当前位置:网站首页>Database learning notes I
Database learning notes I
2022-06-26 07:53:00 【sunshine_ 0224】
The term :
DB: database .-- A file dedicated to storing data .
DBMS: Database management system .-- A system for managing data files .
RDBMS: Relational database management system .-- A management system that stores and manages data in tabular form .
DDL: Data definition language .-- Commands for managing storage structures , For example, create a new table , Modify table structure, etc .
DML: Data operation language .-- Commands for managing data in a storage structure , For example, enter a new record 、 Various queries on existing data 、 Delete or modify existing data .
DCL: Data control language .-- User and rights management , For example, new users 、 Authorization for users, etc .
Sqlserver Some basic commands
One . Database operation
1. Query whether the database exists
if db_id('dbname') is not null;
2. Create database
create database+ Database name ;
3. Modify the name of the database
exec sp_renamedb @dbname= Old database name , @newname= New database name ;
4. Delete the
drop database Database name ;
5. Specified database
use Database name ;
Modify or delete if “ The database cannot be locked with an exclusive lock , To perform the operation .” error , Query which sessions are currently connected to the database , And then kill them .
Inquire about :select spid from master.dbo.sysprocesses where dbid=db_id(' Database name ');
Be careful :spid It's lowercase , Get the process id.
kill :kill spid;
Two . Table operations
---- surface ----
1. Check if the list exists
if object_id('textdb','U') is not null ; among U Represents the user table .
2. new table
CREATE TABLE Product(
[Id] INT PRIMARY KEY, -- Primary key --
[Name] NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, -- Non empty constraint --
[Mark] NVARCHAR(200) NOT NULL UNIQUE, -- Uniqueness constraint --
[Time] DATE DEFAULT GETDATE(), -- Default constraint --
[Price] INT NOT NULL CHECK([Price]>=10 AND [Price]<=100), --check constraint , Ask for a price greater than 10, Less than 100--
[PriceDouble] AS [Price]*2, --as To automatically calculate fields , You cannot enter a value --
)3. Modify the name of the table
exec sp_rename ' Original table name ', ' The new name of the table ';
4. Delete table structure
truncate from Table name ; Delete table structure .
delete and drop Delete table data .
---- A temporary table ----
1. Create a temporary table
select * into #TEMP from Product; from Product Write data to the temporary table .
The temporary table will not disappear until the connection is closed .
---- Column ----
1. Add fields
alter table Table name add Name Field type not null default 0 ;
2. Modify field name
exec sp_rename '[ Table name ].[ Field name ]',' new field name ' ;
3. Modify field type
alter table Table name alter column Field name Field type ;
Be careful : If the modified field is a key field , With primary key , And the field type is user-defined , With default values , Using the above statement will result in an error .
For example, if there is a default value, there will be an error when one or more objects access this column ( Because the field to be modified is originally numeric , There is a default initial value , Then change it to char The data type will be wrong )

The reason is to add Fname1 Field, the default value is set , Lead to SQL Server to Fname1 Fields are associated with 'DF__HACYU_B__id__5562F3F1' constraint . Just delete 'DF__HACYU_B__id__5562F3F1' constraint , I can modify it Fname1 Data type .
Delete the constraint statement as follows
alter table HACYU_B drop constraint DF__HACYU_B__id__5562F3F1;
4. Delete field
alter table Table name drop column Field name ;
3、 ... and . Table data operation
1. Query statement
select*from + The name of the table [+where Conditions ];
2. insert data
insert into The name of the table values ( value 1, value 2,······, value n); The fields of the table are given values in order .
insert into The name of the table ( Field 1, Field 2,······) values ( value 1, value 2,······); Assign individual fields to values .
insert into table2 select * from Ttable1; Batch insert (table2 Is an existing table ).
select * into table2 From table1; Batch insert (table2 Table does not exist , It's automatically created ).
3. Update data
update The name of the table set Field = value [+where Conditions ];
4. Delete table
drop table Table name ; Clear all data in the table , The table structure is in , You cannot add a condition to the back to delete .
truncate from Table name ; Delete table structure .
delete from Table name where Conditions ; Delete table data , With conditions .
delete from Table name ; Delete all records in the table , The operation will be recorded in the log , Can recover .
Query command expansion
1. Column , Table alias
select * from UserInfo as ui
by UserInfo Alias as ui, Of course as It can be omitted . Once the alias is taken , When calling a table column , Must call with an alias .
2.select Query some columns
select top 10 * from UserInfo
top n Name: Indicates before query n That's oktop n percent Name: Indicates the top percent of the view N The data of
3. Sort query
order by Name asc|desc
4. Conditions of the query
where Conditions
between .. and ...: Between intervals ,, Continuous intervalsin(n1,n2): accord with n1 perhaps n2 Conditions , Discontinuous- Logical operators :
and | or | not
Be careful : between Of and Will be looking for sql The nearest in the statement .
5. Fuzzy query
like % _ [] ^
wildcard
- % Express arbitrarily Zero or more character
- _ Signifying Ren Yidan character
- [a-f] Express a To f Medium Any single character
- [a,f] Express a or f
- [^a-c] It means not a To c The characters in
-- Check the class name Zhang
select * from ClassInfo
where sName like ' Zhang %'
-- The second digit of the telephone number is 0-4
where sPhone like '1[^56789]'
Be careful : In the database CHAR When the type data is less than digits , The number of digits will be automatically supplemented with spaces , If you don't need spaces , have access to RTrim() perhaps LTrim().
6. Link query
Internal connection (INNER JOIN): There are two kinds of , Explicit and implicit .
External connections fall into three categories : The left outer join (LEFT OUTER JOIN)、 Right connection (RIGHT OUTER JOIN) And all outside connection (FULL OUTER JOIN).
Student surface

Class surface

1). Internal connection (inner join perhaps join)
The query content strictly corresponds to , Match the rows in the two tables according to the values of the columns common to each table .
Implicit inner join
select * from Student s , Class c where s.Class_num = c.Class_no
Display inner connection
select * from Student s inner join Class c on s.Class_num = c.Class_no
The display and implicit result sets are the same .
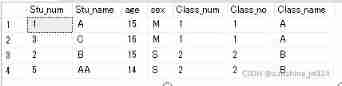
2). Left connection (left join perhaps left outer oin)
The result set of the query includes SQL In the sentence All rows of the left table , Matching rows in the right table .
If a row in the left table does not match a row in the right table , A null value is used to represent .
If the data in the left table , There are multiple rows matching in the right table , The left table of query results is displayed in multiple rows .
select * from Class c left join Student s on Class_num = c.Class_no

select * from Student s left join Class c on s.Class_num = c.Class_no

3). The right connection (right join perhaps right outer join)
The result set of the query includes SQL In the sentence All rows of the right table , Matching rows in the left table .
If a row in the right table has no matching row in the left table , The data in the left table is empty .
If the data in the right table , There are multiple rows matching in the left table , The right table of the query result displays multiple rows .
select * from Class c right join Student s on Class_num = c.Class_no

select * from Student s right join Class c on s.Class_num = c.Class_no

4). Complete external connection (full join perhaps full outer join)
The result set of the query includes all the rows in the left and right tables
select * from Student s full join Class c on s.Class_num = c.Class_no

5). Cross connect
No, WHERE A cross join of a clause produces the Cartesian product of the tables involved in the join .
The number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table is equal to the size of the Cartesian product result set .
select * from Student cross join Class

add WHERE Clause , Return the qualified result set , and inner join The execution result shown is the same .
select * from Student s cross join Class c where s.Class_num = c.Class_no

边栏推荐
- 我想造SQL数据(存储结构)
- Uniapp scrolling load (one page, multiple lists)
- Opencv mouse event + interface interaction drawing rectangle polygon selection ROI
- Jemter 压力测试 -可视化工具-【使用篇】
- Is it legal to open an account for compass stock trading software? Is it safe?
- Jz-063- median in data stream
- buuresevewp
- What are the key points of turnover box management in warehouse management
- In interface testing, several methods to verify the success of deleting interfaces
- Redis(4)----浅谈整数集合
猜你喜欢
![[UVM basics] TLM common data receiving and sending and data receiving examples](/img/4f/6c6e8b26124ba042f949291b944c3d.jpg)
[UVM basics] TLM common data receiving and sending and data receiving examples

Real machine debugging of uniapp custom base

Deeply analyze storage costs and find cost reduction solutions

Jemter 压力测试 -可视化工具支持-【安装篇】

The difference between setstoragesync and setstorage

Here is the command to display the disk space usage. Go ahead and pay attention to more wonderful things!

Chapter 9 (using classes and objects)

Nine hours, nine people and nine doors (01 backpack deformation) - Niuke

Data governance: from top project to data culture!

Median segmentation (find rules) - Niuke
随机推荐
CMDA 3634 image processing
B站增量数据湖探索与实践
Attention mechanism yyds, AI editor finally bid farewell to P and destroyed the whole picture
Junit
Jemter 压力测试 -可视化工具-【使用篇】
Redis (5) -- Talking about compressed list
Jemter 压力测试 -可视化工具支持-【安装篇】
D do not assign references to non domain parameters
信息学奥赛一本通 1354:括弧匹配检验
[UVM practice] Chapter 2: a simple UVM verification platform (3) add various components to the verification platform
Use intent to shuttle between activities -- use implicit intent
45. jumping game II dynamic planning DP
Multi interface switching in one UI of QT
Pic 10B parsing
2022 ranking of bank financial products
Solution to the problem of multi application routing using thinkphp6.0
The difference between setstoragesync and setstorage
Arrangement and insertion structure
[SystemVerilog basics] post_ Randomize function record
Jz-063- median in data stream