当前位置:网站首页>[es practice] safe operation mode on ES
[es practice] safe operation mode on ES
2022-07-01 23:35:00 【Gu Dong】
How security works on ES
List of articles
Elasticsearch A cluster usually consists of many moving parts . There are clusters Elasticsearch node , Usually Logstash example 、Kibana example 、Beats Proxy and client , Communicate with it . Protecting such clusters has many aspects and levels , No wonder .
Elastic Stack Security features provide protection at multiple levels Elastic Cluster approach :
- User authentication User authentication
- User authorization and access control User authorization and access control
- Node/client authentication and channel encryption node / Client authentication and channel encryption
- Auditing Audit
User authentication
User authentication identification . To gain access to restricted resources , The user must pass the password 、 Credentials or other means ( Commonly referred to as an authentication token ) Prove his identity .
Elastic Stack Verify the user's identity by identifying the users behind the requests that hit the cluster and verifying whether they are their claimed identity . The authentication process is handled by one or more authentication services called domains .
You can use native support to manage and authenticate users , Or with the external user management system ( Such as LDAP and Active Directory) Integrate .
Elastic Stack Security features provide built-in areas , for example native、ldap、active_directory、pki、file and saml. If there is no built-in field to meet your needs , You can also build your own custom domains and insert them Elastic Stack.
With security enabled , According to your configured domain , You must attach your user credentials to send to Elasticsearch In the request of . for example , When using domains that support user names and passwords , You can simply attach the basic authentication header to the request .
The security function provides two services : Token service and api Key service . You can use these services to exchange current authentication of tokens or keys . This token or key can then be used as a credential to validate the new request . When it comes to HTTP Enable TLS/SSL when , These services are enabled by default .
Realms
Elastic Stack Safety function use field and one or more Token based authentication service Authenticate users .
realm Used to resolve and authenticate users based on authentication tokens . Security features provide the following built-in areas :
native
Users are stored in private Elasticsearch Internal fields in the index . This domain supports authentication tokens in the form of user names and passwords , And it is available by default when there is no explicit configuration field . User pass User management API Conduct management .See Native user authentication.
ldap
External use LDAP The domain in which the server authenticates users . This domain supports authentication tokens in the form of user names and passwords , And you need explicit configuration to use .See LDAP user authentication.
active_directory
External use Active Directory The domain in which the server authenticates users . Use this field , Users authenticate through user name and password .See Active Directory user authentication.
pki
Use public key infrastructure (PKI) Areas of user authentication . This field is related to SSL/TLS Use a combination of , And through the client X.509 The proper name of the certificate (DN) Identifying users .See PKI user authentication.
file
An internal field , Where the user is Elasticsearch Defined in the file stored on each node in the cluster . This domain supports authentication tokens in the form of user names and passwords , And always available .See File-based user authentication.
saml
Use SAML 2.0 Web SSO The area where protocols facilitate authentication . This area aims to support the adoption of Kibana Authentication performed , Not suitable for REST API Use in .See SAML authentication.
kerberos
Use Kerberos Authentication the field of authenticating users . be based on Kerberos Tickets authenticate users .See Kerberos authentication.
The security feature also supports custom domains . If you need to integrate with another authentication system , You can build a custom domain plug-in .
For more information, see Integrating with other authentication systems.
Internal and external realms
Realm Types can be roughly divided into two categories :
Internal
Elasticsearch Internal areas , No communication with external parties is required . They are completely managed by security functions . At most one domain can be configured for each internal domain type . X-Pack Security provides two types of internal domains :
nativeandfile.External
Need and Elasticsearch External parties / Domain of component interaction , Usually use enterprise level identity management system . Different from the internal field , There can be any number of external domains —— Each has its own unique name and configuration . The security function provides the following types of external domains :
ldap、active_directory、saml、kerberosandpki.
Realm chains
Domains exist in the domain chain . It is essentially a configured domain ( Usually of various types ) Priority list for . The order of the list determines the order of the query fields . You should ensure that each configured domain has a different order setting . If two or more fields have the same order , They will be processed in name order . During authentication ,X-Pack Security will consult and try to authenticate requests in one domain at a time . Once one of the domains successfully validates the request , The verification is considered successful , And the authenticated user will be associated with the request ( Then it will enter the authorization stage ). If a domain cannot verify the request , Then the next online field in the consulting chain . If all domains in the chain cannot authenticate the request , The authentication is considered unsuccessful , And will return an authentication error ( Such as HTTP The status code 401).
The default domain chain contains native Areas and file field . To explicitly configure the domain chain , Please be there. elasticsearch.yml Chain specified in . When configuring the domain chain , Only the domain you specify is used for authentication . To use native Areas and file field , You must include them in the chain .
The following fragment configures a domain chain , These include native Areas and file field , And two LDAP Domain and a Active Directory field .
xpack.security.authc:
realms:
file:
type: file
order: 0
native:
type: native
order: 1
ldap1:
type: ldap
order: 2
enabled: false
url: 'url_to_ldap1'
...
ldap2:
type: ldap
order: 3
url: 'url_to_ldap2'
...
ad1:
type: active_directory
order: 4
url: 'url_to_ad'
As shown above , Each domain has a unique name to identify it , And each domain type has its own set of required and optional settings . in other words , Some settings are common in all fields .
Delegate authority to another domain
Some areas can perform authentication internally , But find and assign roles ( That is, authorization ) Entrust to another field .
for example , You may want to use PKI Domain adoption TLS The client certificate authenticates the user , And then in LDAP Find this user in the domain and use their LDAP Group assignment to make sure they are Elasticsearch The role of .
Any user who supports retrieval ( Don't need their credentials ) All fields can be used as authorization fields ( in other words , Its name may appear as authentication_realms One of the values in the list ). Further instructions on which areas support this feature , See submitting requests on behalf of other users .
For areas that support this function , You can configure in the authentication field authentication_realms Set to enable it . Check the list of support settings for each domain , See if they support authorization_realms Set up .
If delegated authorization is enabled for the domain , It will be in a standard way ( Including related caches ) Authenticate users , Then find the user in the configured authorization domain list . It follows in authorization_realms Try each field in the order specified in the settings . The user is retrieved by the principal - Users must have the same user name in the authentication and authorization fields . If the user cannot be found in any authorized domain , Authentication fails .
User authorization and access control
User authorization authentication and access control
Elastic Stack The security function adds authorization , This is the process of determining whether the user behind the incoming request is allowed to execute the request .
This process occurs after the user is successfully identified and verified .
Role-based access control
The security function provides Role-based access control (RBAC) Mechanism , Enables you to authorize users by assigning permissions to roles and roles to users or groups .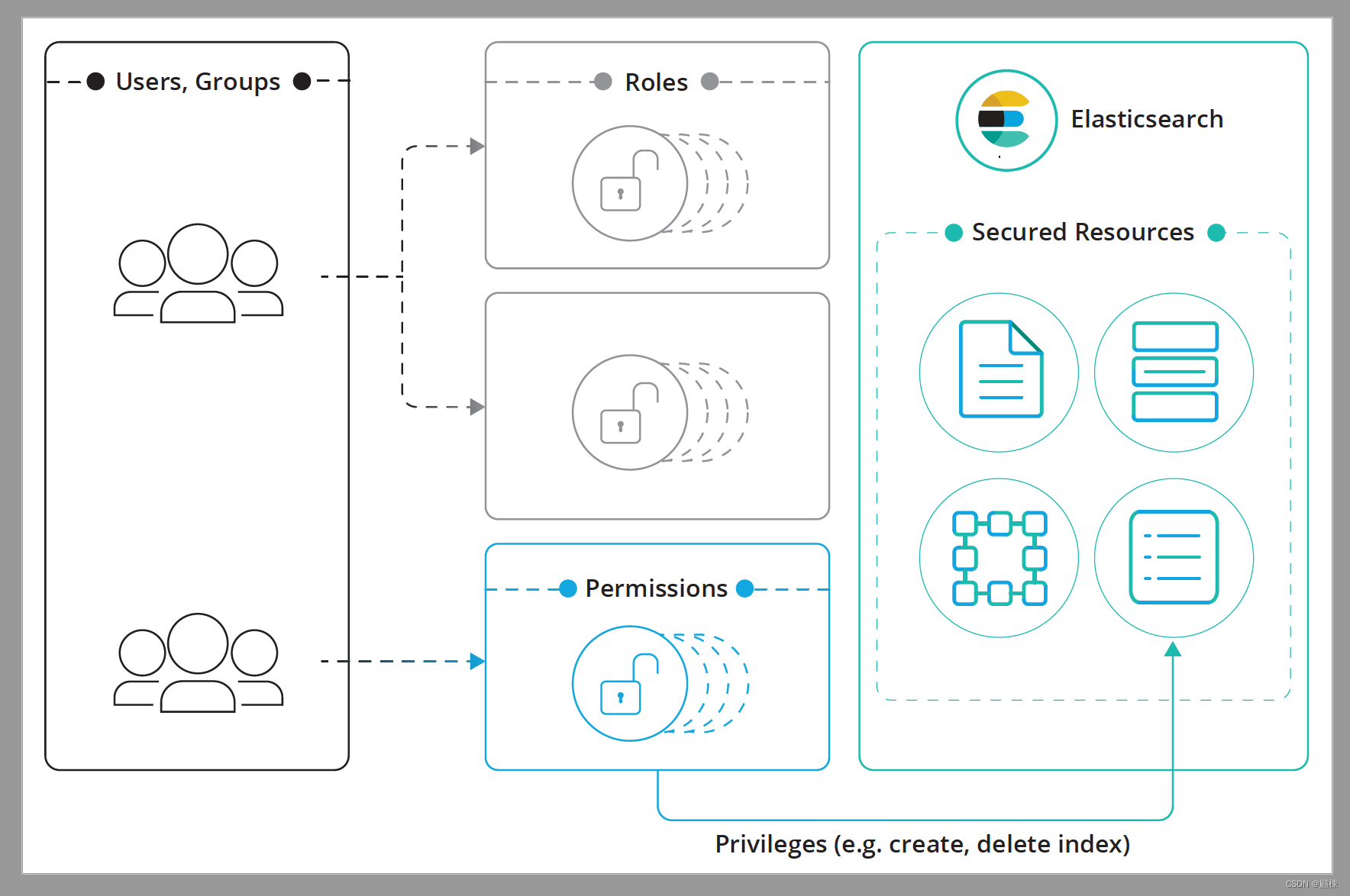
The authorization process revolves around the following structure :
Secured Resource
Access restricted resources . Indices、aliases、 writing documents、fields、users and Elasticsearch The cluster itself is an example of a secure object .
Privilege
A named group of one or more operations that users can perform on secure resources . Each protected resource has its own set of available permissions . for example ,
readIs an index permission , Represents all indexes that can be read / The operation of storing data . A complete list of available permissions , see also security privilege .Permissions
A set of one or more privileges for secure resources . Permissions can be easily described in words , Here are a few examples :
readprivilege on theproductsindex: Read permission of product indexmanageprivilege on the cluster: Manage permissions on the clusterrun_asprivilege onjohnuser: john User run_as jurisdictionreadprivilege on documents that match query X: For matching queries X Read permission of the documentreadprivilege oncredit_cardfield: Yes credit_card Read permission of field
Role
A named set of permissions A set of named permissions
User
The authenticated user. Authenticated users .
Group
One or more groups to which the user belongs . Some domains do not support groups , For example, this machine 、 File or PKI field .
role Have a unique name and identify A set of permissions , These permissions can be converted to resources Authority . You can use Users or groups are associated with any number of roles . When you map roles to groups , The role of the user in the group is a combination of the role assigned to the group and the role assigned to the user . Again , The total permission set owned by a user is jointly defined by the permissions of all its roles .
Attribute-based access control
Property based access control
Security features also provide attribute based access control (ABAC) Mechanism , Enables you to use attributes to restrict access to documents in search queries and aggregations . for example , You can assign attributes to users and documents , Then implement the access policy in the role definition . Users with this role can only read specific documents if they have all the required attributes .
For more information, see Document-level attribute-based access control with X-Pack 6.1.
security privilege
Cluster level
| Permission value | describe |
|---|---|
all | All cluster management operations , Such as snapshot 、 Node shutdown / restart 、 Settings update 、 Rerouting or managing users and roles . |
create_snapshot | Permission to create snapshots for existing repositories . You can also list and view details of existing repositories and snapshots . |
manage | Based on the monitor above , And added the cluster operation of changing the value of the cluster . This includes snapshots 、 Update settings and reroute . It also includes taking snapshots and restoring state . This permission does not include the ability to manage security . |
manage_ccr | All and management follower Indexing and Automation follower Mode related cross cluster replication operations . It also includes grant management follower Indexing and Automation follower The permissions required by the mode . This permission only includes follower Indexing on the cluster is required . |
manage_ilm | All index lifecycle management operations related to management policies |
manage_index_templates | All operations on the index template . |
manage_ingest_pipelines | Ingest all operations on the node pipeline . |
manage_ml | All machine learning operations , For example, create and delete data feeds 、 Job and model snapshots . stay 6.2 Data feeds created before version or when security is disabled run as system users with elevated privileges , Including the permission to read all indexes . Newer data feeds run with the security roles of the users who create or update them . |
manage_pipeline | All operations on the intake pipeline . |
manage_rollup | All summary operations , Including the creation of 、 start-up 、 Stop and delete summary jobs . |
manage_saml | Internal Elasticsearch API To start and manage on behalf of other users SAML Authentication . |
manage_security | All safety related operations , For example, for users and roles CRUD Operation and cache clearing . |
manage_token | from Elasticsearch All security related operations on the token generated by the token service . |
manage_watcher | All observer operations , For example, place observation 、 perform 、 Activate or confirm . stay 6.1 Observations created before version or when the security function is disabled run as system users with elevated privileges , Including the permission to read and write all indexes . Newer observers run with the security role of the user who created or updated them . |
monitor | All cluster read-only operations , Such as cluster health and status 、 Hot thread 、 Node information 、 Node and cluster statistics and pending cluster tasks . |
monitor_ml | All read-only machine learning operations , For example, get relevant data feeds 、 Homework 、 Information about model snapshots or results . |
monitor_rollup | All read-only summary operations , For example, view the history and the list of currently running summary jobs and their functions . |
monitor_watcher | All read-only observer operations , For example, get observer and observer statistics . |
read_ccr | All read-only cross cluster replication operations , For example, in the acquisition cluster leader Index and metadata information of the index . It also includes checking whether the user has followed leader The appropriate permissions of the index . This permission only includes leader Indexing on the cluster is required . |
read_ilm | All read-only index lifecycle management operations , For example, get policies and check the status of index lifecycle management |
transport_client | Transfer all permissions required for client connections . Remote cluster needs to be enabled Cross cluster search . |
Privilege priority
| high | –> | –> | –> | low |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | manage | create_snapshot | ||
| manage_security | manage_ccr | |||
| manage_token | manage_ilm | |||
| manage_saml | manage_index_templates | |||
| manage_ml | ||||
| manage_ingest_pipelines | ||||
| manage_pipeline | ||||
| manage_rollup | ||||
| manage_watcher | ||||
| monitor | monitor_ml | |||
| monitor_rollup | ||||
| monitor_watcher | ||||
| read_ccr | ||||
| read_ilm | ||||
| transport_client |
Index level
| Permission value | describe |
|---|---|
all | Any operation on the index |
create | Privileges to index documents . Access to update mapping operations is also granted . This permission does not restrict indexing operations to creating documents , It's going to be API Use is limited to index API. index API Allow users to overwrite previously indexed documents . |
create_index | Permission to create an index . The create index request may contain aliases to be added to the index after creation . under these circumstances , The request also requires an index and alias name “ management ” jurisdiction . |
delete | Permission to delete documents . |
delete_index | Permission to delete index . |
index | Privileges to index and update documents . Access to update mapping operations is also granted . |
manage | all “ monitor ” Permissions and index management ( Alias 、 analysis 、 Cache clear 、 close 、 Delete 、 There is 、 Refresh 、 mapping 、 open 、 Force a merger 、 Refresh 、 Set up 、 Search slice 、 Templates 、 verification ). |
manage_follow_index | management follower All actions required for the life cycle of the index , Including the creation of follower Indexes 、 Close it and convert it to a regular index . This permission only includes follower Indexing on the cluster is required . |
manage_ilm | All index lifecycle management operations related to managing the execution of index policies, including retry policies and deleting policies from the index . |
manage_leader_index | management leader index All operations required for the life cycle of , Include [forgetting a follower](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.7/ccr-post-forget-follower. html). This permission only includes leader Indexing on the cluster is required . |
monitor | Monitor all operations required ( recovery 、 Segment information 、 Index statistics and status ). |
read | Read only access to operations (count, explain, get, mget, get indexed scripts, more like this, multi percolate/search/termvector, percolate, scroll, clear_scroll, search, suggest, tv). |
read_cross_cluster | from Remote cluster Read only access to search operations . |
view_index_metadata | This privilege is primarily available for use by Kibana users. Read only access to index metadata ( Alias 、 Aliases exist 、 Get index 、 There is 、 Field mapping 、 mapping 、 Search slice 、type exists、 verification 、warmers、settings、ilm). This permission is mainly for Kibana The user to use . |
write | Permission to perform all write operations on the document , Include index 、 Permission to update and delete documents and perform batch operations . Access to update mapping operations is also granted . |
Privilege priority
| high | –> | low |
|---|---|---|
| All | create | |
| create_index | ||
| delete | ||
| delete_index | ||
| index | ||
| manage | manage_follow_index | |
| manage_leader_index | ||
| manage_ilm | ||
| monitor | ||
| read | ||
| read_cross_cluster | ||
| view_index_metadata | ||
| write |
Run as privilege
run_as Permissions enable authenticated users to submit requests on behalf of another user . This value can be a user name or a comma separated list of user names . ( You can also specify the user as a string array or YAML Sequence .)For more information, see Submitting Requests on Behalf of Other Users.
Authority agent ?
Application permissions
Application permissions are Elasticsearch Ongoing management , have access to has privilege API and Get application permissions API. however , They are not granted to Elasticsearch Access to any operation or resource in . Their purpose is to enable applications to Elasticsearch The role represents and stores its own permission model .
To create application permissions , Please use Add application permissions API. then , You can associate these application permissions with roles , Such as Define the role Described in .
Node/client authentication and channel encryption
The security function supports configuration SSL/TLS To protect the communication channels in and out of the cluster . This support illustrates :
Encrypt the data transmitted through the line
Certificate based node authentication - Prevent unauthorized nodes / The client establishes a connection with the cluster .
For more information, see Encrypting Communications.
Security features also enable you to To configure IP filter , This can be regarded as a node / Lightweight mechanism of client authentication . adopt IP Filter , You can IP Address limits the nodes and clients that can connect to the cluster . IP Filter configuration provides IP、 Subnets and DNS Whitelist and blacklist of domains .
Auditing
When dealing with any security system , It is very important to set up an audit tracking mechanism . Audit trail records various activities in the system / event , Enables you to avoid problems ( For example, security vulnerabilities ) Analyze and trace past events .
The security function provides such audit tracking function for all nodes in the cluster . You can configure the audit level , To describe the type of event recorded . These events include the failure of authentication attempts 、 User access denied 、 The node connection is rejected .
For more information on auditing see Auditing security events.
边栏推荐
- Overview of edge calculation
- Switch to software testing, knowing these four points is enough!
- y53.第三章 Kubernetes从入门到精通 -- ingress(二六)
- The essence of software architecture
- 2022年最佳智能家居开源系统:Alexa、Home Assistant、HomeKit生态系统介绍
- Matplotlib common settings
- MT manager test skiing Adventure
- Depth first search and breadth first search of graph traversal
- const // It is a const object...class nullptr_t
- What is mosaic?
猜你喜欢

Zero foundation tutorial of Internet of things development

软件架构的本质

Concepts of dictionary, hash table and array

ConcurrentSkipListMap——跳表原理
2021 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-高职组初赛

2021 RoboCom 世界机器人开发者大赛-高职组复赛

Future trend and development of neural network Internet of things

Chapter 6 data flow modeling
![[understanding of opportunity-35]: Guiguzi - flying clamp - the art of remote connection, remote control and remote testing](/img/08/9ecfd53a04e147022dde3449aec132.png)
[understanding of opportunity-35]: Guiguzi - flying clamp - the art of remote connection, remote control and remote testing
Notes on problems - /usr/bin/perl is needed by mysql-server-5.1.73-1 glibc23.x86_ sixty-four
随机推荐
dat. GUI
Postgresql随手记(10)动态执行EXECUTING语法解析过程
在代码中使用SqlCommand对象
使用uni-simple-router,动态传参 TypeError: Cannot convert undefined or null to object
const // It is a const object...class nullptr_t
Yunxin small class | common cognitive misunderstandings in IM and audio and video
【.Net Core】程序相关各种全局文件
Is it safe to choose mobile phone for stock trading account opening in Shanghai?
TS初次使用、ts类型
Concepts of dictionary, hash table and array
问题随记 —— /usr/bin/perl is needed by MySQL-server-5.1.73-1.glibc23.x86_64
Depth first search and breadth first search of graph traversal
What is mosaic?
软件架构的本质
PostgreSQL notes (10) dynamically execute syntax parsing process
Commemorate becoming the first dayus200 tripartite demo contributor
2021 robocom world robot developer competition - semi finals of higher vocational group
神经网络物联网的发展趋势和未来方向
2022 safety officer-c certificate examination question simulation examination question bank and simulation examination
【C#】依赖注入及Autofac