当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to random and threadlocalrandom analysis
Introduction to random and threadlocalrandom analysis
2022-07-04 12:25:00 【Charming lemon】
List of articles
One 、Random class
1、 brief introduction
Random Class is used to generate a stream of pseudo-random numbers . This kind of use 48 Seeds , It uses the linear congruence formula to modify
Math.random()It is relatively simple to use , But not thread safe ;java.util.RandomOf Random Class is thread safe . But cross thread simultaneous usejava.util.RandomInstances may encounter contention , This leads to performance degradation . Consider using... In multithreading designThreadLocalRandomclass ;java.util.RandomOf Random It's not encrypted . Consider usingSecureRandomGet an encrypted secure pseudo-random number generator , For security sensitive applications .
2、Random Constructor for
- Random(): Create a new random number generator
/** * Creates a new random number generator. This constructor sets * the seed of the random number generator to a value very likely * to be distinct from any other invocation of this constructor. */
public Random() {
//System.nanoTime() Return to running Java The current value of the high-resolution time source of the virtual machine , In nanoseconds .
// The constructor with parameters will be called here
this(seedUniquifier() ^ System.nanoTime());
}
private static long seedUniquifier() {
// Linear congruence generates a meta table
for (;;) {
long current = seedUniquifier.get();
long next = current * 181783497276652981L;
// Multiply two large numbers
if (seedUniquifier.compareAndSet(current, next))
// This compares and exchanges CAS
// Compare the value in the current working memory with the value in the main memory , If this value is expected , Then perform the operation !
// If not, keep cycling ! It is to ensure that even in a multithreaded environment, different numbers are returned
return next;
}
}
// atomic This is juc Atomic modified inside long ,get The method is to get the value in the constructor
private static final AtomicLong seedUniquifier
= new AtomicLong(8682522807148012L);
- random(long seed): Using a single Long Seed creates a new random number generator \
Pseudorandom uses Linear congruence method ( You can refer to the information yourself )
public Random(long seed) {
if (getClass() == Random.class)
this.seed = new AtomicLong(initialScramble(seed));
else {
// Subclasses may override this regardless
this.seed = new AtomicLong(); // Create a new AtomicLong, The initial value is 0
setSeed(seed);
}
}
// eliminate nextGaussian() The use of haveNextNextGaussian sign ,
synchronized public void setSeed(long seed) {
this.seed.set(initialScramble(seed));
haveNextNextGaussian = false;
}
private static long initialScramble(long seed) {
return (seed ^ multiplier) & mask;
}
private static final long multiplier = 0x5DEECE66DL;
// x & [(1L << 48)–1] And x(mod 2^48) Equivalent Take the low position 48 position
// Move left with sign
private static final long mask = (1L << 48) - 1;
3、next() The core approach
Random Concurrency is safe in a multithreaded environment , It solves the competition by using atomic classes , In essence, that is CAS + Volatile Ensure thread safety
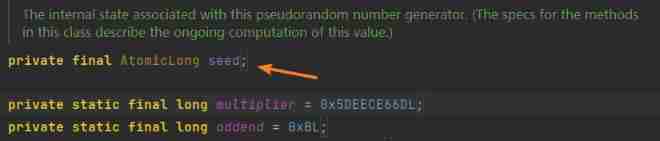
stay Random Class , There is one AtomicLong The domain of , Used to save random seeds . Each time a random number is generated, a shift operation will be performed according to the random seed to obtain the random number .
//Long Type of random
//long Type in the Java Zhongzongnong 64bit, Yes next The return value of the method shifts left 32 As long The high , And then next Method returns a value as low 32 position , As long Type of random number .
// The key here is next Method
public long nextLong() {
return ((long)(next(32)) << 32) + next(32);
}
Here are next The core of the method , Use seed seeds , Constantly generate new seeds , And then use CAS Update it , Then return the shifted value of the seed . There is a constant cycle CAS Operation seed , Until success . so ,Random The implementation principle is mainly to use random seeds to generate random numbers by processing with a certain algorithm , The security of random seeds is guaranteed by using atomic classes AtomicLong.
protected int next(int bits) {
long oldseed, nextseed;
AtomicLong seed = this.seed;
do {
oldseed = seed.get();
nextseed = (oldseed * multiplier + addend) & mask;
} while (!seed.compareAndSet(oldseed, nextseed));
return (int)(nextseed >>> (48 - bits));
}
4、Random Disadvantages under concurrency
although Random Is thread safe , But for concurrent processing, use atomic classes AtomicLong When there is a lot of competition , Use the same Random Object can cause thread blocking , Because of a lot of CAS Operation will cause failure , constantly Spin, And cause CPU The overhead is relatively large and the throughput will decrease .
Here you can test by multithreading , You can find that as the number of threads increases ,Random As the competition gets more and more fierce , Then it takes more and more time . However ThreadLocalRandom As the number of threads increases , Basically no change . So in the case of large concurrency , Random choice , You can consider ThreadLocalRandom Lifting performance .
Two 、ThreadLocalRandom
1、 brief introduction
ThreadLocalRandom yes Random Subclasses of , It is to Seed Random seeds are isolated to the random number generator of the current thread , So it solved Random stay Seed Competitive issues , Its processing thought and ThreadLocal In essence .
Unsafe Methods within classes reveal a “Unsafe” The breath of , The specific performance is that the memory can be operated directly , Without any security checks , If there are questions , Will be thrown at run time Fatal Error, Leading to the exit of the entire virtual machine .
2、 Principle analysis
2.1 ThreadLocalRandom The singleton pattern
You can find from the following code ThreadLocalRandom Used The singleton pattern , In one Java Only one application ThreadLocalRandom object . When UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE) return 0 when , Is executed localInit(), Finally, return to the singleton .
// One java There is only one instance of application
// ThreadLocalRandom Object passing ThreadLocalRandom.current() obtain , Then you can directly return random numbers
static final ThreadLocalRandom instance = new ThreadLocalRandom();
// obtain ThreadLocalRandom Object instances
public static ThreadLocalRandom current() {
if (UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE) == 0)
localInit();
return instance;
}
2.2 Seed Random seeds are isolated to the current thread
The core approach
// From object object var1 Memory address offset var2 Read four bytes as long Type return
public native long getLong(Object var1, long var2);
// Can be object object var1 Memory address offset var2 The last four bytes are set to var4
public native void putLong(Object var1, long var2, long var4);
UNSAFE.getInt(Thread.currentThread(), PROBE) Is to get the current Thread In the thread object PROBE.
First get the variable name SEED、PROBE Offset position of isoparametric relative to object
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long SEED;
private static final long PROBE;
private static final long SECONDARY;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> tk = Thread.class;
SEED = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(tk.getDeclaredField("threadLocalRandomSeed"));
PROBE = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(tk.getDeclaredField("threadLocalRandomProbe"));
SECONDARY = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(tk.getDeclaredField("threadLocalRandomSecondarySeed"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
When the first call ThreadLocalRandom.current() Method, the current thread detected PROBE Uninitialized will call localInit() Method to initialize , And put Of the current thread seed Values and probe The value is stored in the current thread Thread The memory address of the object is offset from the position of the corresponding variable
static final void localInit() {
int p = probeGenerator.addAndGet(PROBE_INCREMENT);
int probe = (p == 0) ? 1 : p; // skip 0
long seed = mix64(seeder.getAndAdd(SEEDER_INCREMENT));
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
UNSAFE.putLong(t, SEED, seed);
UNSAFE.putInt(t, PROBE, probe);
}
threadLocalRandomProbe Used to represent the current thread Thread Whether to initialize , If it is right or wrong 0, Indicates that it has been initialized . let me put it another way , This variable is the state variable , Used to identify the current thread Thread Whether it is initialized .threadLocalRandomSeed It can also be seen from the notes , It is the random seed of the current thread . Random seeds are scattered in each Thread In the object , Thus, the competition point during concurrency is avoided .
3、nextSeed() The core approach
nextSeed() Generate random seeds to generate random number sequences
public long nextLong() {
return mix64(nextSeed());
}
Because at the time of initialization Store the... Of the current thread seed Values and probe The offset position of the value to the memory address of the corresponding thread object , call nextSeed() It's direct Get from the offset position of the current thread object , And generate the next random number seed to this position , At the same time UNSAFE Class method , There is no need for different threads to compete for seed value , Therefore, competitive points can be isolated
final long nextSeed() {
Thread t; long r; // read and update per-thread seed
UNSAFE.putLong(t = Thread.currentThread(), SEED,
r = UNSAFE.getLong(t, SEED) + GAMMA);
return r;
}
3、 ... and 、 summary
Random yes Java Random number generator tool class provided in , But in the case of large concurrency, the throughput will decrease due to the competition of random seeds , To introduce ThreadLocalRandom It isolates contention points into each thread , Thus, the competition problem in the case of large concurrency is eliminated , Improved performance .
The overall optimization idea of concurrent competition :lock -> cas + volatile -> free lock
Reference article
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/f-lfqEUNvY6XRmCL-h0Qfg
https://www.cnblogs.com/lxyit/p/12654374.html
https://blog.csdn.net/tyh18226568070/article/details/105884912
边栏推荐
- 03_ Armv8 instruction set introduction load and store instructions
- VBA, JSON interpretation, table structure -json string conversion
- The latest idea activation cracking tutorial, idea permanent activation code, the strongest in history
- Definition and method of string
- Anti clockwise rotation method of event arrangement -- PHP implementation
- 22 API design practices
- Dos and path
- Login operation (for user name and password)
- MYCAT middleware installation and use
- (August 10, 2021) web crawler learning - Chinese University ranking directed crawler
猜你喜欢
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 13](/img/29/49da279efed22706545929157788f0.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 13
MySQL advanced review
OSI seven layer reference model
Simple understanding of seesion, cookies, tokens
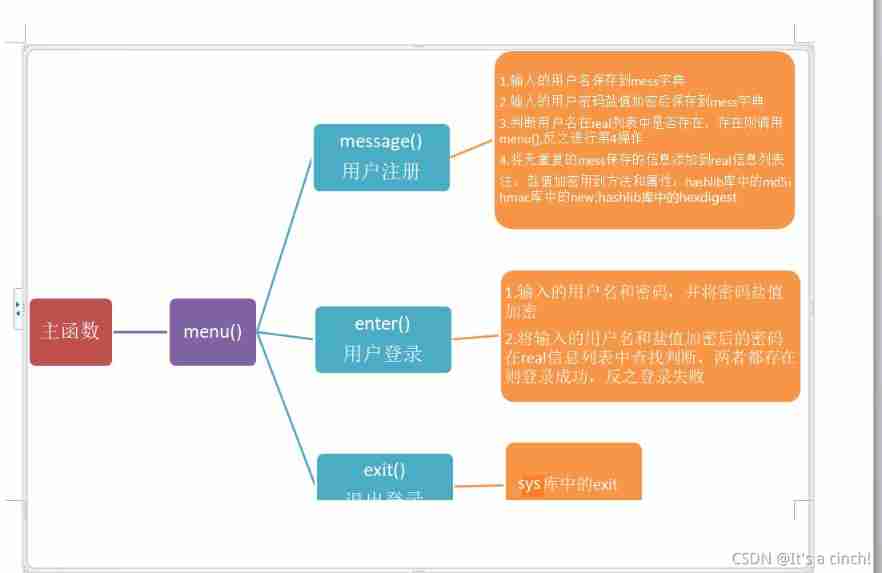
Login operation (for user name and password)
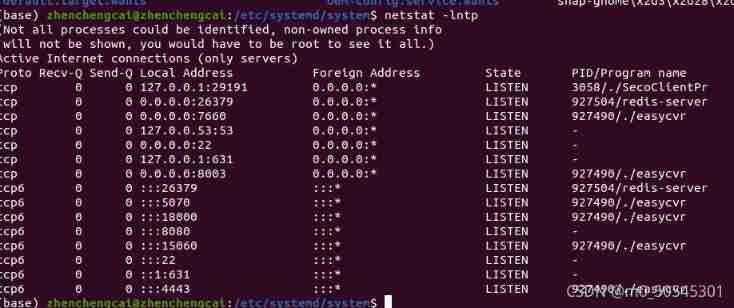
netstat
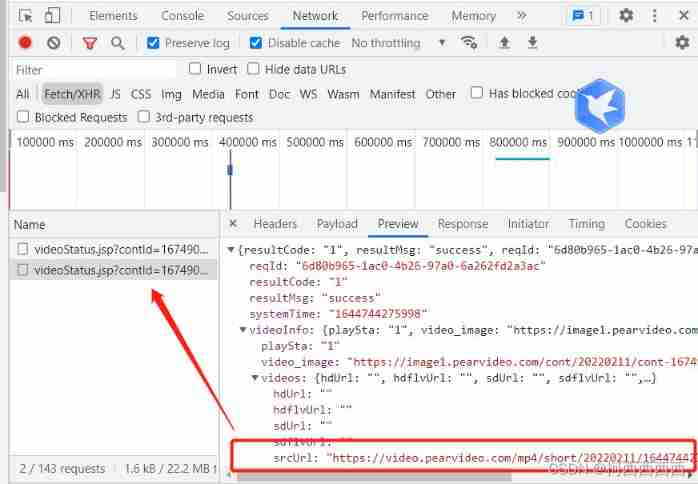
Reptile learning winter vacation series (2)
![[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 21](/img/73/4050a592fdd99bf06e8fd853b157b6.jpg)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 21
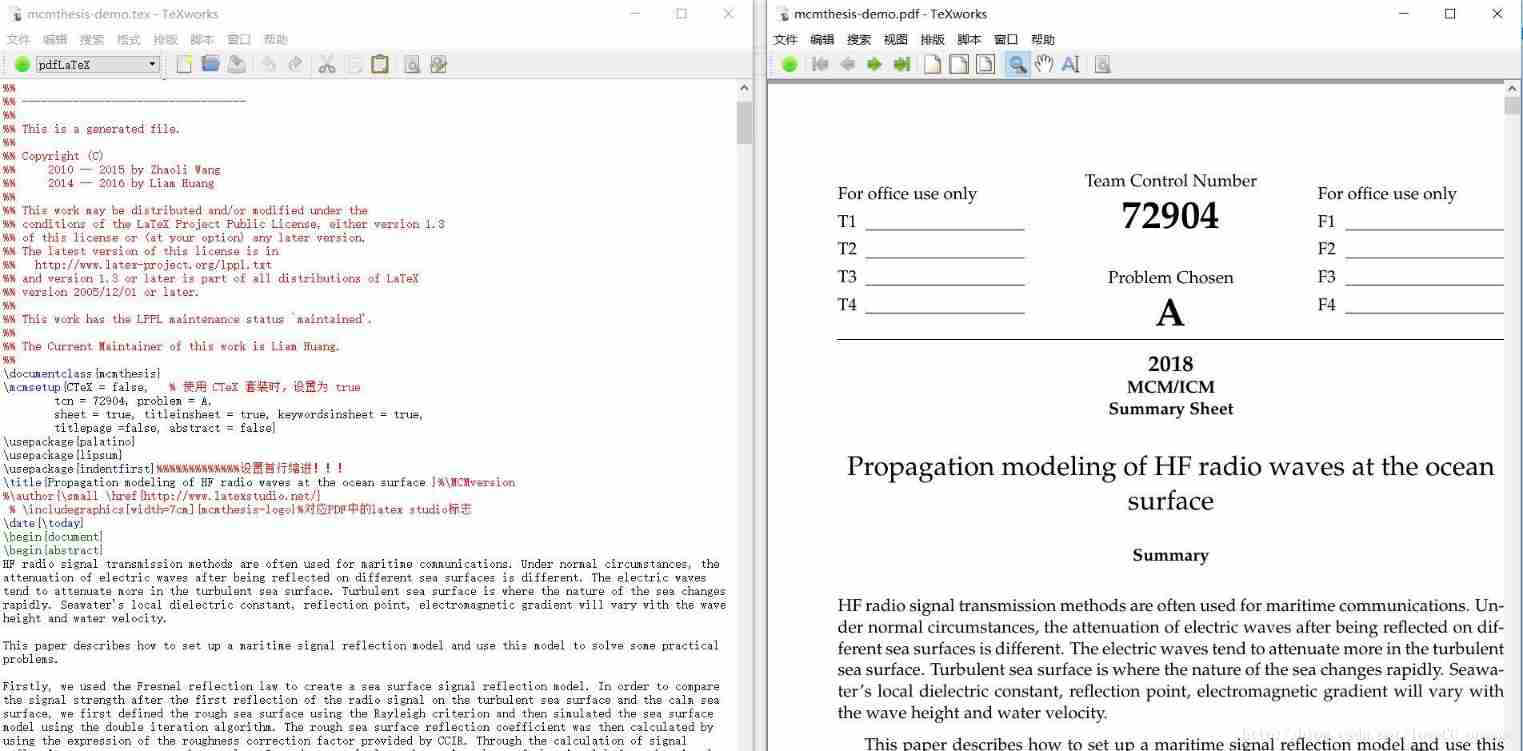
2018 meisai modeling summary +latex standard meisai template sharing
Method of setting default items in C # ComboBox control code
随机推荐
About the use of URL, href, SRC attributes
Alibaba cloud server connection intranet operation
Foreach (system.out:: println) usage
Ultimate bug finding method - two points
MySQL performance optimization index
Single spa, Qiankun, Friday access practice
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 17
QQ group collection
Login operation (for user name and password)
Clockwise rotation method of event arrangement -- PHP implementation
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University spring 2019 2727 tax basis reference questions
Ternsort model integration summary
Haproxy cluster
How to use the mongodb ID array to get multiple documents- How to get multiple document using array of MongoDb id?
. Does net 4 have a built-in JSON serializer / deserializer- Does . NET 4 have a built-in JSON serializer/deserializer?
TCP slicing and PSH understanding
Global function Encyclopedia
Review of week 278 of leetcode II
MySQL advanced review
IPv6 experiment