当前位置:网站首页>Redis introduction complete tutorial: List explanation
Redis introduction complete tutorial: List explanation
2022-07-04 23:00:00 【Gu Ge academic】
list (list) Type is used to store multiple ordered strings , Pictured 2-18 Shown ,a、
b、c、d、e Five elements form an ordered list from left to right , Each string in the list
It's called the element (element), A list can store at most 2 32 -1 Elements . stay Redis in , can
To insert... At both ends of the list (push) And pop up (pop), You can also get the element column of the specified range
surface 、 Get the elements of the specified index subscript, etc ( Pictured 2-18 Sum graph 2-19 Shown ). A list is a comparison
More flexible data structure , It can act as a stack and a queue , There are many applications in practical development
scene .
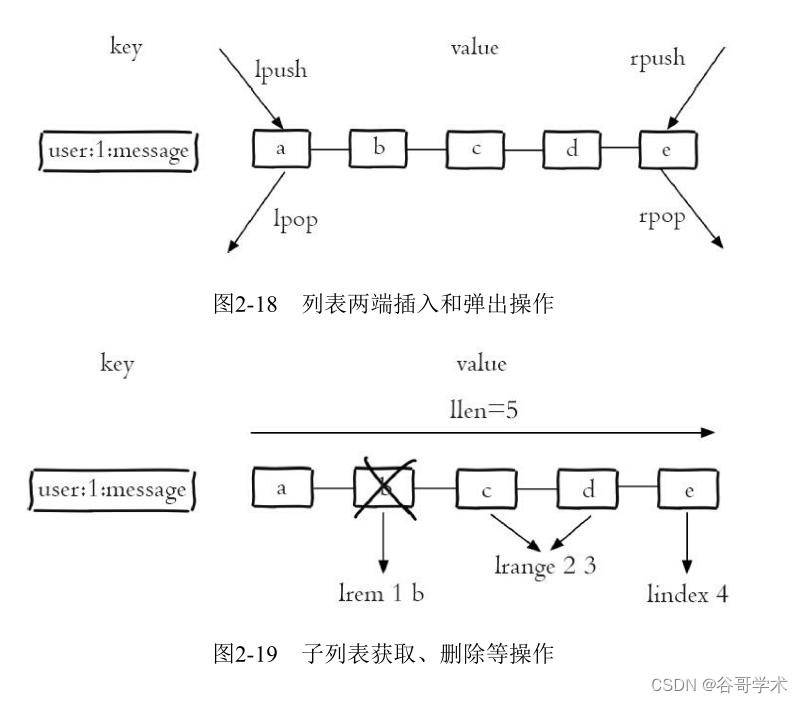
List types have two characteristics : First of all 、 The elements in the list are ordered , That means you can
Get a list of elements or elements in a range by index subscript , For example, to get a graph 2-19
Of the 5 Elements , It can be executed lindex user:1:message4( Index from 0 Count up ) You can get
To the elements e. second 、 Elements in a list can be repetitive , For example, figure 2-20 The list shown contains
Two strings were a.

These two characteristics will be introduced after the introduction of set and ordered set , It's going to be more prominent , So I'm taking the exam
Before considering whether to use this data structure , First of all, we need to understand the characteristics of the list data structure .
2.4.1 command
The following will follow the 5 There are three types of operation to introduce the command , The command is shown in the table 2-4 Shown .
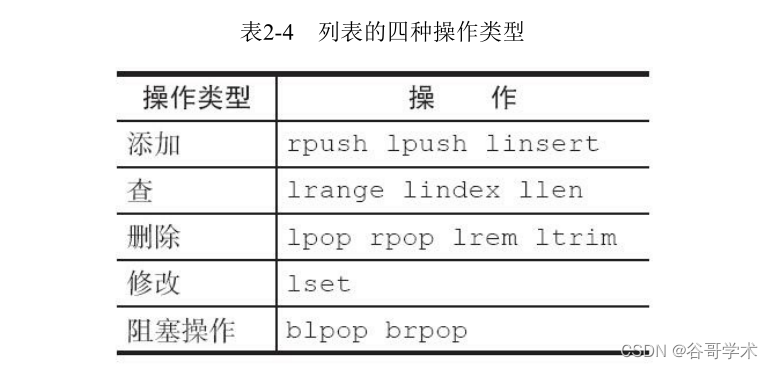
1. Add operation
(1) Insert the element from the right
rpush key value [value ...]
The following code inserts elements from right to left c、b、a:
127.0.0. 1:6379> rpush listkey c b a
(integer) 3
lrange0-1 Command can get all the elements of the list from left to right :
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "c"
2) "b"
3) "a"
(2) Insert the element from the left
lpush key value [value ...]
Usage and rpush identical , Just insert... From the left , No more details here .
(3) Inserts an element before or after an element
linsert key before|after pivot value
linsert The command will find in the list equal to pivot The elements of , In front of it (before) Or after
(after) Insert a new element value, For example, the following operation will be in the list of elements b Insert before
java:
127.0.0.1:6379> linsert listkey before b java
(integer) 4
The return result is 4, Represents the length of the current command , The current list changes to :
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "c"
2) "java"
3) "b"
4) "a"
2. lookup
(1) Gets a list of elements in the specified range
lrange key start end
lrange Operation gets all the elements in the specified index range of the list . The index subscript has two characteristics
spot : First of all , Index subscripts from left to right are 0 To N-1, But from right to left is -1 To -N.
second ,lrange Medium end It contains the option itself , This and many programming languages do not contain end Not really
identical , For example, if you want to get the second 2 To the first 4 Elements , You can do the following :
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 1 3
1) "java"
2) "b"
3) "a"
(2) Gets the element of the list with the specified index index
lindex key index
For example, the last element in the current list is a:
127.0.0.1:6379> lindex listkey -1
"a"
(3) Get list length
llen key
for example , The following example shows that the current list length is 4:
127.0.0.1:6379> llen listkey
(integer) 4
3. Delete
(1) The element pops up from the left side of the list
lpop key
The following operation will list the leftmost elements c Will be a pop-up , After the pop-up, the list changes to java、b、
a:
127.0.0.1:6379>t lpop listkey
"c"
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "java"
2) "b"
3) "a"
(2) Pops up from the right side of the list
rpop key
How to use it and lpop It's the same , Just pop up from the right side of the list , There's no more here
Statement .
(3) Deletes the specified element
lrem key count value
lrem The command will find in the list equal to value To delete the elements of , according to count Different
There are three situations :
·count>0, From left to right , Delete the most count Elements .
·count<0, From right to left , Delete the most count Absolute value element .
·count=0, Delete all .
For example, insert from left to right into the list 5 individual a, So the current list becomes “a a a a a java b a”,
The following operation will start from the left side of the list to delete 4 A for a The elements of :
127.0.0.1:6379> lrem listkey 4 a
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "a"
2) "java"
3) "b"
4) "a"
(4) Trim the list by index range
ltrim key start end
for example , The following operation will only keep the list listkey The first 2 One to the first 4 Elements :
127.0.0.1:6379> ltrim listkey 1 3
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "java"
2) "b"
3) "a"
4. modify
Modifies the element of the specified index index :
lset key index newValue
The following operation will list listkey No 3 The elements are set to python:
127.0.0.1:6379> lset listkey 2 python
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> lrange listkey 0 -1
1) "java"
2) "b"
3) "python"
5. Blocking operations
The blocking pop-up is as follows :
blpop key [key ...] timeout
brpop key [key ...] timeout
blpop and brpop yes lpop and rpop Blocking version of , They're not in the same direction as the pop-up , Use
The method is basically the same , So here is brpop Command to explain ,brpop The command has two parameters :
·key[key...]: Keys for multiple lists .
·timeout: Blocking time ( Company : second ).
1) The list is empty. : If timeout=3, So the client has to wait until 3 Seconds later , If
timeout=0, So the client has been blocking and waiting :
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:test 3
(nil)
(3.10s)
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:test 0
... Blocking ...
If data is added during this period element1, The client immediately returns :
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:test 3
1) "list:test"
2) "element1"
(2.06s)
2) The list is not empty : The client will immediately return .
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:test 0
1) "list:test"
2) "element1"
In the use of brpop when , There are two points to note .
The first point , If it's multiple keys , that brpop Will traverse the key from left to right , Once there is a key
Can pop up elements , The client immediately returns :
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:1 list:2 list:3 0
.. Blocking ..
At this point, the other client will send list:2 and list:3 Insert elements :
client-lpush> lpush list:2 element2
(integer) 1
client-lpush> lpush list:3 element3
(integer) 1
The client will immediately return list:2 Medium element2, because list:2 The first thing to pop up
Elements :
127.0.0.1:6379> brpop list:1 list:2 list:3 0
1) "list:2"
2) "element2_1"
Second point , If multiple clients execute on the same key brpop, Then execute first brpop life
So that the client can get the pop-up value .
client 1:
client-1> brpop list:test 0
... Blocking ...
client 2:
client-2> brpop list:test 0
... Blocking ...
client 3:
client-3> brpop list:test 0
... Blocking ...
At this point, another client lpush An element to list:test In the list :
client-lpush> lpush list:test element
(integer) 1
So the client 1 You'll get the most elements , Because the client 1 The first to perform brpop, And the client 2
And the client 3 Keep blocking :
client> brpop list:test 0
1) "list:test"
2) "element"
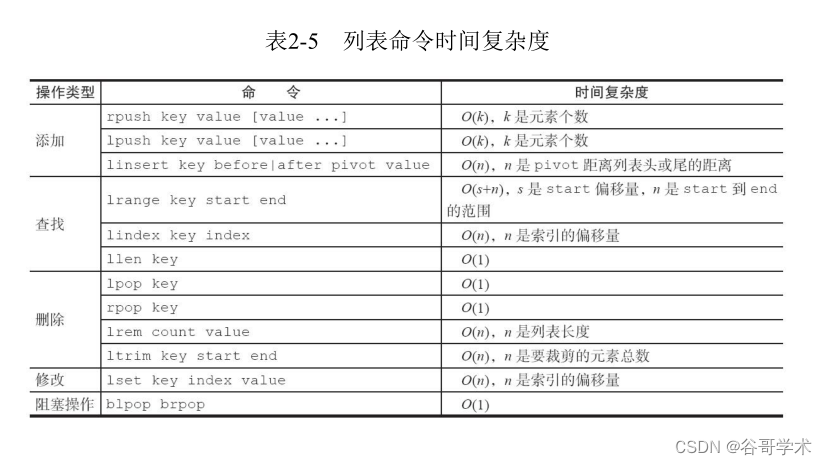
I've finished with the basic list commands , surface 2-5 It's the time complexity of these commands ,
Developers can refer to this table to select the appropriate command .
2.4.2 Internal encoding
There are two types of internal encoding for list types .
·ziplist( Compressed list ): When the number of elements in the list is less than list-max-ziplist-entries To configure
( Default 512 individual ), At the same time, the value of each element in the list is less than list-max-ziplist-value When the configuration
( Default 64 byte ),Redis Will choose ziplist As an internal implementation of the list to reduce memory
use .
·linkedlist( Linked list ): When the list type cannot satisfy ziplist The condition of ,Redis Will use
linkedlist As an internal implementation of the list .
The following example demonstrates the internal encoding of a list type , And the corresponding changes .
1) When the number of elements is small and there are no large elements , The internal code is ziplist:
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush listkey e1 e2 e3
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding listkey
"ziplist"
2.1) When the number of elements exceeds 512 individual , The internal code becomes linkedlist:
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush listkey e4 e5 ... Ignore ... e512 e513
(integer) 513
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding listkey
"linkedlist"
2.2) Or when an element exceeds 64 byte , The internal code will also become linkedlist:
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush listkey "one string is bigger than 64 byte...............
................."
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding listkey
"linkedlist"
边栏推荐
- 攻防世界 misc 进阶区 2017_Dating_in_Singapore
- Three stage operations in the attack and defense drill of the blue team
- A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: hyperloglog
- 【ODX Studio編輯PDX】-0.2-如何對比Compare兩個PDX/ODX文件
- Google Earth engine (GEE) - globfire daily fire data set based on mcd64a1
- 质量体系建设之路的分分合合
- How to send a reliable request before closing the page
- Redis入门完整教程:GEO
- Photoshop batch adds different numbers to different pictures
- Wechat official account solves the cache problem of entering from the customized menu
猜你喜欢
Install the gold warehouse database of NPC
Complete tutorial for getting started with redis: bitmaps
Unity Xiuxian mobile game | Lua dynamic sliding function (specific implementation of three source codes)

【剑指offer】1-5题
Redis入门完整教程:事务与Lua
攻防世界 MISC 進階區 Erik-Baleog-and-Olaf

Redis入门完整教程:列表讲解
Redis入門完整教程:Pipeline

攻防世界 misc 高手进阶区 a_good_idea
A complete tutorial for getting started with redis: redis shell
随机推荐
Lost in the lock world of MySQL
攻防世界 MISC 進階區 Erik-Baleog-and-Olaf
Feature scaling normalization
华泰证券是国家认可的券商吗?开户安不安全?
Duplicate ADMAS part name
Google collab trample pit
[Lua] Int64 support
sobel过滤器
Redis入门完整教程:有序集合详解
蓝队攻防演练中的三段作战
安装人大金仓数据库
攻防世界 MISC 进阶区 3-11
Breakpoint debugging under vs2019 c release
该如何去选择证券公司,手机上开户安不安全
【ODX Studio編輯PDX】-0.2-如何對比Compare兩個PDX/ODX文件
Redis入门完整教程:Redis Shell
Close system call analysis - Performance Optimization
Record: how to scroll screenshots of web pages on Microsoft edge in win10 system?
SHP data making 3dfiles white film
剑指Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先