当前位置:网站首页>7. Integrated learning
7. Integrated learning
2022-07-03 04:30:00 【CGOMG】
What is integrated learning
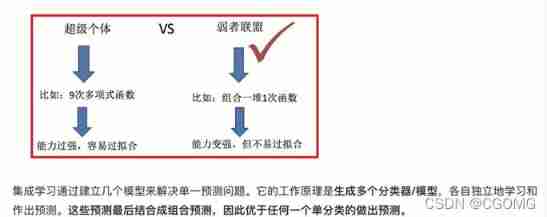
Two core tasks of machine learning

Integrated learning boosting and Bagging

Baggin
Integration principle

Implementation process
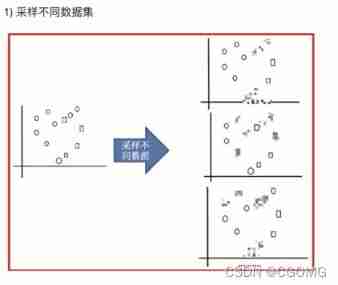
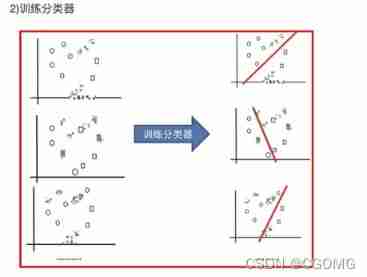
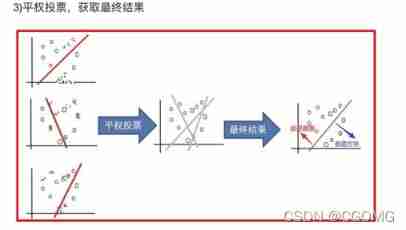
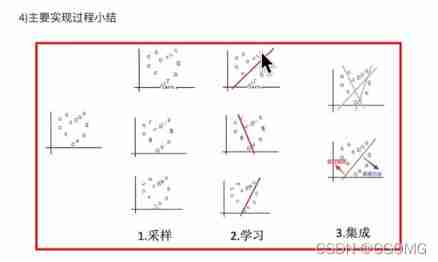
Random forest construction process


Interview questions

Out of the bag estimate (Out-of-Bag Estimate)

Definition
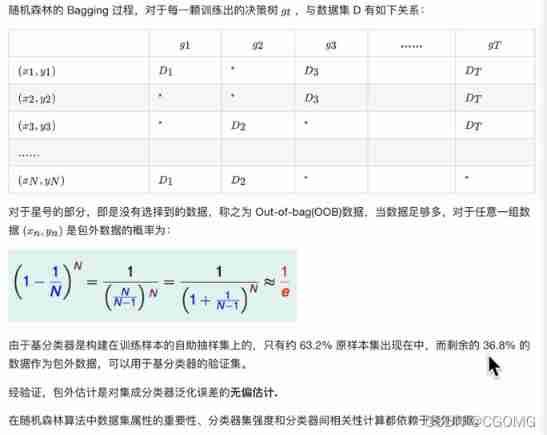

purpose

Random forests API



bagging Integration benefits

Random forest case ( Take Titanic passenger survival prediction as an example )
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor,export_graphviz
# get data
titan = pd.read_csv("titanic.csv")
# Basic data processing
# Determine eigenvalue , The target
x = titan[["pclass","age","sex"]]
y = titan["survived"]
# Missing value processing
x["age"].fillna(value=titan["age"].mean(),inplace=True)
# Data set partitioning
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,random_state=22,test_size=0.2)
# Feature Engineering - Dictionary feature extraction
x_train = x_train.to_dict(orient="records")
x_test = x_test.to_dict(orient="records")
transfer = DictVectorizer()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test)
# machine learning - Decision tree
estimator = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=5)
estimator.fit(x_train,y_train)
# Model to evaluate
print(" score :\n",estimator.score(x_test,y_test))

rf = RandomForestClassifier()
# Through super parameter tuning
param = {
"n_estimators":[100,120,300],"max_depth":[3,7,11]}
gc = GridSearchCV(rf,param_grid=param,cv=3)
gc.fit(x_train,y_train)
print(" The result of random forest prediction is :\n",gc.score(x_test,y_test))

otto Case study -Otto Group Product
Data set introduction

Standard for evaluation

Import dependence
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
Data acquisition
data = pd.read_csv("train.csv")
data.head()

Basic data processing
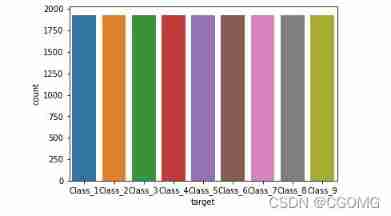
## Data categories are uneven
sns.countplot(data.target)
plt.show()

# Random undersampling to obtain data
## Determine eigenvalue , The target
y = data["target"]
x = data.drop(["id","target"],axis=1)
x.head(),y.head()
## Under sampling data acquisition
rus = RandomUnderSampler(random_state=0)
X_resampled,Y_resampled = rus.fit_resample(x,y)
sns.countplot(Y_resampled)
plt.show()
# Convert tag values to numbers
le = LabelEncoder()
Y_resampled = le.fit_transform(Y_resampled)
# Split data
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X_resampled,Y_resampled,test_size=0.2,random_state=22)
x_train.shape,y_train.shape,x_test.shape,y_test.shape
model training
## Open the estimation outside the package
rf = RandomForestClassifier(oob_score=True)
rf.fit(x_train,y_train)
y_pre = rf.predict(x_test)
score = rf.score(x_test,y_test)
rf.oob_score_ #0.7587845622119815
score1 #0.7840483731644111
score
# logloss Parameter requirements one-hot Format
one_hot = OneHotEncoder(sparse=False)
y_test1 = one_hot.fit_transform(y_test.reshape(-1,1))
y_pre1 = one_hot.fit_transform(y_pre.reshape(-1,1))
log_loss(y_test1,y_pre1,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
7.4587049513916055
Change the predicted value output mode , Let the output result be percentage , reduce logloss value
y_pre_probae = rf.predict_proba(x_test)
y_pre_probae
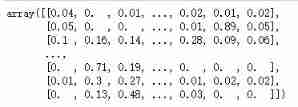
rf.oob_score_ #0.7587845622119815
log_loss(y_test1,y_pre_probae,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
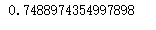
Model tuning
Determine the optimal n_estimators
tuned_parameters = range(10,200,10)
# Create add accuracy One of the numpy
accuracy_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# Create add error One of the numpy
error_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# tuning
for j,one_parameter in enumerate(tuned_parameters):
rf2 = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=one_parameter,
max_depth=10,
max_features=10,
min_samples_leaf=10,
oob_score=True,
n_jobs=-1)
rf2.fit(x_train,y_train)
# Output accuracy
accuracy_t[j] = rf2.oob_score_
# Output log_loss
y_pre_proba = rf2.predict_proba(x_test)
error_t[j] = log_loss(y_test,y_pre_proba,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
# Visualization of optimization results
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(20,4),dpi=100)
axes[0].plot(tuned_parameters,error_t)
axes[1].plot(tuned_parameters,accuracy_t)
axes[0].set_xlabel("n_estimators")
axes[0].set_ylabel("errot_t")
axes[1].set_xlabel("n_estimators")
axes[1].set_ylabel("accuracy_t")
axes[0].grid(True)
axes[1].grid(True)
plt.show()

From the image we can see , determine n_estimators=170 When , Good performance
Determine the optimal max_features
tuned_parameters = range(5,40,5)
# Create add accuracy One of the numpy
accuracy_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# Create add error One of the numpy
error_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# tuning
for j,one_parameter in enumerate(tuned_parameters):
rf2 = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=170,
max_depth=10,
max_features=one_parameter,
min_samples_leaf=10,
oob_score=True,
n_jobs=-1)
rf2.fit(x_train,y_train)
# Output accuracy
accuracy_t[j] = rf2.oob_score_
# Output log_loss
y_pre_proba = rf2.predict_proba(x_test)
error_t[j] = log_loss(y_test,y_pre_proba,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
# Visualization of optimization results
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(20,4),dpi=100)
axes[0].plot(tuned_parameters,error_t)
axes[1].plot(tuned_parameters,accuracy_t)
axes[0].set_xlabel("max_features")
axes[0].set_ylabel("errot_t")
axes[1].set_xlabel("max_features")
axes[1].set_ylabel("accuracy_t")
axes[0].grid(True)
axes[1].grid(True)
plt.show()
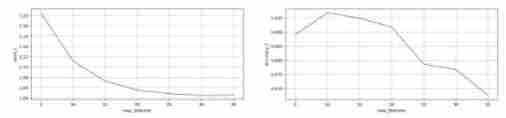
From the image we can see , determine max_features=15 When , Good performance
Determine the optimal max_depth
tuned_parameters = range(10,100,10)
# Create add accuracy One of the numpy
accuracy_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# Create add error One of the numpy
error_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# tuning
for j,one_parameter in enumerate(tuned_parameters):
rf2 = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=170,
max_depth=one_parameter,
max_features=15,
min_samples_leaf=10,
oob_score=True,
n_jobs=-1)
rf2.fit(x_train,y_train)
# Output accuracy
accuracy_t[j] = rf2.oob_score_
# Output log_loss
y_pre_proba = rf2.predict_proba(x_test)
error_t[j] = log_loss(y_test,y_pre_proba,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
# Visualization of optimization results
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(20,4),dpi=100)
axes[0].plot(tuned_parameters,error_t)
axes[1].plot(tuned_parameters,accuracy_t)
axes[0].set_xlabel("max_depth")
axes[0].set_ylabel("errot_t")
axes[1].set_xlabel("max_depth")
axes[1].set_ylabel("accuracy_t")
axes[0].grid(True)
axes[1].grid(True)
plt.show()

From the image we can see , determine max_depth=30 When , Good performance
Determine the optimal min_samples_leaf
tuned_parameters = range(1,10,2)
# Create add accuracy One of the numpy
accuracy_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# Create add error One of the numpy
error_t = np.zeros(len(tuned_parameters))
# tuning
for j,one_parameter in enumerate(tuned_parameters):
rf2 = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=170,
max_depth=30,
max_features=15,
min_samples_leaf=one_parameter,
oob_score=True,
n_jobs=-1)
rf2.fit(x_train,y_train)
# Output accuracy
accuracy_t[j] = rf2.oob_score_
# Output log_loss
y_pre_proba = rf2.predict_proba(x_test)
error_t[j] = log_loss(y_test,y_pre_proba,eps=1e-15,normalize=True)
# Visualization of optimization results
fig,axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1,ncols=2,figsize=(20,4),dpi=100)
axes[0].plot(tuned_parameters,error_t)
axes[1].plot(tuned_parameters,accuracy_t)
axes[0].set_xlabel("min_samples_leaf")
axes[0].set_ylabel("errot_t")
axes[1].set_xlabel("min_samples_leaf")
axes[1].set_ylabel("accuracy_t")
axes[0].grid(True)
axes[1].grid(True)
plt.show()
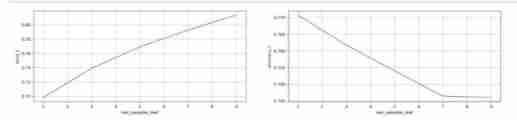
From the image we can see , determine min_samples_leaf=1 When , Good performance
Determine the optimal model
rf3 = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=170,
max_depth=30,
max_features=15,
min_samples_leaf=1,
oob_score=True,
random_state=40,
n_jobs=-1)
rf3.fit(x_train,y_train)
rf3.score(x_test,y_test) #0.788367405701123
rf3.oob_score_ #0.7647609447004609
y_pre_probal = rf3.predict_proba(x_test)
log_loss(y_test,y_pre_probal) #0.6964344507957512
Generate submission data
test_data = pd.read_csv("test.csv")
test_data.head()
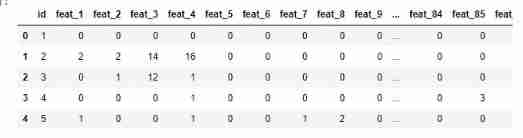
test_data_drop_id = test_data.drop(["id"],axis=1)
test_data_drop_id.head()

y_pre_test = rf3.predict_proba(test_data_drop_id)
y_pre_test

result_data = pd.DataFrame(y_pre_test,columns=["Class_"+str(i) for i in range(1,10)])
result_data.head()

result_data.insert(loc=0,column="id",value=test_data.id)
result_data.head()

result_data.to_csv("submissson.csv",index=False)
Boosting

Implementation process
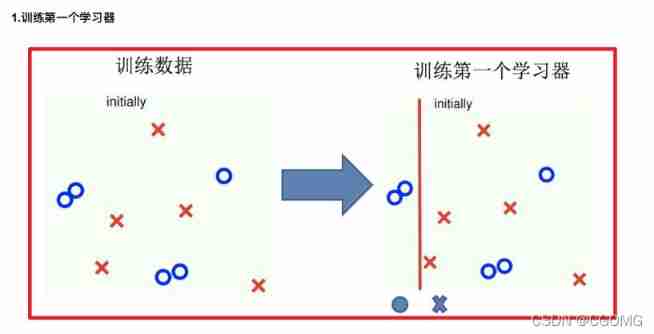


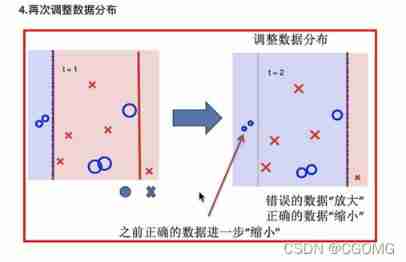

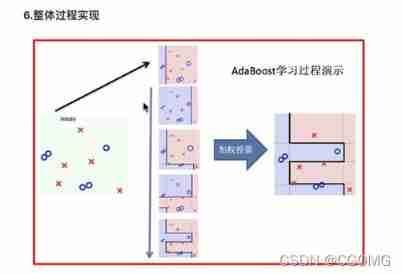
baggin Integration and boosting The difference between integration
- difference ⼀: data ⽅⾯
- Bagging: Enter... Into the data ⾏ Sampling training ;
- Boosting: According to the former ⼀ The importance of adjusting data for round learning results .
- difference ⼆: vote ⽅⾯
- Bagging: Equal voting for all learners ;
- Boosting: Go to the learner ⾏ Weighted voting .
- Difference three : Learning order
- Bagging Learning is and ⾏ Of , Each learner has no dependencies ;
- Boosting Learning is a string ⾏, There is a sequence of learning .
- Difference 4 : The main work is ⽤
- Bagging The main ⽤ Yuti ⾼ Generalization performance ( Solve over fitting , It can also be said to reduce ⽅ Bad )
- Boosting The main ⽤ Yuti ⾼ Training accuracy ( solve ⽋ fitting , It can also be said to reduce the deviation )
AdaBoost( understand )
Construction process

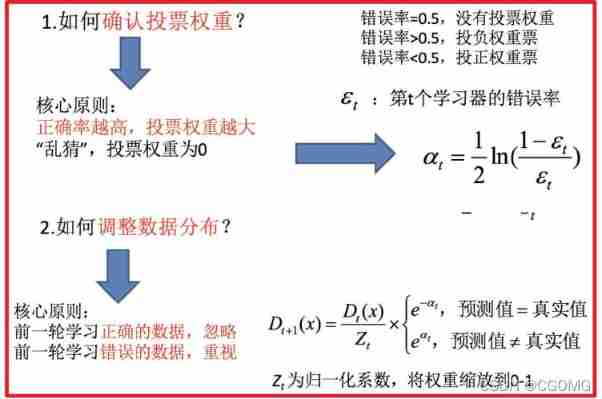
Case study





API
GBDT( understand )

Decision Tree: CART Back to the tree

Gradient Boosting: Fit negative gradient



principle

边栏推荐
- 2022 Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination content and Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination questions and analysis
- sd卡数据损坏怎么回事,sd卡数据损坏怎么恢复
- Bugku CTF daily question baby_ flag. txt
- Use the benchmarksql tool to perform a data prompt on kingbases. The jdbc driver cannot be found
- 2022 registration of G2 utility boiler stoker examination and G2 utility boiler stoker reexamination examination
- 2022-02-14 (394. String decoding)
- Library management system based on SSM
- GFS分布式文件系统(光是遇见已经很美好了)
- What's wrong with SD card data damage? How to recover SD card data damage
- Pdf editing tool movavi pdfchef 2022 direct download
猜你喜欢

Youdao cloud notes

2022 Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination content and Shandong Province safety officer C certificate examination questions and analysis

拆一辆十万元的比亚迪“元”,快来看看里面的有哪些元器件。
Arthas watch grabs a field / attribute of the input parameter

After job hopping at the end of the year, I interviewed more than 30 companies in two weeks and finally landed
![[fxcg] market analysis today](/img/ac/294368e3496a5b808b38833053ee81.jpg)
[fxcg] market analysis today

Php+mysql registration landing page development complete code

Prefix and (continuously updated)

The time has come for the domestic PC system to complete the closed loop and replace the American software and hardware system

Joint set search: merge intervals and ask whether two numbers are in the same set
随机推荐
xrandr修改分辨率與刷新率
RSRS index timing and large and small disc rotation
GFS分布式文件系统(光是遇见已经很美好了)
2022-02-12 (338. Bit count)
[graduation season · aggressive technology Er] Confessions of workers
FFMpeg example
智能合约安全审计公司选型分析和审计报告资源下载---国内篇
Basic use of continuous integration server Jenkins
[Chongqing Guangdong education] reference materials for design and a better life of Zhongyuan Institute of science and technology
Prefix and (continuously updated)
[literature reading] sparse in deep learning: practicing and growth for effective information and training in NN
使用BENCHMARKSQL工具对KingbaseES预热数据时执行:select sys_prewarm(‘NDX_OORDER_2 ‘)报错
[set theory] set operation (Union | intersection | disjoint | relative complement | symmetric difference | absolute complement | generalized union | generalized intersection | set operation priority)
What are the Bluetooth headsets with good sound quality in 2022? Inventory of four high-quality Bluetooth headsets
After job hopping at the end of the year, I interviewed more than 30 companies in two weeks and finally landed
540. Single element in ordered array
RSRS指标择时及大小盘轮动
Kubernetes源码分析(一)
[nlp] - brief introduction to the latest work of spark neural network
Drf--- quick start 01
