当前位置:网站首页>[combinatorics] recursive equation (summary of the solution process of recursive equation | homogeneous | double root | non-homogeneous | characteristic root is 1 | exponential form | the bottom is th
[combinatorics] recursive equation (summary of the solution process of recursive equation | homogeneous | double root | non-homogeneous | characteristic root is 1 | exponential form | the bottom is th
2022-07-03 17:24:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 The solution process of linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients
- Two 、 The solution process of linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ( General solution form with multiple roots )
- 3、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form (
n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial | The characteristic root is not
1
1
1 )
- Four 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form (
n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial | The characteristic root is
1
1
1 )
- 5、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( The nonhomogeneous part is exponential | The bottom is not the characteristic root )
- 6、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( The nonhomogeneous part is exponential | The bottom is the characteristic root )
Solution of recurrence equation :

One 、 The solution process of linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients
The solution process of linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients :
1 . Characteristic equation :
( 1 ) The standard form of recurrence equation : Write the recurrence equation Standard form , All items are to the left of the equal sign , On the right is
0
0
0 ;
( 2 ) Number of terms of characteristic equation : determine Number of terms of characteristic equation , And The recurrence equation has the same number of terms ;
( 3 ) The characteristic equation is sub idempotent : The highest power is Number of terms of characteristic equation
−
1
-1
−1 , Lowest power
0
0
0 ;
( 4 ) Write There is no coefficient The characteristic equation of ;
( 5 ) The coefficients of the recursive equation will be deduced bit by bit Copy Into the characteristic equation ;
2 . Solution characteristic root : take Characteristic equation Characteristic root Work it out ,
x
=
−
b
±
b
2
−
4
a
c
2
a
x = \cfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
x=2a−b±b2−4ac
3 . Construct the general solution of recurrence equation :
( 1 ) No double root : structure
c
1
q
1
n
+
c
2
q
2
n
+
⋯
+
c
k
q
k
n
c_1q_1^n + c_2q_2^n + \cdots + c_kq_k^n
c1q1n+c2q2n+⋯+ckqkn Linear combination of forms , This linear combination is the of recursive equations general solution ;
( 2 ) Double root : Refer to the following “ The general solution form under the double root is listed ” Content ;
4 . Find the constant in the general solution :
( 1 ) Substitute the initial values to obtain the equations : Substitute the initial value of the recursive equation into the general solution , obtain
k
k
k individual
k
k
k Finite element equations , adopt Solve the equations , obtain Constants in general solutions ;
( 2 ) Substitute constants to obtain the general solution : Substitute constants into the general solution , You can get the final solution of the recursive equation ;
Recurrence equation -> Characteristic equation -> Characteristic root -> general solution -> Substitute the initial value to find the general solution constant
Two 、 The solution process of linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ( General solution form with multiple roots )
1 . Number of characteristic elements :
q
1
,
q
2
,
⋯
,
q
t
q_1, q_2, \cdots , q_t
q1,q2,⋯,qt Is the characteristic root of recursive equation , Unequal characteristic roots
t
t
t ;
2 . according to Characteristic root Write the items in the general solution
H
i
(
n
)
H_i(n)
Hi(n) : Characteristic root
q
i
q_i
qi , Repeatability
e
i
e_i
ei , among
i
i
i The value is
0
0
0 To
t
t
t; The first
i
i
i The general solution term corresponding to characteristic roots , Write it down as
H
i
(
n
)
H_i(n)
Hi(n) ;
( 1 ) form : Coefficient term multiply
q
i
n
q_i^n
qin ;
( 2 ) Coefficient term :
① Number : Yes
e
i
e_i
ei term ; Number of coefficient terms , Is the repeatability of the characteristic root ;
② form : constant multiply
n
n
n Power of power ; Such as :
n
e
i
−
1
n^{e_i-1}
nei−1 , Here you are
e
i
e_i
ei It's a constant ;
③ constant : The constant subscript is from
c
i
1
c_{i1}
ci1 To
c
i
e
i
c_{ie_i}
ciei , The right part of the subscript is
1
1
1 To
e
i
e_i
ei ;
④
n
n
n Power of power : The value of power is from
0
0
0 To
e
i
−
1
e_i - 1
ei−1 ;
⑤ Suggested arrangement : constant and The next power , It's best to arrange them from small to large , Constant subscript And
n
n
n The power of Difference between
1
1
1 ;
( 3 ) General explanation
i
i
i term :
H
i
(
n
)
=
(
c
i
1
+
c
i
2
n
+
⋯
+
c
i
e
i
n
e
i
−
1
)
q
i
n
H_i(n) = (c_{i1} + c_{i2}n + \cdots + c_{ie_i}n^{e_i - 1})q_i^n
Hi(n)=(ci1+ci2n+⋯+cieinei−1)qin
3 . Write a general solution :
( 1 ) Number of general solutions : Number of characteristic elements
t
t
t ;
( 2 ) General solution composition : The general solution term corresponding to each characteristic root , Put it all together , Is the complete general solution ;
( 3 ) final result :
H
(
n
)
=
∑
i
=
1
t
H
i
(
n
)
H(n) = \sum\limits_{i=1}^tH_i(n)
H(n)=i=1∑tHi(n)
3、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial | The characteristic root is not
1
1
1 )
1 . Special solution form :
( 1 ) Special solution form : Special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
H^*(n)
H∗(n) yes
n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial ,
n
n
n The power of is taken from
0
0
0 To
t
t
t , Therefore, its Number of items
t
+
1
t+1
t+1 term ;
( 2 ) Understand each component :
① Number of items :
t
+
1
t+1
t+1 term
② form : The special solution term consists of constant multiply
n
n
n Power of power form , Constants are unknown ;
③ constant :
t
+
1
t+1
t+1 It's a constant , Use subscripts to identify ;
④
n
n
n The power of : The power value is from
0
0
0 To
t
t
t ;
2 . give an example : Special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
H^*(n)
H∗(n) yes
n
n
n Of
2
2
2 Sub polynomial ;
Number of special solutions : be Number of special solutions yes
2
+
1
=
3
2 + 1 = 3
2+1=3 term ;
Understand each component : Each term is explained by constant multiply
n
n
n Power of power form ,
3
3
3 It's a constant Set to
P
1
,
P
2
,
P
3
P_1, P_2, P_3
P1,P2,P3 ,
3
3
3 individual
n
n
n Power of power , Power value from
0
0
0 To
2
2
2 ,
Therefore, the form of the special solution is
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
1
n
2
+
P
2
n
1
+
P
3
n
0
H^*(n) = P_1n^2 + P_2n^1 + P_3n^0
H∗(n)=P1n2+P2n1+P3n0 ,
It is reduced to :
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
1
n
2
+
P
2
n
+
P
3
H^*(n) = P_1n^2 + P_2n + P_3
H∗(n)=P1n2+P2n+P3
Four 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial | The characteristic root is
1
1
1 )
Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients :
H
(
n
)
−
a
1
H
(
n
−
1
)
−
⋯
−
a
k
H
(
n
−
k
)
=
f
(
n
)
H(n) - a_1H(n-1) - \cdots - a_kH(n-k) = f(n)
H(n)−a1H(n−1)−⋯−akH(n−k)=f(n) ,
n
≥
k
,
a
k
≠
0
,
f
(
n
)
≠
0
n\geq k , a_k\not= 0, f(n) \not= 0
n≥k,ak=0,f(n)=0
The left side of the above equation And “ Linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” It's the same , But not on the right
0
0
0 , It's based on
n
n
n Of function
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) , This type of recursive equation is called “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” ;
Special solutions and “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” The right part of
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) of ,
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) by
n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial ,
If homogeneous part Characteristic root Not for
1
1
1 , Then the special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
H^*(n)
H∗(n) also yes
n
n
n Of
t
t
t Sub polynomial ;
If homogeneous part Characteristic root by
1
1
1 , The repeatability is
e
e
e , Then the special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
H^*(n)
H∗(n) also yes
n
n
n Of
t
+
e
t + e
t+e Sub polynomial ;
The power of increase is Characteristic root
1
1
1 The repeatability of , If the repetition is
2
2
2 , You need to improve
2
2
2 The next power ;
In order to solve the above problems , Here we need to
n
n
n To the power of
1
1
1 , Let the first power term in the form of special solution , Set to square , The constant term is not set , Even if it is set, it will offset , Cannot find the value of the constant term ;
5、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( The nonhomogeneous part is exponential | The bottom is not the characteristic root )
Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients :
H
(
n
)
−
a
1
H
(
n
−
1
)
−
⋯
−
a
k
H
(
n
−
k
)
=
f
(
n
)
H(n) - a_1H(n-1) - \cdots - a_kH(n-k) = f(n)
H(n)−a1H(n−1)−⋯−akH(n−k)=f(n) ,
n
≥
k
,
a
k
≠
0
,
f
(
n
)
≠
0
n\geq k , a_k\not= 0, f(n) \not= 0
n≥k,ak=0,f(n)=0
The left side of the above equation And “ Linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” It's the same , But not on the right
0
0
0 , It's based on
n
n
n Of function
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) , This type of recursive equation is called “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” ;
The non-homogeneous part is exponential :
If the above “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” Of Nonhomogeneous part
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) It's an exponential function ,
β
n
\beta^n
βn ,
If
β
\beta
β Not a characteristic root ,
Then the special solution form of the nonhomogeneous part is :
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
β
n
H^*(n) = P\beta^n
H∗(n)=Pβn ,
P
P
P Is constant ;
The above special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
β
n
H^*(n) = P\beta^n
H∗(n)=Pβn , Into the recursive equation , Solve the constant
P
P
P Value , Then the complete special solution is obtained ;
“ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” The general solution is
H
(
n
)
=
H
(
n
)
‾
+
H
∗
(
n
)
H(n) = \overline{H(n)} + H^*(n)
H(n)=H(n)+H∗(n)
Use the above solution Special solution , And recurrence equation General solution of homogeneous part , Form the complete general solution of the recursive equation ;
6、 ... and 、 Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients Special solution form ( The nonhomogeneous part is exponential | The bottom is the characteristic root )
Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients :
H
(
n
)
−
a
1
H
(
n
−
1
)
−
⋯
−
a
k
H
(
n
−
k
)
=
f
(
n
)
H(n) - a_1H(n-1) - \cdots - a_kH(n-k) = f(n)
H(n)−a1H(n−1)−⋯−akH(n−k)=f(n) ,
n
≥
k
,
a
k
≠
0
,
f
(
n
)
≠
0
n\geq k , a_k\not= 0, f(n) \not= 0
n≥k,ak=0,f(n)=0
The left side of the above equation And “ Linear homogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” It's the same , But not on the right
0
0
0 , It's based on
n
n
n Of function
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) , This type of recursive equation is called “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” ;
The nonhomogeneous part is Exponential function And The bottom is the case of characteristic root :
If the above “ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” Of Nonhomogeneous part
f
(
n
)
f(n)
f(n) It's an exponential function ,
β
n
\beta^n
βn ,
If
β
\beta
β yes
e
e
e Heavy characteristic root ,
The special solution form of the nonhomogeneous part is :
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
n
e
β
n
H^*(n) = P n^e \beta^n
H∗(n)=Pneβn ,
P
P
P Is constant ;
The above special solution
H
∗
(
n
)
=
P
n
e
β
n
H^*(n) = P n^e \beta^n
H∗(n)=Pneβn , Into the recursive equation , Solve the constant
P
P
P Value , Then the complete special solution is obtained ;
“ Linear Nonhomogeneous recurrence equation with constant coefficients ” The general solution is
H
(
n
)
=
H
(
n
)
‾
+
H
∗
(
n
)
H(n) = \overline{H(n)} + H^*(n)
H(n)=H(n)+H∗(n)
Use the above solution Special solution , And recurrence equation General solution of homogeneous part , Form the complete general solution of the recursive equation ;
边栏推荐
- One brush 142 monotone stack next larger element II (m)
- Dagong 21 autumn "power plant electrical part" online operation 1 [standard answer] power plant electrical part
- 【RT-Thread】nxp rt10xx 设备驱动框架之--Audio搭建和使用
- [combinatorics] recursive equation (characteristic equation and characteristic root | example of characteristic equation | root formula of monadic quadratic equation)
- [RT thread] NXP rt10xx device driver framework -- pin construction and use
- Collection of the most beautiful graduation photos in the graduation season, collection of excellent graduation photos
- kubernetes资源对象介绍及常用命令(四)
- AcWing 4489. Longest subsequence
- C language modifies files by line
- VM11289 WAService. js:2 Do not have __ e handler in component:
猜你喜欢
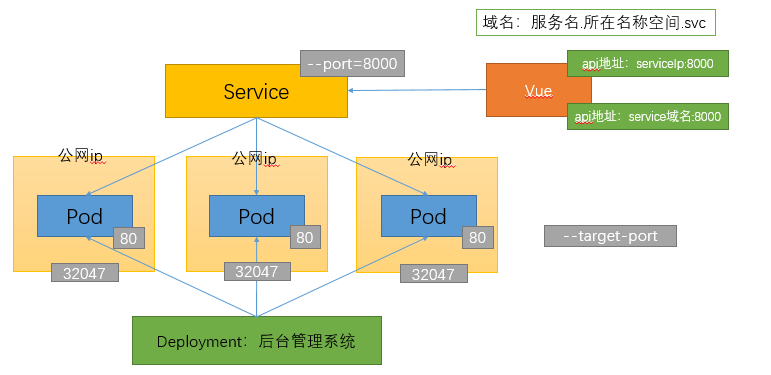
kubernetes资源对象介绍及常用命令(三)
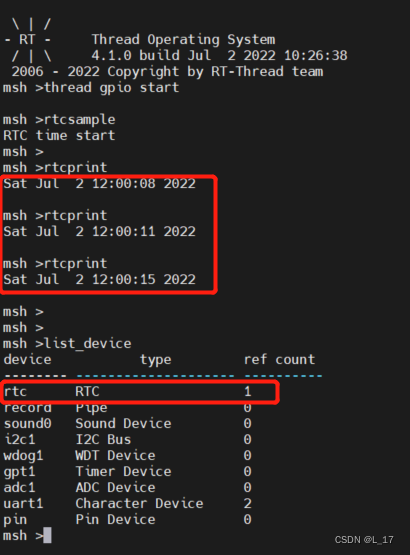
【RT-Thread】nxp rt10xx 设备驱动框架之--rtc搭建和使用
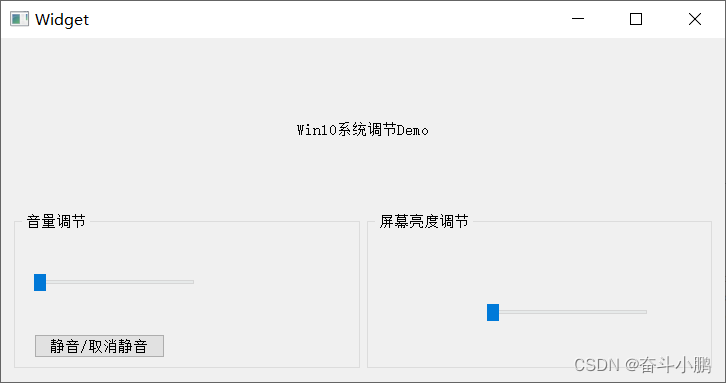
QT adjust win screen brightness and sound size
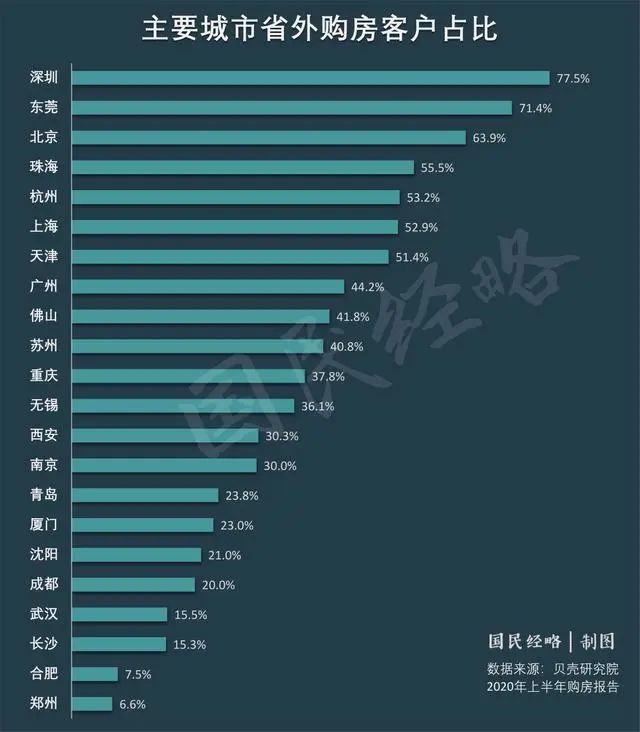
Great changes! National housing prices fell below the 10000 yuan mark

線程池:業務代碼最常用也最容易犯錯的組件
Golang unit test, mock test and benchmark test

Redis:关于列表List类型数据的操作命令
Free data | new library online | cnopendata complete data of China's insurance intermediary outlets

【RT-Thread】nxp rt10xx 设备驱动框架之--hwtimer搭建和使用

IntelliJ 2021.3 short command line when running applications
随机推荐
Pools de Threads: les composants les plus courants et les plus sujets aux erreurs du Code d'affaires
Kubernetes resource object introduction and common commands (V) - (NFS & PV & PVC)
The difference between i++ and ++i: tell their differences easily
AcWing 3438. Number system conversion
One brush 149 force deduction hot question-10 regular expression matching (H)
vs code 插件 koroFileHeader
[combinatorics] recursive equation (the problem of solving recursive equation with multiple roots | the problem is raised)
Apache服务挂起Asynchronous AcceptEx failed.
[RT thread] NXP rt10xx device driver framework -- pin construction and use
QT adjust win screen brightness and sound size
[RT thread] NXP rt10xx device driver framework -- RTC construction and use
Electronic technology 20th autumn "Introduction to machine manufacturing" online assignment 3 [standard answer]
SSH连接远程主机等待时间过长的解决方法
Web-ui automated testing - the most complete element positioning method
Qt调节Win屏幕亮度和声音大小
Examination questions for the assignment of selected readings of British and American Literature in the course examination of Fujian Normal University in February 2022
PHP online confusion encryption tutorial sharing + basically no solution
A day's work list of an ordinary programmer
[combinatorics] recursive equation (special solution example 1 Hannover tower complete solution process | special solution example 2 special solution processing when the characteristic root is 1)
Where is the database account used when running SQL tasks in data warehouse tasks configured