当前位置:网站首页>Review of week 278 of leetcode II
Review of week 278 of leetcode II
2022-07-04 11:31:00 【What a sacrifice】
2156. Find the substring of the given hash value
Given integer p and m , A length of k And subscript from 0 Starting string s The hash value of is calculated according to the following function :
hash(s, p, m) = (val(s[0]) * p0 + val(s[1]) * p1 + ... + val(s[k-1]) * pk-1) mod m.
among val(s[i]) Express s[i] Subscript in the alphabet , from val('a') = 1 To val('z') = 26 .
Give you a string s And integer power,modulo,k and hashValue . Please return s in first The length is k Of Substring sub , Satisfy hash(sub, power, modulo) == hashValue .
The test data ensure that There is At least one such substring .
Substring Defined as a sequence of consecutive non null characters in a string .
Write and display by yourself, and simply calculate the hash value WA Once , Considering that there may be a large amount of data , Fast power algorithm is adopted , But still WA, This makes me very confused , What's going on ? This is the ironmaking week .
class Solution {
public String subStrHash(String s, int power, int modulo, int k, int hashValue) {
int n=s.length();
for(int i=0;i<=n-k;i++){
String str=s.substring(i,i+k);
System.out.println(str);
if(hash(str,power,modulo)==hashValue){
return str;
}
}
return null;
}
int hash(String s,int power,int modulo){
int h=0;
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char c=s.charAt(i);
h+=(int)(c-'a'+1)*pow(power,i,modulo);
h%=modulo;
}
return h;
}
int pow(int a,int n,int m){
if(n==0) return 1;
int ans=pow(a,n/2,m);
ans=ans*ans%m;
if(n%2==1) ans=ans*a%m;
return ans;
}
}What's wrong with this topic ?

The explanation found is like this , Need to use reverse sliding window , And I used the forward sliding window , This will result in one more tail for each new value minus the head , This will lead to division and modulus , Difficult to calculate , So take reverse sliding window , Replace division with multiplication
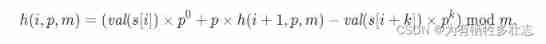
In this way, the hash value calculated above can be used , And prevent the inverse of multiplication , Very elegant
class Solution {
public String subStrHash(String s, int power, int modulo, int k, int hashValue) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
int len = cs.length;
long hash = 0;
long pp = 1;
for (int i = len - k; i < len; i++) {
hash += (cs[i] - 'a' + 1) * pp;
hash %= modulo;
pp = pp * power % modulo;
}
int ans = len - k;
int p = len - k - 1;
while (p >= 0) {
hash *= power;
hash -= (cs[p + k] - 'a' + 1) * pp % modulo;
hash += (cs[p] - 'a' + 1) % modulo;
hash = (hash + modulo) % modulo;
if (hash == hashValue) {
ans = p;
}
p--;
}
return new String(cs, ans, k);
}
}
I'll give you a subscript from 0 Starting string array words . Each string contains only Small letters .words In any substring of , Each letter appears at most once .
If you do one of the following , We can s1 The set of letters obtained s2 Set of letters for , Then we call these two strings The associated :
Go to s1 Add a letter to the letter set of .
from s1 Delete a letter from the set of letters .
take s1 Replace one letter in with any other letter ( You can also replace it with the letter itself ).
Array words Can be divided into one or more non intersecting Group . If one string is associated with another , Then they should belong to the same group .
Be careful , You need to make sure you're in groups , Any string in one group is not associated with strings in other groups . It can be proved that under this condition , The grouping scheme is unique .
Please return a length of 2 Array of ans :
ans[0] yes words Grouped Total number of groups .
ans[1] Is the number of strings contained in the group with the largest number of strings
Method : State compression +BFS
State compression : Because each string has only lowercase letters , And there's no repetition , So we can use a 26 In figures int Numeric values to store strings ,1 The corresponding letter exists ,0 Correspondence does not exist , thus , If two strings s1 and s2 There are four related situations ( Corresponding bit by i1,i2):
1.i1==i2 Need to enumerate 1 A string
2.i1 Some one is 0,i2 The same person is 1 Need to enumerate 26 A string
3.i1 Some one is 1,i2 The same person is 2 Need to enumerate 26 A string
4.i1 Some one is 0,i2 The same person is 1; meanwhile i1 The other is 1,i2 The same person is 2 Need to enumerate 26*26 A string
After storage , We think of the string as a node of the graph ,words Look at it as a picture , The association relationship is saved as an edge , In this way, we count the number of connected components in the graph , And return the maximum number of connected component points , To achieve such a goal , We can use BFS/DFS/ Union checking set , I can't search the collection , So use BFS
Note that there are 2*10^4, If enumerating one by one , Absolutely TLE, So we have to think about , For each node, consider whether its possible associated nodes are in the graph , The maximum number of associated nodes is 26*26 individual , Again *2*10^4 Not even TLE, In this way, we can AC 了
class Solution {
public int[] groupStrings(String[] words) {
// Record the number of nodes ( Consider the same node )
Map<Integer, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
int xor = getBits(word);
cnt.put(xor, cnt.getOrDefault(xor, 0) + 1);
}
// Record the current bit Whether the value is accessed
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>();
// Count the number of connected components and the size of the maximum connected components
int count = 0,maxn = 0;
// Traversal node , Drawing
for (int node : cnt.keySet()) {
// Start accessing a new connected component
if(vis.add(node)){
// The size of this component should consider the number of times a string appears
int size=cnt.get(node);
//BFS Queue used
Deque<Integer>queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(node);
// Enumerate a connected component
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int cur=queue.poll();
// Enumerate possible neighbors
for(int neigh:getNeighbours(cur)){
// Exists and has not been visited , Update the data and list
if(cnt.containsKey(neigh)&&!vis.contains(neigh)){
vis.add(neigh);
queue.offer(neigh);
size+=cnt.get(neigh);
}
}
}
// Update data
maxn=Math.max(maxn,size);
count++;
}
}
return new int[]{count, maxn};
}
// For each node , Calculate all its possible neighbors
private List<Integer> getNeighbours(int root) {
List<Integer> adj = new ArrayList<>();
// Change any 0 or 1
// and 1 XOR is change
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
adj.add(root ^ (1 << i));
}
// Any pair of 0 1 exchange
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if ((root & (1 << i)) > 0) {
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if ((root & (1 << j)) == 0) {
adj.add(root ^ (1 << i) ^ (1 << j));
}
}
}
}
return adj;
}
// State compression , Compress the string into int
private int getBits(String word) {
int ans = 0;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int index = c - 'a';
ans |= 1 << index;
}
return ans;
}
}边栏推荐
- Using terminal connection in different modes of virtual machine
- Getting started with window functions
- Locust learning record I
- Summary of Shanghai Jiaotong University postgraduate entrance examination module -- cryptography
- 3W word will help you master the C language as soon as you get started - the latest update is up to 5.22
- Reptile learning 4 winter vacation learning series (1)
- [Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 11
- Definition and method of string
- How do std:: function and function pointer assign values to each other
- 2021-08-09
猜你喜欢
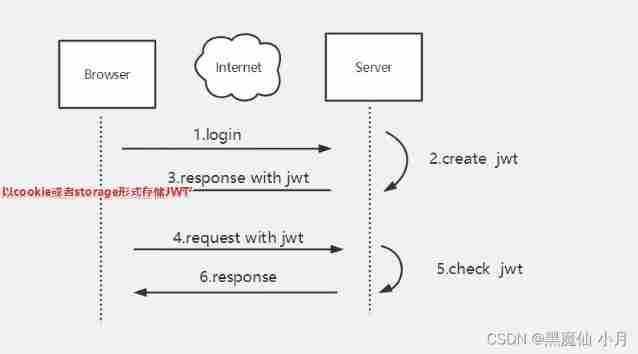
Simple understanding of seesion, cookies, tokens
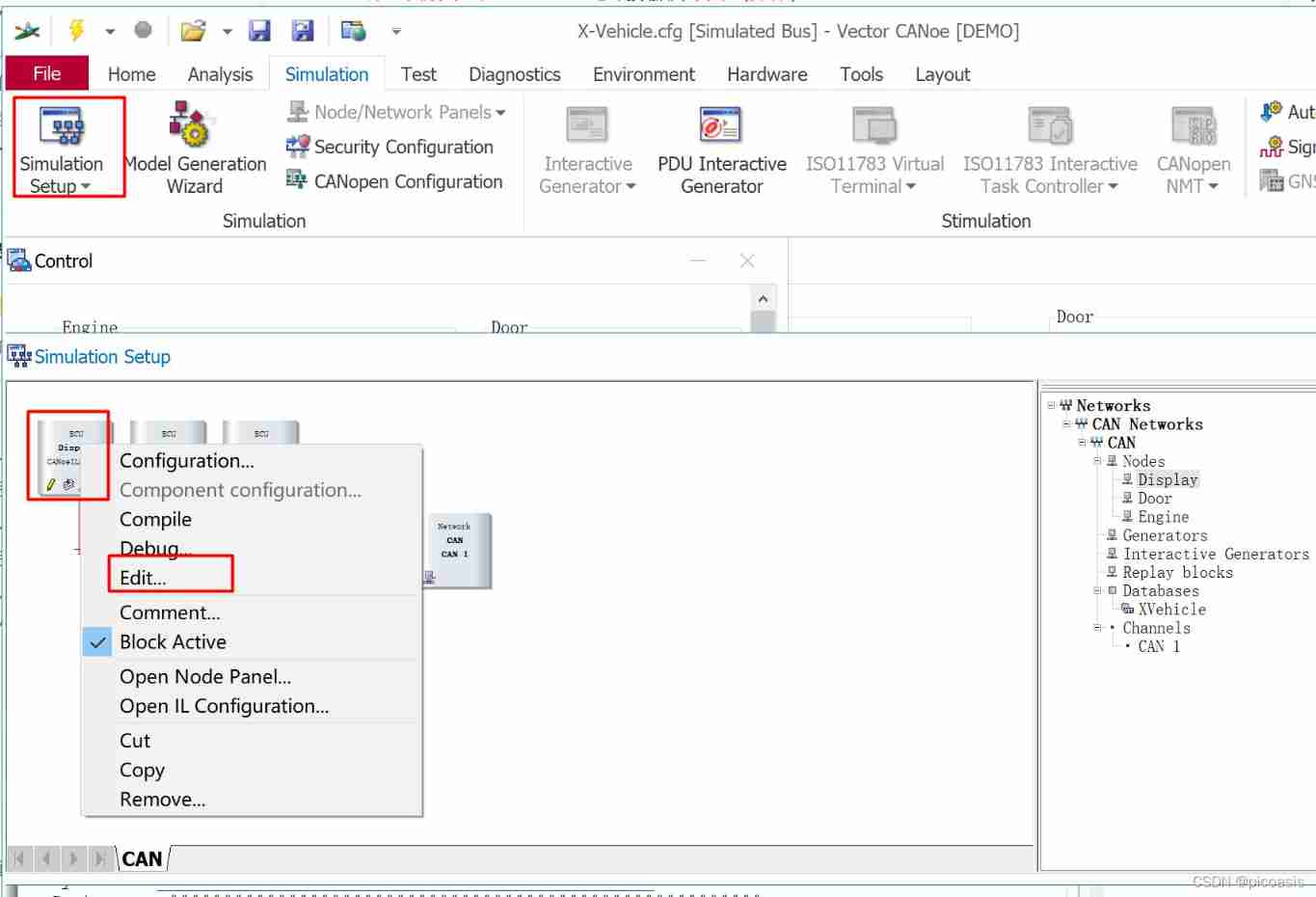
Canoe the second simulation engineering xvehicle 3 CAPL programming (operation)
Replace() function
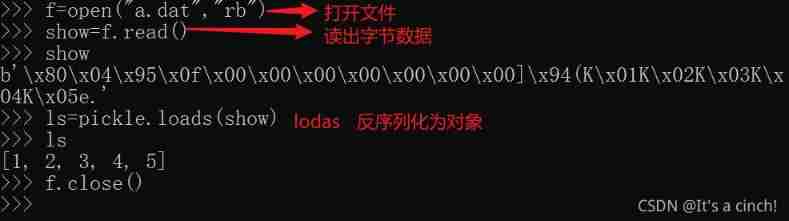
Serialization oriented - pickle library, JSON Library

SQL greatest() function instance detailed example
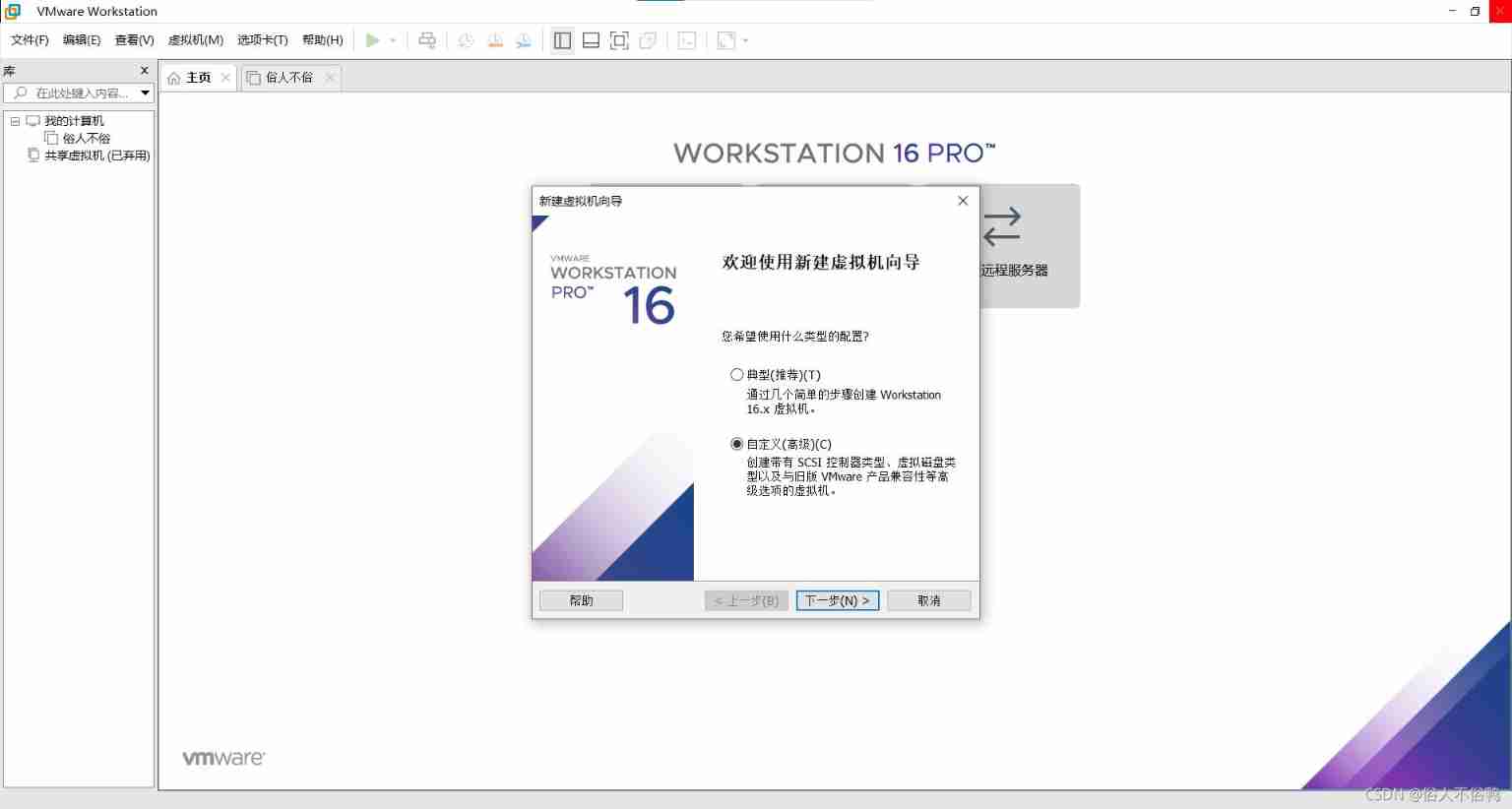
How to create a new virtual machine

2020 Summary - Magic year, magic me

CSDN documentation specification

Application of slice
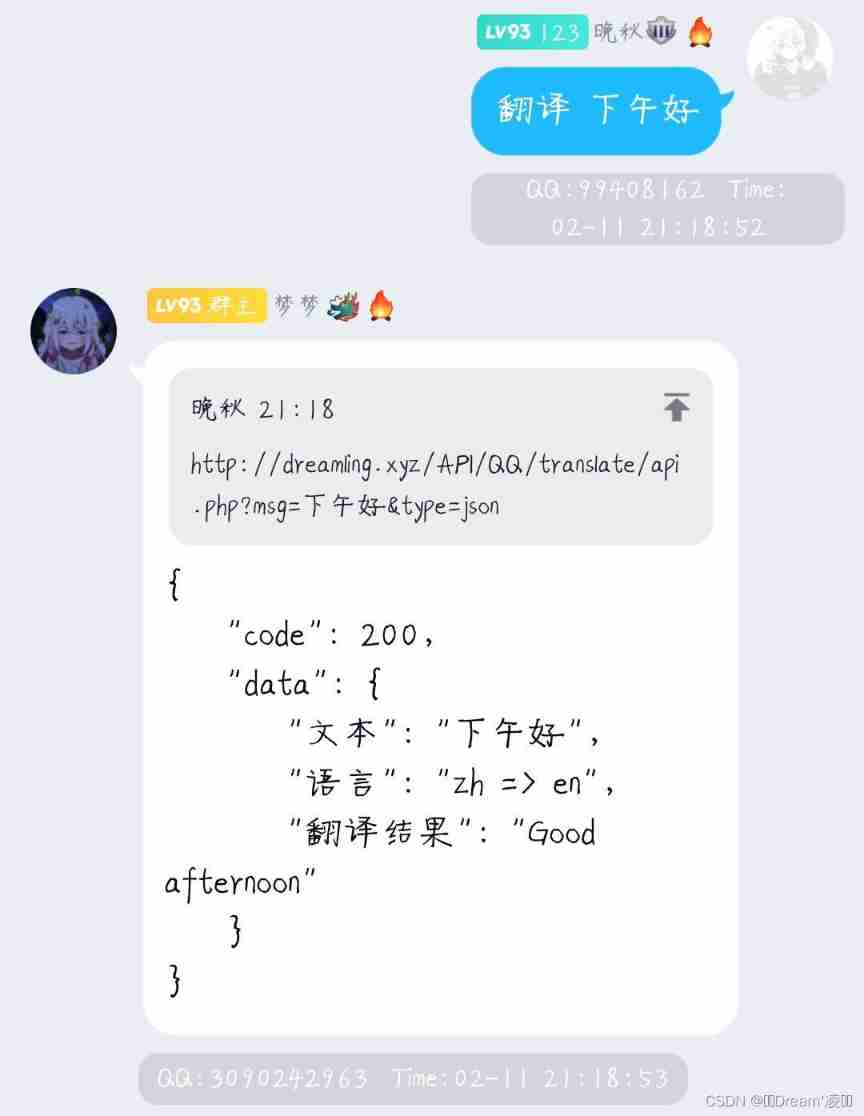
Automatic translation between Chinese and English
随机推荐
Force buckle 142 Circular linked list II
Application of slice
Foreach (system.out:: println) usage
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 15
(August 9, 2021) example exercise of air quality index calculation (I)
Some summaries of the 21st postgraduate entrance examination 823 of network security major of Shanghai Jiaotong University and ideas on how to prepare for the 22nd postgraduate entrance examination pr
Configure SSH key to realize login free
Detailed explanation of classic process synchronization problems
Configure SSH certificate login
OSI seven layer reference model
Heartbeat error attempted replay attack
Getting started with window functions
Elevator dispatching (pairing project) ①
Locust learning record I
Reptile learning 4 winter vacation series (3)
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 6
[Yunju entrepreneurial foundation notes] Chapter II entrepreneur test 7
Xiaobing · beauty appraisal
Climb Phoenix Mountain on December 19, 2021
Solaris 10 network services