当前位置:网站首页>[acwing] solution of the 58th weekly match
[acwing] solution of the 58th weekly match
2022-07-04 22:12:00 【Xuanche_】
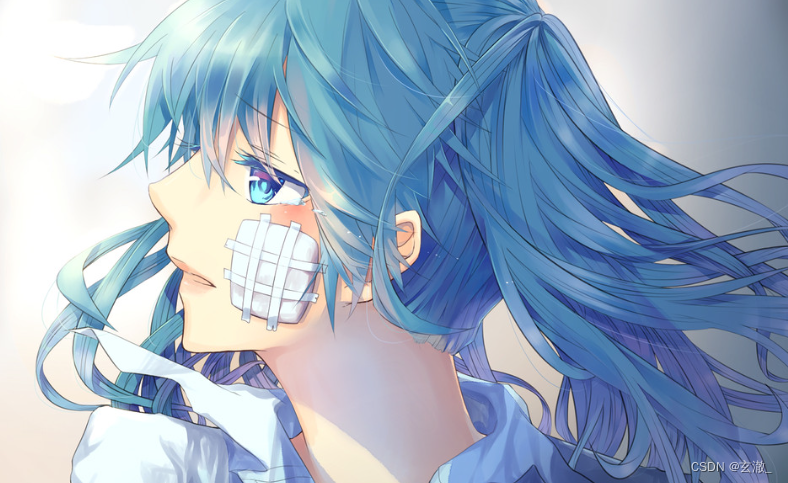

AcWing 4488. seek 1
AC Code
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; bool f = false; while(n -- ) { int num; cin >> num; if(num == 1) f = true; } if(f) puts("YES"); else puts("NO"); return 0; }
AcWing 4489. The longest subsequence
sample input 1:
10 1 2 5 6 7 10 21 23 24 49sample output 1:
4sample input 2:
5 2 10 50 110 250sample output 2:
1sample input 3:
6 4 7 12 100 150 199sample output 3:
3
Make full use of Strictly monotonically increasing This condition
about  , The next satisfied number should meet these two conditions
, The next satisfied number should meet these two conditions
We can know from monotonicity , The scope of completely covers
The scope of completely covers  , So choosing the following number can make the selection range larger
, So choosing the following number can make the selection range larger
Sum up , When the following number is less than or equal to twice the previous number , This number is required ( greedy )
AC Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200010;
int a[N];
int main()
{
int res = 0;
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int j = i + 1;
while(a[j] <= 2 * a[j - 1] && j < n) j ++ ; j -- ;
res = max(res, j - i + 1);
i = j;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}AcWing 4490. dyeing
sample input 1:
6 1 2 2 1 5 2 1 1 1 1 1sample output 1:
3sample input 2:
7 1 1 2 3 1 4 3 3 1 1 1 2 3sample output 2:
5
Because the dyeing operation has Coverage , And for a tree ( Son ) Root node of tree Only at the root node This can dye it
If you dye from child nodes , Finally, the coloring when reaching the root node will overwrite the previous operation , dissatisfaction At least operation This is the nature of
So we need to dye from the root node , And then on and on Recursively process each child node to the leaf node ( Greedy thought )
- If the child node and the parent node Same color , There is no need to repeat dyeing
- If the child node and the parent node Different colors , You need one more dyeing operation , ret ++
AC Code
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int n;
int e[N], ne[N], h[N], idx;
int w[N];
int ret;
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
if(u == 1) ret ++ ;
// Leaf nodes
if(h[u] == -1) return;
for(int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
// Root node
int j = e[i];
if(h[j] == -1)
{
if(w[j] != w[u]) ret ++ ;
}
else
{
// Not the root node
if(w[j] != w[u]) ret ++ ;
dfs(j);
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int p; cin >> p;
add(p, i);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> w[i];
}
dfs(1);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- 一文掌握数仓中auto analyze的使用
- HBuilder X 常用的快捷键
- Hash table
- Master the use of auto analyze in data warehouse
- Nat. Commun.| Machine learning jointly optimizes the affinity and specificity of mutagenic therapeutic antibodies
- 傳智教育|如何轉行互聯網高薪崗比特之一的軟件測試?(附軟件測試學習路線圖)
- leetcode 72. Edit Distance 编辑距离(中等)
- # 2156. Find the substring of the given hash value - post order traversal
- Exclusive interview of open source summer | new committer Xie Qijun of Apache iotdb community
- 【Acwing】第58场周赛 题解
猜你喜欢
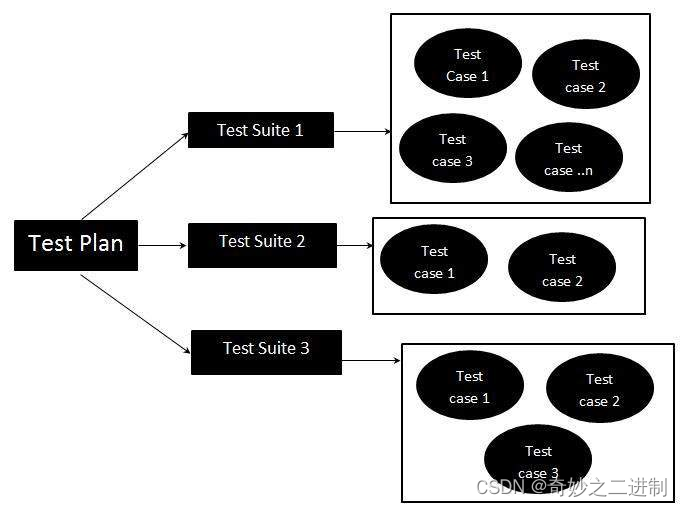
gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(3)什么是test suite和test case
凭借了这份 pdf,最终拿到了阿里,字节,百度等八家大厂 offer
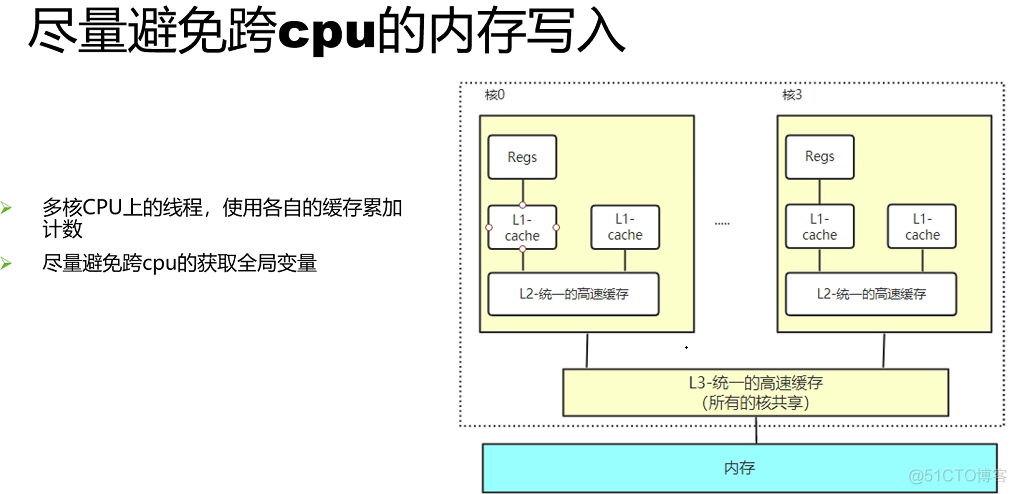
并发优化总结
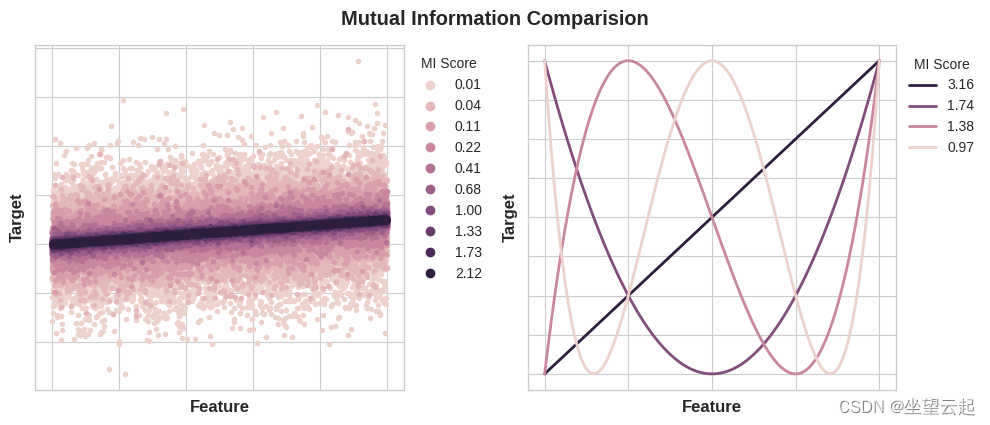
Machine learning notes mutual information

Nat. Commun.| 机器学习对可突变的治疗性抗体的亲和力和特异性进行共同优化

能源势动:电力行业的碳中和该如何实现?
常用的开源无代码测试工具
![[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox](/img/ef/65379499df205c068ee9bc9df797ac.png)
[optimtool.unconstrained] unconstrained optimization toolbox
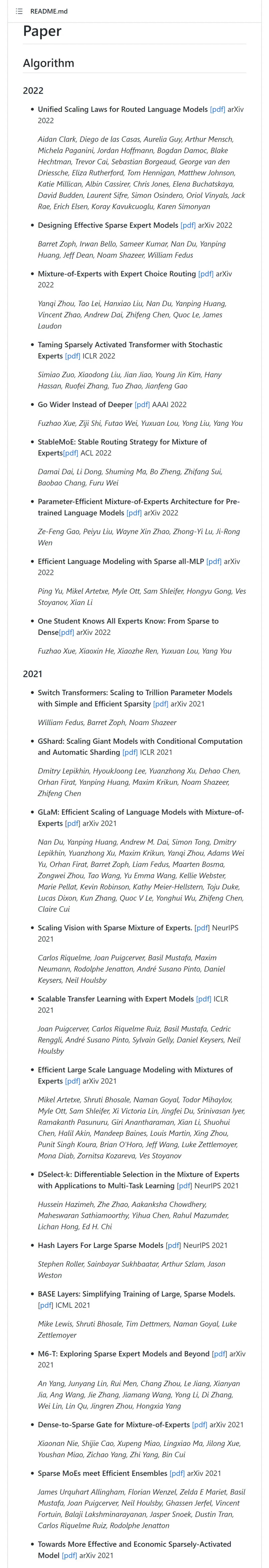
Sorting and sharing of selected papers, systems and applications related to the most comprehensive mixed expert (MOE) model in history
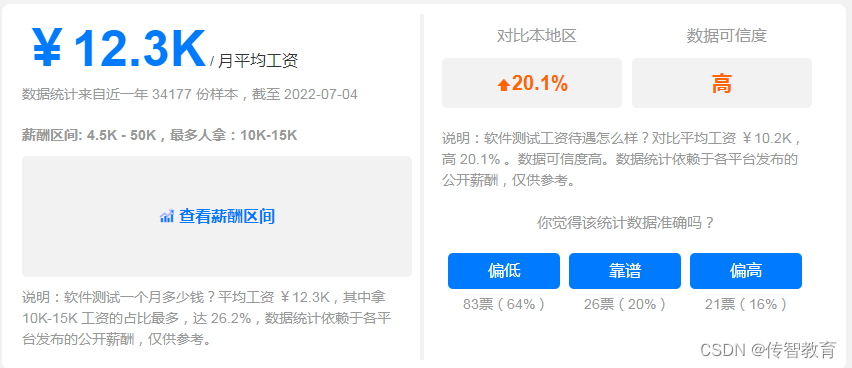
Éducation à la transmission du savoir | Comment passer à un test logiciel pour l'un des postes les mieux rémunérés sur Internet? (joindre la Feuille de route pour l'apprentissage des tests logiciels)
随机推荐
TLA+ 入门教程(1):形式化方法简介
面试题 01.08. 零矩阵
时空预测3-graph transformer
智洋创新与华为签署合作协议,共同推进昇腾AI产业持续发展
283. Moving zero-c and language assisted array method
开户哪家券商比较好?网上开户安全吗
Machine learning notes mutual information
Locust性能测试 —— 环境搭建及使用
Exclusive interview of open source summer | new committer Xie Qijun of Apache iotdb community
【Acwing】第58场周赛 题解
Enabling digital economy Fuxin software attends the BRICs high level Forum on Sustainable Development
从RepVgg到MobileOne,含mobileone的代码
能源势动:电力行业的碳中和该如何实现?
大厂的广告系统升级,怎能少了大模型的身影
KDD2022 | 什么特征进行交互才是有效的?
Use blocconsumer to build responsive components and monitor status at the same time
QT - plot other problems
NAACL-22 | 在基于Prompt的文本生成任务上引入迁移学习的设置
机器人相关课程考核材料归档实施细则2022版本
服务线上治理



