当前位置:网站首页>Fundamentals of container technology
Fundamentals of container technology
2022-07-04 12:40:00 【kk_ forward】
Record
Always use containers docker, But yes docker Little is known about the principle of implementation , Recently I was reading Zhang Lei's 《 In depth analysis of Kubernetes》, Further understand the implementation principle of container . Here is a summary of the second chapter of the book .
Basic problems of containers
Summarize the basic problems of containers as follows :
What is a container
process
1、 How does the operating system run an addition program :
The operating system finds that the input data is saved in a file from the program , These documents will The slave disk can only be loaded into memory for standby ;
The operating system reads the instruction to calculate addition , Now , It needs instructions CPU To complete the addition operation .
CPU Add with memory writing , Will use registers to store values 、 Memory stack to store the executed commands and variables .
In the process ,I/O The device will constantly modify its state .
As mentioned above , Once this addition program is run , It changes from binary file on disk to From the data in the computer memory 、 The value in the register 、 Instructions in the stack 、 Open file 、 And the status information of various devices A collection of components . The total environment of this set , It's called a process .
therefore , For processes , Its static performance is the program on the disk . Dynamic performance is the sum of the data and state of the computer after the program runs .
Containers
A container is a special process . There will be constraints on this process : It has its own “ The border “, It cannot see beyond the boundary , There will also be resource constraints . The detailed methods of these will be introduced later .
How do containers achieve environmental isolation
Example
# Run a program called busybox The container of , And run the program in the container /bin/sh
docker run -it busybox /bin/sh
# In the host /bin/sh Process situation
ps -ef | grep /bin/sh

You can see that the process number on the host is 5009
# Containers busybox Medium bin/sh Process situation
ps -ef
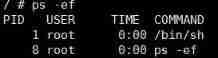
You can see inside the container ,/bin/sh The process number is 1, It's from this container 1 Process of no. .
The different process numbers above mean , Two /bin/bash In different environments . But actually , In container 1 Process of no. , In the host computer, it is the corresponding 5009 Process of no. , It's just that you can't see the process in the host in the container .
Realization
The isolation mechanism described above actually tampers with the process space of the isolated application , This technology is linux Medium Namespace Mechanism .
stay linux The system call to create a process on is :
int pid = clone(main_function, stack_size, SIGCHLD, NULL);
This system call will create a new process for us , And return its PID.
We can also specify in this system call CLONE_NEWPID Parameters :
int pid = clone(main_function, stack_size, CLONE_NEWPID | SIGCHLD, NULL);
Now , The newly created process will be in a new process space , In this process space , His PID by 1, But in the real process space of the host , This PID It's still the original real value , Like the one above 5009.
In addition to the above mentioned PID Namespace,Linux The operating system also provides Mount、Network etc. Namespace To implement various process contexts “ Smoke screen ”. such as Mount Namespace Used to make the quarantined process only see the information of the current mount point ,Network Namespace Used to let the quarantined process see the current Namespace Network equipment and configuration inside .
The difference between container and virtual machine
virtual machine
Virtualization technology ( virtual machine ) It can also isolate different processes , Its structure is as follows :
among Hypervisor Software is the most important part of virtual machine , It simulates all kinds of hardware needed to run an operating system through the hardware virtualization function , such as CPU、 Memory 、I/O Equipment etc. , Then a new operating system is installed on these virtual hardware —— Client operating system . Then the user's application process can run in the virtual machine , It can only see the files and directories of the operating system , And the virtual devices in this machine .
Containers

As can be seen from the container architecture diagram , Unlike virtual machines , What is really responsible for the isolated environment is the host operating system itself .
Container vs. virtual machine
Because the virtual machine must be Hypervisor To be responsible for creating , This virtual machine is real , A separate guest operating system is required , This brings additional resource consumption and occupation . by comparison , User applications after containerization are still ordinary processes on the host , The resource occupation caused by virtualization is negligible .
be based on Linux Namespace Isolated containers also have shortcomings , The main problem is Incomplete isolation . Because the container is just a special process running on the host , There are so many The operating system kernel of the same host is used between containers . The problem this brings is : If you want to in window Host running linux Containers , Or in a lower version of linux The host is running a higher version of linux Containers , It's impossible .
Many resources and objects cannot be Namespace turn . For example, time, time . This means that if the time is modified using system calls in the container , Then the time of the entire host will be modified .
How do containers limit resources
Why do we need to limit the resources of containers ?
Mentioned earlier , Although the system has been used Namespace The container is isolated , But the container is also a process of the operating system , Have the same position as other processes , The resources he uses can be occupied by other processes of the host at any time , It may also run out of resources .
use Cgroups To set resource limits for processes
Cgroups The main function is to limit the upper limit of resources that a process group can use , Include cpu、 Memory 、 disk 、 Bandwidth, etc. .
Cgroups The operating interface exposed to the user is the file system :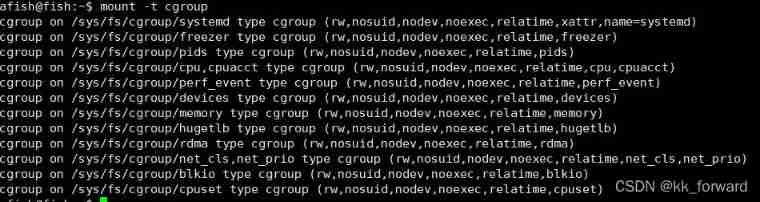
stay /sys/fs/cgroup The following are examples cpuset、cpu、memory These subsystems , At present, this machine can be Cgroups Limited resource types .
Under the resource category corresponding to the subsystem , You can see how to limit such resources :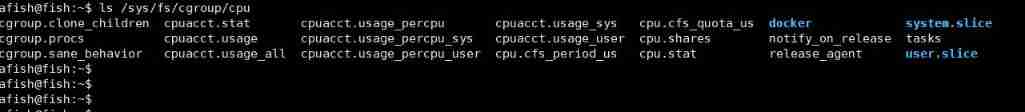
for example cpu.cfs_period_us It can be used to limit the length to cfs_period For a while , Can only be allocated to a total of
cfs_quota Of cpu Time .
Example
How to use Cgroups The configuration file is a process limit cpu Use your time :
stay /sys/fs/groups/cpu/ Create directories under the subsystem
cd /sys/fs/groups/cpu/ && mkdir test_container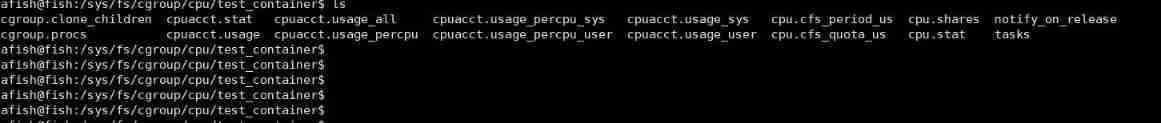
The operating system will automatically create test_container Under the table of contents , Automatically generate the resource restriction file corresponding to the subsystem .Execute the script in the system background , Full system cpu
while : ; do : ; done &

Of the process PID by 7472
use top see cpu Occupancy rate :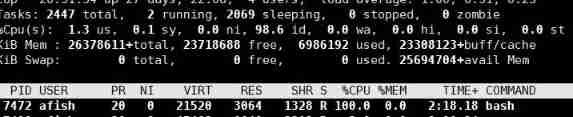
It can be seen that the process has now put CPU completely fill
Change the cpu Highest utilization rate :
echo 20000 > /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/test_container/cpu.cfs_quota_us # change cpu Occupancy rate ,20us Equivalent to the default 100us It is 20%
echo 7472 > /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu/test_container/tasks # Put the above script PID 7472 Write to resource restriction group tasks in
Use... Again top Command view cpu Occupancy rate , Now it's down to 20% Around the 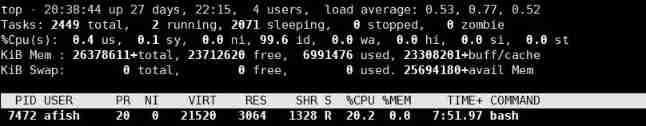
in general ,Linix Of Cgroups Design is a combination of a subsystem directory and a set of resource limitation files . about docker For containers , Just create a control group for the container under each subsystem ( Create a new directory ), Then start the container process , Put the container process PID Fill in the corresponding control group tasks In the file .
docker run The command can also specify the value of the resource file ,eg:
docker run -it --cpu-period=100000 --cpu-quota=20000 ubuntu /bin/bash # Limit this ubuntu Containers can only be used 20% Of cpu bandwidth
It's in /sys/fs/cgroups/cpu/docker/{docker id} You can see the filled value under the corresponding resource directory
The container's file system
In order to make the file system in the container easier to operate , We usually mount the file system of a complete operating system under the root directory of the container , such as Ubuntu 18.04 Of ISO, This file system is the container image , Also known as roofs( The root file system ).
roofs Is all the files and directories of the operating system , Does not contain the operating system kernel .( The kernel is shared with the host )
Container mirroring can solve the problem of environment consistency :
Because the container image contains an entire operating system , Including the application and the dependencies it needs , In different circumstances , Just unzip the packaged container image , The complete execution environment required for the application to run can be reproduced .
There is still a problem to be solved , Although mirroring solves the consistency problem , But every time you upgrade or develop an application , All need to be remade roofs Do you ? It's still quite troublesome if necessary , Can it be based on an old roofs, Incrementally treat roofs Making a change ?
Docker The concept of layer is introduced into the design of image , Every step of the user's image making operation will generate a layer , That's an increment rootfs.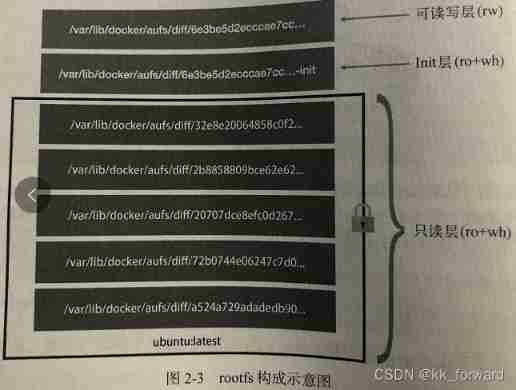
3 The three types of layers store different types of file information . for example Init The layer is specially used to store /ect/host/、/etc/resolv.conf Etc , The read-write layer is specially used to store your modifications rootfs The resulting increment , Whether it is to add, delete, modify or check this container , It all happened here , The mount point declared by the container will also be declared here .
this 3 Layers of types are jointly mounted to /var/lib/docker/aufs/mnt/ Under the table of contents , Act as a complete Ubuntu The operating system is used by the container .
Here are some common docker Command implementation principle :
docker exec Get into docker:
A process can choose to join one of its existing Namespace in , To enter the container where the process is located .
docker commit:
After the container is running , Add the top read-write layer to the read-only layer of the original container image , Then package it into a new image .commit Will not submit Init layer , Avoid putting /etc/hosts And other privacy documents are also submitted .
边栏推荐
- Bottom Logic -- Mind Map
- C語言函數
- C language: find the palindrome number whose 100-999 is a multiple of 7
- Ultimate bug finding method - two points
- When synchronized encounters this thing, there is a big hole, pay attention!
- [Yu Yue education] 233 pre school children's language education reference questions in the spring of 2019 of the National Open University
- . Does net 4 have a built-in JSON serializer / deserializer- Does . NET 4 have a built-in JSON serializer/deserializer?
- 【数据聚类】第四章第一节3:DBSCAN性能分析、优缺点和参数选择方法
- Global and Chinese market for naval vessel maintenance 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- C language: find the length of string
猜你喜欢
Error: Failed to download metadata for repo ‘AppStream‘: Cannot download repomd. XML solution
Introduction to the button control elevatedbutton of the fleet tutorial (the tutorial includes the source code)

How to realize the function of Sub Ledger of applet?
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7](/img/44/1861f9016e959ed7c568721dd892db.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7

Here, the DDS tutorial you want | first experience of fastdds - source code compilation & Installation & Testing
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16](/img/c3/f3746b161012acc3751b2bd0b8f663.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 16

VIM, another program may be editing the same file If this is the solution of the case
Communication tutorial | overview of the first, second and third generation can bus

The frost peel off the purple dragon scale, and the xiariba people will talk about database SQL optimization and the principle of indexing (primary / secondary / clustered / non clustered)
DDS-YYDS
随机推荐
Pat 1059 prime factors (25 points) prime table
. Does net 4 have a built-in JSON serializer / deserializer- Does . NET 4 have a built-in JSON serializer/deserializer?
C language: find the length of string
ASP. Net razor – introduction to VB loops and arrays
Wechat video Number launches "creator traffic package"
13、 C window form technology and basic controls (3)
C语言数组
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 12
Introduction to random and threadlocalrandom analysis
The database connection code determines whether the account password is correct, but the correct account password always jumps to the failure page with wrong account password
How to realize the function of Sub Ledger of applet?
C语言:围圈报号排序问题
LVS load balancing cluster deployment - Dr direct routing mode
VBA, JSON interpretation, table structure -json string conversion
C語言:求100-999是7的倍數的回文數
Kivy tutorial 08 countdown app implements timer call (tutorial includes source code)
Global and Chinese market of piston rod 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
【数据聚类】第四章第一节3:DBSCAN性能分析、优缺点和参数选择方法
Awk getting started to proficient series - awk quick start
Lvs+kept highly available cluster