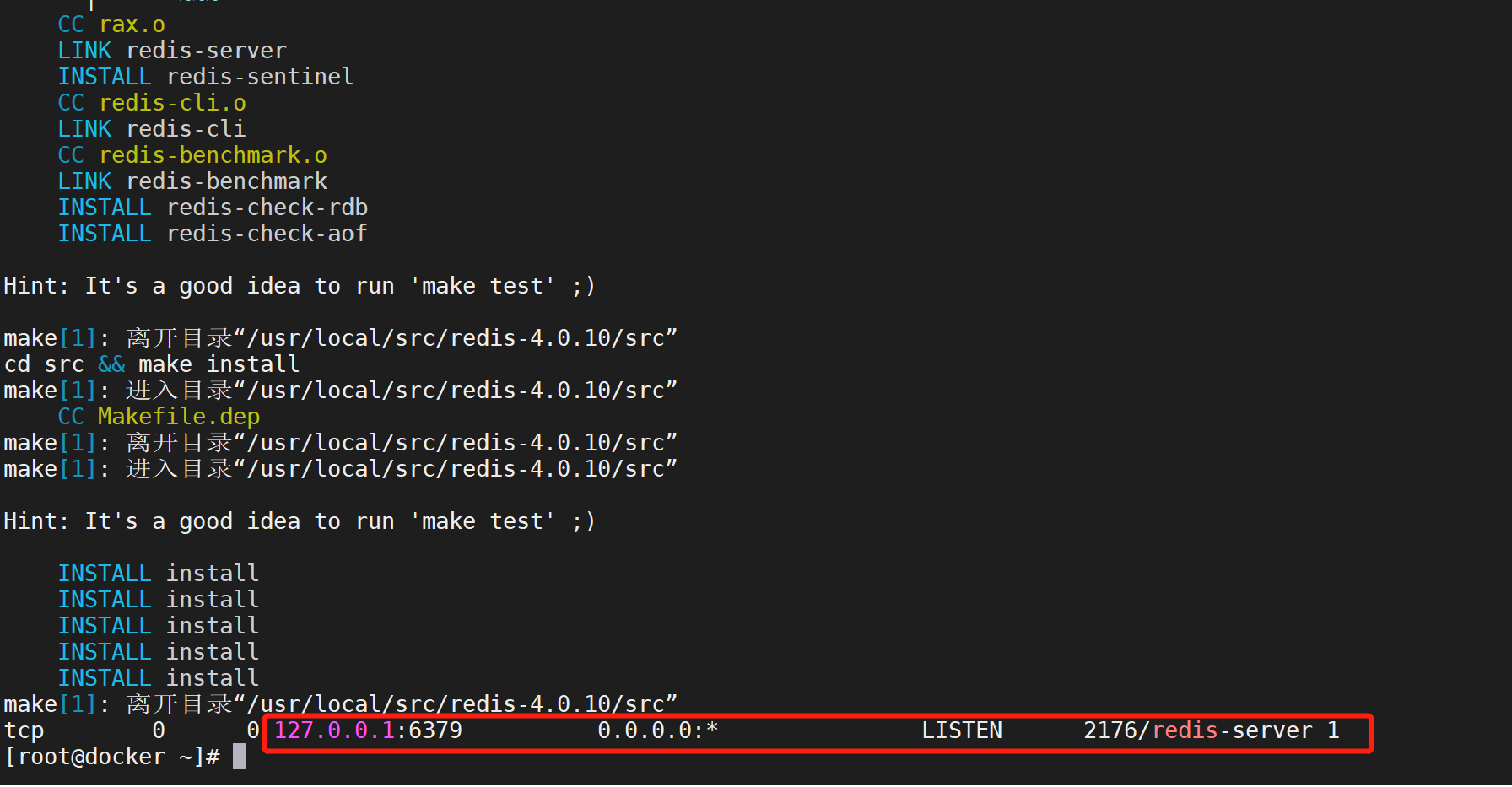
当前位置:网站首页>Network principle (1) - overview of basic principles
Network principle (1) - overview of basic principles
2022-07-07 20:17:00 【Skinny monkey 117】
Catalog
This paper briefly introduces network communication from the perspective of hardware
Network principle
The network in the eyes of application developers : Cross host 、 Communication between two processes .
The background and history of the emergence of the network : Communication discipline
Country -> Institutions / organization -> family -> personal
Overview of basic principles
This paper briefly introduces network communication from the perspective of hardware
The data is on the transmission medium ( Ethernet cable ) Spread on ( There may be signal decay 、 Signal error and other problems ), Incoming receiver .
thus , Only one network medium can be used to connect the two hosts , Data exchange can be realized from the perspective of hardware .
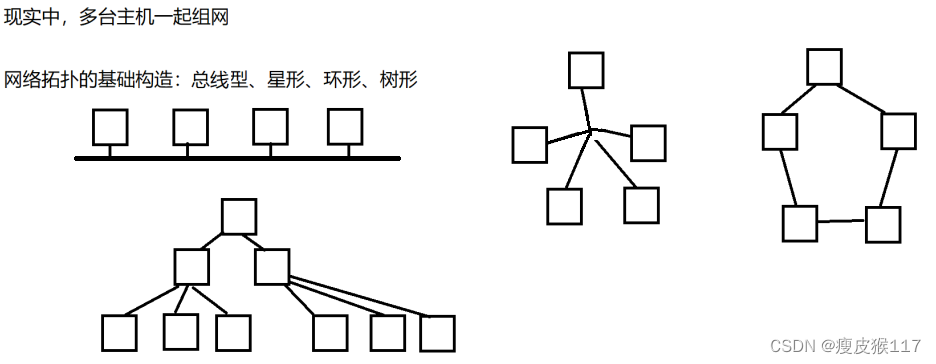
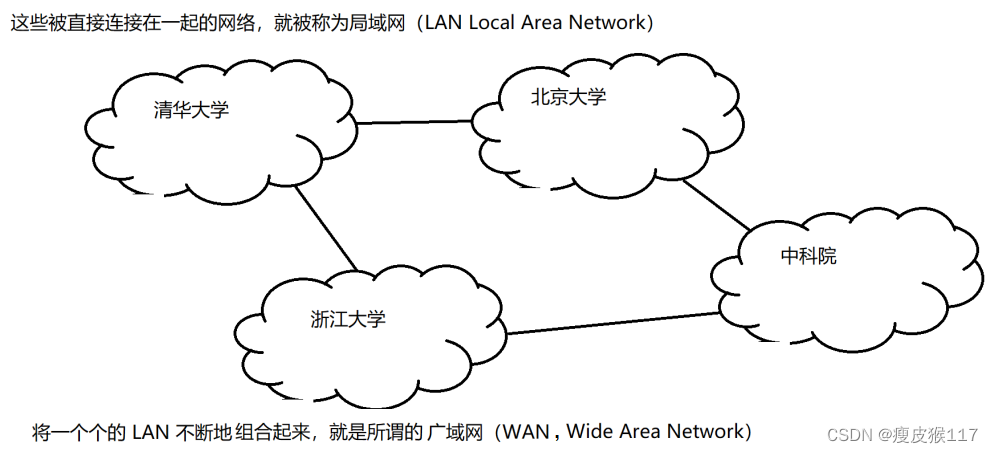
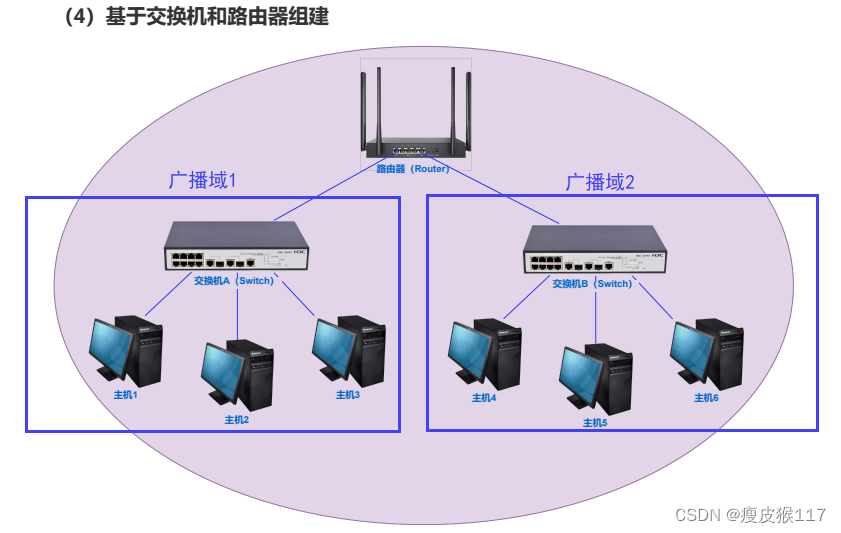
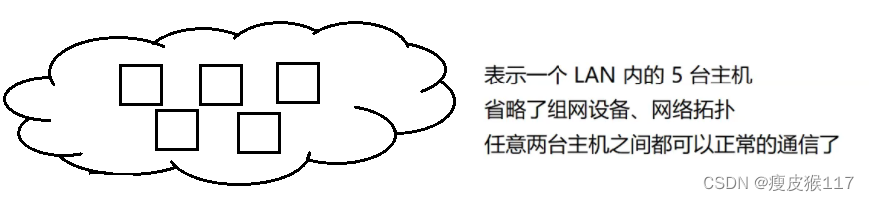
Networking of multiple hosts
Protocol and layering
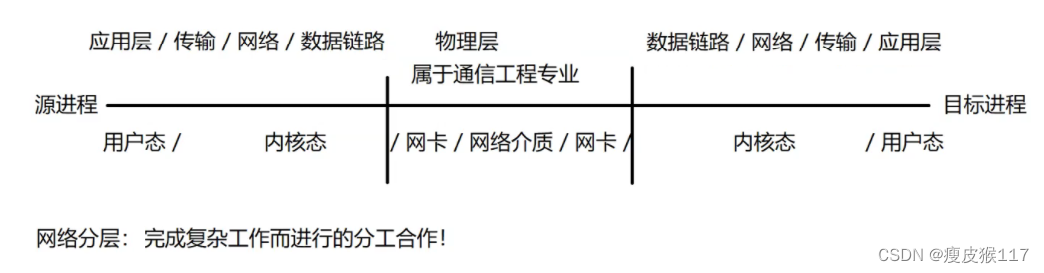
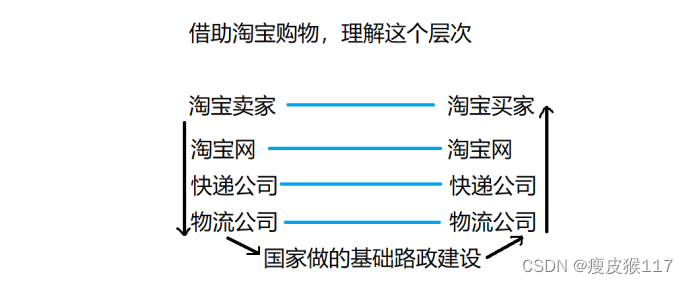
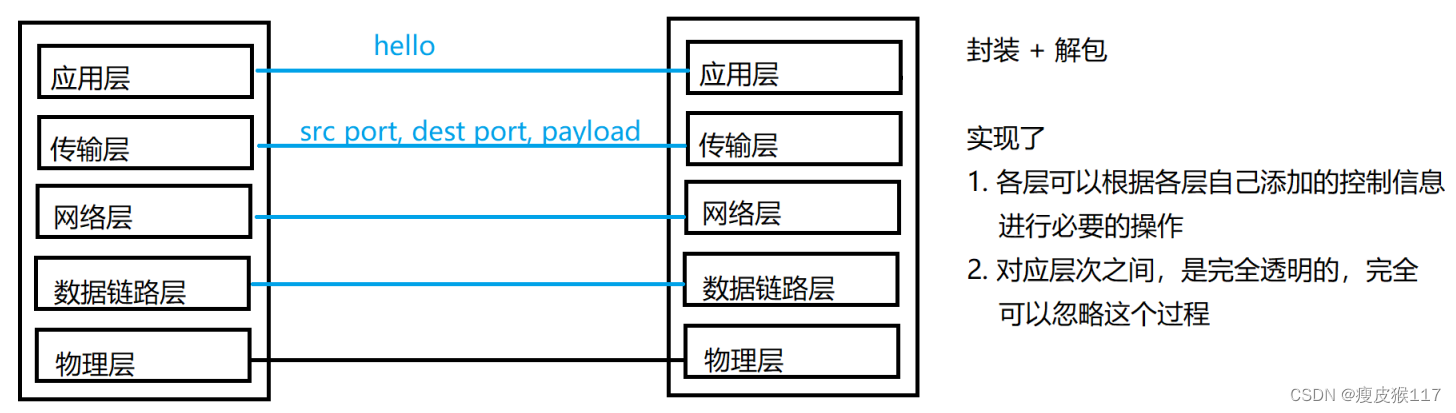
To complete the whole communication , The problems to be dealt with in the middle are still very complex . Therefore, it is necessary to carry out division of labor and cooperation .
When there is layering , You need to target each layer , Specify some specifications , Let everyone abide by , So as to better complete the work . These norms have certain authority , Under the network discipline , Call it an agreement (protocol)
Protocol layer
For network protocols , It is often defined at several levels .
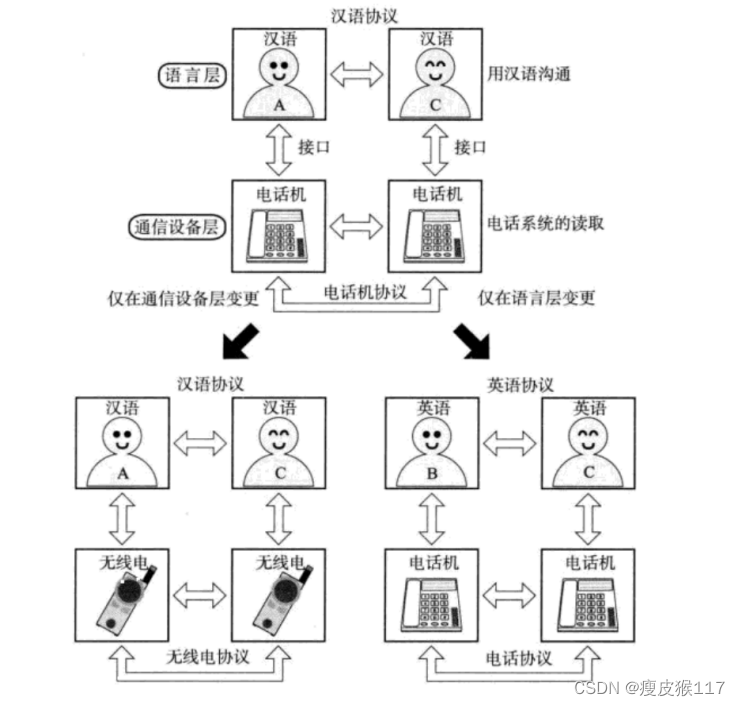
What is protocol layering
Protocol layering is similar to when making a phone call , Define different levels of protocols :
In this case , The agreement has only two layers ; But the actual network communication will be more complex , It needs to be divided into more levels .
Network standard layering
layered
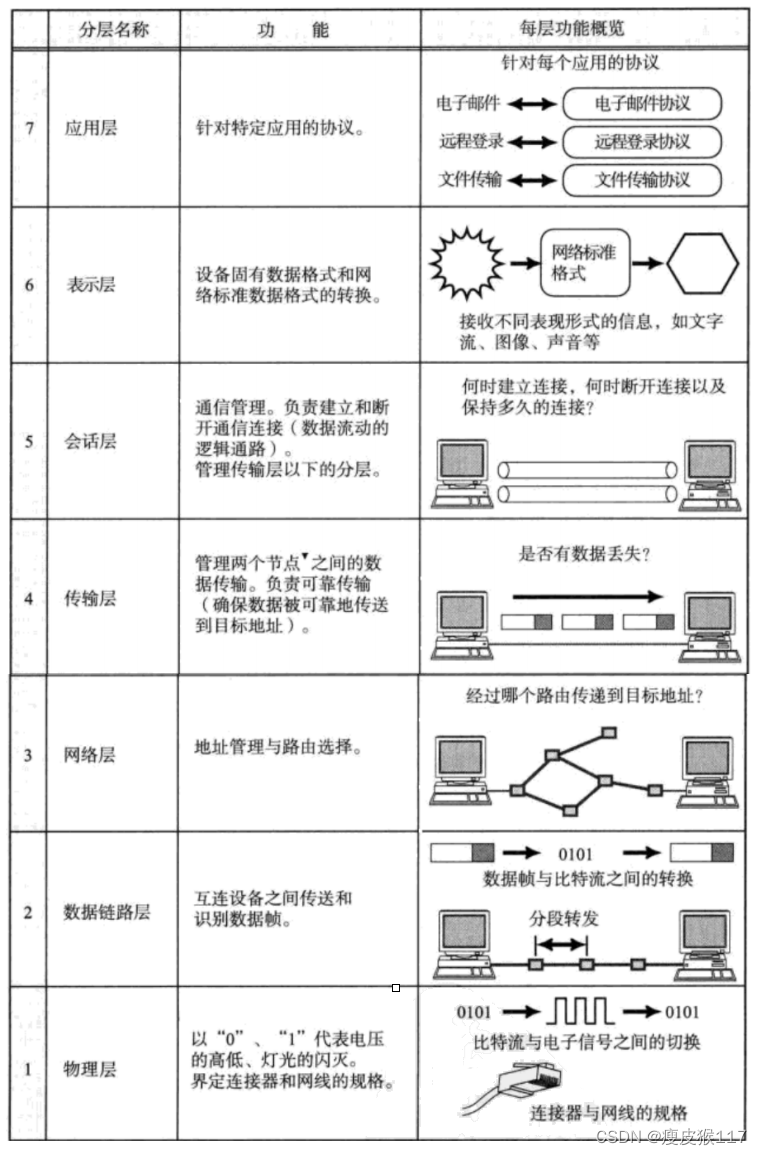
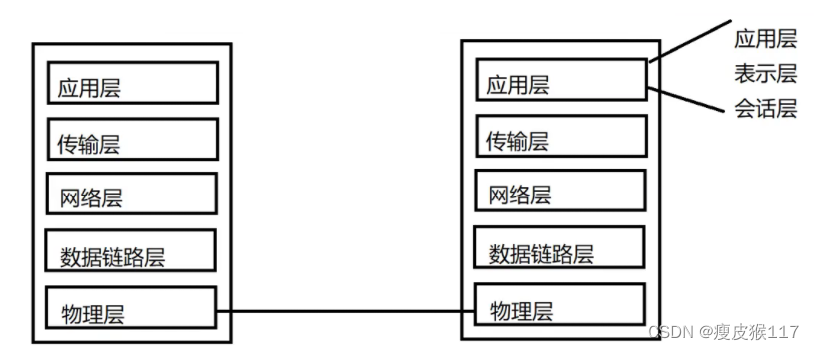
1. Academic school :OSI (Open System Interconnect) Provides a total of 7 Layer solution .
2. Practical school :TCP/IP 5 Layer protocol (4 Layer protocol , The physical layer is omitted in the expression ).
Network devices
3 An important network device (network deivce), Be careful : These network devices are not hosts .
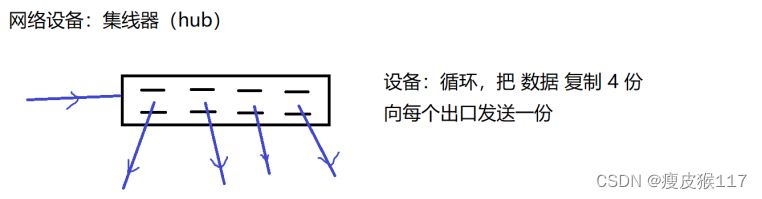
1. A hub (hub)
2. Switch (switch sw)3. Router (router)
A hub ( The physical layer )
LAN Internal communication problems
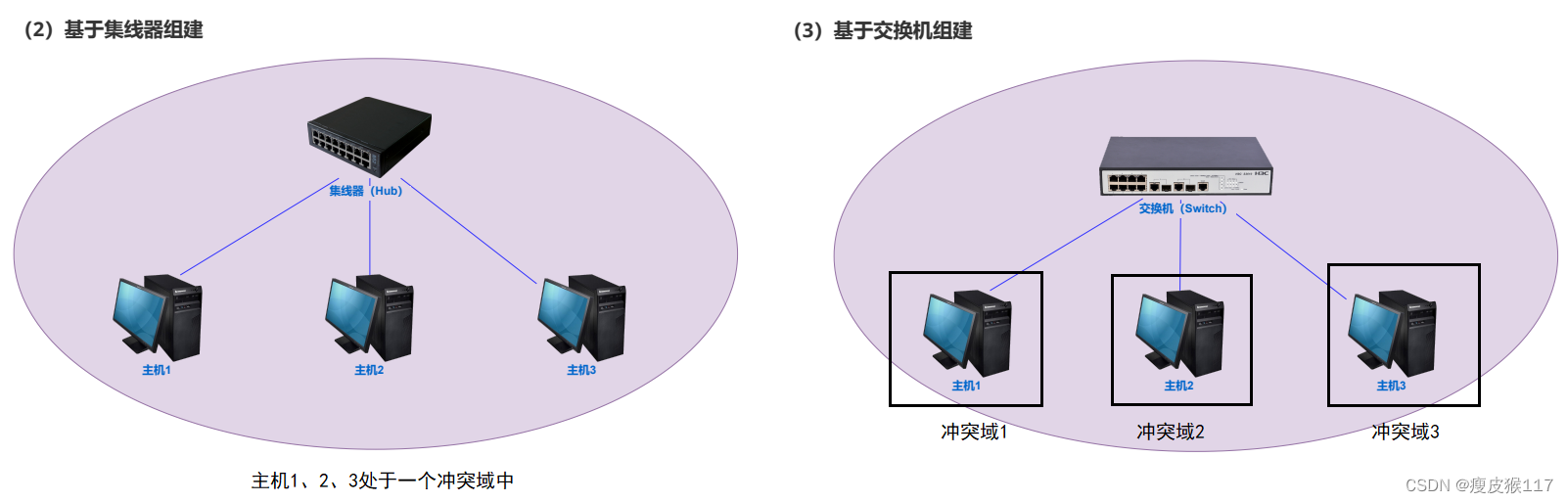
1. The simplest LAN : Two hosts are directly connected .2. LAN with certain topology :
Use a hub for networking , Born in the same conflict domain . This is caused by the working principle of the hub .
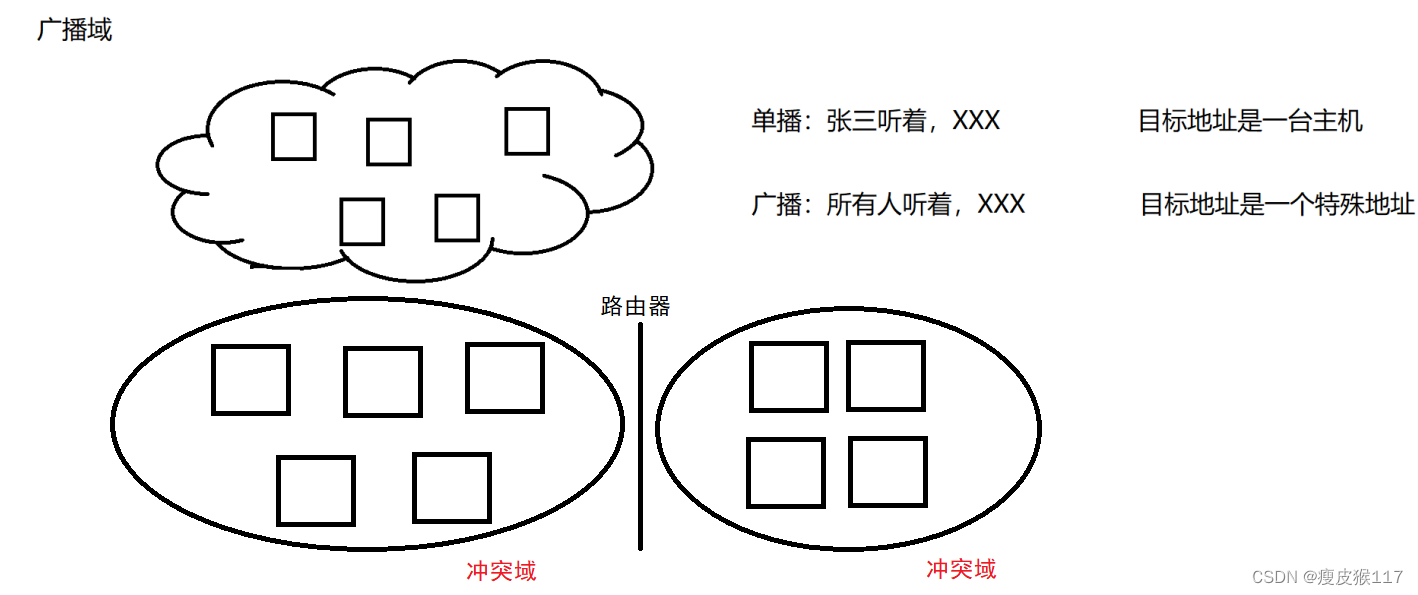
Conflict domain
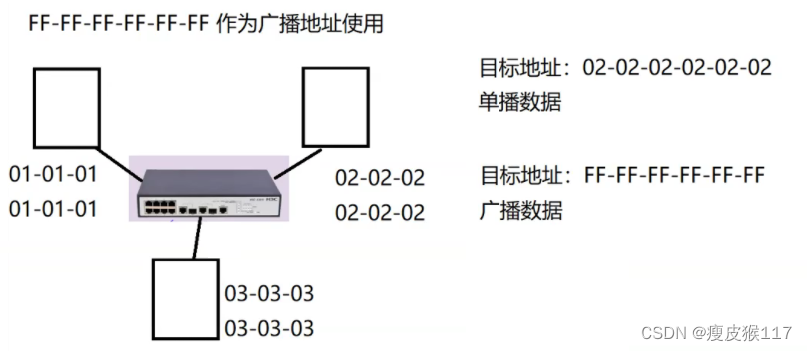
The teacher said :“ Zhang San , Please answer a question ”, Who can hear this sentence ? Everyone can hear .
however , Only Zhang San will respond . Because the data we transmit carries the destination address (“ Zhang San ”).
Self study scene , Everyone can take the initiative to speak . As a result, they can't hear each other .—— Conflict domain .Already under the same conflict domain , How to solve ?
Through a certain conflict avoidance algorithm , Avoid conflicts ( Data link layer to solve ).
The most common conflict avoidance algorithm : After discovering the conflict , Silent random time , Send... Again .
Even if there is a conflict avoidance algorithm , The data in the same conflict domain can be effectively transmitted , But the efficiency of signal transmission will still have an impact . So we need to :
1. Don't have too many hosts in the conflict domain .
2. Minimize the occurrence of conflict domains .
Switch ( Data link layer )
Switch (switch) appear , To reduce the conflict domain 、 Divide the conflict domain .
A hub : Only do tool copying , I don't know what the data is .Switch : You need to understand the target address put into the data link layer ( Need to be able to parse the data link layer protocol ), According to the destination address of the data , Decide who to give the data 、 Not to anyone .
The switch works at the data link layer .
According to the destination address in the data , Send the data only to the corresponding target . You can also set up a LAN through a switch .
Broadcast area
Address
Address : The address of the data link layer refers to MAC Address ( Physical address )
MAC The length of the address is 48 position (6 Bytes ), Usually expressed as 12 individual 16 Hexadecimal number .Such as :00-16-EA-AE-3C-40 It's just one. MAC Address
The network card was fixed when it was produced , Network cards all over the world MAC The address will not conflict .
One LAN Inside , No matter what kind of equipment , Which topology , The host and the host can communicate normally —— Responsibilities of data link layer protocol .
The above is the responsibility of the data link + Two devices (hub、switch) On which floor do you work , How it works .
domain name (domain)
www.baidu.com -> 182.193.33.232
localhost -> 127.0.0.1: Represents a domain name of this machine
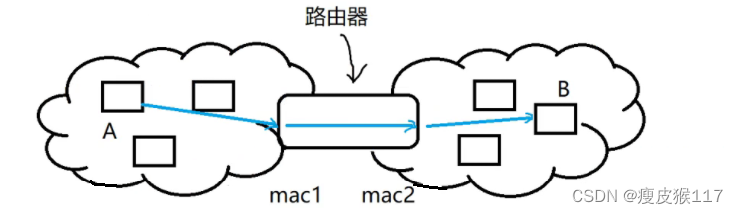
Router ( The network layer )
The network layer : Through data routing , Solve cross LAN Communication problems between hosts . Routers work on the network layer .
The router is in at least two LANs ( There are at least two network cards ).
Data can only be in the same LAN The transmission router spans two LAN. therefore , Span LAN The transmission of needs to pass through the router
route (route): Also known as pathfinding ; Router (router) : A device used to complete the pathfinding function .
The network layer has its own address :IP Address
IP The address is a 32 The binary number of bits , Usually divided into 4 individual “8 Bit binary number ”( That is to say 4 Bytes ), Such as :01100100.00000100.00000101.00000110.
Usually use “ dotted decimal ” In the way of , namely a.b.c.d In the form of (a,b,c,d All are 0~255 A decimal integer between ). Such as :100.4.5.6.
IP The address is the software address : Within the same network IP It shouldn't be “ repeat ” Of .IP The address changes at any time .
Transport layer
Transport layer : City comparison host . The host to host is all connected .
for example : A person in the city ( process ) Want another person in another city ( process ) communicate .( Interprocess communication )port (port) 0-65525 Unsigned number of two bytes .
process <-> port , Analogist <-> cell-phone number
Write the port , Corresponding to specific people ,
use express delivery , Write the recipient's phone number to correspond to that person .A process can have multiple ports ( No conflict )
Only one person can be assigned to a port ( Can't repeat )
Five levels
Important agreement :
HTTP/HTTPS/DNS Belongs to application layerTCP/UDP Belongs to the transport layer
IP It belongs to the network layer
application layer
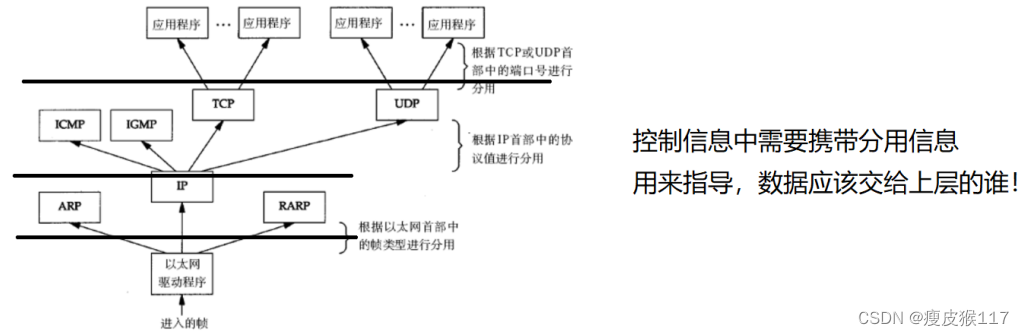
send out : encapsulation ( You must carry the distribution and unpacking information )
receive : Unpack / Divide up ( According to the control information of this layer )
send out
receive
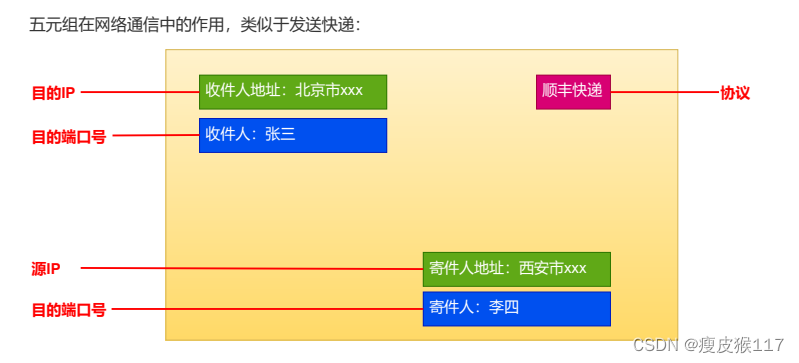
Quintuples
stay TCP/IP Agreement , Five tuples are used to identify a network communication :
1. Source IP: Identify the source host
2. Source port number : Identify the process of sending data for this communication in the source host
3. Purpose IP: Identify the destination host
4. Destination port number : Identify the process of receiving data for this communication in the destination host
5. Agreement No : Identify the data format agreed by both sending process and receiving process
边栏推荐
- Chapter 9 Yunji datacanvas was rated as 36 krypton "the hard core technology enterprise most concerned by investors"
- Semantic slam source code analysis
- EasyGBS级联时,上级平台重启导致推流失败、画面卡住该如何解决?
- torch. nn. functional. Pad (input, pad, mode= 'constant', value=none) record
- 九度 1201 -二叉排序数遍历- 二叉排序树「建议收藏」
- 怎样用Google APIs和Google的应用系统进行集成(1)—-Google APIs简介
- 力扣 1037.有效的回旋镖
- Simulate the implementation of string class
- Force buckle 643 Subarray maximum average I
- 使用 BR 恢复 Azure Blob Storage 上的备份数据
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
恢复持久卷上的备份数据
Some important knowledge of MySQL
写了个 Markdown 命令行小工具,希望能提高园友们发文的效率!
vulnhub之school 1
[solution] package 'XXXX' is not in goroot
Kubernetes -- detailed usage of kubectl command line tool
有用的win11小技巧
POJ 1742 coins (monotone queue solution) [suggestions collection]
Force buckle 1037 Effective boomerang
AIRIOT助力城市管廊工程,智慧物联守护城市生命线
Simulate the implementation of string class
力扣 1790. 仅执行一次字符串交换能否使两个字符串相等
使用高斯Redis实现二级索引
Version selection of boot and cloud
CSDN语法说明
MSE API learning
力扣 1232.缀点成线
JVM 类加载机制
有了ST7008, 蓝牙测试完全拿捏住了
Traversée des procédures stockées Oracle