当前位置:网站首页>Handler message mechanism - FWK layer
Handler message mechanism - FWK layer
2022-07-26 01:20:00 【xhBruce】
Handler Message mechanism -FWK layer
android12-release
1. Function introduction summary
1.1 Introduction summary
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Handler.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Message.java
Activity in UI Information transmission in components Handler,Android For thread safety , We are not allowed to UI Out of thread operation UI; Many times we need to refresh the interface through Handler To inform UI Component update ! In addition to using Handler Complete the interface update , You can also use runOnUiThread() To update , Even more advanced transaction bus , Of course , Here we only talk about Handler.
When our child thread wants to modify Activity Medium UI When the component , We can build a new Handler object , Send information to the main thread through this object ; The information we send will go to the main thread first MessageQueue Wait for , from Looper Take out in first in first out order , According to message Object's what Attributes are distributed to the corresponding Handler To deal with !
Handler: The function is to send and process information , If you want to Handler Normal work , There must be a in the current thread Looper objectMessage: Handler Received and processed message objectsMessageQueue: Message queue , FIFO management Message, Initializing Looper Object creates an associated MessageQueueLooper: Each thread can only have one Looper, management MessageQueue, Keep taking it out Message Distribute to the corresponding Handler Handle
1.2 Use cases
UI Thread is our main thread , The system is creating Activity UI Thread will initialize a Looper object , It also creates a MessageQueue
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
final Handler myHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
For use in sub lines, you need to execute Looper.prepare() Initialize a Looper object ,Looper We'll create a MessageQueue object , then Looper Object is saved to the current thread TLS.Looper.prepare() Only one execution per thread is allowed .
class SubThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
//TODO Define message processing logic .
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
1.2.1 UI Thread initialization Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper()stay fork Create create process callbackActivityThread.main(),Activity UI Thread initializes a Looper object
- prepare(false) At present Looper You are not allowed to exit , That is, the main line Looper No exit allowed ;
prepare()Default call prepare(true), It means this Looper Allow to exit .
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ... ...
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// ... ...
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
1.3 Approximate process
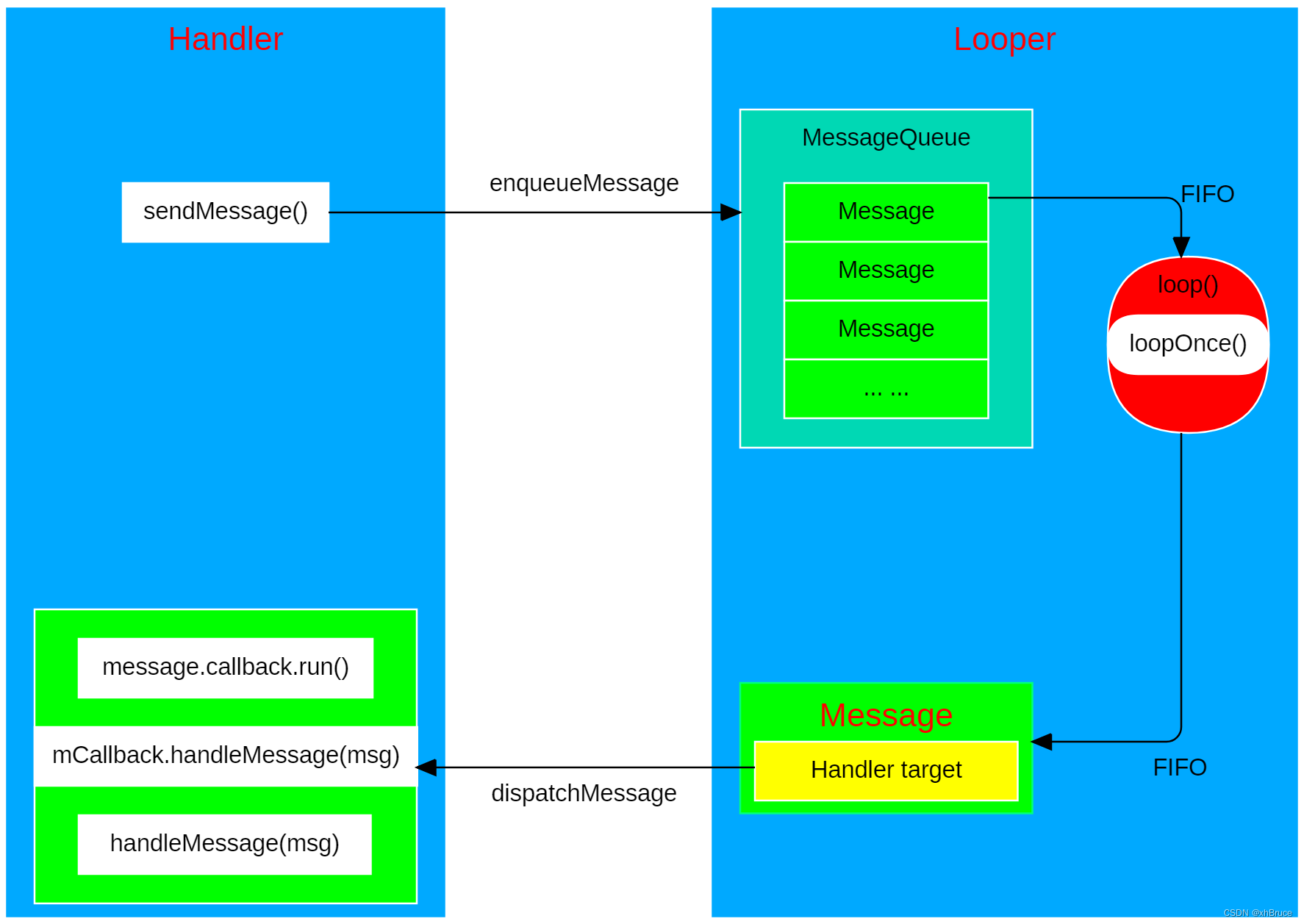
2. Process analysis
2.1 The general relationship between related classes
- Handler contain Loooper and MessageQueue
- Looper contain MessageQueue
- MessageQueue contain Message; Here we need to pay attention to
mPtr = nativeInit(), Connect Native layer - Message contain Handler, Use
Handler.obtainMessage()obtain
2.2 obtainMessage obtain Message
above 1.2 Use cases Said initialization precautions , Here's to say Message obtain
In the use of Handler when , Usually by Handler.obtainMessage() To get Message Object's , And its internal call is Message.obtain() Method , So here comes the question , Why not directly new One Message, But through Message Static method of obtain() To get it ?
Use obtain obtain Message The object is because Message Internally maintains a data cache pool , The recycling Message Will not be destroyed immediately , Instead, it is put into the cache pool , In obtaining Message It will get from the cache pool first , The cache pool is null To create a new Message.

There will also be Handler Give to the Message, If the cache pool is null Or directly
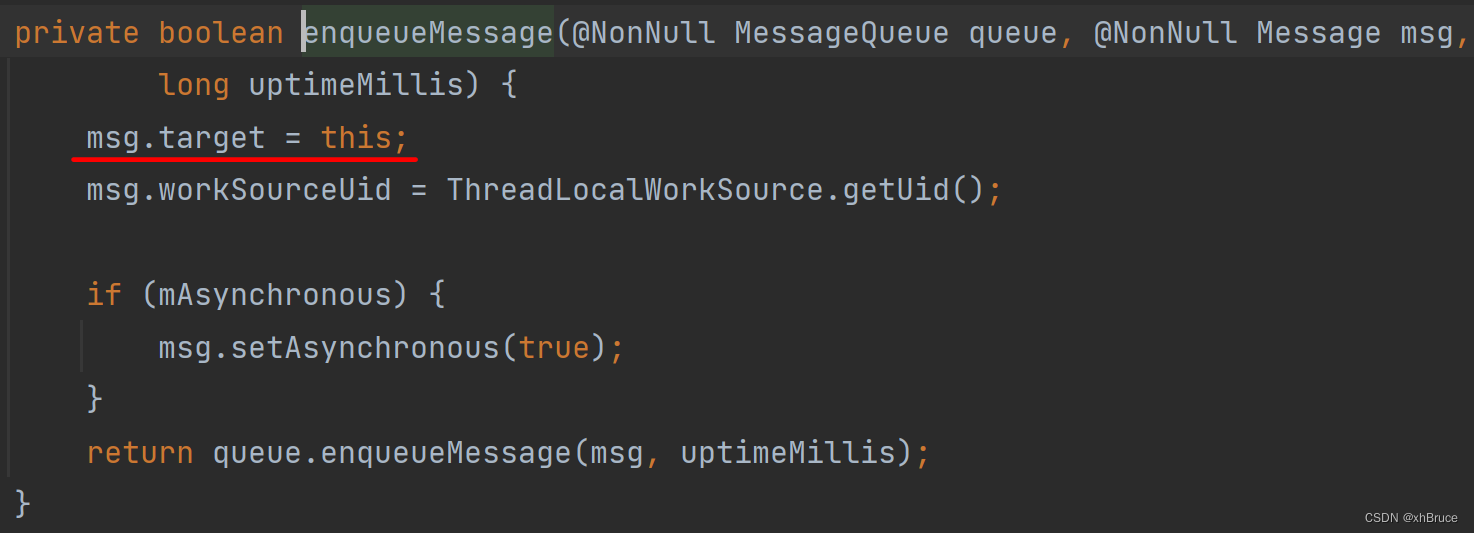
new Message(),Message Medium variabletarget:HandlerWill also be inHandler.sendMessage(msg)It's assignment
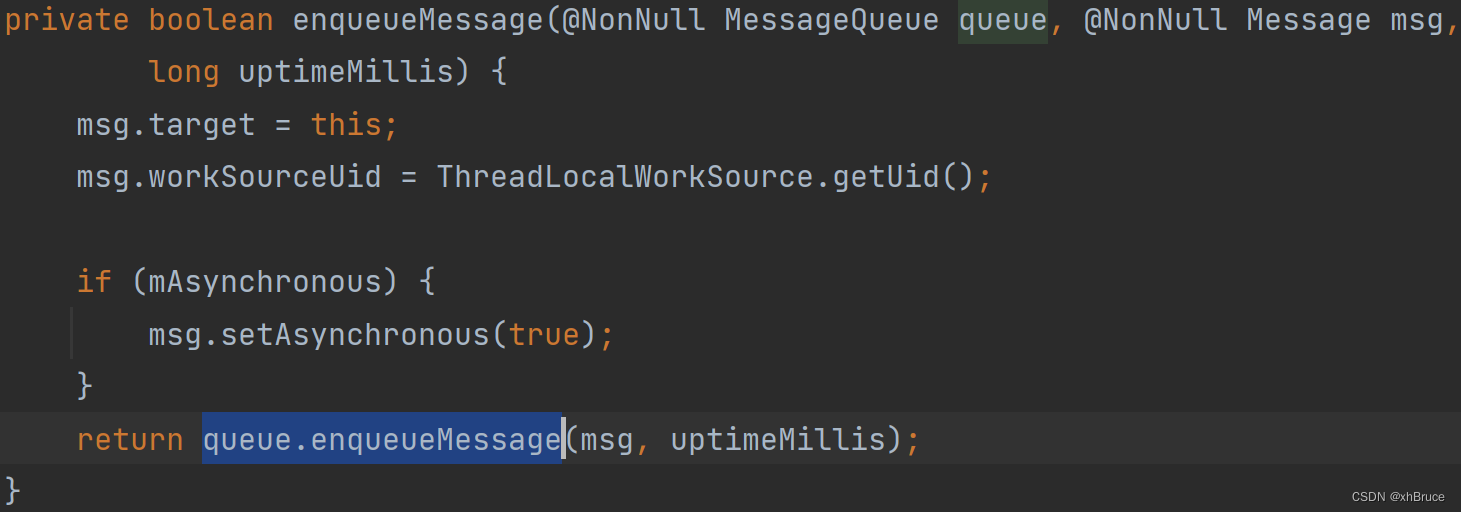
2.3 message sending sendMessage、Looper.loop Processing target handler.dispatchMessage
Handler Message sending will eventually call
MessageQueue.enqueueMessage():handler.sendMessage --> sendMessageDelayed --> sendMessageAtTime --> enqueueMessage --> queue.enqueueMessage
loop() Enter cycle mode , Keep repeating the following , Exit the loop until there is no message
- Read MessageQueue The next one Message;
- hold Message Distribute to the appropriate Handler target;
msg.recycleUnchecked()Give out the Message Recycle to message pool , To reuse .
private static boolean loopOnce(final Looper me,
final long ident, final int thresholdOverride) {
Message msg = me.mQueue.next(); // might block
// ... ...
final Observer observer = sObserver;
// ... ...
if (observer != null) {
token = observer.messageDispatchStarting();
}
long origWorkSource = ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(msg.workSourceUid);
try {
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (observer != null) {
observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);
}
dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
} catch (Exception exception) {
if (observer != null) {
observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);
}
throw exception;
} finally {
// ... ...
}
// ... ...
msg.recycleUnchecked();
return true;
}
2.4 Looper Wake up the (MessageQueue Connect Native layer )
- sendMessage Can be triggered when
nativeWake(mPtr) Message msg = me.mQueue.next()loop() obtain MessageQueue Triggered when messages are queuednativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis)
It's all through MessageQueue call native Layer
mLooper->wake()\mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis)
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Handler.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
// ... ...
synchronized (this) {
// ... ...
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting is false.
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
return true;
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Looper.java
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/MessageQueue.java
private static boolean loopOnce(final Looper me,
final long ident, final int thresholdOverride) {
Message msg = me.mQueue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null) {
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return false;
}
// ... ...
}
Message next() {
// ... ...
for (;;) {
// ... ...
nativePollOnce(ptr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);
// ... ...
}
}
2.4 removeMessages remove Message
- Final execution
Message.recycleUnchecked();Message Not destroyed immediately , Instead, it is put into the cache poolsPool, Cache pool sizeMAX_POOL_SIZE = 50, In obtaining Message It will get from the cache pool first .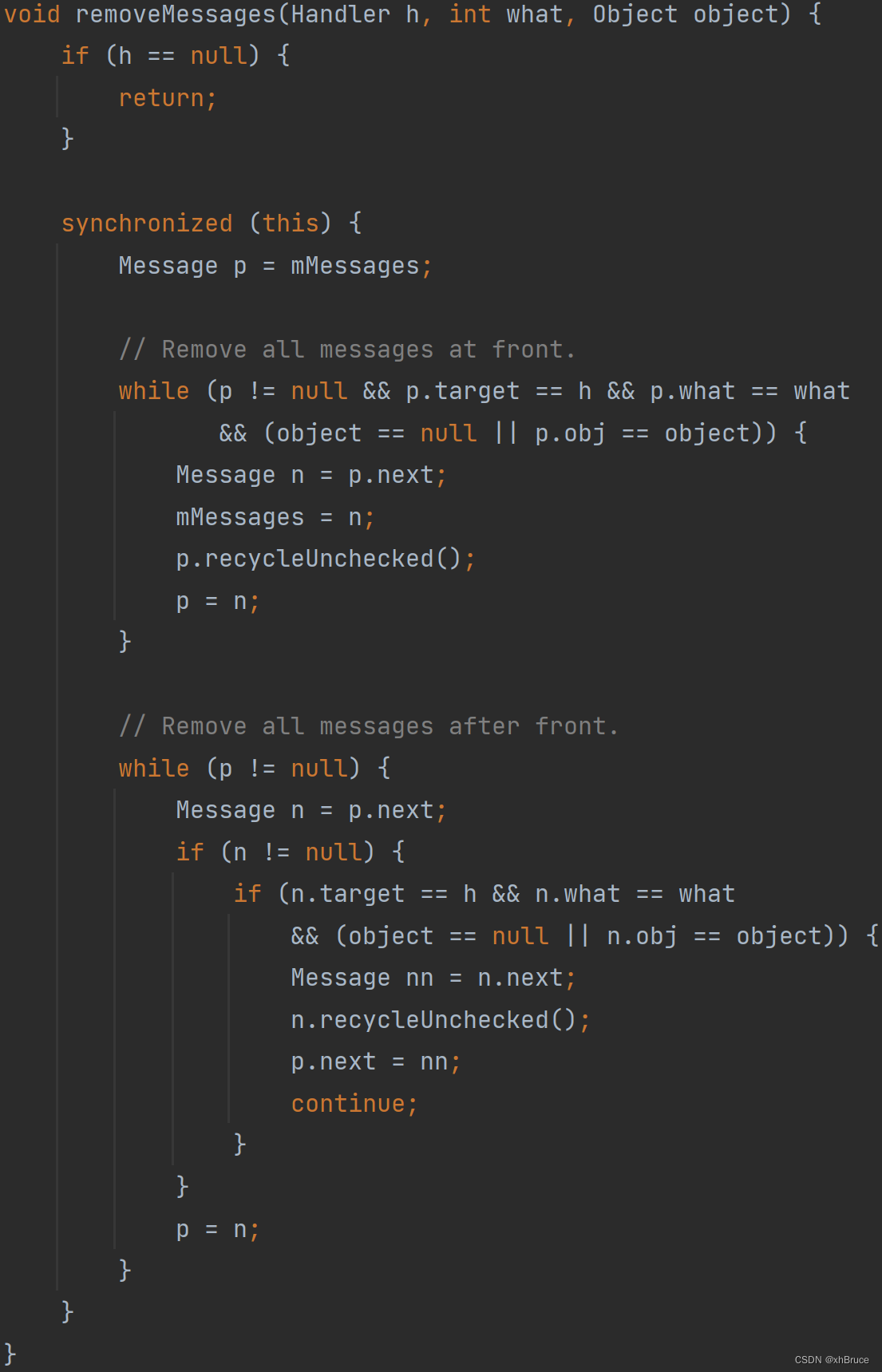
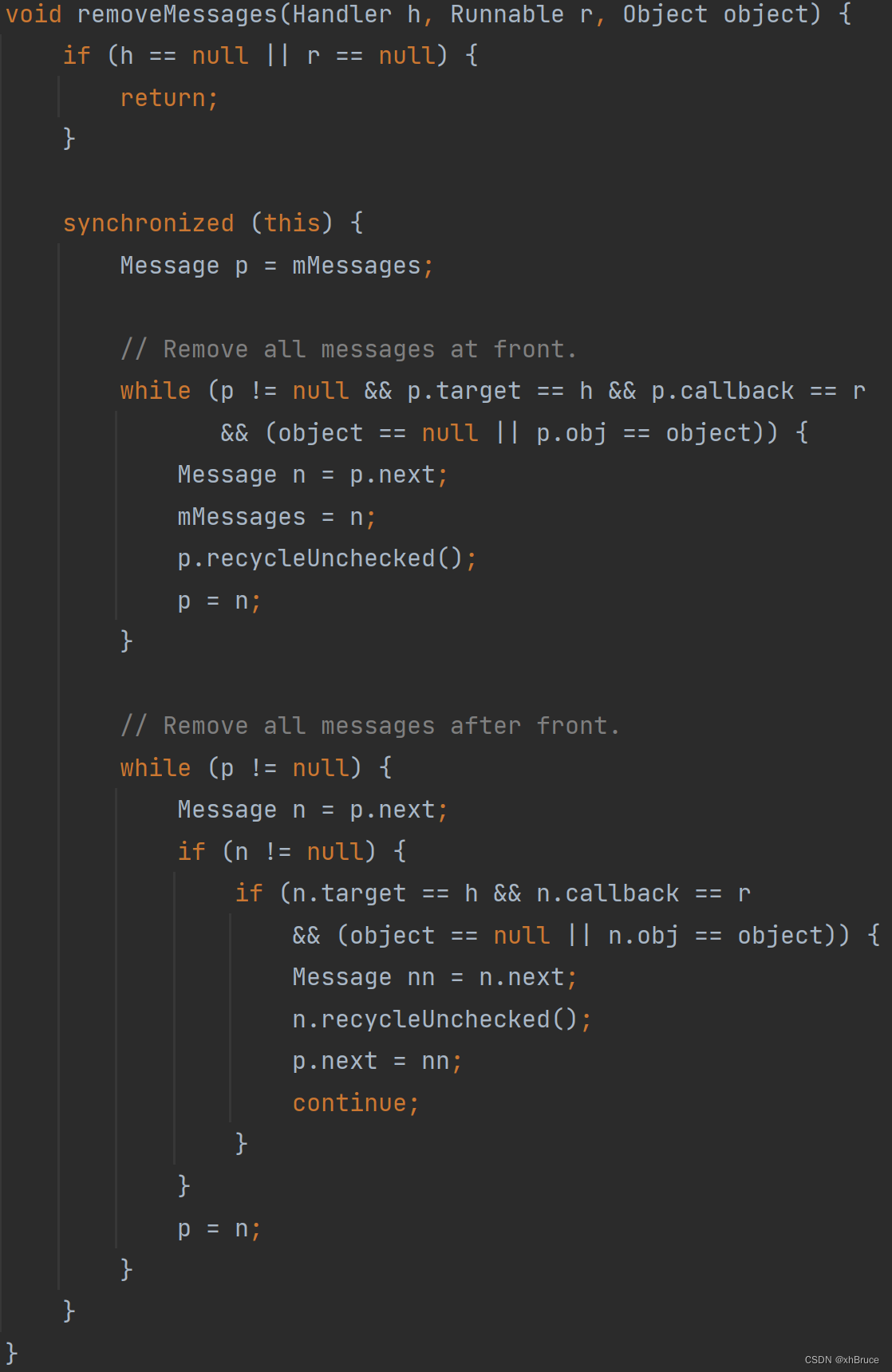
void recycleUnchecked() {
// Mark the message as in use while it remains in the recycled object pool.
// Clear out all other details.
flags = FLAG_IN_USE;
what = 0;
arg1 = 0;
arg2 = 0;
obj = null;
replyTo = null;
sendingUid = UID_NONE;
workSourceUid = UID_NONE;
when = 0;
target = null;
callback = null;
data = null;
synchronized (sPoolSync) {
if (sPoolSize < MAX_POOL_SIZE) {
next = sPool;
sPool = this;
sPoolSize++;
}
}
}
3. MessageQueue Connect Native layer To be continued ~
Take a look at the general process 
边栏推荐
- C语言进阶(一)动态分配内存
- Prime Ring Problem
- ORACLE——iSupplier 门户开票错误
- U++学习笔记 UStruct、UEnum声明以及函数库简单函数实现
- Machine learning: Bayesian Networks
- Kubernetes pod start process
- Arthas watch 命令查看数组中对象的属性
- NodeJS 基于 Dapr 构建云原生微服务应用,从 0 到 1 快速上手指南
- [software development specification iv] application system security coding specification
- MulDA: A Multilingual Data Augmentation Framework for Low-Resource Cross-Lingual NER 阅读笔记
猜你喜欢

Detailed explanation of redis data structure, combined with books

Arthas watch command to view the properties of objects in the array

Introduction to API testing

NLP introduction + practice: Chapter 4: using pytorch to manually realize linear regression

What if win11 cannot open its own anti-virus software? Win11's built-in anti-virus function cannot be turned on

Detailed explanation of rest assured interface testing framework
网络性能评估工具 ping/mtr
![[RTOS training camp] learn C language from a higher perspective](/img/4c/bbbec489abb781a1de1e99bbf12c6f.png)
[RTOS training camp] learn C language from a higher perspective

机器学习:贝叶斯网络

Kubernetes Pod启动流程
随机推荐
Dot screen precautions
Small sample learning data set
NIO简易示例
Zombie‘s Treasure Chest(枚举)
Gcdqueue encapsulation
光纤通信中信号劣化的原因
Oracle - isupplier portal Invoicing error
Fastjason handles generics
"Yuanqi Cola" is not the end point, "China Cola" is
动态IP地址是什么?为什么大家会推荐用动态ip代理?
FastJson 处理泛型
Small sample learning - getting started
换ip软件的用途很广及原理 动态IP更换的四种方法来保护网络隐私
【纪中】2022.7.16 1432.输油管道
Causes of signal degradation in optical fiber communication
Handler消息机制-FWK层
Introduction to API testing
TV software burning
Leetcode 537. 复数乘法(网友思路,自愧不如)
Tencent employees' salary: the real 985 graduation salary, do you think I can be saved? Netizen: daily salary?