当前位置:网站首页>[noi Simulation Competition] add points for noi (heavy chain dissection, line segment tree)
[noi Simulation Competition] add points for noi (heavy chain dissection, line segment tree)
2022-06-29 09:32:00 【DD(XYX)】
Background
OID Doing it NOI2021 The first question of Light and heavy edge when , Just code a modified version of the dynamic tree , It is found that the positive solutions are two l o g log log Board tree section of .
He felt very unconvinced , This simple problem made him lose the pleasure of a perfect and positive solution collision , So I intend to add some materials on the basis of this problem , A disgusting board tree section was made .
Since it's a board ,OID He mercifully adjusted the data range to 1 0 5 10^5 105 了 .
Topic
Given a tree n n n A point to 1 1 1 For rooted trees , Edge has color , Initially all white .
There are three operations :
1 u
To modify u u u The color of the edge on the path to the root , The specific modification method is as follows :
- First , Will be taken from u u u The chain to the root is pulled out , That is to say l i s 1 , l i s 2 , . . . , l i s m lis_1,lis_2,...,lis_m lis1,lis2,...,lism, among l i s 1 = u , l i s m = 1 , ∀ 1 ≤ i < m , l i s i + 1 = f a l i s i lis_1=u,lis_m=1,\forall 1\leq i<m,lis_{i+1}=fa_{lis_i } lis1=u,lism=1,∀1≤i<m,lisi+1=falisi .
- then , remove u u u To the edge on the root path , Compare the rest with l i s 1 , l i s 3 , l i s 5 , . . . lis_1,lis_3,lis_5,... lis1,lis3,lis5,... The connected edges are dyed black , Will work with l i s 2 , l i s 4 , l i s 6 , . . . lis_2,lis_4,lis_6,... lis2,lis4,lis6,... The connected edges are dyed white .
- Last , For in u u u To the edge on the root path , take ( l i s 1 , l i s 2 ) , ( l i s 3 , l i s 4 ) , ( l i s 5 , l i s 6 ) , . . . (lis_1,lis_2),(lis_3,lis_4),(lis_5,lis_6),... (lis1,lis2),(lis3,lis4),(lis5,lis6),... Dyed black , take ( l i s 2 , l i s 3 ) , ( l i s 4 , l i s 5 ) , ( l i s 6 , l i s 7 ) , . . . (lis_2,lis_3),(lis_4,lis_5),(lis_6,lis_7),... (lis2,lis3),(lis4,lis5),(lis6,lis7),... Dye it white .
2 u
Represents a query u u u The number of black edges on the root path .
3 u
Represents a query u u u The number of black edges in the subtree .
Input format
The first line is an integer n n n Indicates the number of nodes in the tree .
Next line n − 1 n-1 n−1 It's an integer , The first i i i It's an integer f a i + 1 fa_{i+1} fai+1 It means the first one i + 1 i+1 i+1 A little father .
Next an integer q q q Represents the number of operations .
Next q q q That's ok , Two integers per line , The meaning is shown in the title .
Output format
For each 2 , 3 2,3 2,3 operation , Output an integer for the answer .
Examples
7
1 2 1 1 4 6
10
3 2
1 4
1 4
3 4
1 6
3 4
3 1
1 2
1 4
2 5
0
1
2
4
0
Data range
1 ≤ n , q ≤ 1 0 5 , f a i < i 1\leq n,q\leq 10^5,fa_i<i 1≤n,q≤105,fai<i .
Answer key
This problem is maintained in two parts , operation 2 And operation 3 .
Operation two , We found and NOI2021 The light and light sides are very similar , We can give point coverage point weight ,
In particular , Let's split the tree chain , Mark the interval coverage t a g tag tag( Of each operation t a g tag tag At least increase 2), Indicates that in this interval Odd position marker t a g tag tag , Even position mark t a g ⊕ 1 tag\oplus1 tag⊕1 , With this mark, the number of black edges in the interval can be easily calculated , This tag is also very convenient for downloading and merging .
This is how we calculate the color of the edge between two points : If the mark of two points XOR sum 1, Then the mark on the right shall prevail , Otherwise, the larger mark shall prevail . If it is marked as an odd number, it is black edged , Otherwise, it is white edge . This rule facilitates merging on the segment tree .
So every time you modify the chain , It just happens that all the adjacent edges are “ modify ” 了 , And the color of the upper part of the chain is also correct .
Operation three , We will find a conclusion : The number of black edges that each dot connects to the son will only be The number of sons 、 The number of sons -1、1 Three . And each time it is modified, the black edge of a point will be changed into the number of sons , The points on the remaining chain are assigned as 1, The number of sons -1,1, The number of sons -1,……
This process can also be maintained with lazy tags , Because the shape of the tree does not change , The number of sons per point does not change , There are only two kinds of collective assignment in each interval .
Time complexity O ( n log 2 n ) O(n\log^2n) O(nlog2n) .
I can't understand the way caterpillars do
CODE
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<random>
#include<bitset>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 100005
#define LL long long
#define ULL unsigned long long
#define ENDL putchar('\n')
#define DB double
#define lowbit(x) (-(x) & (x))
#define FI first
#define SE second
#define PR pair<int,int>
int xchar() {
static const int maxn = 1000000;
static char b[maxn];
static int pos = 0,len = 0;
if(pos == len) pos = 0,len = fread(b,1,maxn,stdin);
if(pos == len) return -1;
return b[pos ++];
}
#define getchar() xchar()
LL read() {
LL f = 1,x = 0;int s = getchar();
while(s < '0' || s > '9') {
if(s<0)return -1;if(s=='-')f=-f;s = getchar();}
while(s >= '0' && s <= '9') {
x = (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (s^48);s = getchar();}
return f*x;
}
void putpos(LL x) {
if(!x)return ;putpos(x/10);putchar((x%10)^48);}
void putnum(LL x) {
if(!x) {
putchar('0');return ;}
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
return putpos(x);
}
void AIput(LL x,int c) {
putnum(x);putchar(c);}
int n,m,s,o,k;
int hd[MAXN],nx[MAXN],fa[MAXN],ind[MAXN];
int siz[MAXN],son[MAXN],tp[MAXN],d[MAXN];
int dfn[MAXN],rr[MAXN],tim,id[MAXN];
void dfs0(int x) {
d[x] = d[fa[x]] + 1;
siz[x] = 1; son[x] = 0;
for(int y = hd[x];y;y = nx[y]) {
dfs0(y);
siz[x] += siz[y];
if(siz[y] > siz[son[x]]) son[x] = y;
}
return ;
}
void dfs1(int x) {
if(son[fa[x]] == x) tp[x] = tp[fa[x]];
else tp[x] = x;
dfn[x] = ++ tim; id[tim] = x;
if(son[x]) dfs1(son[x]);
for(int y = hd[x];y;y = nx[y]) {
if(y != son[x]) {
dfs1(y);
}
} rr[x] = tim;
return ;
}
struct it{
int le,l,r,bl;
it(){
le=l=r=bl=0;}
void fl(int tg) {
l = tg; r = tg^(le&1);
if(tg&1) bl = le>>1;
else bl = (le+1)>>1;
}
}tre[MAXN<<2];
it merg(it a,it b) {
if(a.le < 0) return b;
if(b.le < 0) return a;
a.le += b.le+1; a.bl += b.bl;
if(a.r == (b.l^1)) a.bl += (b.l&1);
else a.bl += (max(a.r,b.l)&1);
a.r = b.r; return a;
}
int sm[MAXN<<2],sm1[MAXN<<2],sm2[MAXN<<2],sz[MAXN<<2];
int lz1[MAXN<<2],lz2[MAXN<<2],M,bt;
inline void upd(int s) {
if(s>=M) return ;
tre[s] = merg(tre[s<<1],tre[s<<1|1]);
sm[s] = sm[s<<1] + sm[s<<1|1];
return ;
}
inline void sts(int s,int tg) {
lz2[s] = tg;
if(tg) sm[s] = sm1[s];
else sm[s] = sm2[s];
return ;
}
inline void pushdown(int s) {
if(s>=M) return ;
if(lz1[s]) {
tre[s<<1].fl(lz1[s<<1] = lz1[s]);
tre[s<<1|1].fl(lz1[s<<1|1] = lz1[s]^((sz[s<<1]&1) ? 1:0));
lz1[s] = 0;
}
if(lz2[s] >= 0) {
sts(s<<1,lz2[s]); sts(s<<1|1,lz2[s]^((sz[s<<1]&1) ? 1:0));
lz2[s] = -1;
} return ;
}
void maketree(int n) {
M=1; bt=0; while(M<n+2) M<<=1,bt++;
memset(lz2,-1,sizeof(lz2));
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) sm1[i+M] = ind[id[i]]-1,sm2[i+M] = 1,sz[i+M] = 1;
for(int s = M-1;s > 0;s --) {
sz[s] = sz[s<<1] + sz[s<<1|1];
if(sz[s<<1]&1) sm1[s] = sm1[s<<1] + sm2[s<<1|1],sm2[s] = sm2[s<<1] + sm1[s<<1|1];
else sm1[s] = sm1[s<<1] + sm1[s<<1|1],sm2[s] = sm2[s<<1] + sm2[s<<1|1];
upd(s);
} return ;
}
void addp(int x,int y) {
int s = M+x;
for(int i = bt;i > 0;i --) pushdown(s>>i);
sm[s] = y; s >>= 1;
for(;s > 0;s >>= 1) sm[s] = sm[s<<1] + sm[s<<1|1];
return ;
}
void addseg(int l,int r,int tg) {
if(l > r) return ;
int ls = 0,rs = r-l+1,s = M+l-1,t = M+r+1;
for(int i = bt;i > 0;i --) pushdown(s>>i),pushdown(t>>i);
for(;s || t;s >>= 1,t >>= 1) {
upd(s); upd(t);
if((s>>1) ^ (t>>1)) {
if(!(s&1)) {
tre[s^1].fl(lz1[s^1] = tg^(ls&1));
sts(s^1,(tg^ls)&1); ls += sz[s^1];
}
if(t & 1) {
rs -= sz[t^1]; sts(t^1,(tg^rs)&1);
tre[t^1].fl(lz1[t^1] = tg^(rs&1));
}
}
} return ;
}
it findtree(int l,int r) {
it ls = it(),rs = it(); ls.le = rs.le = -1;
if(l > r) return ls;
int s = M+l-1,t = M+r+1;
for(int i = bt;i > 0;i --) pushdown(s>>i),pushdown(t>>i);
for(;(s>>1) ^ (t>>1);s >>= 1,t >>= 1) {
if(!(s&1)) ls = merg(ls,tre[s^1]);
if(t & 1) rs = merg(tre[t^1],rs);
} return merg(ls,rs);
}
int findsum(int l,int r) {
if(l > r) return 0;
int as = 0,s = M+l-1,t = M+r+1;
for(int i = bt;i > 0;i --) pushdown(s>>i),pushdown(t>>i);
for(;(s>>1) ^ (t>>1);s >>= 1,t >>= 1) {
if(!(s&1)) as += sm[s^1];
if(t & 1) as += sm[t^1];
} return as;
}
void setline(int x,int tg) {
addseg(dfn[x],dfn[x],tg^1);
addp(dfn[x],ind[x]);
int de = d[x]-1; x = fa[x];
while(x) {
addseg(dfn[tp[x]],dfn[x],tg ^ ((de - d[tp[x]]) & 1));
x = fa[tp[x]];
} return ;
}
int findline(int x) {
it as = it();as.le = -1;
while(x) {
as = merg(findtree(dfn[tp[x]],dfn[x]),as);
x = fa[tp[x]];
} return as.bl;
}
int main() {
freopen("chain.in","r",stdin);
freopen("chain.out","w",stdout);
n = read();
for(int i = 2;i <= n;i ++) {
s = fa[i] = read(); ind[s] ++;
nx[i] = hd[s]; hd[s] = i;
}
dfs0(1); dfs1(1);
maketree(n);
m = read();
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i ++) {
k = read(); s = read();
if(k == 1) {
setline(s,i*2);
}
else if(k == 2) {
AIput(findline(s),'\n');
}
else {
AIput(findsum(dfn[s],rr[s]),'\n');
}
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

YOLACT实时实例分割

The former security director of Uber faced fraud allegations and concealed the data leakage event

Yotact real-time instance segmentation

UE4 VS的Visual Assist插件设置

Five heart charity matchmaker team

AugFPN:改进多尺度特征学习用于目标检测
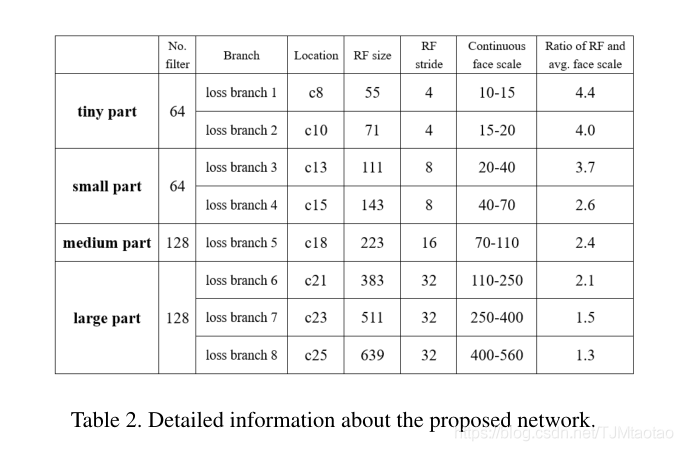
Lffd: a lightweight fast face detector for edge detection

What is the difference between hyperconverged architecture and traditional architecture?

Redo after JS rotation view (longer full version, can be run)

Write down some written test questions
随机推荐
Wechat applet wx Navigateback returns the parameters carried on the previous page
AugFPN:改進多尺度特征學習用於目標檢測
Universal target detection based on region attention
Go deep into RC, RS, daemonset and statefulset (VII)
Redo after JS rotation view (longer full version, can be run)
Difference between factory mode and strategy mode
AugFPN:改进多尺度特征学习用于目标检测
MATLAB小技巧(21)矩阵分析--偏最小二乘回归
easyexecl导出100万行execl报字体错误的解决办法
Mongodb persistence
The principle of session and cookie
Simplicity Studio无法识别新买的JLink v9解决方法
Iso16000-9 testing of volatile organic compounds in building products and furniture
pytorch总结学习系列-数据操作
Pat (basic level) practice (Chinese) 1003 I want to pass! (20 points) C language implementation
How is epoll encapsulated in golang?
LC236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
SSD improvements cfenet
Laravel 8 enables the order table to be divided by month level
How to implement observer mode