当前位置:网站首页>Embedded system driver primary [4] - under the basis of character device driver _ concurrency control
Embedded system driver primary [4] - under the basis of character device driver _ concurrency control
2022-08-04 05:35:00 【imysy_22_】
In order to achieve multiple processes using our character device at the same time,我们引入“并发控制”这一概念.
一、上下文和并发场合
执行流:有开始有结束总体顺序执行的一段代码 context
应用编程:任务上下文
内核编程:
1. 任务上下文:五状态 可阻塞
a. 应用进程或线程运行在用户空间
b. 应用进程或线程运行在内核空间(通过调用syscall来间接使用内核空间)
c. 内核线程始终在内核空间
2. 异常上下文:不可阻塞
中断上下文
竞态:多任务并行执行时,If the same resource is operated at the same time,会引起资源的错乱,这种错乱情形被称为竞态
共享资源:可能会被多个任务同时使用的资源
临界区:操作共享资源的代码段
为了解决竞态,需要提供一种控制机制,来避免在同一时刻使用共享资源,This mechanism is called a concurrency control mechanism
并发控制机制分类:
1. 原子操作类
2. 忙等待类
3. 阻塞类
通用并发控制机制的一般使用套路:
/*互斥问题:*/
并发控制机制初始化为可用
P操作
临界区
V操作
/*同步问题:*/
//并发控制机制初始化为不可用
//先行方:
.....
V操作
//后行方:
P操作
.....
二、中断屏蔽(了解)
一种同步机制的辅助手段
禁止本cpu中断 使能本cpu中断
local_irq_disable(); local_irq_enable();
local_irq_save(flags); local_irq_restore(flags); 与cpu的中断位相关
local_bh_disable(); local_bh_enable(); 与中断低半部有关,关闭、打开软中断
禁止中断
临界区 //临界区代码不能占用太长时间,需要很快完成
打开中断
适用场合:中断上下文与某任务共享资源时,或多个不同优先级的中断上下文间共享资源时
三、原子变量(掌握)
原子变量:存取不可被打断的特殊整型变量
a.设置原子量的值
void atomic_set(atomic_t *v,int i); //设置原子量的值为i
atomic_t v = ATOMIC_INIT(0); //定义原子变量v并初始化为0
v = 10;//错误
b.获取原子量的值
atomic_read(atomic_t *v); //返回原子量的值
c.原子变量加减
void atomic_add(int i,atomic_t *v);//原子变量增加i
void atomic_sub(int i,atomic_t *v);//原子变量减少i
d.原子变量自增自减
void atomic_inc(atomic_t *v);//原子变量增加1
void atomic_dec(atomic_t *v);//原子变量减少1
e.操作并测试:运算后结果为0则返回真,否则返回假
int atomic_inc_and_test(atomic_t *v);
int atomic_dec_and_test(atomic_t *v);
int atomic_sub_and_test(int i,atomic_t *v);
原子位操作方法:
a.设置位
void set_bit(nr, void *addr); //设置addr的第nr位为1
b.清除位
void clear_bit(nr , void *addr); //清除addr的第nr位为0
c.改变位
void change_bit(nr , void *addr); //改变addr的第nr位为1
d.测试位
void test_bit(nr , void *addr); //测试addr的第nr位是否为1
适用场合:共享资源为单个整型变量的互斥场合
示例代码:atomic.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/atomic.h>
struct openonce_dev {
struct cdev mydev;
atomic_t open_flag;
};
int major = 11;
int minor = 0;
int num = 1;
struct openonce_dev gmydev;
int myopen (struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)
{
struct openonce_dev *pgmydev = NULL;
pfile->private_data = (void *)container_of(pnode->i_cdev,struct openonce_dev,mydev);
pgmydev = (struct openonce_dev *)pfile->private_data;
if(atomic_dec_and_test(&pgmydev->open_flag))
{
return 0;
}
else
{
atomic_inc(&pgmydev->open_flag);
printk("The device is open already\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int myclose (struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)
{
struct openonce_dev *pgmydev = (struct openonce_dev *)pfile->private_data;
atomic_set(&gmydev.open_flag,1);
return 0;
}
struct file_operations myops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = myopen,
.release = myclose,
};
int __init atomic_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
dev_t devno = MKDEV(major,minor);
ret = register_chrdev_region(devno,num,"openonce");
if(ret)
{
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno,minor,num,"openonce");
if(ret)
{
printk("devno failed.\n");
return -1;
}
major = MAJOR(devno);
minor = MINOR(devno);
}
/*给mydev指定操作函数集*/
cdev_init(&gmydev.mydev,&myops);
/*将mydev添加到内核对应的数据结构里*/
gmydev.mydev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_add(&gmydev.mydev,devno,num);
atomic_set(&gmydev.open_flag,1);
return 0;
}
void __exit atomic_exit(void)
{
dev_t devno = MKDEV(major,minor);
cdev_del(&gmydev.mydev);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, num);
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("imysy_22");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("This is a script explained by the author who's name is imysy_22.");
MODULE_ALIAS("HI");
module_init(atomic_init);
module_exit(atomic_exit);
openonce_app.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("The argument is too few.\n");
return -1;
}
int fd = -1;
fd = open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open failed\n");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
}
close(fd);
fd = -1;
return 0;
}
Makefile:
ifeq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
ifeq ($(ARCH),arm)
KERNELDIR ?= /home/linux/fs4412/linux-3.14
ROOTFS ?= /opt/4412/rootfs
else
KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
endif
PWD := $(shell pwd)
modules:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
modules_install:
$(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules INSTALL_MOD_PATH=$(ROOTFS) modules_install
clean:
rm -rf *.o *.ko .*.cmd *.mod.* modules.order Module.symvers .tmp_versions
else
obj-m += atomic.o
endif
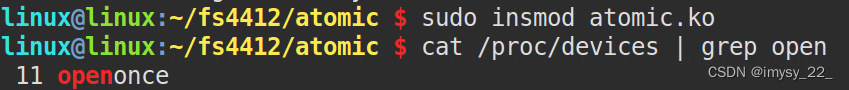
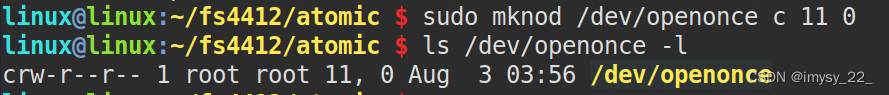
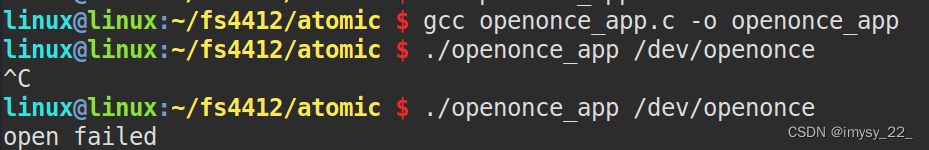
There is only one application at a timeappThis driver can be opened.
四、自旋锁:基于忙等待的并发控制机制
a.定义自旋锁
spinlock_t lock;
b.初始化自旋锁
spin_lock_init(spinlock_t *);
c.获得自旋锁
spin_lock(spinlock_t *); //成功获得自旋锁立即返回,否则自旋在那里直到该自旋锁的保持者释放
spin_trylock(spinlock_t *); //成功获得自旋锁立即返回真,否则返回假,而不是像上一个那样"在原地打转”
d.释放自旋锁
spin_unlock(spinlock_t *);
```
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
定义spinlock_t类型的变量lock
spin_lock_init(&lock)后才能正常使用spinlock
spin_lock(&lock);
临界区
spin_unlock(&lock);
```
适用场合:
1. 异常上下文之间或异常上下文与任务上下文之间共享资源时
2. 任务上下文之间且临界区执行时间很短时
3. 互斥问题
示例代码:spinlock.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/spinlock.h>
struct openonce_dev {
struct cdev mydev;
int open_flag;
spinlock_t lock;
};
int major = 11;
int minor = 0;
int num = 1;
struct openonce_dev gmydev;
int myopen (struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)
{
struct openonce_dev *pgmydev = NULL;
pfile->private_data = (void *)container_of(pnode->i_cdev,struct openonce_dev,mydev);
pgmydev = (struct openonce_dev *)pfile->private_data;
spin_lock(&pgmydev->lock);
if(pgmydev->open_flag)
{
spin_unlock(&pgmydev->lock);
pgmydev->open_flag = 0;
return 0;
}
else
{
spin_unlock(&pgmydev->lock);
printk("The device is open already\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int myclose (struct inode *pnode, struct file *pfile)
{
struct openonce_dev *pgmydev = (struct openonce_dev *)pfile->private_data;
spin_lock(&pgmydev->lock);
pgmydev->open_flag = 1;
spin_unlock(&pgmydev->lock);
return 0;
}
struct file_operations myops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = myopen,
.release = myclose,
};
int __init spinlock_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
dev_t devno = MKDEV(major,minor);
ret = register_chrdev_region(devno,num,"openonce");
if(ret)
{
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno,minor,num,"openonce");
if(ret)
{
printk("devno failed.\n");
return -1;
}
major = MAJOR(devno);
minor = MINOR(devno);
}
/*给mydev指定操作函数集*/
cdev_init(&gmydev.mydev,&myops);
/*将mydev添加到内核对应的数据结构里*/
gmydev.mydev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_add(&gmydev.mydev,devno,num);
gmydev.open_flag = 1;
spin_lock_init(&gmydev.lock);
return 0;
}
void __exit spinlock_exit(void)
{
dev_t devno = MKDEV(major,minor);
cdev_del(&gmydev.mydev);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, num);
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("imysy_22");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("This is a script explained by the author who's name is imysy_22.");
MODULE_ALIAS("HI");
module_init(spinlock_init);
module_exit(spinlock_exit);
Others are exactly the same as atomic variables
五、信号量:基于阻塞的并发控制机制
a.定义信号量
struct semaphore sem;
b.初始化信号量
void sema_init(struct semaphore *sem, int val);
c.获得信号量P
int down(struct semaphore *sem);//深度睡眠
int down_interruptible(struct semaphore *sem);//浅度睡眠
d.释放信号量V
void up(struct semaphore *sem);
```
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
```
适用场合:任务上下文之间且临界区执行时间较长时的互斥或同步问题
六、互斥锁:基于阻塞的互斥机制
a.初始化
struct mutex my_mutex;
mutex_init(&my_mutex);
b.获取互斥体
void mutex_lock(struct mutex *lock);
c.释放互斥体
void mutex_unlock(struct mutex *lock);
1. 定义对应类型的变量
2. 初始化对应变量
P/加锁
临界区
V/解锁
```
#include <linux/mutex.h>
```
适用场合:任务上下文之间且临界区执行时间较长时的互斥问题
七、选择并发控制机制的原则
1. Contexts that do not allow sleep require a busy-wait class,A sleepable context can take a blocking class.Competing resources accessed in an exception context must use the busy-wait class.
2. The blocking class is recommended for applications with long critical section operations,It is recommended to use the busy-wait class for operations with very short critical sections.
3. 中断屏蔽仅在有与中断上下文共享资源时使用.
4. Use atomic variables when the shared resource is just a simple integer
边栏推荐
- Teenage Achievement Hackers Need These Skills
- Resolved error: npm WARN config global `--global`, `--local` are deprecated
- Write golang simple C2 remote control based on gRPC
- How to view sql execution plan offline collection
- Get the selected content of the radio box
- 动态规划总括
- word 公式编辑器 键入技巧 | 写数学作业必备速查表
- 8.03 Day34---BaseMapper查询语句用法
- The string class introduction
- Unity Visual Effect Graph入门与实践
猜你喜欢
8.03 Day34---BaseMapper query statement usage
![[Cloud Native--Kubernetes] Pod Resource Management and Probe Detection](/img/1a/b3bdf9b62c82b0fc4d913045981d94.png)
[Cloud Native--Kubernetes] Pod Resource Management and Probe Detection

败给“MySQL”的第60天,我重振旗鼓,四面拿下蚂蚁金服offer
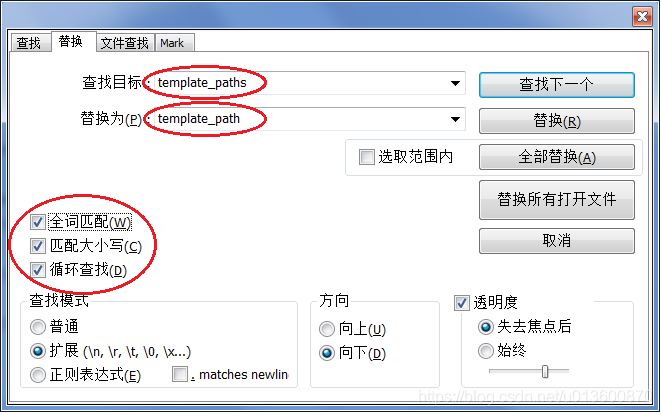
解决安装nbextensions后使用Jupyter Notebook时出现template_paths相关错误的问题

触觉智能分享-SSD20X实现升级显示进度条
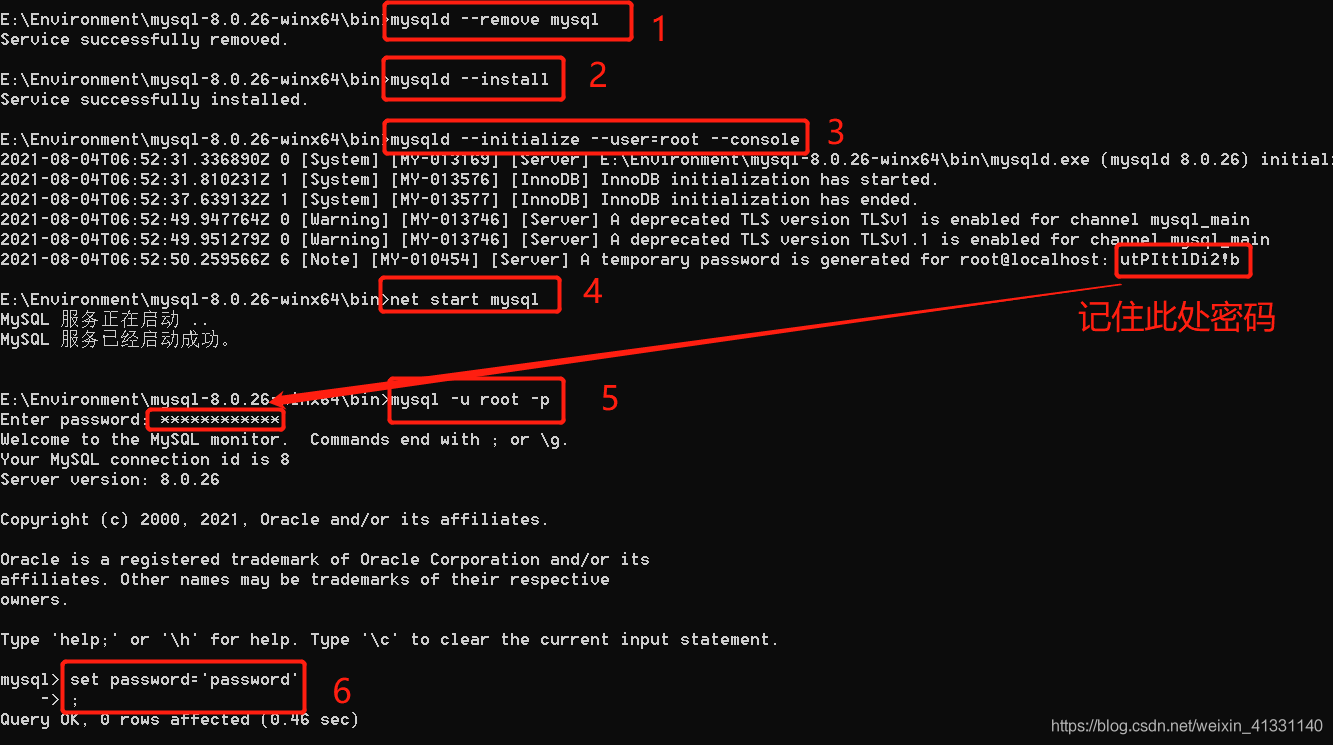
Can 't connect to MySQL server on' localhost3306 '(10061) simple solutions
FPGA学习笔记——知识点总结

应届生软件测试薪资大概多少?
![[Evaluation model] Topsis method (pros and cons distance method)](/img/e7/c24241faced567f3e93f6ff3f20074.png)
[Evaluation model] Topsis method (pros and cons distance method)

嵌入式系统驱动初级【4】——字符设备驱动基础下_并发控制
随机推荐
MySql数据恢复方法个人总结
【JS】js给对象动态添加、设置、删除属性名和属性值
力扣:343. 整数拆分
JS basics - forced type conversion (error-prone, self-use)
Shocked, 99.9% of the students didn't really understand the immutability of strings
力扣:509. 斐波那契数
利用Jenkins实现Unity自动化构建
自动化测试的成本高效果差,那么自动化测试的意义在哪呢?
4.3 基于注解的声明式事务和基于XML的声明式事务
warning C4251: “std::vector&lt;_Ty&gt;”需要有 dll 接口由 class“Test”的客户端使用错误
MySQL日志篇,MySQL日志之binlog日志,binlog日志详解
7.16 Day22---MYSQL (Dao mode encapsulates JDBC)
[Evaluation model] Topsis method (pros and cons distance method)
应届生软件测试薪资大概多少?
C Expert Programming Chapter 4 The Shocking Fact: Arrays and Pointers Are Not the Same 4.5 Other Differences Between Arrays and Pointers
C Expert Programming Chapter 4 The Shocking Fact: Arrays and pointers are not the same 4.4 Matching declarations to definitions
谷粒商城-基础篇(项目简介&项目搭建)
你以为border-radius只是圆角吗?【各种角度】
Unity Visual Effect Graph入门与实践
TensorRTx-YOLOv5工程解读(二)