当前位置:网站首页>Luogu: p2685 [tjoi2012] Bridge
Luogu: p2685 [tjoi2012] Bridge
2022-07-03 17:09:00 【Elucidation】
Bridge

The question :
Boss Will guard a road , Make players from 1 Go to the n The shortest distance is as large as possible ;
Ideas :
obviously Boss Must guard 1 To n The shortest way , Otherwise, players can definitely take the shortest path .
So this problem becomes : Delete any edge on the shortest path , bring 1 To n The shortest distance is the largest
violence : We can certainly enumerate and delete every edge on the shortest path , Then run the shortest path again , But don't think the time complexity will explode ;
Then can we preprocess these situations , So you don't need to run the shortest circuit every time ?
The answer is yes :
- First of all 1、n Run for the starting point once each, the shortest way , In this way, we can get the graph formed by the interweaving of two shortest path trees ;
- Then we will start from the roots of these two shortest trees ( One left one right ) Run each time bfs, Record every point on the way from 1 ~ n Which point on the shortest path came from

Red is our shortest path , Green represents which point on the red side the point comes from ; With 1、n Run around for the root bfs, Every point has about l[i]、r[i] The mark of
- Since then, our pretreatment has been completed , You can find , Now we enumerate every edge that is not on the shortest path {a、b、w} , route {1 ~ n} It can be used {1 ~ l[a] ~ a ~ b ~ r[b] ~ n} Instead of
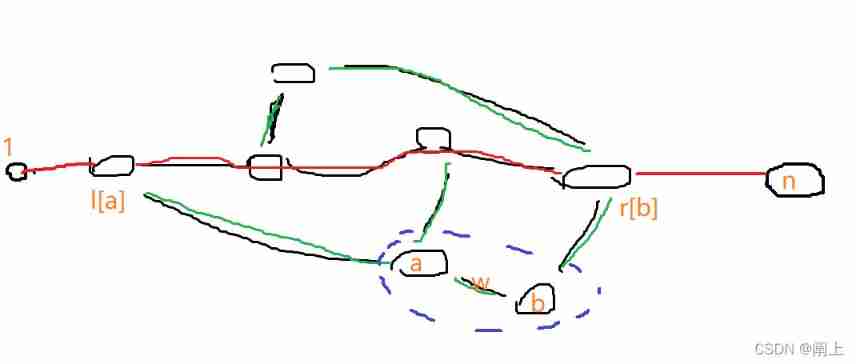
- What is the premise of this substitution ? Is the path {l[a] ~ r[b]} Any edge on the is occupied , When this path is occupied , We can use it dist1[a] + distn[b] + w Try to replace dist1[n]
- It can be found that this is an interval problem ,1 ~ n All the edges on the path are regarded as intervals , The information of interval maintenance is : When an edge in this interval is deleted, the 1 ~ n The shortest circuit value
- We can use segment tree to maintain this interval , Enumerate every side except the shortest path , For this side {a、b、w} , Modify on the segment tree {l[a],r[b]} Value
- Finally, traverse our segment tree , Take one of the information of each side in the end max That's our answer
See the notes for details
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a)
#define cinios (ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0))
#define sca scanf
#define pri printf
#define ul (u << 1)
#define ur (u << 1 | 1)
#define forr(a,b,c) for(int a=b;a<=c;a++)
#define rfor(a,b,c) for(int a=b;a>=c;a--)
//#define x first
//#define y second
//[ Blog address ](https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51797626?t=1)
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1, ch = getchar(); while (ch < '0' || ch>'9') {
if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); } return x * f; }
inline void write(int x) {
if (x < 0) putchar('-'), x = -x; if (x >= 10) write(x / 10); putchar(x % 10 + '0'); }
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 100010, M = 1000010, MM = N;
int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f, mod = 998244353;
ll LNF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, k, T, S, D;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx;
int dist1[N], distn[N], l[N], r[N];
bool st[N], isdis[M];
vector<int> arr;
int id[N], mx = -1, cnt;
inline void add(int a, int b, int x) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = x, h[a] = idx++;
}
void dj(int* d, int x) {
mem(st, 0);
d[x] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> q;
q.push({
0,x });
while (q.size())
{
int ver = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (st[ver])continue;
st[ver] = true;
for (int i = h[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[j] > d[ver] + w[i]) {
d[j] = d[ver] + w[i];
q.push({
d[j],j });
}
}
}
}
void bfs(int* l, int* d) {
queue<int> q;
for (auto j : arr) {
l[j] = j;
q.push(j);
}
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (d[t] + w[i] == d[j] && !l[j]) {
// Maintain on the shortest path tree l[i]、r[i]
l[j] = l[t];
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
struct tree
{
int l, r, w;
}tr[N << 2]; // Line segment tree board
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u] = {
l,r,INF };
if (l == r)return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(ul, l, mid), build(ur, mid + 1, r);
}
inline void pushdown(int u) {
tr[ul].w = min(tr[ul].w, tr[u].w);
tr[ur].w = min(tr[ur].w, tr[u].w);
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r, int d) {
if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r) {
tr[u].w = min(tr[u].w, d);// Not normally required pushdown
return;
}
int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
if (mid >= l)modify(ul, l, r, d);
if (mid < r)modify(ur, l, r, d);
}
void query(int u) {
if (tr[u].l == tr[u].r) {
if (mx < tr[u].w && tr[u].w != INF) {
mx = tr[u].w;
cnt = 1;
}
else if (mx == tr[u].w)cnt++;// Cumulative number of schemes
return;
}
pushdown(u);// At the end of the query pushdown that will do
query(ul); query(ur);
}
int main() {
cinios;
cin >> n >> m;
mem(h, -1);
forr(i, 1, m) {
int a, b, x;
cin >> a >> b >> x;
add(a, b, x), add(b, a, x);
}
mem(dist1, 0x3f);
mem(distn, 0x3f);
dj(distn, n);
dj(dist1, 1);// Two shortest paths
int z = 1;
arr.push_back(z);// Record path
while (z != n) {
for (int k = h[z]; ~k; k = ne[k]) {
int j = e[k];
if (distn[z] == distn[j] + w[k]) {
// Remember to run from leaves to roots , Otherwise, there will be mistakes if there are forks
z = j;
arr.push_back(z);
isdis[k] = isdis[k ^ 1] = true;// The marking point will be wrong , To mark edges
break;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < arr.size(); j++)
id[arr[j]] = j + 1;// Discrete to points on the line segment tree
bfs(l, dist1);
bfs(r, distn);// Handle each point l[i]、r[i]
build(1, 1, arr.size() - 1);// Build up trees , Is interval , Pay attention to the scope
for (int i = 0; i < idx; i++) {
if (isdis[i])continue;// Enumerate all edges that are not on the shortest path
int b = e[i], a = e[i ^ 1];
if (dist1[a] < dist1[b]) {
// Meet the context
modify(1, id[l[a]], id[r[b]] - 1, dist1[a] + distn[b] + w[i]);
}
}
query(1);
if (mx == dist1[n])cnt = m;// If the modification cannot reduce the shortest circuit length , Obviously, you can delete any side
cout << mx << ' ' << cnt;
return 0;
}
/* */
Marika ( A simplified version of this question , It doesn't seem to simplify much )
边栏推荐
- How to promote cross department project collaboration | community essay solicitation
- 设计电商秒杀
- CC2530 common registers for watchdog
- 新库上线 | CnOpenData中国保险机构网点全集数据
- LeetCode 1658. Minimum operand to reduce x to 0
- [combinatorics] recursive equation (characteristic equation and characteristic root | example of characteristic equation | root formula of monadic quadratic equation)
- 数据分析必备的能力
- Solution to long waiting time of SSH connection to remote host
- HP 阵列卡排障一例
- [2. Basics of Delphi grammar] 2 Object Pascal data type
猜你喜欢

Redis: operation commands for list type data
ANOVA example
智慧之道(知行合一)

CC2530 common registers for ADC single channel conversion
![[try to hack] active detection and concealment technology](/img/43/d48f851268fec566ce0cc83bd9557e.png)
[try to hack] active detection and concealment technology

Design e-commerce spike

【RT-Thread】nxp rt10xx 设备驱动框架之--hwtimer搭建和使用

CC2530 common registers for crystal oscillator settings
Analysis of variance summary

关于学习Qt编程的好书精品推荐
随机推荐
CC2530 common registers for port interrupts
Why is WPA3 security of enterprise business so important?
Take you to API development by hand
HP 阵列卡排障一例
13mnnimo5-4 German standard steel plate 13MnNiMo54 boiler steel 13MnNiMo54 chemical properties
One brush 144 force deduction hot question-1 sum of two numbers (E)
function overloading
RF Analyze Demo搭建 Step by Step
Rsync remote synchronization
Execute script unrecognized \r
数据分析必备的能力
New library online | cnopendata complete data of Chinese insurance institution outlets
Résolution de l'instance d'assemblage - - affichage à l'écran en mode réel
Answer to the homework assessment of advanced English reading (II) of the course examination of Fuzhou Normal University in February 2022
Mysql database DDL and DML
New library online | cnopendata China bird watching record data
C language modifies files by line
[combinatorics] recursive equation (definition of general solution | structure theorem of general solution of recursive equation without multiple roots)
聊聊接口优化的几个方法
Mysql database -dql
