当前位置:网站首页>All questions and answers of database SQL practice niuke.com
All questions and answers of database SQL practice niuke.com
2022-06-11 05:45:00 【A long journey begins with a single step】
1. Find all the information about the latest employee
Find all the information about the latest employee , In order to reduce the difficulty of getting started , At present, in all the data, the employee's entry date is not the same day
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL comment ‘ Employee number ’,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
select * from employees
where hire_date =
(select max(hire_date) from employees)
2. Find all the information about the employee who is the third from the bottom in the time rank of the employee
Find all the information about the employee who is the third from the bottom in the time rank of the employee , In order to reduce the difficulty of getting started , At present, in all the data, the employee's entry date is not the same day
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :

Ideas :
-- LIMIT m,n : Says from the first m+1 Bar start , take n Data ;
select * from employees
where hire_date = (
select hire_date from employees order by hire_date desc limit 2,1
)
3. Find current salary details and department number dept_no
Find the current (dept_manager.to_date=‘9999-01-01’) Lead the current (salaries.to_date=‘9999-01-01’) Salary details and their corresponding department numbers dept_no( Note the output ,dept_no Column is the last column )
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL comment ‘ Department number ’,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL comment ‘ Employee number ’,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL comment ‘ Employee number ’,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas : The requirements are salary and department number , Combined with the output dept_no Was placed in the last column , It can be seen that the main table is “salaries”.
select s.* ,d.dept_no
from salaries as s
join dept_manager as d
on s.emp_no=d.emp_no
where s.to_date = '9999-01-01'
and d.to_date='9999-01-01';
)
4. Find all the employees in the assigned department last_name and first_name as well as dept_no
Find all the employees in the assigned department last_name and first_name as well as dept_no( Notice the order of the columns in the output description )
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
select e.last_name,e.first_name,d.dept_no
from employees as e
join dept_emp as d
on e.emp_no=d.emp_no
5. Find all employees last_name and first_name And the corresponding department number dept_no
Find all employees last_name and first_name And the corresponding department number dept_no, It also includes employees who are not assigned to specific departments for the time being ( Notice the order of the columns in the output description )
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
select e.last_name,e.first_name,d.dept_no
from employees as e
left join dept_emp as d -- Left connection
on e.emp_no=d.emp_no
6. Find the salary of all employees when they are on the job
Find the salary of all employees when they are on the job , give emp_no as well as salary, And in accordance with the emp_no In reverse order ( Please note that , An employee may have multiple salary increases )
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
1、 Because the test data ,salaries.emp_no Is not the only ( Because the number is emp_no I'm a member of the team *** There is the possibility of multiple salary increases , So in salaries There is more than one corresponding record in ),employees.emp_no only , namely salaries There will be more data than employees, So you need to find employees.emp_no stay salaries The corresponding records in the table salaries.emp_no, There are restrictions e.emp_no = s.emp_no
2、 According to the meaning of the question, notice salaries.from_date and employees.hire_date The values of should be equal , So there are restrictions e.hire_date = s.from_date
3、 According to the meaning of the question, we should follow emp_no Values are arranged in reverse order , So finally add ORDER BY e.emp_no DESC
on The condition is for foreign key connections , Often with join Continuous use ,where Conditions are used to filter records .
-- Method 1 : utilize INNER JOIN Join two tables
SELECT e.emp_no, s.salary FROM employees AS e INNER JOIN salaries AS s
ON e.emp_no = s.emp_no AND e.hire_date = s.from_date
ORDER BY e.emp_no DESC
-- Method 2 : Directly use commas to query two tables in parallel
SELECT e.emp_no, s.salary FROM employees AS e, salaries AS s
WHERE e.emp_no = s.emp_no AND e.hire_date = s.from_date
ORDER BY e.emp_no DESC
7. Find salary changes that exceed 15 Second employee number emp_no And the corresponding number of changes t
Find salary changes that exceed 15 Second employee number emp_no And the corresponding number of changes t
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
WHERE Statements in GROUP BY The statement before ;SQL Will calculate... Before grouping WHERE sentence .
HAVING Statements in GROUP BY After statement ;SQL Will be calculated after grouping HAVING sentence .
SELECT emp_no, COUNT(emp_no) AS t FROM salaries
GROUP BY emp_no HAVING t > 15
8. Find out the current salary of all employees salary situation
Find out all employees' current (to_date=‘9999-01-01’) Specific salary salary situation , Only once for the same salary , And in reverse order
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
select salary from salaries
where to_date='9999-01-01'
group by salary
order by salary desc
/* Large watches are usually used distinct The efficiency is not high , It is forbidden to use when there is a large amount of data distinct, Suggest using group by Solve duplicate problems . */
9. Get the current manager My current salary , give
Get the current (dept_manager.to_date=‘9999-01-01’)manager The current (salaries.to_date=‘9999-01-01’) Salary situation , give dept_no, emp_no as well as salary( Please note that , The same person may have multiple salary records )
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
select d.dept_no, d.emp_no, s.salary
from salaries as s
join dept_manager as d
on s.emp_no=d.emp_no
where s.to_date = '9999-01-01'
and d.to_date='9999-01-01';
10. Get all non manager The employees' emp_no
Get all non manager The employees' emp_no
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
-- Method 1 : Use NOT IN Selected in employees But not here. dept_manager Medium emp_no Record
SELECT emp_no FROM employees
WHERE emp_no NOT IN (SELECT emp_no FROM dept_manager)
-- Method 2 : First use LEFT JOIN Join two tables , Then choose from this list dept_no The value is NULL Corresponding emp_no Record
SELECT emp_no FROM (SELECT * FROM employees LEFT JOIN dept_manager
ON employees.emp_no = dept_manager.emp_no)
WHERE dept_no IS NULL
11. Get all employees' current manager
Get all employees' current (dept_manager.to_date=‘9999-01-01’)manager, If the employee is manager Do not show ( That is, if the current manager If it's your own, it doesn't show ). The first column of the output result shows the current employee's emp_no, The second column gives its manager Corresponding emp_no.
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL comment ‘ All employee numbers ’,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL comment ‘ Department number ’,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL comment ‘ Department number ’,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL comment ‘ Manager number ’,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
The following three points should be paid attention to :
1、 use INNER JOIN Join two tables , Because I have to output my own manager , Know that you and your manager have the same department , Therefore, there are restrictions de.dept_no = dm.dept_no
2、 Reuse WHERE Conditions that limit current employees and current managers , namely dm.to_date be equal to ‘9999-01-01’ 、de.to_date be equal to ‘9999-01-01’ 、 de.emp_no It's not equal to dm.emp_no
3、 To enhance code readability , take dept_emp Use alias de Instead of ,dept_manager use dm Instead of , Finally, according to the meaning of the title, I will de.emp_no Use alias manager_no Output after substitution
SELECT de.emp_no, dm.emp_no AS manager_no
FROM dept_emp AS de INNER JOIN dept_manager AS dm
ON de.dept_no = dm.dept_no
WHERE dm.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND de.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND de.emp_no <> dm.emp_no
12. Get information about the highest paid employees in all departments
Find all the information about the employee who is the third from the bottom in the time rank of the employee , In order to reduce the difficulty of getting started , At present, in all the data, the employee's entry date is not the same day
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
SELECT d.dept_no, s.emp_no, MAX(s.salary) AS salary
FROM salaries AS s INNER JOIN dept_emp As d
ON d.emp_no = s.emp_no -- Current employee
WHERE d.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01'
GROUP BY d.dept_no -- Find the largest salary by department
13. from titles The table is obtained according to title Grouping
from titles The table is obtained according to title Grouping , The number of each group is greater than or equal to 2, give title And the corresponding number t.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS “titles” (emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,titlevarchar(50) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate DEFAULT NULL);
Output description :
Ideas :
SELECT title,COUNT(*) AS t
FROM titles
GROUP BY title
HAVING t > 1;
14. from titles The table is obtained according to title Grouping , Pay attention to the repeated emp_no Proceed suddenly
from titles The table is obtained according to title Grouping , The number of each group is greater than or equal to 2, give title And the corresponding number t.
Pay attention to the repeated emp_no Ignore ( namely emp_no Repetitive title Don't count ,title Corresponding number t Don't add ).
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTStitles(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,titlevarchar(50) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate DEFAULT NULL);
Output description :
Ideas :
This question should pay attention to the following three points :
1、 First use GROUP BY title Place the table in title grouping , Reuse COUNT(DISTINCT emp_no) The same can be counted title Value without duplicates emp_no Number of records of value
2、 According to the meaning , Output each title The number of t, So use AS Statement will COUNT(DISTINCT emp_no) The value of is converted to t
3、 because WHERE Don't follow COUNT() function , So use HAVING Statement to qualify t>=2 Conditions
SELECT title, COUNT(DISTINCT emp_no) AS t FROM titles
GROUP BY title HAVING t >= 2
15. lookup employees surface
lookup employees Table all emp_no It's odd , And last_name Not for Mary( Pay attention to case ) Employee information , And in accordance with the hire_date In reverse order ( The title cannot be used mod function )
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
select * from employees
where emp_no % 2 = 1
and last_name != 'Mary'
order by hire_date desc
/* 1、 Employee number is odd , be emp_no The remainder should be 1 2、last_name Not for Mary, use ‘!=’ Express 3. according to hire_date In reverse order , use desc */
16. Count out the current title The average salary corresponding to the current salary of the employee corresponding to the type
Count out the current title The type corresponds to the employee's current (to_date=‘9999-01-01’) The average wage corresponding to salary . The results show that title And the average wage avg.
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS “titles” (emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,titlevarchar(50) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate DEFAULT NULL);
Output description :
Ideas :
SELECT t.title,AVG(s.salary) as avg
FROM salaries as s INNER JOIN titles as t
ON s.emp_no = t.emp_no
AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01'
AND t.to_date = '9999-01-01'
GROUP BY title
17. Get the salary of the employee with the second highest salary emp_no And the corresponding salary salary
Get current (to_date=‘9999-01-01’) The second highest paid employee emp_no And the corresponding salary salary
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
-- LIMIT m,n : Says from the first m+1 Bar start , take n Data ;
select emp_no,salary from salaries order by salary desc limit 1,1
18. Find all the information about the employee who is the third from the bottom in the time rank of the employee
Find current salary (to_date=‘9999-01-01’) The second most ranked employee number emp_no、 salary salary、last_name as well as first_name, You may not use order by Is it finished
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
select e.emp_no, max(s.salary) AS salary, e.last_name, e.first_name
from employees AS e inner join salaries AS s on e.emp_no=s.emp_no
where to_date='9999-01-01'and salary not in
(select max (salary) from salaries where to_date='9999-01-01')
19. Find all employees last_name and first_name And corresponding dept_name
Find all employees last_name and first_name And corresponding dept_name, It also includes employees who have no assigned department for the time being
CREATE TABLEdepartments(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,dept_namevarchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
The idea of this question is to use twice LEFT JOIN Connection nesting
1、 for the first time LEFT JOIN Connect employees Table and dept_emp surface , Get... From all employees last_name and first_name And corresponding dept_no, It also includes employees who have no assigned department for the time being
2、 The second time LEFT JOIN Connect the above table to departments surface , I.e. connection dept_no And dept_name, Get... From all employees last_name and first_name And corresponding dept_name, It also includes employees who have no assigned department for the time being
SELECT em.last_name, em.first_name, dp.dept_name
FROM (employees AS em LEFT JOIN dept_emp AS de ON em.emp_no = de.emp_no)
LEFT JOIN departments AS dp ON de.dept_no = dp.dept_no
20. Find the employee number emp_no by 10001 His salary since he joined the company salary gains ( How much has it gone up in total )growth
Find the employee number emp_no by 10001 His salary since he joined the company salary gains ( How much has it gone up in total )growth( There may be many salary increases , There was no pay cut )
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
The rigorous thinking of this topic is as follows :
1、 First of all, find emp_no=10001 The first salary record and the last salary record of the employee
2、 Then subtract the first salary record from the last salary record to get the salary record salary The gains , Finally, use alias growth Instead of
SELECT (
(SELECT salary FROM salaries WHERE emp_no = 10001 ORDER BY to_date DESC LIMIT 1) -
(SELECT salary FROM salaries WHERE emp_no = 10001 ORDER BY to_date ASC LIMIT 1)
) AS growth
21. Find out the salary increase of all employees since they joined the company
Find out the salary increase of all employees since they joined the company , Give the employee number emp_no And the corresponding salary increase growth, And in accordance with the growth Ascending order
( notes : There may be employees Table and salaries Employees with records in the table , There are corresponding employee numbers and salary increase records , But I have left , Resigned employees salaries The latest of the table to_date!=‘9999-01-01’, Such data is not displayed in the search results )
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL comment ‘ Entry time ’,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL comment ‘ Start time of a salary record ’,to_datedate NOT NULL comment ‘ End time of a salary record ’,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
select a.emp_no, (b.salary - c.salary) as growth
from
employees as a
inner join salaries as b
on a.emp_no = b.emp_no and b.to_date = '9999-01-01' -- The current salary of each employee
inner join salaries as c
on a.emp_no = c.emp_no and a.hire_date = c.from_date -- The salary of each new employee
order by growth asc
22. Count the salary records of each department
Count the salary records of each department , Give the department code dept_no、 Department name dept_name And the number of times sum
CREATE TABLEdepartments(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,dept_namevarchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Ideas :
The key to this question is to Each department is grouped , And separately count the total number of wage records , Ideas as follows :
1、 use INNER JOIN Connect dept_emp Table and salaries surface , And dept_emp.no grouping , Count the total number of records of wages of all employees in each department
2、 Then use the above table INNER JOIN Connect departments surface , The restriction is two tables dept_no equal , find dept_no And dept_name Correspondence of , Finally, output in turn dept_no、dept_name、sum
SELECT de.dept_no, dp.dept_name, COUNT(s.salary) AS sum
FROM (dept_emp AS de INNER JOIN salaries AS s ON de.emp_no = s.emp_no)
INNER JOIN departments AS dp ON de.dept_no = dp.dept_no
GROUP BY de.dept_no
23. The salary of all employees shall be in accordance with salary Carry on according to 1-N Ranking
The current... For all employees (to_date=‘9999-01-01’) The salary is based on salary Carry on according to 1-N Ranking , identical salary Side by side and in accordance with emp_no Ascending order
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Ideas :
The main idea of this topic is to reuse salaries Table for comparison ranking , The idea is as follows :
1、 From two identical salaries surface ( Respectively s1 And s2) Make a comparative analysis , First set the limiting conditions of the two tables to to_date = ‘9999-01-01’, Pick out the salaries of all current employees .
2、 The essence of this question is s1.salary <= s2.salary, It means outputting s1.salary Under the circumstances , How many s2.salary Greater than or equal to s1.salary, For example, when s1.salary=94409 when , Yes 3 individual s2.salary( Respectively 94692,94409,94409) Greater than or equal to it , But because of 94409 repeat , utilize COUNT(DISTINCT s2.salary) The salary available for weight removal is 94409 Of rank be equal to 2. And so on .
3、 Don't forget GROUP BY s1.emp_no, Otherwise, only one record will be output ( It could be the first or last , Depending on the database ), Because the total function is used COUNT()
4、 Finally, start with s1.salary In reverse order , And then to s1.emp_no Arrange the output results in sequence
SELECT s1.emp_no, s1.salary, COUNT(DISTINCT s2.salary) AS rank
FROM salaries AS s1, salaries AS s2
WHERE s1.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND s2.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND s1.salary <= s2.salary
GROUP BY s1.emp_no
ORDER BY s1.salary DESC, s1.emp_no ASC
24. Get all non manager The current salary situation of employees
Get all non manager The current salary situation of employees , give dept_no、emp_no as well as salary , The current expression is to_date=‘9999-01-01’
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :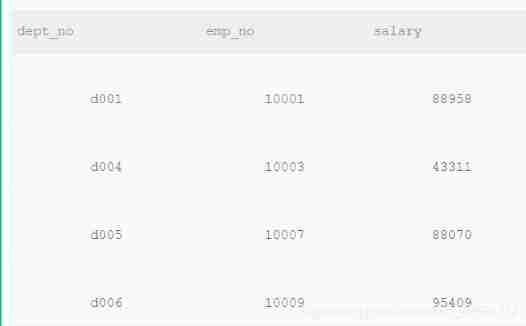
Ideas :
1、 First use INNER JOIN Connect employees and salaries, Find out the salary status of all current employees
2、 Reuse INNER JOIN Connect dept_emp surface , Find all employees' departments
3、 Finally, with restrictions de.emp_no NOT IN (SELECT emp_no FROM dept_manager WHERE to_date = ‘9999-01-01’) Select all current non manager staff , And then output dept_no、emp_no、salary
SELECT de.dept_no, s.emp_no, s.salary
-- relation
FROM (employees AS e INNER JOIN salaries AS s ON s.emp_no = e.emp_no AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01')
INNER JOIN dept_emp AS de ON e.emp_no = de.emp_no
-- Limit
WHERE s.emp_no NOT IN (SELECT emp_no FROM dept_manager WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01')
25. Get employees whose current salary is higher than their manager Information about the current high salary
Get employees whose current salary is higher than their manager Information about the current high salary , The current expression is to_date=‘9999-01-01’,
The first column of the results gives the employee's emp_no,
The second column gives its manager Of manager_no,
The third column gives the employee's current salary emp_salary,
The fourth column is for the employee manager Current salary manager_salary
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
The main idea of this question is to create two tables ( A record of the salaries of all current employees , The other one only records the salary of the Department Manager ) Compare , The idea is as follows :
1、 First use INNER JOIN Connect salaries and demp_emp, Establish salary records for all current employees sem
2、 Reuse INNER JOIN Connect salaries and demp_manager, Establish salary records for all current employees sdm
3、 Finally, with restrictions sem.dept_no = sdm.dept_no AND sem.salary > sdm.salary Find employees in the same department who are paid more than the manager , And output in turn according to the meaning of the question emp_no、manager_no、emp_salary、manager_salary
SELECT sem.emp_no AS emp_no, sdm.emp_no AS manager_no, sem.salary AS emp_salary, sdm.salary AS manager_salary
FROM (SELECT s.salary, s.emp_no, de.dept_no FROM salaries s INNER JOIN dept_emp de
ON s.emp_no = de.emp_no AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01' ) AS sem,
(SELECT s.salary, s.emp_no, dm.dept_no FROM salaries s INNER JOIN dept_manager dm
ON s.emp_no = dm.emp_no AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01' ) AS sdm
WHERE sem.dept_no = sdm.dept_no AND sem.salary > sdm.salary
26. Summarize the current employees of each department title Number of assignments of type
Summarize the current employees of each department title Number of assignments of type , That is, the result gives the department number dept_no、dept_name、 All current under its department (dept_emp.to_date = ‘9999-01-01’) Employee's current (titles.to_date = ‘9999-01-01’)title And this type title Corresponding number count
( notes : Because employees may leave , all dept_emp Inside to_date Not for ’9999-01-01’ I've left , Not included in the statistics , And employees may be promoted , So if titles.to_date Not for ‘9999-01-01’, So this may be the employee's previous position information , Not included in the statistics )
CREATE TABLEdepartments(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,dept_namevarchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (dept_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTStitles(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,titlevarchar(50) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate DEFAULT NULL);
Output description :
Ideas :
The key to this question is to use GROUP BY At the same time de.dept_no and t.title Grouping , The idea is as follows :
1、 First use INNER JOIN Connect dept_emp And salaries, Add qualification based on test data de.to_date = ‘9999-01-01’ AND t.to_date = ‘9999-01-01’, The current title of the current employee
2、 Reuse INNER JOIN Connect departments, The limiting conditions are de.dept_no = dp.dept_no, That is, the department number is the same
3、 Last use GROUP BY At the same time de.dept_no and t.title Grouping , use COUNT(t.title) Count the number of employees with the same title in the same department
SELECT de.dept_no, dp.dept_name, t.title, COUNT(t.title) AS count
FROM titles AS t INNER JOIN dept_emp AS de
ON t.emp_no = de.emp_no AND de.to_date = '9999-01-01' AND t.to_date = '9999-01-01'
INNER JOIN departments AS dp
ON de.dept_no = dp.dept_no
GROUP BY de.dept_no, t.title
27. Give each employee an annual salary increase of more than 5000 Employee number of emp_no
Give each employee an annual salary increase of more than 5000 Employee number of emp_no、 Salary change start date from_date And salary increases salary_growth, And in accordance with the salary_growth In reverse order .
Tips : stay sqlite In order to get datetime The year function corresponding to time is strftime(’%Y’, to_date)
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
The difficulty of this question lies in how to understand Annual salary increase , And reuse salaries The table calculates that the annual salary increase exceeds 5000 The employees' , The idea is as follows :
1、 hypothesis s1 It's the watch before the salary rise ,s2 It's the watch after the salary rise , Because each employee's salary rise time is not fixed , It may rise twice a year , It may rise once every two years , So the annual salary increase , It should be understood as the of two salary records from_date Same or to_date identical .
If only to_date identical , Of the third original test data 52668 Change to 62668 when , There will be one less 【62668-48584=14084】 The record of
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10008,46671,‘1998-03-11’,‘1999-03-11’);
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10008,48584,‘1999-03-11’,‘2000-03-10’);
INSERT INTO salaries VALUES(10008, 62668 ,‘2000-03-10’,‘2000-07-31’); **/
2、 find s1 And s2 After the records meet the requirements , use s2 Your salary minus s1 's salary , use salary_growth Express , Add qualifications s1.emp_no = s2.emp_no AND salary_growth > 5000, That is, the annual increase of the same employee exceeds 5000 The record of
3、 Finally, output in turn emp_no、from_date、salary_growth, And salary_growth In reverse order
SELECT s2.emp_no, s2.from_date, (s2.salary - s1.salary) AS salary_growth
FROM salaries AS s1, salaries AS s2
WHERE s1.emp_no = s2.emp_no
AND salary_growth > 5000
AND (strftime("%Y",s2.to_date) - strftime("%Y",s1.to_date) = 1
OR strftime("%Y",s2.from_date) - strftime("%Y",s1.from_date) = 1 )
ORDER BY salary_growth DESC
28. Find descriptions that contain robot The corresponding category name and number of films , It also needs the classification corresponding to
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS film (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
title varchar(255) NOT NULL,
description text,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id));
CREATE TABLE category (
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL ,
name varchar(25) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp,
PRIMARY KEY ( category_id ));
CREATE TABLE film_category (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL,
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp);
Find description information (film.description) Contained in the robot The category name corresponding to the movie (category.name) And the number of films (count(film.film_id)), And the number of films corresponding to this category (film_category.category_id)>=5 Ministry
Ideas :
The meaning of the title is to first include the description information “robot” The classification and quantity statistics of films , Then for each category ,
stay film_category The number of all films under this category in the summary table needs to be >=5, Finally, filter out the statistical results that meet the conditions .
Be careful , Count it out “robot” The number of movies is the same , And >=5 It doesn't matter. .
SELECT c.name AS name, COUNT(f.film_id) AS amount
FROM film AS f, film_category AS fc, category AS c,
(SELECT category_id FROM film_category GROUP BY category_id HAVING COUNT(category_id) >= 5) AS cc
WHERE f.description LIKE '%robot%'
AND f.film_id = fc.film_id
AND fc.category_id = c.category_id
AND c.category_id = cc.category_id
29. Use join Search to find movies without classification id And the name
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS film (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
title varchar(255) NOT NULL,
description text,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id));
CREATE TABLE category (
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL ,
name varchar(25) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp,
PRIMARY KEY ( category_id ));
CREATE TABLE film_category (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL,
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp);
Use join Search to find movies without classification id And the name
Ideas :
The idea of solving problems is to use LEFT JOIN Connect two meters , use IS NULL Statement qualifier :
1、 use LEFT JOIN Connect film and film_category, The limiting conditions are f.film_id = fc.film_id, Connect movies id And movie categories id, If the movie is not classified , Film classification id Show null
2、 Reuse WHERE To qualify fc.category_id IS NULL Pick out movies that don't fall into categories
SELECT f.film_id, f.title FROM film f LEFT JOIN film_category fc
ON f.film_id = fc.film_id WHERE fc.category_id IS NULL
30. Use a subquery to find out what belongs to Action All movies in the category correspond to title,description
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS film (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
title varchar(255) NOT NULL,
description text,
PRIMARY KEY (film_id));
CREATE TABLE category (
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL ,
name varchar(25) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp,
PRIMARY KEY ( category_id ));
CREATE TABLE film_category (
film_id smallint(5) NOT NULL,
category_id tinyint(3) NOT NULL,last_updatetimestamp);
You can use subqueries to find out which ones belong to Action All movies in the category correspond to title,description Do you
Ideas :
/* Subquery solution */
select f.title,f.description from film as f
where f.film_id in (select fc.film_id from film_category as fc
where fc.category_id in (select c.category_id from category as c
where c.name = 'Action'));
-- Non subquery solution :
select f.title,f.description
from film as f inner join film_category as fc on f.film_id = fc.film_id
inner join category as c on c.category_id = fc.category_id
where c.name = 'Action';
31. obtain select * from employees Corresponding execution plan
obtain select * from employees Corresponding execution plan
Ideas :
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees
32. take employees Table for all employees last_name and first_name Spliced together as Name
take employees Table for all employees last_name and first_name Spliced together as Name, Use a space in the middle to distinguish
( notes : The database system is sqllite, String concatenation as || Symbol , I won't support it concat function )
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Ideas :
Different database connection strings have different methods ,MySQL、SQL Server、Oracle Equal database support CONCAT Method ,
And this question uses SQLite The database only supports connection symbols "||" To connect strings
SELECT last_name||" "||first_name AS Name FROM employees
33. Create a actor surface , Include the following information
Create a actor surface , Include the following information ( notes : Get the system default time is datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’))
list type Is it NULL meaning
actor_id smallint(5) not null Primary key id
first_name varchar(45) not null name
last_name varchar(45) not null surname
last_update timestamp not null Last update time , The default is the current time of the system
Ideas :
According to the meaning , The key point of this question is actor_id The primary key settings of are the same as last_update Get the system time by default :
1、 stay actor_id Add... At the end of the field PRIMARY KEY Set this field as the primary key , Or add... To the last row of the table PRIMARY KEY(actor_id)
2、 stay last_update Add... At the end DEFAULT Is to set the default value for this field , And the default value is (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)),
That is, get the system time , Note that the outermost parentheses cannot be omitted
CREATE TABLE actor
(
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime('now','localtime')) -- ,
-- PRIMARY KEY(actor_id)
)
34. Bulk insert data
For tables actor Batch insert the following data ( Can not have 2 strip insert Sentences !)
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS actor (
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)))
actor_id first_name last_name last_update
1 PENELOPE GUINESS 2006-02-15 12:34:33
2 NICK WAHLBERG 2006-02-15 12:34:33
Ideas :
/* Method 1 : utilize VALUES(value1, value2, ...), (value1, value2, ...), ...(value1, value2, ...),*/
INSERT INTO actor
VALUES (1, 'PENELOPE', 'GUINESS', '2006-02-15 12:34:33'),
(2, 'NICK', 'WAHLBERG', '2006-02-15 12:34:33')
-- Method 2 : utilize UNION SELECT Batch insert
INSERT INTO actor
SELECT 1, 'PENELOPE', 'GUINESS', '2006-02-15 12:34:33'
UNION SELECT 2, 'NICK', 'WAHLBERG', '2006-02-15 12:34:33'
35. Bulk insert data , Don't use replace operation
For tables actor Batch insert the following data , If the data already exists , Please ignore ( Unsupported use replace operation )
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS actor (
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)))
actor_id first_name last_name last_update
‘3’ ‘ED’ ‘CHASE’ ‘2006-02-15 12:34:33’
Ideas :
-- stay SQLite in , use INSERT OR IGNORE To insert records , Or ignore insert and table UNIQUE Records with the same fields
INSERT OR IGNORE INTO actor VALUES (3, 'ED', 'CHASE', '2006-02-15 12:34:33')
-- use INSERT OR REPLACE To insert records , Or update the substitution and table UNIQUE Records with the same fields
INSERT OR REPLACE INTO actor VALUES (3, 'ED', 'CHASE', '2006-02-15 12:34:33')
36. Create a actor_name surface

Ideas :
According to the meaning , This question is to be completed in two sentences , First use CREATE TABLE Sentence creation actor_name surface , contain first_name And last_name Field ,
And then use INSERT INTO … SELECT … Statement to actor_name Table inserts data from another table
CREATE TABLE actor_name
(
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO actor_name SELECT first_name, last_name FROM actor;
37. Create a actor_name surface
For the following table actor Structure creation index :
( notes : stay SQLite in , In addition to renaming tables and adding columns to existing tables ,ALTER TABLE The command does not support other operations )
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS actor (
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)))
Yes first_name Create unique index uniq_idx_firstname, Yes last_name Create a normal index idx_lastname
Ideas :
-- Create unique index
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX uniq_idx_firstname on actor(first_name);
-- Create a normal index
CREATE INDEX idx_lastname on actor(last_name);
38. in the light of actor Tables create views actor_name_view
in the light of actor Tables create views actor_name_view, Contains only first_name as well as last_name Two , And rename the two columns ,first_name by first_name_v,last_name It is amended as follows last_name_v:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS actor (
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)))
Ideas :
CREATE VIEW actor_name_view (first_name_v, last_name_v) AS
SELECT first_name, last_name FROM actor
39. For the top salaries surface emp_no Field creation index idx_emp_no
in the light of salaries surface emp_no Field creation index idx_emp_no, Inquire about emp_no by 10005, Use force index .
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
create index idx_emp_no on salaries(emp_no);
Ideas :
-- MYSQL Forced index query usage in :FORCE INDEX(indexname);
-- SQLite Forced index query usage in :INDEXED BY indexname; Notice that the index has been created in the table
SELECT * FROM salaries INDEXED BY idx_emp_no WHERE emp_no = 10005
40. stay last_update A new column named create_date
There is actor surface , Include the following information :
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS actor (
actor_id smallint(5) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
first_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
last_update timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT (datetime(‘now’,‘localtime’)));
Now in last_update A new column named create_date, The type is datetime, NOT NULL, The default value is ’0000-00-00 00:00:00’
Ideas :
ALTER TABLE actor ADD COLUMN create_date datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00';
41. Construct a trigger audit_log
Construct a trigger audit_log, In the employees_test When inserting a piece of data into a table , Trigger to insert relevant data into audit in .
CREATE TABLE employees_test(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50),
SALARY REAL
);
CREATE TABLE audit(
EMP_no INT NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL
);
Ideas :
Pay attention to the following points when constructing triggers :
1、 use CREATE TRIGGER Statement constructs a trigger , use BEFORE or AFTER To specify... After execution SQL Before or after the statement TRIGGER
2、 The contents executed by the trigger are written out BEGIN And END Between
3、 have access to NEW And OLD Keyword access after or before triggering employees_test Form record
CREATE TRIGGER audit_log AFTER INSERT ON employees_test
BEGIN
INSERT INTO audit VALUES (NEW.ID, NEW.NAME);
END;
42. Delete emp_no Duplicate records , Keep only the smallest id Corresponding records .
Delete emp_no Duplicate records , Keep only the smallest id Corresponding records .
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS titles_test (
id int(11) not null primary key,
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
title varchar(50) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date DEFAULT NULL);
insert into titles_test values (‘1’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘2’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘3’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘4’, ‘10004’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘5’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘6’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘7’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’);
Ideas :
First use GROUP BY and MIN() Select each emp_no The smallest in the group id,
And then use DELETE FROM … WHERE … NOT IN … Statement delete “ Not every group is the smallest id All the corresponding records ”
DELETE FROM titles_test WHERE id NOT IN
(SELECT MIN(id) FROM titles_test GROUP BY emp_no)
43. Will all to_date by 9999-01-01 Update all of to NULL
Will all to_date by 9999-01-01 Update all of to NULL, And from_date Updated to 2001-01-01.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS titles_test (
id int(11) not null primary key,
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
title varchar(50) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date DEFAULT NULL);
insert into titles_test values (‘1’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘2’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘3’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘4’, ‘10004’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘5’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘6’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘7’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’);
Ideas :
update table1 set field1=value1, field2=value2 where Range
UPDATE titles_test SET to_date = NULL , from_date = '2001-01-01'
WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01';
44. take id=5 as well as emp_no=10001 Replace the row data with id=5 as well as emp_no=10005
take id=5 as well as emp_no=10001 Replace the row data with id=5 as well as emp_no=10005, Other data remain unchanged , Use replace Realization .
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS titles_test (
id int(11) not null primary key,
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
title varchar(50) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date DEFAULT NULL);
insert into titles_test values (‘1’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘2’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘3’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘4’, ‘10004’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘5’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘6’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘7’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’);
Ideas :
Use replace The two methods , If used directly REPLACE INTO Words , You need to re insert a complete new record ,sql Will automatically replace id The same record ;
You can also use UPDATE combination ,REPLACE(colname,oldval,newval) To assign to colnamejik
UPDATE titles_test SET emp_no = REPLACE(emp_no,10001,10005) WHERE id = 5
45. take titles_test Change the table name to titles_2017
take titles_test Change the table name to titles_2017.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS titles_test (
id int(11) not null primary key,
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
title varchar(50) NOT NULL,
from_date date NOT NULL,
to_date date DEFAULT NULL);
insert into titles_test values (‘1’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘2’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘3’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘4’, ‘10004’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘5’, ‘10001’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1986-06-26’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘6’, ‘10002’, ‘Staff’, ‘1996-08-03’, ‘9999-01-01’),
(‘7’, ‘10003’, ‘Senior Engineer’, ‘1995-12-03’, ‘9999-01-01’);
Ideas :
ALTER TABLE titles_test RENAME TO titles_2017
46. stay audit Create a foreign key constraint on the table , Its emp_no Corresponding employees_test Primary Key id
stay audit Create a foreign key constraint on the table , Its emp_no Corresponding employees_test Primary Key id.
(audit Created , It needs to be done first drop)
CREATE TABLE employees_test(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50),
SALARY REAL
);
CREATE TABLE audit(
EMP_no INT NOT NULL,
create_date datetime NOT NULL
);
Ideas :
A primary key is the unique identifier of a relationship , For example, the student relationship table ( Student number , full name , Is don't ), take ‘ Student number ’ Defined as primary key , Because a student ID can only correspond to one student ,‘ Student number ’ You can uniquely identify this relationship table .
A foreign key means that an attribute is not a primary key in the current relational table , This attribute is the primary key of another table . And through foreign keys, you can bai Link the two tables . For example, the student relationship table above ,‘ Is don't du’ Not the primary key. ,
And if there is such a relational table ( Is don't , The dean of the Department ), ad locum ‘ Is don't ’ It's the primary key , It can uniquely identify this table , We can say ‘ Is don't ’ It is the foreign key of the student relationship table . And in the database zhi If you want to inquire the name of the dean of a student's Department ,
Through foreign keys ‘ Is don't ’ Put two dao You can establish a relationship query between tables .
DROP TABLE audit;
CREATE TABLE audit(
EMP_no INT NOT NULL,
create_date datetime NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY(EMP_no) REFERENCES employees_test(ID));
47. How to get emp_v and employees There's the same data no
There are the following views :
create view emp_v as select * from employees where emp_no >10005;
How to get emp_v and employees There's the same data ?
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Ideas :
Because of the view emp_v The record of is from employees The , Therefore, it is necessary to judge the equal data between the two , Just judge emp_no Equal is enough
Method 1 : use WHERE Select both emp_no Equal records */
SELECT em.* FROM employees AS em, emp_v AS ev WHERE em.emp_no = ev.emp_no
-- Method 2 : use INTERSECT Keyword search employees and emp_v Intersection
SELECT * FROM employees INTERSECT SELECT * FROM emp_v
-- Method 3 : Think carefully ,emp_v All records of are made by employees export , Therefore, you can take opportunistic measures , Direct output emp_v All records
SELECT * FROM emp_v
48. Increase the current salary of all employees who receive bonuses 10%
Increase the current salary of all employees who receive bonuses 10%.
create table emp_bonus(
emp_no int not null,
recevied datetime not null,
btype smallint not null);
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Ideas :
First select the one that meets the conditions emp_no, The box INNER JOIN Connect salaries and emp_bonus,
And use s.to_date = ‘9999-01-01’ Indicates current salary , And then use UPDATE … SET … WHERE … IN … Statement to update the data in the table .
UPDATE salaries SET salary = salary * 1.1 WHERE emp_no IN
(SELECT s.emp_no FROM salaries AS s INNER JOIN emp_bonus AS eb
ON s.emp_no = eb.emp_no AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01')
49. Generate... For all tables in the library select count(*) Corresponding SQL sentence
Generate... For all tables in the library select count(*) Corresponding SQL sentence , If there are the following tables in the database ,
employees
departments
dept_emp
dept_manage
salaries
titles
emp_bonus
Then it will output the following image :
Output description :
Ideas :
There are two key points in this question :
1、 stay SQLite The system tables sqlite_master The indexes of all tables can be obtained in , Which field name Is the name of all the tables , And for the tables you create ,
Field type Forever ‘table’,
2、 stay SQLite of use “||” Symbolic connection string
SELECT "select count(*) from " || name || ";" AS cnts
FROM sqlite_master WHERE type = 'table'
50. take employees All employees in the table have last_name and first_name adopt (’) Connect .
take employees All employees in the table have last_name and first_name adopt (’) Connect .( I won't support it concat, Please use || Realization )
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
SELECT last_name || "'" || first_name FROM employees
51. obtain Employees Medium first_name
obtain Employees Medium first_name, Query according to first_name The last two letters , Arrange in ascending order
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
SELECT first_name FROM employees ORDER BY substr(first_name,length(first_name)-1,2);
52. according to dept_no To summarize
according to dept_no To summarize , Belonging to the same department emp_no Connect by comma , The results show that dept_no And the connected results employees
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
This question will use SQLite Aggregate function of group_concat(X,Y), among X Is the field to be connected ,Y Is the symbol used for connection , Omission , Default to comma .
This function must be associated with GROUP BY In combination with .
SELECT dept_no, group_concat(emp_no) AS employees
FROM dept_emp GROUP BY dept_no
53. Find and exclude the current maximum 、 Minimum salary The average salary of employees after avg_salary
Find and exclude the maximum 、 Minimum salary After the current (to_date = ‘9999-01-01’ ) Average salary of employees avg_salary.
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Ideas :
SELECT AVG(salary) AS avg_salary FROM salaries
WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01'
AND salary NOT IN (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM salaries WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01')
AND salary NOT IN (SELECT MIN(salary) FROM salaries WHERE to_date = '9999-01-01')
54. Paging query employees surface , Every time 5 Line one page , Back to page 2 Pages of data
Paging query employees surface , Every time 5 Line one page , Back to page 2 Pages of data
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Ideas :
According to the meaning , Each row 5 page , Back to page 2 Pages of data , That is, return to the second page 6~10 Bar record , There are two ways to solve :
/* Method 1 : utilize LIMIT and OFFSET keyword .LIMIT The following number represents the number of records returned , OFFSET The number after represents the number of records from which to return ( The serial number of the first record is 0), It can also be understood as how many records to skip and start to return . */
SELECT * FROM employees LIMIT 5 OFFSET 5
-- Method 2 : Using only LIMIT keyword . Be careful : stay LIMIT X,Y in ,Y The representative returns several records ,X The representative returns from the record ( The serial number of the first record is 0)
SELECT * FROM employees LIMIT 5,5
55. Get the of all employees emp_no
Get the of all employees emp_no、 Department number dept_no And corresponding bonus type btype and recevied, If no specific employee is assigned, it will not be displayed
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemp_bonus(
emp_no int(11) NOT NULL,
recevied datetime NOT NULL,
btype smallint(5) NOT NULL);
CREATE TABLEdept_manager(dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
The precise thinking of this topic is , First the employees And dept_emp use INNER JOIN Connect , Select the employees assigned to the Department ,
Reuse LEFT JOIN Connect emp_bonus( You can see this table in the previous question ), Employees who have been allocated bonuses display the type of bonuses and the time of Award , Employees who have not been allocated bonus will not display .
SELECT em.emp_no, de.dept_no, eb.btype, eb.recevied
FROM employees AS em INNER JOIN dept_emp AS de
ON em.emp_no=de.emp_no
LEFT JOIN emp_bonus AS eb
ON de.emp_no=eb.emp_no
56. Use keywords exists Find all information about employees who are not assigned a specific department .
Use keywords exists Find all information about employees who are not assigned a specific department .
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
Ideas :
This topic uses EXISTS The keyword method is as follows : It means in employees Pick out the order
(SELECT emp_no FROM dept_emp WHERE emp_no = employees.emp_no) Unfounded records
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE NOT EXISTS
(SELECT emp_no FROM dept_emp WHERE emp_no = employees.emp_no)
57. obtain employees Row data in , And these lines also exist in emp_v in
There are the following views :
create view emp_v as select * from employees where emp_no >10005;
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
obtain employees Row data in , And these lines also exist in emp_v in . Be careful not to use intersect keyword .
Output description :
Ideas :
-- Method 1 : use WHERE Select both emp_no Equal records
SELECT em.* FROM employees AS em, emp_v AS ev WHERE em.emp_no = ev.emp_no
-- Method 2 : because emp_v All records of are made by employees export , Therefore, you can take opportunistic measures , Direct output emp_v All records
SELECT * FROM emp_v
58. Get information about employees with bonuses .
Get information about employees with bonuses .
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
CREATE TABLEdept_emp(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,dept_nochar(4) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,dept_no));
create table emp_bonus(
emp_no int not null,
recevied datetime not null,
btype smallint not null);
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
give emp_no、first_name、last_name、 Bonus type btype、 Corresponding current salary salary And the amount of bonus bonus. bonus type btype by 1 The bonus is salary salary Of 10%,btype by 2 The bonus is... Of the salary 20%, Other types are salary 30%. Current salary means to_date=‘9999-01-01’
Output description :
Ideas :
This question mainly examines SQLite in CASE Expression usage . When btype = 1 when , obtain salary X0.1; When btype = 2 when , obtain salary X 0.2; Other situations have been salary X0.3.
SELECT e.emp_no, e.first_name, e.last_name, b.btype, s.salary,
(CASE b.btype
WHEN 1 THEN s.salary * 0.1
WHEN 2 THEN s.salary * 0.2
ELSE s.salary * 0.3 END) AS bonus
FROM employees AS e INNER JOIN emp_bonus AS b ON e.emp_no = b.emp_no
INNER JOIN salaries AS s ON e.emp_no = s.emp_no AND s.to_date = '9999-01-01'
59. Statistics salary The cumulative sum of running_total
according to salary The cumulative sum of running_total, among running_total For the former N A current ( to_date = ‘9999-01-01’) Staff salary Cumulative sum , And so on . The results are as follows Demo Exhibition ..
CREATE TABLEsalaries(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,salaryint(11) NOT NULL,from_datedate NOT NULL,to_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no,from_date));
Output description :
Ideas :
The idea of this question is to reuse salaries Table for sub query , Finally s1.emp_no Sort output summation results .
1、 The third field of the output , Is written by a SELECT Subqueries make up . Reuse in subquery salaries Record as s2, Of the main query salaries Record as s1, When the main query s1.emp_no When it's certain , No greater than in subquery s1.emp_no Of s2.emp_no Sum the corresponding salary
2、 Pay attention to the sum of employees' current salary , Therefore, qualification conditions should be added to both the main query and the sub query to_date = ‘9999-01-01’
SELECT s1.emp_no, s1.salary,
(SELECT SUM(s2.salary) FROM salaries AS s2
WHERE s2.emp_no <= s1.emp_no AND s2.to_date = '9999-01-01') AS running_total
FROM salaries AS s1 WHERE s1.to_date = '9999-01-01'
60. about employees In the table , For an odd number of lines first_name
about employees In the table , For an odd number of lines first_name
CREATE TABLEemployees(emp_noint(11) NOT NULL,birth_datedate NOT NULL,first_namevarchar(14) NOT NULL,last_namevarchar(16) NOT NULL,genderchar(1) NOT NULL,hire_datedate NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (emp_no));
Output description :
Ideas :
【 about employees surface , In the face of first_name After ranking , Select the... Corresponding to the odd ranking first_name】.
1、 This question uses three levels SELECT Inquire about , For the sake of understanding , Layer by indent , And the outermost layer corresponds to e1, The innermost layer corresponds to e3;
2、 stay e3 Layer , use COUNT() Function pair e2.first_name Rank and label , That is, given e2.first_name Under the circumstances ,
No more than e2.first_name Of e3.first_name What's the number of , This number coincides with e2.first_name The ranking labels match ,
And name the value rowid;
3、 stay e1 Layer , Directly under the limiting conditions e1.rowid % 2 = 1 Next , Representing odd rows rowid, Choose the corresponding e1.first_name;
4、e2 Layer is equivalent to connecting e1 layer ( Select the presentation layer ) And e3 layer ( Label layer ) The bridge .
There is no ranking after the ranking label
SELECT e1.first_name FROM
(SELECT e2.first_name,
(SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees AS e3
WHERE e3.first_name <= e2.first_name)
AS rowid FROM employees AS e2) AS e1
WHERE e1.rowid % 2 = 1
61. Find string ’10,A,B’ Middle comma ’,' Number of occurrences cnt
Find string ’10,A,B’ Middle comma ’,' Number of occurrences cnt.
Ideas :
because SQLite There is no function to directly count the occurrence times of substrings in a string , Therefore, this topic uses length() Function and replace() The combination of functions
It flexibly solves the problem of counting the occurrence times of substrings , It belongs to skill problem , Use first replace Function to replace the substring in the original string with an empty string ,
Then the length of the replaced string is subtracted from the length of the original string , Finally, divide by the length of the substring ( This step in this question can be omitted , If the substring length is greater than 1 It cannot be saved )
SELECT (length("10,A,B")-length(replace("10,A,B",",","")))/length(",") AS cnt
62. The little red book searches by situation
There is an order transaction table orders:
There is a collection transaction table favorites:
Please use one sentence SQL Take out the behavioral characteristics of all users on the product , Features are divided into purchased 、 Buy not collected 、 Collection not purchased 、 Collect and buy ( The output results are shown in the following table )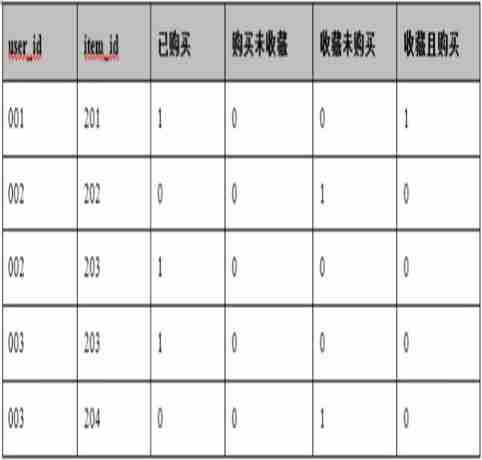
** Ideas :** Join two tables first id And get the table again a, Then connect to the left in turn b,c, Judge according to whether it is empty
SELECT
a.user_id,a.item_id,
if(b.user_id is not null,1,0) Have purchased ,
if(b.user_id is not null and c.user_id is null,1,0) Buy not collected ,
if(b.user_id is null and c.user_id is not null,1,0) Collection not purchased ,
if(b.user_id is not null and c.user_id is not null,1,0) Collect and buy
FROM
( SELECT user_id,item_id FROM orders UNION SELECT user_id,item_id FROM favorites ) as a
LEFT JOIN orders as b ON a.user_id = b.user_id AND a.item_id=b.item_id
LEFT JOIN favorites as c ON a.user_id = c.user_id AND a.item_id = c.item_id
63. Dissection
- Split a column of long strings
General term : Beautiful Jiayuan 3 building 2 unit 201 room
SELECT id, house_no as ' General term ',
SUBSTR(house_no, 1, 4) AS ' Community name ',
SUBSTR(house_no, 5, 3) AS ' Building ',
SUBSTR(house_no, -7,3) AS ' unit ',
SUBSTRING(house_no,-4) AS ' Your room number, '
FROM aa;
- Intercept the contents of large fields

#get_json_object( Large field ,' The title of the content to be intercepted ')
select
user_id,
get_json_object(user_info, '$.gender') as gender,
get_json_object(user_info, '$.city') as city,
get_json_object(user_info, '$.year_old') as year_old
from table
边栏推荐
- 使用Batch设置IP地址
- Reading the registry using batch
- More than 20 cloud collaboration functions, 3 minutes to talk through the enterprise's data security experience
- Wechat applet text built-in component newline character does not newline reason
- Get the value of program exit
- 使用Batch管理VHD
- [元数据]LinkedIn-DataHub
- Getting started with kotlin
- [project - what are the supporting materials in the annexes? (18 kinds of 2000 word summary)] project plan of innovation and entrepreneurship competition and supporting materials of Challenge Cup entr
- GAMES101作业7-Path Tracing实现过程&代码详细解读
猜你喜欢

If the MAC fails to connect with MySQL, it will start and report an error

智能门锁为什么会这么火,米家和智汀的智能门锁怎么样呢?

NDK learning notes (14) create an avi video player using avilib+window

袋鼠雲數棧基於CBO在Spark SQL優化上的探索

20多种云协作功能,3分钟聊透企业的数据安全经

Why is the smart door lock so popular? What about the smart door locks of MI family and zhiting?

初步了解多任务学习

“All in ONE”一个平台解决所有需求,运维监控3.0时代已来

Recherche sur l'optimisation de Spark SQL basée sur CBO pour kangourou Cloud Stack
NFC Development -- the method of using NFC mobile phones as access control cards (II)
随机推荐
NDK learning notes (VII) system configuration, users and groups
安装Oracle数据库
1. use alicloud object OSS (basic)
Big meal count (time complexity) -- leetcode daily question
Yoyov5's tricks | [trick8] image sampling strategy -- Sampling by the weight of each category of the dataset
Customize the layout of view Foundation
Get the full link address of the current project request URL
数据接入平台方案实现(游族网络)
那个酷爱写代码的少年后来怎么样了——走近华为云“瑶光少年”
Wechat applet, automatic line feed for purchasing commodity attributes, fixed number of divs, automatic line feed for excess parts
微信自定义组件---样式--插槽
What is a thread pool?
Wechat applet learning record
Further efficient identification of memory leakage based on memory optimization tool leakcanary and bytecode instrumentation technology
微信小程序text内置组件换行符不换行的原因-wxs处理换行符,正则加段首空格
getBackgroundAudioManager控制音乐播放(类名的动态绑定)
Redis setup (sentinel mode)
【深入kotlin】 - 初识 Flow
【深入kotlin】 - Flow 进阶
Combing route - Compaction Technology




