当前位置:网站首页>Study Notes-----Left-biased Tree
Study Notes-----Left-biased Tree
2022-08-05 02:43:00 【Oops_Corsini】
true left-biased tree:

忽略忽略
Below is(图源百度):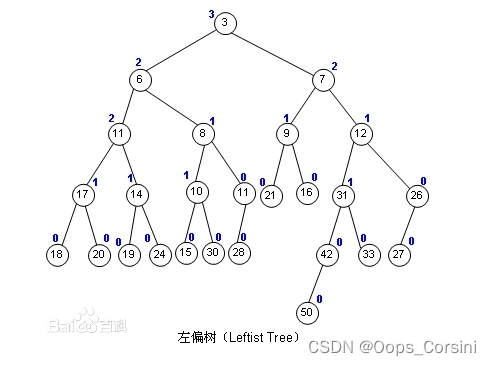
概念:
A left-biased tree is a binary tree with heap properties.属于可并堆.
Its nodes have pointers to the left and right subtrees in addition to the nodes of the binary tree ( l i g h t , r i g h t ) (light,right) (light,right)外,Words have two properties:Key value and distance ( d i s t ) (dist) (dist).
键值Used to compare the size of nodes
距离定义: 当且仅当节点 i i iWhen the left subtree and right subtree are empty trees,Nodes are called outer nodes,A node's distance is a node i i iThe number of edges to the nearest outer node among its descendants.特别的,如果节点 i i iitself is an outer node,Then its distance is 0;And the distance of empty nodes is regarded as − 1 -1 −1
性质
节点的键值小于或等于它的左右子节点的键值
The distance of the left node of the node is not less than the distance of the right child node
推论
The distance of a node is equal to the distance of its right child+1
一棵 N N N个节点的左偏树 r o o t root rootThe distance of nodes is at most l o g ( N + 1 ) − 1 log(N+1)-1 log(N+1)−1
证明: The distance from the left-biased tree root node is constant,Then it is a complete binary tree with the fewest nodes,节点数是 2 d + 1 − 1 2^{d+1}-1 2d+1−1,那么 n n nThe distance of the left-biased tree of each node is the same ≤ l o g ( n + 1 ) − 1 \leq log(n+1)-1 ≤log(n+1)−1.
This is also the guarantee of the time complexity of left-biased trees.
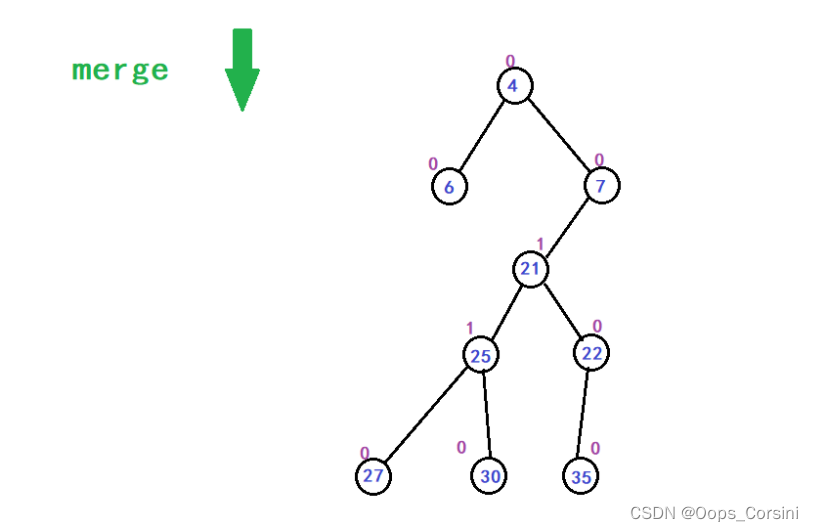
合并操作
The merge operation is the most basic operation of left-biased trees.merge打天下!!
A left-biased tree adds one node,删除根节点,Initializing a batch of data is based on a merge operation.
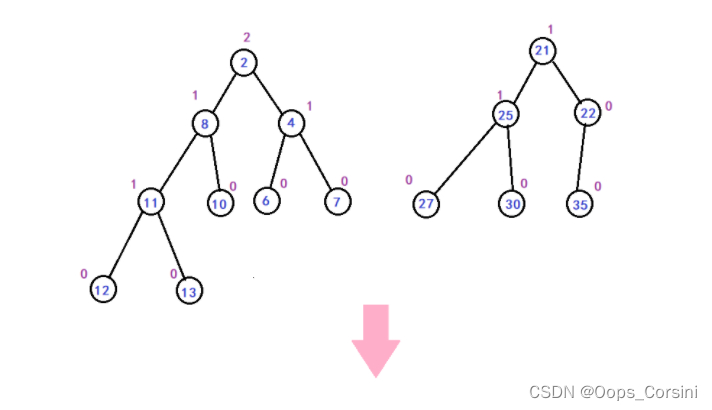
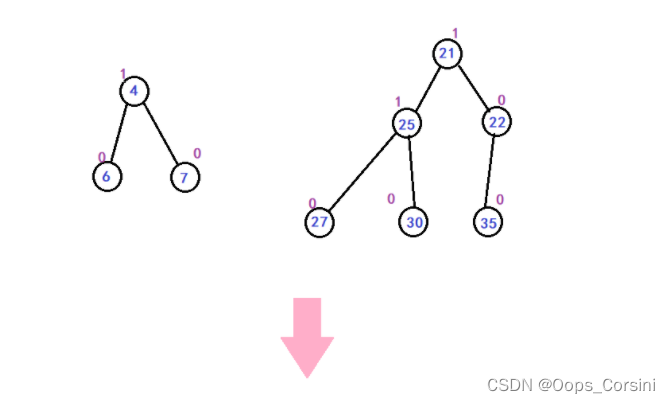
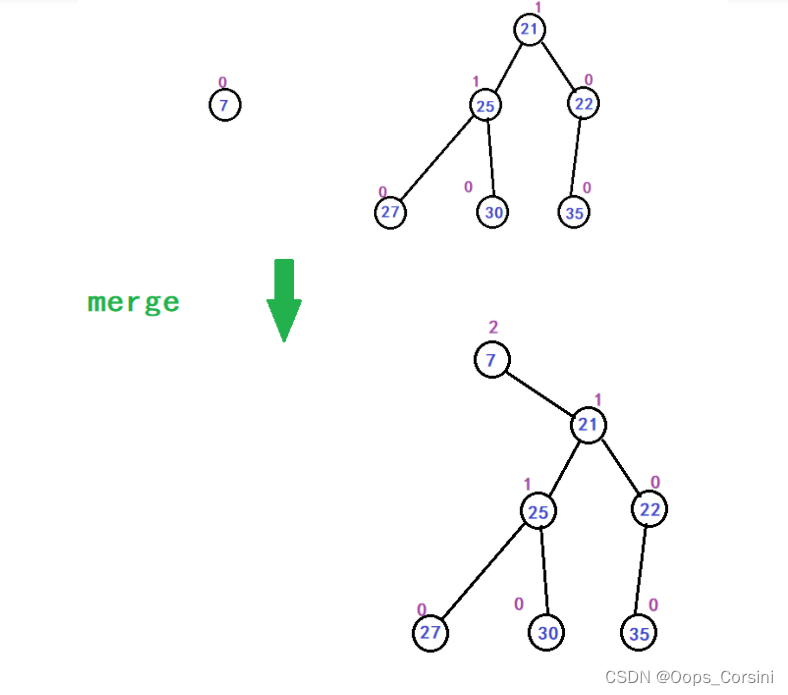
Suppose we merge now x x x和 y y y两棵树
Compare the magnitude of two tree values,假设 x . v a l < y . v a l x.val < y.val x.val<y.val
Nodes with smaller values ( x ) (x) (x)作为根节点,递归合并 x x x的右子树和 y y y
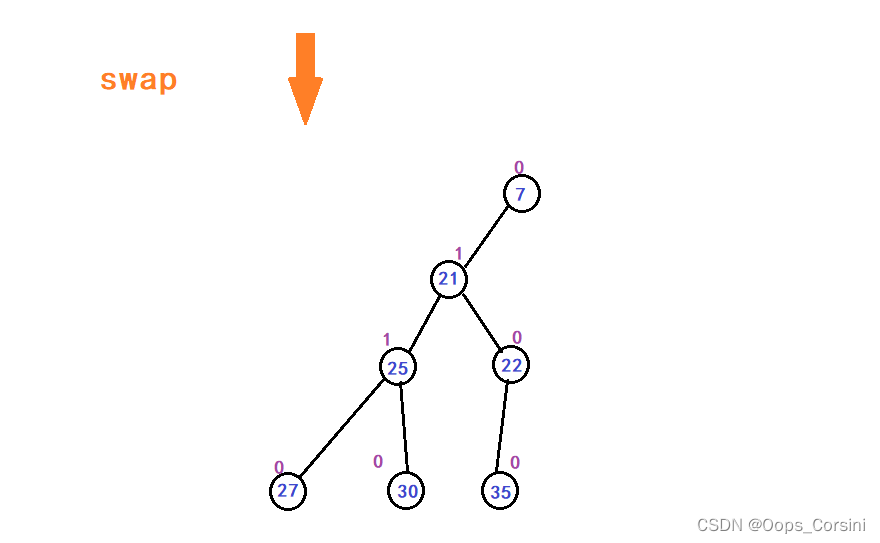
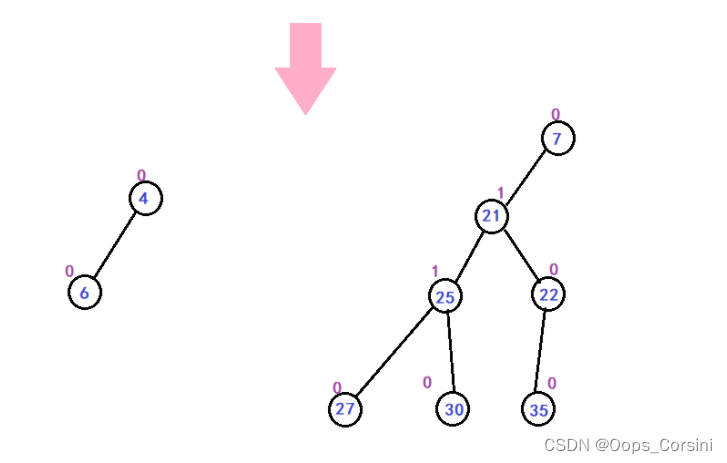
If the left-biased property is not satisfied after merging,交换左右子树
当 x x xthe right subtree or y y yMerge ends when empty
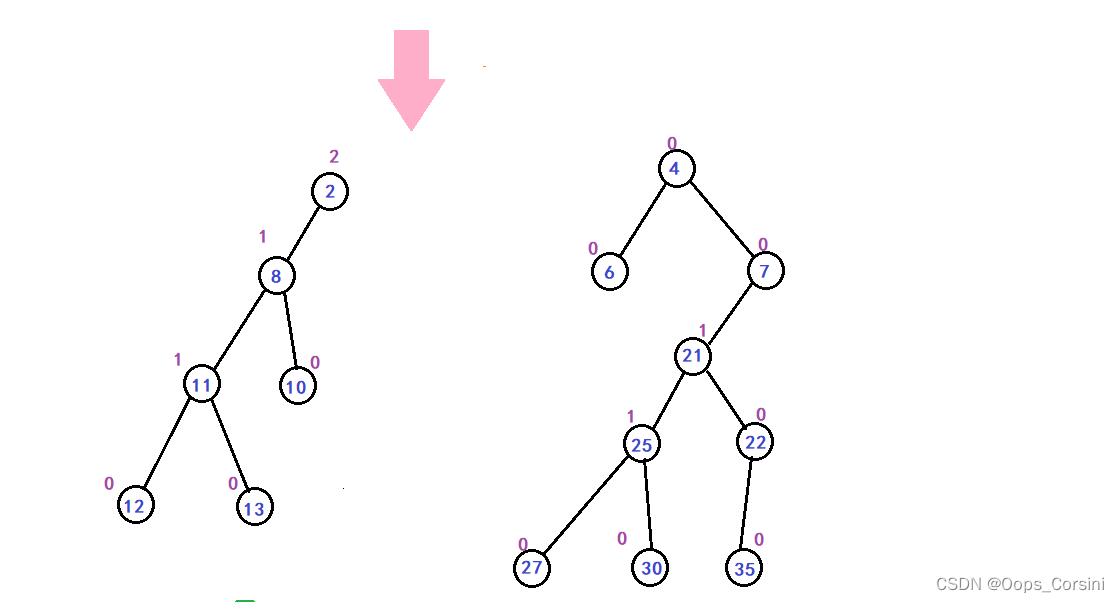
图解(Made by myself Trees are rubbish):
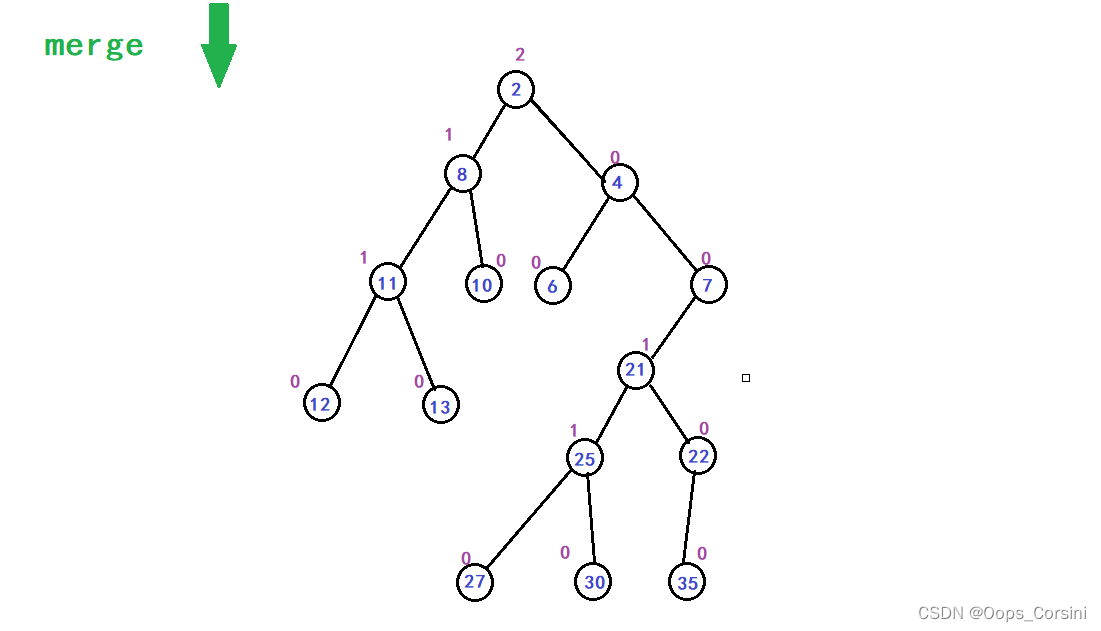
动图(Figure source Luo Valley):
code
int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x+y;
if(e[x].val>e[y].val)swap(x,y);//保证x的val比y的小
e[x].r=merge(e[x].r,y);
if(e[e[x].r].dist>e[e[x].l].dist)swap(e[x].l,e[x].r)//does not satisfy the left-biased property,交换左右子树
e[x].dist=e[e[x].r].dist+1;
return x;//返回root
}
其它操作
插入
Treat a node as a heap for merge operations.
时间复杂度是 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn)
删除
删堆顶:
Merge the left and right sons at the top of the pile,and process the information
任意元素:
First merge the left and right sons,Then merge the new heap formed by the left and right sons to the father of the deleted element.
A bottom-up update is also required d i s t dist dist,If the left-biased property is not satisfied, the left and right sons are exchanged
Build a left-biased tree
It just doesn't work,Also build trees,There is no tree where you operate??
This is also a common operation
方法一
Insert one by one:
Merge left-biased trees with only one node one by one.
复杂度: O ( l o g 1 ) + O ( l o g 2 ) + . . . + O ( l o g n ) = O ( n l o g n ) O(log1)+O(log2)+...+O(logn)=O(nlogn) O(log1)+O(log2)+...+O(logn)=O(nlogn)
方法二
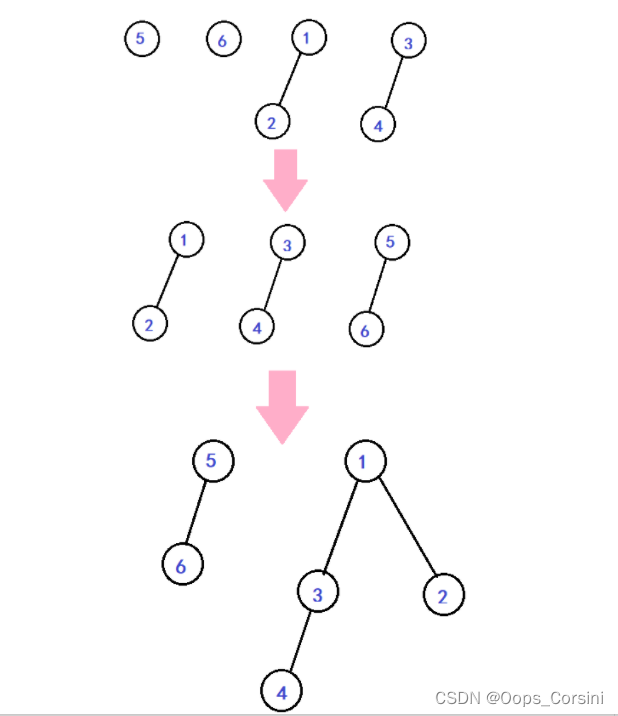
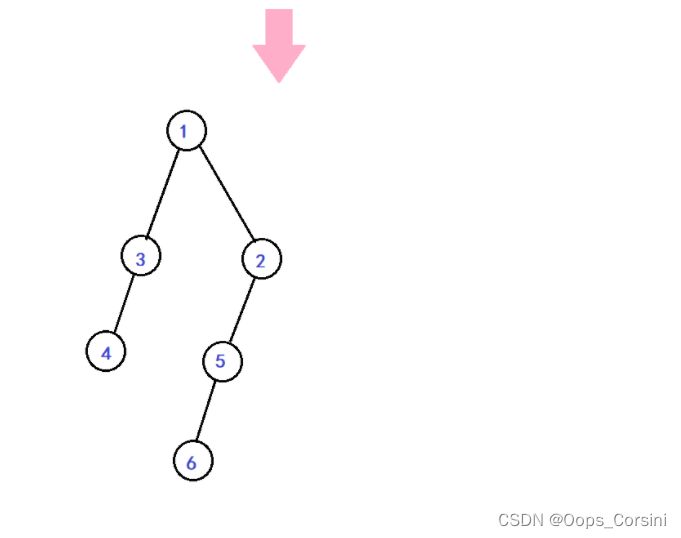
合并法:
It is obtained by imitating the construction algorithm of binary heap:
过程:
将 n n n个节点(Each node is regarded as a left-biased tree)Put into a first-in, first-out priority queue
Keep taking two left-biased trees from the head of the team,After merging, join the tail of the queue
When there is only one left-biased tree left in the queue,算法结束
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
水图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ux49r2SW-1659532605333)(file://C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\marktext\images\2022-08-03-17-36-58-image.png?msec=1659519418977)]](/img/3d/86b0762c66940f067446aa6802db60.png)
例题
Forgot to add in the example codee[0].dist=-1,But it's all over
Know that the city has been occupied.....
1.
To find the root node, the idea of union search can be adopted,Use path compression to find the root node of a node;
v i s vis visDetermine if it has been deleted
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000010
using namespace std;
int n,rt[maxn],m;
struct node{
int val,l,r,dist;
}e[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int find(int x){
if(rt[x]==x)return x;
else return rt[x]=find(rt[x]);
}
int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x+y;
if(e[x].val>e[y].val)swap(x,y);
e[x].r=merge(e[x].r,y);
if(e[e[x].r].dist>e[e[x].l].dist)swap(e[x].l,e[x].r);
e[x].dist=e[e[x].r].dist+1;
return x;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&e[i].val);
rt[i]=i;
}
for(int opt,x,y,i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&opt,&x);
if(opt==1){
scanf("%d",&y);
if(vis[x]||vis[y])continue;
int fx=find(x);
int fy=find(y);
int c;
if(fx!=fy)c=rt[fx]=rt[fy]=merge(fx,fy);
}
else{
if(vis[x]){
puts("-1");continue;
}
int fx=find(x);
printf("%d\n",e[fx].val);
vis[fx]=1;
rt[fx]=rt[e
[fx].l]=rt[e[fx].r]=merge(e[fx].l,e[fx].r);
//rt[fx]It is also assigned because it is possible that the path compression is present on the nodert等于x,但是x已经删除,So point to the new node
e[fx].l=e[fx].r=e[fx].dist=0;
}
}
return 0;
}
2.
Almost exactly the same as the template
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000010
using namespace std;
int n,m,rt[maxn];
struct node{
int l,r,dist,val;
}e[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
int find(int x){
return rt[x]==x?x:rt[x]=find(rt[x]);
}
int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x+y;
if(e[x].val>e[y].val)swap(x,y);
e[x].r=merge(e[x].r,y);
if(e[e[x].r].dist>e[e[x].l].dist)swap(e[x].l,e[x].r);
e[x].dist=e[e[x].r].dist+1;
return x;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&e[i].val);
rt[i]=i;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int x,y,i=1;i<=m;i++){
char opt;
cin>>opt;
if(opt=='M'){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(vis[x]||vis[y])continue;
int fx=find(x);
int fy=find(y);
if(fx!=fy)rt[fx]=rt[fy]=merge(fx,fy);
}
else {
scanf("%d",&x);
if(vis[x]){
puts("0");continue;
}
int fx=find(x);
printf("%d\n",e[fx].val);
vis[fx]=1;
rt[fx]=rt[e[fx].l]=rt[e[fx].r]=merge(e[fx].l,e[fx].r);
e[fx].l=e[fx].r=e[fx].dist=0;
}
}
return 0;
}
3.
This is a huge pile of questions...
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000010
using namespace std;
int n,m,rt[maxn];
struct node{
int l,r,dist,val;
}e[maxn];
int find(int x){
if(rt[x]==x)return x;
else return rt[x]=find(rt[x]);
}
int merge(int x,int y){
if(!x||!y)return x+y;
if(e[x].val<e[y].val)swap(x,y);
e[x].r=merge(e[x].r,y);
if(e[e[x].l].dist<e[e[x].r].dist)swap(e[x].l,e[x].r);
e[x].dist=e[e[x].r].dist+1;
return x;
}
int weak(int x){
e[x].val>>=1;
int rot=merge(e[x].l,e[x].r);
e[x].l=e[x].r=e[x].dist=0;
return rt[rot]=rt[x]=merge(rot,x);
}
int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
e[i].l=e[i].r=e[i].dist=0;
scanf("%d",&e[i].val);
rt[i]=i;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int x,y,i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
int fx=find(x);
int fy=find(y);
if(fx==fy){
puts("-1");continue;
}
int xx=weak(fx),yy=weak(fy);
rt[xx]=rt[yy]=merge(xx,yy);
printf("%d\n",e[rt[xx]].val);
}
}
return 0;
}
4.
5.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
matlab绘制用颜色表示模值大小的箭头图
![[LeetCode Brush Questions] - Sum of Numbers topic (more topics to be added)](/img/ee/6b52072c841af99488dc0c1141c74c.png)
[LeetCode Brush Questions] - Sum of Numbers topic (more topics to be added)
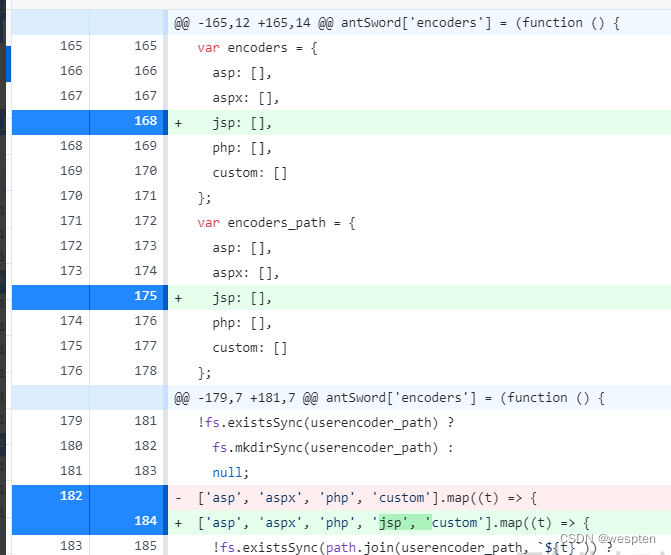
蚁剑高级模块开发
leetcode 15
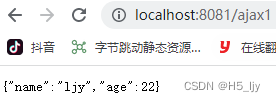
nodeJs--encapsulate routing
VSCode Change Default Terminal how to modify the Default Terminal VSCode
Matlab画图3
mysql没法Execute 大拿们求解
云原生(三十二) | Kubernetes篇之平台存储系统介绍
Using OpenVINO to implement the flying paddle version of the PGNet inference program
随机推荐
leetcode-对称二叉树
线性表的查找
力扣-二叉树的前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
1527. 患某种疾病的患者
select 标签自定义样式
01 [Foreword Basic Use Core Concepts]
mysql没法Execute 大拿们求解
常见的硬件延迟
Flink 1.15.1 集群搭建(StandaloneSession)
[ROS] (10) ROS Communication - Service Communication
[LeetCode Brush Questions] - Sum of Numbers topic (more topics to be added)
1667. Fix names in tables
shell语句修改txt文件或者sh文件
ARM Mailbox
01 【前言 基础使用 核心概念】
力扣-二叉树的最大的深度
Intel XDC 2022 Wonderful Review: Build an Open Ecosystem and Unleash the Potential of "Infrastructure"
Access Characteristics of Constructor under Inheritance Relationship
dmp(dump)转储文件
倒计时 2 天|云原生 Meetup 广州站,等你来!