policy is initiated ,Redis 4.0 Previously, there were mainly the following six strategies :
- noenviction: Do not clear data , It just returns an error , This leads to a waste of more memory , Write commands for most (DEL Orders and a few other exceptions )
- allkeys-lru: From all data sets (server.db[i].dict) Select the least recently used data in , For new data
- volatile-lru: From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) Select the least recently used data in , For new data
- allkeys-random: From all data sets (server.db[i].dict) In the arbitrary selection of data elimination , For new data
- volatile-random: From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) In the arbitrary selection of data elimination , For new data
- volatile-ttl: From the set of data for which the expiration time has been set (server.db[i].expires) To select the data to be expired , For new data
Redis 4.0 Two new LFU Elimination strategy :
- allkeys-lfu, Eliminate the least used key value in the whole key value , That's what we often say LRU Algorithm .
- volatile-lfu, Eliminate the least used key value among all key values with expiration time .
LRU(Least Recently Used, Recently at least use ), According to the time of recent use , The data furthest away from the current will be eliminated first ; When using memory as a cache , The size of the cache is generally fixed . When the cache is full , At this time, continue to add data to the cache , We need to eliminate some old data , Free up memory to store new data . It can be used at this time LRU The algorithm . The central idea is this : If a data hasn't been used in the last period of time , So the possibility of being used in the future is very small , So it can be eliminated
LFU(Least Frequently Used, The least used ), Over a period of time , The cache data that is used the least times will be eliminated ; according to key The frequency of recent visits is eliminated , Rarely visited priorities are eliminated , Many of the people interviewed were left behind
Redis Why use approximation LRU Algorithms eliminate data , Not the real LRU?
because LRU The algorithm needs to manage all the data with a linked list , It will cause a lot of additional space consumption
besides , A large number of nodes are accessed, which will lead to frequent movement of linked list nodes , So it reduces Redis performance
therefore Redis The algorithm is simplified ,Redis LRU The algorithm is not really LRU,Redis Through a small amount of key sampling , And eliminate the most inaccessible data in the sampled data key
because LRU The algorithm needs to manage all the data with a linked list , It will cause a lot of additional space consumption .
besides , A large number of nodes are accessed, which will lead to frequent movement of linked list nodes , So it reduces Redis performance .
therefore Redis The algorithm is simplified ,Redis LRU The algorithm is not really LRU,Redis adopt Yes, a small amount of key sampling , And eliminate the most inaccessible data in the sampled data key.
That means Redis Cannot eliminate the longest accessed data in the database .
Redis LRU An important point of the algorithm is that the number of samples can be changed to adjust the accuracy of the algorithm , Make it close to the real LRU Algorithm , At the same time, it avoids the consumption of memory , Because only a small number of samples need to be taken at a time , Not all the data .
The configuration is as follows :
maxmemory-samples 50
Java Realization LRU Cahce
LinkedHashMap Realization
Make full use of Java Of LinkedHashMap Realization , It can be realized by combination or inheritance ,「 Margo 」 Use the form of combination to complete .
public class LRUCache<K, V> {
private Map<K, V> map;
private final int cacheSize;
public LRUCache(int initialCapacity) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(initialCapacity, 0.75f, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest) {
return size() > cacheSize;
}
};
this.cacheSize = initialCapacity;
}
}
The point is LinkedHashMap On the third constructor of , To set this construction parameter accessOrder Set to true, representative LinkedHashMap Maintain access order internally .
in addition , It needs to be rewritten removeEldestEntry(), If this function returns true, Represents removing the node that has not been accessed for the longest time , So as to eliminate data .
Realize it by yourself
Where the code is from LeetCode 146. LRU Cache Taken off the . There are comments in the code .
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/** * Put the longest unused element at the head of the chain , The end of the chain places the element just added or accessed */
class LRUCache {
class Node {
int key, value;
Node pre, next;
Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
pre = this;
next = this;
}
}
private final int capacity;// LRU Cache The capacity of
private Node dummy;// dummy A node is a redundant node ,dummy Of next Is the first node of the list ,dummy Of pre Is the last node of the list
private Map<Integer, Node> cache;// preservation key-Node Yes ,Node It's a two-way linked list node
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
dummy = new Node(0, 0);
cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
public int get(int key) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) return -1;
remove(node);
add(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
if (cache.size() >= capacity) {
cache.remove(dummy.next.key);
remove(dummy.next);
}
node = new Node(key, value);
cache.put(key, node);
add(node);
} else {
cache.remove(node.key);
remove(node);
node = new Node(key, value);
cache.put(key, node);
add(node);
}
}
/** * Add a new node at the end of the linked list * * @param node New node */
private void add(Node node) {
dummy.pre.next = node;
node.pre = dummy.pre;
node.next = dummy;
dummy.pre = node;
}
/** * Delete the node from the two-way linked list * * @param node The node to be deleted */
private void remove(Node node) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Line fitting (least square method)
- Deep learning -- feature point detection and target detection
- Investment and financing analysis report of Supply Chain & logistics industry in 2021
- Development technology sharing of Jingtan NFT digital collection system
- 深度学习——循环神经网络
- 想转行,却又不知道干什么?此文写给正在迷茫的你
- Research Report on search business value in the era of big search in 2022
- Deep learning vocabulary representation
- 全栈最全性能测试理论-总结
- November 16, 2021 [reading notes] - macro genome analysis process
猜你喜欢

2022 retail industry strategy: three strategies for consumer goods gold digging (in depth)

AcrelEMS能效管理平台为高层小区用电安全保驾护航

Final review -php learning notes 8-mysql database
![January 23, 2022 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 6: multiple sequence alignment)](/img/48/cfe6ab95b4d4660e3ac3d84ae5303b.jpg)
January 23, 2022 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 6: multiple sequence alignment)

安科瑞高等学校校园建筑节能监管系统建设

Deep learning -- Realization of convolution by sliding window

Use of nested loops and output instances

深度学习——BRNN和DRNN

Deep learning -- using word embedding and word embedding features

回文子串、回文子序列
随机推荐
2021 China Enterprise Cloud index insight Report
深度学习——卷积的滑动窗口实现
C. Fishingprince Plays With Array
Permutation and combination of probability
November 9, 2020 [wgs/gwas] - whole genome analysis (association analysis) process (Part 2)
Hit the industry directly | the flying propeller launched the industry's first model selection tool
Recurrence relation (difference equation) -- Hanoi problem
Lodash filter collection using array of values
Halcon12+vs2013 C # configuration
深度学习——嵌入矩阵and学习词嵌入andWord2Vec
Final review -php learning notes 3-php process control statement
CRM能为企业带来哪些管理提升
ACM. HJ48 从单向链表中删除指定值的节点 ●●
July 30, 2021 [wgs/gwas] - whole genome analysis process (Part I)
跳槽字节跳动很难嘛?掌握这些技巧,你也能轻松通过
Final review -php learning notes 2-php language foundation
2021-10-29 [microbiology] a complete set of 16s/its analysis process based on qiime2 tool (Part I)
为什么大学毕业了还不知道干什么?
Given a fixed point and a straight line, find the normal equation of the straight line passing through the point
期末复习-PHP学习笔记1