当前位置:网站首页>Practice and principle of PostgreSQL join
Practice and principle of PostgreSQL join
2022-07-04 22:28:00 【Hua Weiyun】
Recently the project used PostgreSQL Simple learning join Grammar and principle , Have time to do it later SQLite Source code .
PostgreSQL JOIN Clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables , Based on the common fields between these tables .
stay PostgreSQL in ,JOIN There are five connection types :
CROSS JOIN : Cross connect
INNER JOIN: Internal connection
LEFT OUTER JOIN: The left outer join
RIGHT OUTER JOIN: Right connection
FULL OUTER JOIN: Full outer join
1. Data preparation
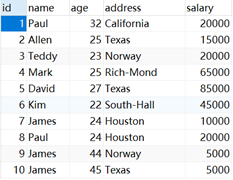
establish company Table and department surface among company The table stores basic employee information department The table stores department information .
company The table definition and initialization data are as follows :
DROP TABLE COMPANY;
CREATE TABLE COMPANY(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50),
SALARY REAL
);
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond ', 65000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (5, 'David', 27, 'Texas', 85000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) VALUES (6, 'Kim', 22, 'South-Hall', 45000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY VALUES (7, 'James', 24, 'Houston', 10000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY VALUES (8, 'Paul', 24, 'Houston', 20000.00);
INSERT INTO COMPANY VALUES (9, 'James', 44, 'Norway', 5000.00);
INSERT INTO COMPANY VALUES (10, 'James', 45, 'Texas', 5000.00);
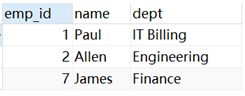
department The table definition and initialization are as follows :
CREATE TABLE DEPARTMENT(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
DEPT CHAR(50) NOT NULL,
EMP_ID INT NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT (ID, DEPT, EMP_ID) VALUES (1, 'IT Billing', 1 );
INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT (ID, DEPT, EMP_ID) VALUES (2, 'Engineering', 2 );
INSERT INTO DEPARTMENT (ID, DEPT, EMP_ID) VALUES (3, 'Finance', 7 );

2. Connection operation
2.1 Cross connect
Cross connect (CROSS JOIN) Match each row of the first table with each row of the second table . If the two input tables have x and y That's ok , Then the result table has x*y That's ok .
SELECT EMP_ID, NAME, DEPT FROM COMPANY CROSS JOIN DEPARTMENT;

The corresponding query plan is as follows :

2.2 Internal connection
Internal connection (INNER JOIN) Combine two tables according to the join predicate (table1 and table2) To create a new result table . The query will table1 Every line in is related to table2 Compare each line in , Find matching pairs for all rows that satisfy the join predicate . When the join predicate is satisfied ,A and B The column values of each matching pair of rows are merged into a result row . Internal connection (INNER JOIN) Is the most common connection type , Is the default connection type .INNER Keywords are optional .
SELECT EMP_ID, NAME, DEPT FROM COMPANY INNER JOIN DEPARTMENT ON COMPANY.ID = DEPARTMENT.EMP_ID;

2.3 The left outer join
For left outer connection , First, execute an inner connection . then , For tables T1 Table... Is not satisfied in T2 Each line in the join condition , among T2 There are... In the column of null Value will also add a connection line . therefore , Connected tables in T1 At least one line in each line .


2.4 Right connection
First , Perform internal connection . then , For tables T2 Table... Is not satisfied in T1 Each line in the join condition , among T1 An empty value in the column will also add a join row . This is the opposite of the left join ; about T2 Each line in , The result table always has one row .


2.5 External connection
First , Perform internal connection . then , For tables T1 Table... Is not satisfied in T2 Each line of any line connection condition in , If T2 There are... In the column of null A value is also added to the result . Besides , about T2 Dissatisfaction and T1 Any row in the join condition for each row , Will be added T1 Column contains null Value into the result .
It can be seen from the above operation that Most connections will use Hash Join Algorithm to achieve .postgreSQL in join There are three algorithms nested loop join merge join as well as hash join
3. Connection principle
3.1 nested loop join
nested loop join: The right relation is scanned once for every row found in the left relation. This strategy is easy to implement but can be very time consuming. (However, if the right relation can be scanned with an index scan, this can be a good strategy. It is possible to use values from the current row of the left relation as keys for the index scan of the right.)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM COMPANY JOIN DEPARTMENT ON DEPARTMENT.EMP_ID = COMPANY.ID WHERE company."id" = 1;
1. surface company according to id To filter the results
2. For each row of filtered results , utilize id from department Match in the table
3.2 merge join
merge join: Each relation is sorted on the join attributes before the join starts. Then the two relations are scanned in parallel, and matching rows are combined to form join rows. This kind of join is more attractive because each relation has to be scanned only once. The required sorting might be achieved either by an explicit sort step, or by scanning the relation in the proper order using an index on the join key.
set enable_hashjoin=off;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM COMPANY JOIN DEPARTMENT ON DEPARTMENT.emp_id = COMPANY.ID;

- First company Table associated fields id Is ordered Direct index scan
- Deparpment First of all, in accordance with the emp_id Sort And then execute merge join
3.3 hash join
hash join: the right relation is first scanned and loaded into a hash table, using its join attributes as hash keys. Next the left relation is scanned and the appropriate values of every row found are used as hash keys to locate the matching rows in the table.
set enable_hashjoin=on;
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM COMPANY JOIN DEPARTMENT ON DEPARTMENT.emp_id = COMPANY.ID WHERE company."id" = 1;

EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM COMPANY JOIN DEPARTMENT ON DEPARTMENT.emp_id = COMPANY.ID WHERE company.age = 32;

First, scan sequentially department surface structure hash surface key=department.emp_id That is, the associated field ,
And then sequential scanning company surface use company surface Id To match hash surface key If the match is successful The output .
hash join and merge join Both associated tables are scanned only once , nested loop join Is scanned once by one of the associated tables , ( If the scan result of the previous table has multiple rows output ) The other scans many times .
HASH JOIN principle
Refer to hash join Implementation source code :
Take the associated fields of the main drive table as key, The fields required by the master driver table are used as value To build hash surface .
Traverse every row of the driven table Calculate whether the line is consistent with hash In the table key identical If key The same will be driven by the corresponding fields and hits of the table hash surface key Corresponding value Output together , As a line in the result . because hash The use of a watch , The search time complexity of each row of the driven table is constant .
for (j = 0; j < length(inner); j++)
hash_key = hash(inner[j]);
append(hash_store[hash_key], inner[j]);
for (i = 0; i < length(outer); i++)
hash_key = hash(outer[i]);
for (j = 0; j < length(hash_store[hash_key]); j++)
if (outer[i] == hash_store[hash_key][j])
output(outer[i], inner[j]);
Explain the following :
// utilize inner surface , To construct the hash surface ( Put it in memory )
for (j = 0; j < length(inner); j++)
{
hash_key = hash(inner[j]);
append(hash_store[hash_key], inner[j]);
}
// Yes outer Every element of the table , Traversal
for (i = 0; i < length(outer); i++)
{
// Get outer In the table Some element , Conduct hash operation , Get it hash_key value
hash_key = hash(outer[i]);
// Use the one just got above hash_key value , Come on Yes hash table Probe ( Assume hash This is in the table key value )
// use length (hash_store[hash_Key]) Because ,hash The algorithm is constructed hash After the table , There may be a key There are multiple elements at the value .
// Yes Have the same Of ( Here is the operation just above , specific )hash_key Traversal of each element of value
for (j = 0; j < length(hash_store[hash_key]); j++)
{
// If a match is found , Then output a line of results
if (outer[i] == hash_store[hash_key][j])
output(outer[i], inner[j]);
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

嵌入式开发:技巧和窍门——提高嵌入式软件代码质量的7个技巧
保证接口数据安全的10种方案

Use blocconsumer to build responsive components and monitor status at the same time

B站大量虚拟主播被集体强制退款:收入蒸发,还倒欠B站;乔布斯被追授美国总统自由勋章;Grafana 9 发布|极客头条
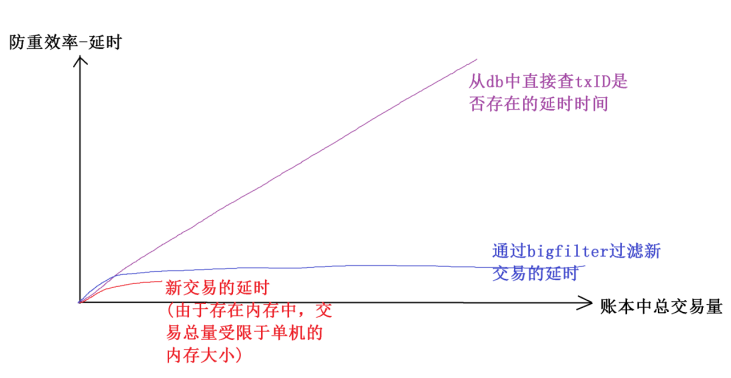
BigFilter全局交易防重组件的介绍与应用
【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 003-IDE的安装和基本使用

能源势动:电力行业的碳中和该如何实现?
i. Mx6ull driver development | 24 - platform based driver model lights LED
可视化任务编排&拖拉拽 | Scaleph 基于 Apache SeaTunnel的数据集成

More than 30 institutions jointly launched the digital collection industry initiative. How will it move forward in the future?
随机推荐
WebGIS framework -- kalrry
Nat. Commun.| 机器学习对可突变的治疗性抗体的亲和力和特异性进行共同优化
HBuilder X 常用的快捷键
Implementation rules for archiving assessment materials of robot related courses 2022 version
Tiktok actual combat ~ the number of comments is updated synchronously
Common open source codeless testing tools
PMO:比较25种分子优化方法的样本效率
国产数据库乱象
Logo special training camp section 1 Identification logo and logo design ideas
With this PDF, we finally got offers from eight major manufacturers, including Alibaba, bytek and Baidu
广电五舟与华为签署合作协议,共同推进昇腾AI产业持续发展
Jvm-Sandbox-Repeater的部署
面试题 01.01. 判定字符是否唯一
并发网络模块化 读书笔记转
如何实现轻松管理1500万员工?
Cadre WebGIS - kalrry
ApacheCN 翻译、校对、笔记整理活动进度公告 2022.7
卷积神经网络模型之——LeNet网络结构与代码实现
Relational database
php短视频源码,点赞时会有大拇指动画飘起

