当前位置:网站首页>Close system call analysis - Performance Optimization
Close system call analysis - Performance Optimization
2022-07-04 22:31:00 【51CTO】
Today, I was pulled to work overtime to deal with performance problems :
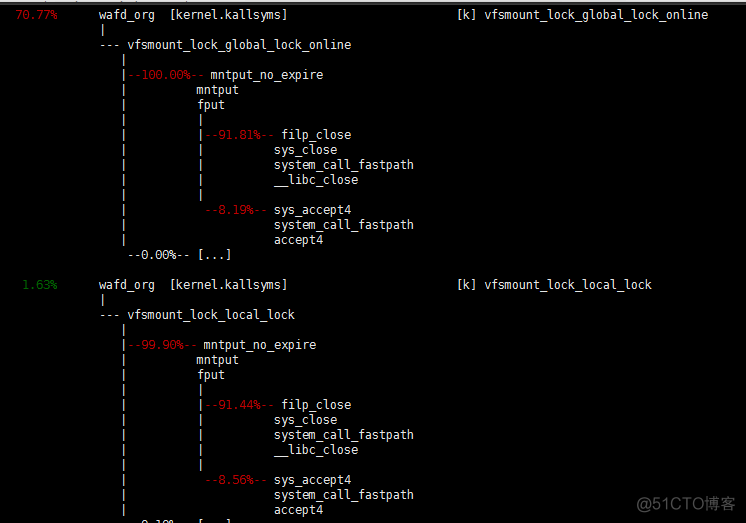
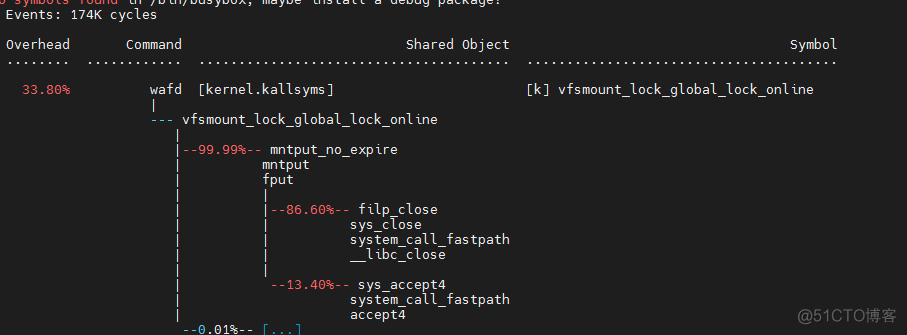
The comparison result after optimization is : Also in 5wcps Under the circumstances , Former cpu Usage rate is 90%, Now? cpu Usage rate is 30%! from cpu From the angle of view, it has been improved a lot , meanwhile perf top It turns out , close Percentage of system calls cpu Also reduced a lot
There are the following problems due to the previous multi-threaded architecture :
1、 In bulk close System calls cause problems ; Here is the business that has not been handled well , meanwhile close Do exist vfs Of lock Conflict
2、 Multithreaded batch accept open fd It will also trigger vfs The global lock of
/*
* cloning flags:
*/
#define CSIGNAL 0x000000ff /* signal mask to be sent at exit */
#define CLONE_VM 0x00000100 /* set if VM shared between processes */
#define CLONE_FS 0x00000200 /* set if fs info shared between processes Each process has its own root directory and current working directory , The kernel using struct fs_struct To record this information , Of the process descriptor fs Field refers to the process fs_struct structure .*/
#define CLONE_FILES 0x00000400 /* set if open files shared between processes The process also needs to record the files it opens . All files opened by the process are used struct files_struct To record */
#define CLONE_SIGHAND 0x00000800 /* set if signal handlers and blocked signals shared */
#define CLONE_PTRACE 0x00002000 /* set if we want to let tracing continue on the child too */
#define CLONE_VFORK 0x00004000 /* set if the parent wants the child to wake it up on mm_release */
#define CLONE_PARENT 0x00008000 /* set if we want to have the same parent as the cloner */
#define CLONE_THREAD 0x00010000 /* Same thread group? */
#define CLONE_NEWNS 0x00020000 /* New namespace group? */
#define CLONE_SYSVSEM 0x00040000 /* share system V SEM_UNDO semantics */
#define CLONE_SETTLS 0x00080000 /* create a new TLS for the child */
#define CLONE_PARENT_SETTID 0x00100000 /* set the TID in the parent */
#define CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID 0x00200000 /* clear the TID in the child */
#define CLONE_DETACHED 0x00400000 /* Unused, ignored */
#define CLONE_UNTRACED 0x00800000 /* set if the tracing process can't force CLONE_PTRACE on this clone */
#define CLONE_CHILD_SETTID 0x01000000 /* set the TID in the child */
/* 0x02000000 was previously the unused CLONE_STOPPED (Start in stopped state)
and is now available for re-use. */
#define CLONE_NEWUTS 0x04000000 /* New utsname group? */
#define CLONE_NEWIPC 0x08000000 /* New ipcs */
#define CLONE_NEWUSER 0x10000000 /* New user namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWPID 0x20000000 /* New pid namespace */
#define CLONE_NEWNET 0x40000000 /* New network namespace */
#define CLONE_IO 0x80000000 /* Clone io context */
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
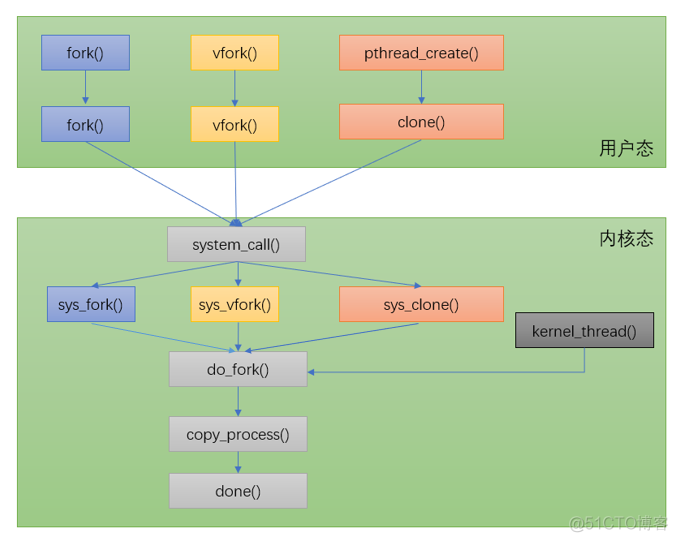
int sys_fork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return do_fork(SIGCHLD, regs->sp, regs, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
/*
* This is trivial, and on the face of it looks like it
* could equally well be done in user mode.
*
* Not so, for quite unobvious reasons - register pressure.
* In user mode vfork() cannot have a stack frame, and if
* done by calling the "clone()" system call directly, you
* do not have enough call-clobbered registers to hold all
* the information you need.
*/
int sys_vfork(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
return do_fork(CLONE_VFORK | CLONE_VM | SIGCHLD, regs->sp, regs, 0,
NULL, NULL);
}
long
sys_clone(unsigned long clone_flags, unsigned long newsp,
void __user *parent_tid, void __user *child_tid, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
if (!newsp)
newsp = regs->sp;
return do_fork(clone_flags, newsp, regs, 0, parent_tid, child_tid);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
Generally speaking fork The post parent-child process is separated
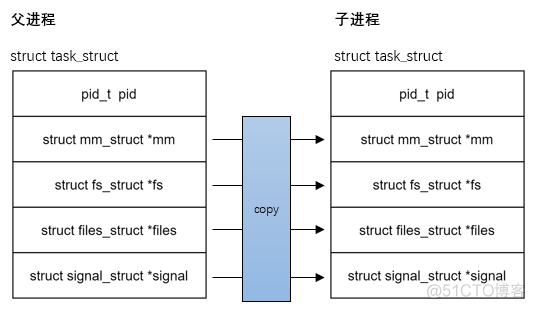
vfork: The parent-child process shares mm;vfork System call is different from fork, use vfork The child processes created share the address space , That is, the child process runs entirely in the address space of the parent process , The modification of any data in the virtual address space by the child process is also seen by the parent process . But with vfork After creating a subprocess , The parent process is blocked until the child process calls exec or exit. This benefit is in Zijin
After the procedure is created, it is only for calling exec When executing another program , Because it will not have any reference to the address space of the parent process , So copying the address space is redundant , adopt vfork Can reduce unnecessary expenses .
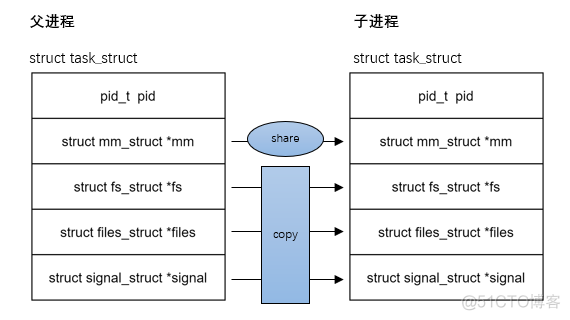
pthread_create: Parent child processes share the main mm fs file signal And so on
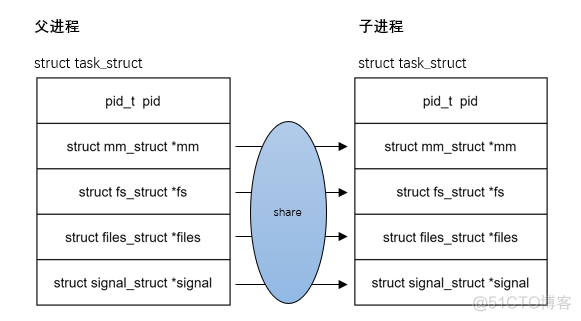
So in open as well as close fd yes Overall files File lock needs to be locked ;
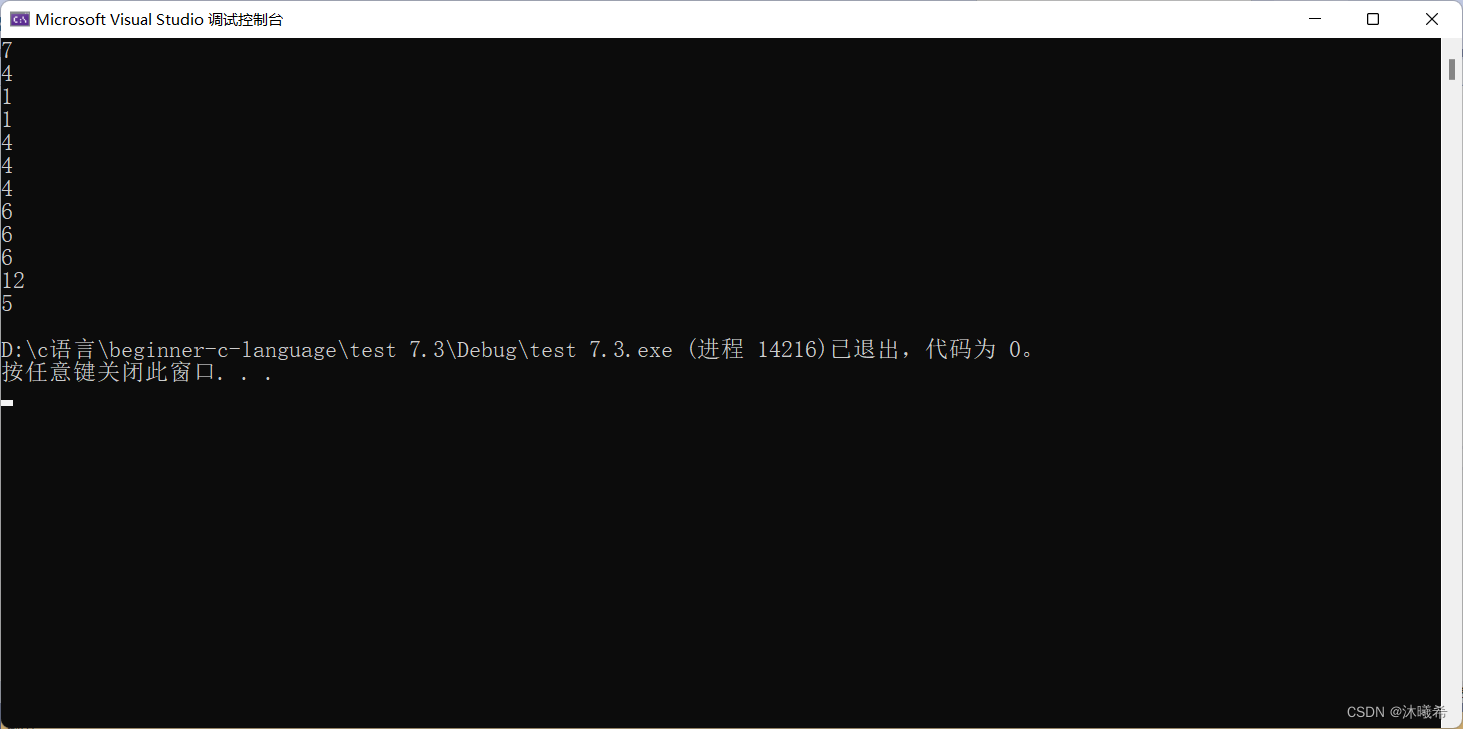
Also refer to : The analysis of this article ; Compare the following two pictures : Find a close by 30us One for ns Level ( Show 0us)
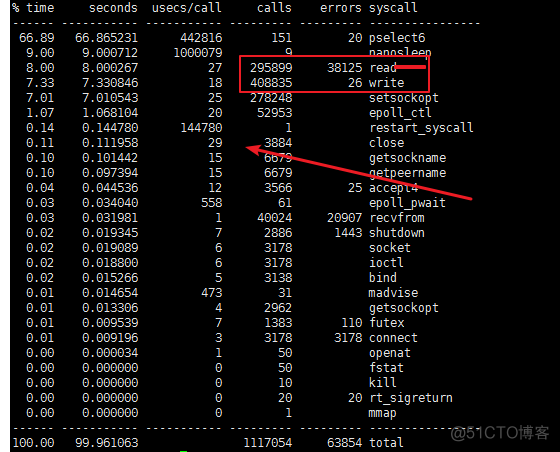
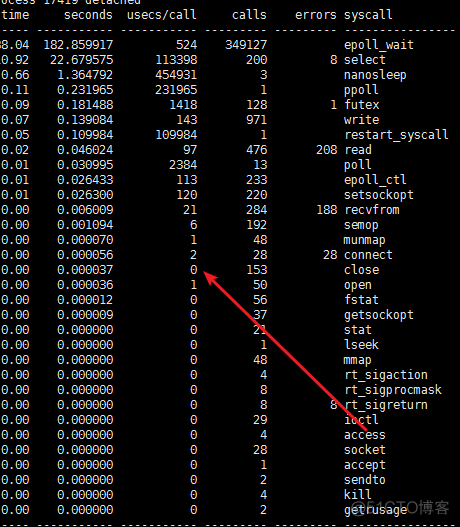
close System call analysis
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(close, unsigned int, fd)
{
struct file * filp;
struct files_struct *files = current->files;
struct fdtable *fdt;
int retval;
spin_lock(&files->file_lock);
fdt = files_fdtable(files);
if (fd >= fdt->max_fds)
goto out_unlock;
filp = fdt->fd[fd];
if (!filp)
goto out_unlock;
rcu_assign_pointer(fdt->fd[fd], NULL);
FD_CLR(fd, fdt->close_on_exec);
__put_unused_fd(files, fd);
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
retval = filp_close(filp, files);
/* can't restart close syscall because file table entry was cleared */
if (unlikely(retval == -ERESTARTSYS ||
retval == -ERESTARTNOINTR ||
retval == -ERESTARTNOHAND ||
retval == -ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK))
retval = -EINTR;
return retval;
out_unlock:
spin_unlock(&files->file_lock);
return -EBADF;
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
/*
* "id" is the POSIX thread ID. We use the
* files pointer for this..
*/
int filp_close(struct file *filp, fl_owner_t id)
{
int retval = 0;
if (!file_count(filp)) {
printk(KERN_ERR "VFS: Close: file count is 0\n");
return 0;
}
if (filp->f_op && filp->f_op->flush)
retval = filp->f_op->flush(filp, id);
if (likely(!(filp->f_mode & FMODE_PATH))) {
dnotify_flush(filp, id);
locks_remove_posix(filp, id);
}
fput(filp);
return retval;
}
void fput(struct file *file)
{// Pay attention to fput function , This function will first count the references of the file -1, Then judge whether it is 0, by 0 And then continue the process , That is to say, when socket When there are multiple references , Only the last one close Will trigger the subsequent scheduling destruction process ,
if (atomic_long_dec_and_test(&file->f_count))
__fput(file);
}
/* the real guts of fput() - releasing the last reference to file
*/
static void __fput(struct file *file)
{
struct dentry *dentry = file->f_path.dentry;
struct vfsmount *mnt = file->f_path.mnt;
struct inode *inode = dentry->d_inode;
might_sleep();
fsnotify_close(file);
/*
* The function eventpoll_release() should be the first called
* in the file cleanup chain.
*/
eventpoll_release(file);
locks_remove_flock(file);
if (unlikely(file->f_flags & FASYNC)) {
if (file->f_op && file->f_op->fasync)
file->f_op->fasync(-1, file, 0);
}
if (file->f_op && file->f_op->release)
file->f_op->release(inode, file);// stay close The file will be called in the system call release operation
security_file_free(file);
ima_file_free(file);
if (unlikely(S_ISCHR(inode->i_mode) && inode->i_cdev != NULL &&
!(file->f_mode & FMODE_PATH))) {
cdev_put(inode->i_cdev);
}
fops_put(file->f_op);
put_pid(file->f_owner.pid);
file_sb_list_del(file);
if ((file->f_mode & (FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE)) == FMODE_READ)
i_readcount_dec(inode);
if (file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE)
drop_file_write_access(file);
file->f_path.dentry = NULL;
file->f_path.mnt = NULL;
file_free(file);
dput(dentry);
mntput(mnt);
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
- 46.
- 47.
- 48.
- 49.
- 50.
- 51.
- 52.
- 53.
- 54.
- 55.
- 56.
- 57.
- 58.
- 59.
- 60.
- 61.
- 62.
- 63.
- 64.
- 65.
- 66.
- 67.
- 68.
- 69.
- 70.
- 71.
stay close The file will be called in the system call release operation ;socket The file operation structure of the implementation is as follows , Among them, this paper discusses release The function is implemented as sock_close;
/*
* Socket files have a set of 'special' operations as well as the generic file ones. These don't appear
* in the operation structures but are done directly via the socketcall() multiplexor.
*/
static const struct file_operations socket_file_ops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.aio_read = sock_aio_read,
.aio_write = sock_aio_write,
.poll = sock_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = sock_ioctl,
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
.compat_ioctl = compat_sock_ioctl,
#endif
.mmap = sock_mmap,
.open = sock_no_open, /* special open code to disallow open via /proc */
.release = sock_close,
.fasync = sock_fasync,
.sendpage = sock_sendpage,
.splice_write = generic_splice_sendpage,
.splice_read = sock_splice_read,
};
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
static int sock_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
/*
* It was possible the inode is NULL we were
* closing an unfinished socket.
*/
if (!inode) {
printk(KERN_DEBUG "sock_close: NULL inode\n");
return 0;
}
sock_release(SOCKET_I(inode));
return 0;
}
/**
* sock_release - close a socket
* @sock: socket to close
*
* The socket is released from the protocol stack if it has a release
* callback, and the inode is then released if the socket is bound to
* an inode not a file.
*/
void sock_release(struct socket *sock)
{
if (sock->ops) {
struct module *owner = sock->ops->owner;
sock->ops->release(sock);/* call socket In operation release At present, it is mainly for use inet_release If you use tcp sock Last
call tcp_close*/
sock->ops = NULL;
module_put(owner);
}
if (rcu_dereference_protected(sock->wq, 1)->fasync_list)
printk(KERN_ERR "sock_release: fasync list not empty!\n");
percpu_sub(sockets_in_use, 1);/* Reduce cpu Number of sockets */
if (!sock->file) {
iput(SOCK_INODE(sock));
return;
}
sock->file = NULL; /* Socket is closed , Carry on close The system calls other processes */
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
- 42.
- 43.
- 44.
- 45.
http proxy server (3-4-7 Layer of the agent )- Network event library common component 、 kernel kernel drive Camera drive tcpip Network protocol stack 、netfilter、bridge Seems to have seen !!!! But he that doeth good Don't ask future -- Height and weight 180 Fat man
边栏推荐
- How to manage 15million employees easily?
- Interview essential leetcode linked list algorithm question summary, whole process dry goods!
- 机器人相关课程考核材料归档实施细则2022版本
- 能源势动:电力行业的碳中和该如何实现?
- Postgresqlql advanced skills pivot table
- NAACL-22 | 在基于Prompt的文本生成任务上引入迁移学习的设置
- Ascendex launched Walken (WLKN) - an excellent and leading "walk to earn" game
- Practice and principle of PostgreSQL join
- Force buckle 2_ 1480. Dynamic sum of one-dimensional array
- Service online governance
猜你喜欢
【C语言进阶篇】数组&&指针&&数组笔试题

LOGO special training camp section I identification logo and Logo Design Ideas

Energy momentum: how to achieve carbon neutralization in the power industry?

LOGO特训营 第四节 字体设计的重要性
卷积神经网络模型之——LeNet网络结构与代码实现
2022-07-04: what is the output of the following go language code? A:true; B:false; C: Compilation error. package main import “fmt“ func main() { fmt.Pri

30余家机构联合发起数字藏品行业倡议,未来会如何前进?

Embedded development: skills and tricks -- seven skills to improve the quality of embedded software code
Éducation à la transmission du savoir | Comment passer à un test logiciel pour l'un des postes les mieux rémunérés sur Internet? (joindre la Feuille de route pour l'apprentissage des tests logiciels)
Scala下载和配置
随机推荐
Microservices -- Opening
阿里推出新品牌“瓴羊”,致力成为“数字化领头羊”
将QA引入软件开发生命周期是工程师要遵循的最佳实践
并发网络模块化 读书笔记转
力扣2_1480. 一维数组的动态和
好用app推荐:扫描二维码、扫描条形码并查看历史
【Acwing】第58场周赛 题解
TLA+ 入门教程(1):形式化方法简介
能源势动:电力行业的碳中和该如何实现?
大厂的广告系统升级,怎能少了大模型的身影
Enabling digital economy Fuxin software attends the BRICs high level Forum on Sustainable Development
嵌入式开发:技巧和窍门——提高嵌入式软件代码质量的7个技巧
It is said that software testing is very simple, but why are there so many dissuasions?
广电五舟与华为签署合作协议,共同推进昇腾AI产业持续发展
More than 30 institutions jointly launched the digital collection industry initiative. How will it move forward in the future?
Short video system source code, click the blank space of the screen, the keyboard does not automatically stow
PMO:比较25种分子优化方法的样本效率
The proofreading activity of data science on the command line second edition was restarted
idea中pom.xml依赖无法导入
close系统调用分析-性能优化