当前位置:网站首页>Advanced C language - pointer 2 - knowledge points sorting
Advanced C language - pointer 2 - knowledge points sorting
2022-07-03 23:45:00 【Confused boy】
Catalog
One 、 One dimensional array parameters :
Two 、 Two dimensional array parameters :
3、 ... and 、 First level pointer parameter transfer :
Four 、 The secondary pointer transmits parameters :
5、 ... and 、 A function pointer :
6、 ... and 、 Two interesting pieces of code :
7、 ... and 、 Function pointer array :
8、 ... and 、 Application of function pointer array : Calculator
Nine 、 identify 3 A pointer to the :
1. Pointer to an integer array
2. Pointer to the array of integer pointers
3. A pointer to an array of function pointers
One 、 One dimensional array parameters :
// Code 1:
// One dimensional array parameters , It can be written as an array , It can also be written as a pointer
//1.
void test(int arr[])
{}
//2.
void test(int arr[10])
{}
//3.
void test(int *arr)
{}
//1.
void test2(int* arr[20])
{}
//2.
void test2(int** arr)
{}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {0};
int* arr2[20] = {0};
test(arr);
test2(arr2);
}Two 、 Two dimensional array parameters :
// Code 2:
// Two dimensional array parameters
void test(int arr[3][5])
{}//ok
void test(int arr[][])// You can omit lines , But you cannot omit columns
{}//err
void test(int arr[][5])
{} //ok
void test(int (*p)[5])// The element in the first line , Is the total 5 Elements , Every element is int type , So use the pointer of one-dimensional array to receive
{}//ok, Array uses array pointer to receive
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {0};
test(arr);//arr It represents the address of the first element , The first element represents the address of the first line , It's a one-dimensional array -- In the first row 5 Column , Arrays receive with array pointers
// What passed is the address of one-dimensional array , Then use the pointer of one-dimensional array to receive
return 0;
}
3、 ... and 、 First level pointer parameter transfer :
// Code 3:
// First level pointer parameter transfer
void print(int* p ,int sz)// The pointer p Is the first level pointer , So use the first level pointer to receive
{
// Array elements
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < sz;i++)
{
printf("%d ",p[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
int*p = arr;// First element address
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
print(p,sz);
return;
}Four 、 The secondary pointer transmits parameters :
// Code 4:
// The secondary pointer transmits parameters
void test(int **ppa)
{}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* pa = &a;
int** ppa = &pa;
int* arr[5];
test(ppa);// The way 1
test(&pa);// The way 2
test(arr);// The way 3:arr Represents the address of the first element , The first element is int* type ,int* Type addresses are received with secondary pointers
// The array name of pointer array is received with secondary pointer
return 0;
}5、 ... and 、 A function pointer :
// Code 5:
// Shaping the pointer -- The address where the plastic surgery is stored
// Character pointer -- The address where the characters are stored
// Array pointer -- The address where the array is stored
// Function pointer variable -- Address where the function is stored
//& Array name -- Address of array
// Array name -- Address of the first element of the array
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n",&Add);//007F13E3
printf("%p\n",Add);//007F13E3
// Function name
//& Function name The addresses indicated by the two are the same
// Array pointer
int arr[10] = {0};
int(*parr)[10] = &arr;//*parr Express parr It's a pointer ,[10] Express arr Point to 10 Array of elements ,int Indicates that each element in the array is int type
// A function pointer
int (*pf)(int,int)= &Add;//*pf Express pf It's a pointer ,(int,int) Indicates the type of parameter ,int Represents the return type
// Summary type : Removing the function name is the type
int a = 10;//int
int arr[10];//int [10]
int(*parr)[10] = &arr;//int (*)[10] ,parr Array pointer variable
int (*pf)(int, int) = &Add;//int(*)(int,int)
//pf Is the address used to store the function - pf Is a function pointer variable
// The application of function pointer : Sometimes what you get is not a function , It's the address of the function
//1. Conventional application
int ret = Add(2,3);
printf("%d",ret);//5
//2. A function pointer
// Writing a : It is written so that beginners can better understand -- Take the address and dereference it
int(*pf)(int, int) = &Add;
ret = (*pf)(3, 4);// By dereferencing first pf, find Add() This function , And then in the
printf("%d", ret);//7
return 0;
// Write two : because &Add and Add Both represent function addresses , So it can also be written directly as Add
int(*pf)(int, int) = Add;// here Add and pf Same type , therefore pf and Add It's the same thing
ret = pf(3, 4);// So you can use it directly pf, Call directly
printf("%d", ret);//7
}
6、 ... and 、 Two interesting pieces of code :
// Code 6:
typedef void(* pfun_t)(int);// hold void(*)(int) Redefined as pfun_t
//typedef int int32 // But the formal grammar written above does not allow
int main()
{
// Code 1:
(*((void(*)()) 0))();
// This code is a function call
// analysis :
//1. In the code 0 Cast to type void(*)() The address of a function of
//2. Quoting 0 Address , To call 0 Address this function , The called function is parameterless , The return type is void
// Code 2
void (*signal(int, void(*)(int)))(int);
// This code is a function declaration
// The declared function name is signal
//signal Function has two parameters , The first is int type , The second is void(*)(int) The type of
//signal The return type of the function is still :void(*)(int) Function pointer type of
// Removing the function name and parameters is the return type , Such as int Add();int That is, the return type
// The above declaration code can be simplified into the following form :
pfun_t signal2(int,pfun_t);
}
7、 ... and 、 Function pointer array :
// Code 7:
int Add(int x ,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
int main()
{
//int* arr[10];// An array of plastic pointers
// Function pointer array -- An array of function pointers
int (*pf1)(int,int) = Add;
int (*pf2)(int, int) = Sub;
int (*pf3)(int, int) = Mul;
int (*pf4)(int, int) = Div;
// Function pointer array --- First, an array
int (*pfArr[4])(int, int) = {Add,Sub,Mul,Div};
//pfArr[4] Is an array ,4 Elements , The type of each element is a int (*)(int, int)-- A function pointer
}
8、 ... and 、 Application of function pointer array : Calculator
// Code 8:
// Functions , Parameters , type , identical , So you can apply function pointer arrays
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("1.add 2. sub 3. mul 4.div 0.exit\n");
}
int main()
{
int (*pfArr[5])(int, int) = {0,Add,Sub,Mul,Div};
// 0 1 2 3 4
int input = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf(" Please select \n");
scanf("%d",&input);
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
if (input == 0)
{
printf(" Exit calculator \n");
}
else if (input >= 1 && input <= 4)
{
printf(" Please enter two operands \n");
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
int ret = pfArr[input](x, y);
printf("%d\n",ret);
}
else
{
printf(" Please re-enter ");
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Nine 、 identify 3 A pointer to the :
1. Pointer to an integer array
2. Pointer to the array of integer pointers
3. A pointer to an array of function pointers
// Code 9:
// Example 1 :
int arr[10];// Shape array
int (*p)[10]= &arr;//int [10] ,p It's a pointer , Point to an array , Array has 10 Elements , The type of each element is int type
// therefore p Is a pointer to an integer array
// Example 2 :
int* arr[10];// Integer pointer array
int* (*p)[10] = &arr;// The address of the integer pointer array
//p It's a pointer , Point to an array , Array has 10 Elements , The type of each element is int* type
// therefore p It's a point ( int* [10]) Integer pointer array pointer
// Example 3 : A pointer to an array of function pointers
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int (*p)(int, int) = Add;//Add It represents the address of the function , The address of the function is received by the function pointer
int (*pA[5])(int, int);//pA Is an array of function pointers ,pA Is an array , There are function pointer types stored in the array
int(*(*pAA)[5])(int,int) = &pA;// The first thing to receive should be a pointer , This pointer points to an array , Every element in the array should be of function pointer type , Is to point to the above array with a pointer
//pAA Is a pointer to an array of function pointers
}This paper sorts out the knowledge points of the pointer , Such as incorrect , Please comment in the comment area , thank
边栏推荐
- Exclusive download! Alibaba cloud native brings 10 + technical experts to bring "new possibilities of cloud native and cloud future"
- [untitled]
- Report on prospects and future investment recommendations of China's assisted reproductive industry, 2022-2028 Edition
- Recursion and recursion
- Common mode interference of EMC
- Interpretation of corolla sub low configuration, three cylinder power configuration, CVT fuel saving and smooth, safety configuration is in place
- Pandaoxi's video
- What are the securities companies with the lowest Commission for stock account opening? Would you recommend it? Is it safe to open an account on your mobile phone
- FPGA tutorial and Allegro tutorial - link
- [MySQL] sql99 syntax to realize multi table query
猜你喜欢

Bufferpool caching mechanism for executing SQL in MySQL

2022 free examination questions for hoisting machinery command and hoisting machinery command theory examination
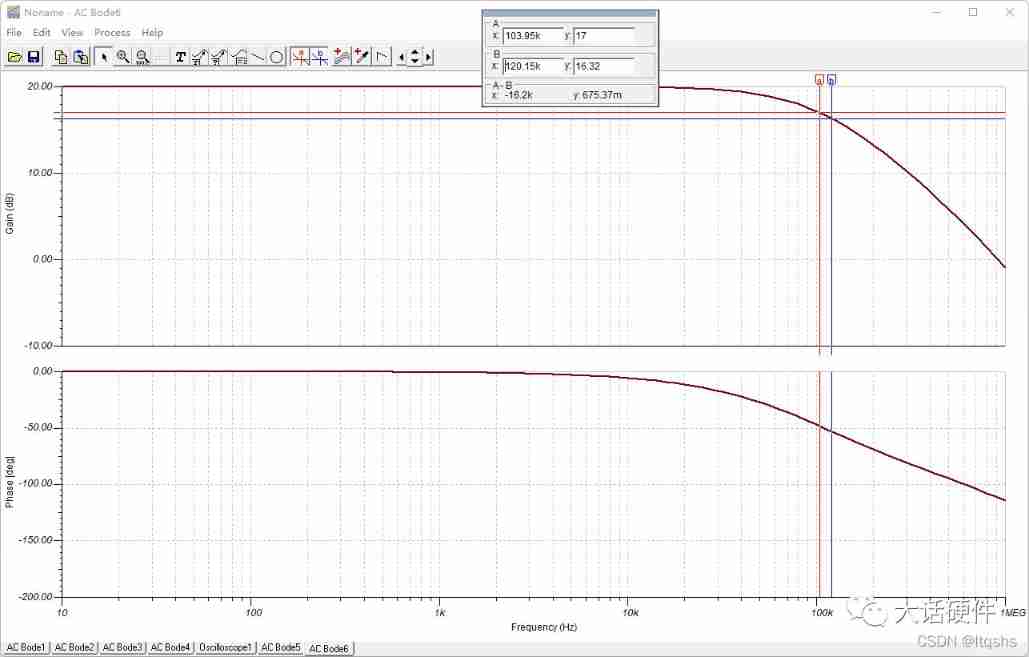
How to understand the gain bandwidth product operational amplifier gain

Briefly understand the operation mode of developing NFT platform

Interpretation of corolla sub low configuration, three cylinder power configuration, CVT fuel saving and smooth, safety configuration is in place
Fluent learning (5) GridView
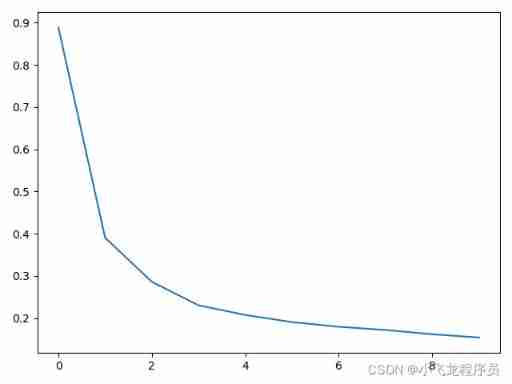
Deep learning ----- using NN, CNN, RNN neural network to realize MNIST data set processing

Ningde times and BYD have refuted rumors one after another. Why does someone always want to harm domestic brands?

Interesting 10 CMD commands

2022 chemical automation control instrument examination content and chemical automation control instrument simulation examination
随机推荐
How to prevent malicious crawling of information by one-to-one live broadcast source server
C # basic knowledge (3)
Ramble 72 of redis source code
2022.02.14
Arc135 partial solution
Investment demand and income forecast report of China's building ceramics industry, 2022-2028
C # basic knowledge (1)
D25:sequence search (sequence search, translation + problem solving)
D23:multiple of 3 or 5 (multiple of 3 or 5, translation + solution)
The difference between single power amplifier and dual power amplifier
Learning methods of zynq
[source code] VB6 chat robot
Comment obtenir une commission préférentielle pour l'ouverture d'un compte en bourse? Est - ce que l'ouverture d'un compte en ligne est sécurisée?
Selenium library 4.5.0 keyword explanation (I)
Day30-t540-2022-02-14-don't answer by yourself
股票开户最低佣金炒股开户免费,网上开户安全吗
Idea set class header comments
Cgb2201 preparatory class evening self-study and lecture content
X Opencv feature point detection and matching
Hcip day 16 notes