当前位置:网站首页>2.1 Dynamic programming and case study: Jack‘s car rental
2.1 Dynamic programming and case study: Jack‘s car rental
2022-07-03 10:09:00 【Most appropriate commitment】
Catalog
Second Edition ( with visualization )
Dynamic programming
Policy evaluation
![v_{\pi } (s) = = \sum_{a}^{}\pi (a|s)\sum_{s^{'}}^{}\sum_{r}^{}r p(r,s^{'} | a, s) [ r+ \gamma v_\pi ( s^{'} ) ]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202202/15/202202150539010515_17.gif)
By iterations, we could get value function set ( v(s) ) for specific policy, given the environment's dynamics.
Pesudocode
while error==True:
error = false
for  :
:

![v_{\pi } (s) = = \sum_{a}^{}\pi (a|s)\sum_{s^{'}}^{}\sum_{r}^{}r p(r,s^{'} | a, s) [ r+ \gamma v_\pi ( s^{'} ) ]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202202/15/202202150539010515_17.gif)
# To iterate
if  :
:
error = True # Judge whether convergence or not
Policy Improvement
For a specific policy, for s in state, if  , we could obtain a better policy
, we could obtain a better policy 


So, there is an achievement of policy improvement.
Although we could not prove we could get the optimal policy, we could get convergent consequence of the policy.
Pesudocode
![\pi^{'}=[\ ]](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202202/15/202202150539010515_3.gif%3D%5B%5C%20%5D)
While judge == True:
judge = False
for  :
:

for  :
:


if  :
:
judge=True;
If there is no any policy improvement in this loop, we could know the policy has converged.
Case study:Jack‘s car rental
Case

Case Analysis
 : Current state is the number of current cars at two locationsin the evening after cars requested and car returned.
: Current state is the number of current cars at two locationsin the evening after cars requested and car returned.  : Action is the number of car movd from the first location to the second location. And negative number means moving cars from second location to the first location. ( limitation: -5~5 )
: Action is the number of car movd from the first location to the second location. And negative number means moving cars from second location to the first location. ( limitation: -5~5 ) : Next state is the number of cars at two locations after cars requested and cars returned in the second day. ( car requested or returned: p(n|s,a) =
: Next state is the number of cars at two locations after cars requested and cars returned in the second day. ( car requested or returned: p(n|s,a) =  ,
,  is 3 and 4 for rental requests, and 3 and 2 for returns )
is 3 and 4 for rental requests, and 3 and 2 for returns ) : Reward is the cost of moving cars and rewards of renting cars out. ( cost of moving per car is $2, rewards of renting per car is $10.
: Reward is the cost of moving cars and rewards of renting cars out. ( cost of moving per car is $2, rewards of renting per car is $10.
Code
First edition
import math
import numpy
import random
'''
state: car number at first location, car number at second location in the evening
(finish renting cars and getting rented cars) (no more 20 cars at each location)
action: move cars from two locations (no more than 5 cars at the evening,
cost: $2 per car) action=3 means move 3 cars at first location to those at second location
environment:
1. people rent cars the probability for people renting n cars in first location and
second location is lambda^n * e^(-lambda)/n! lambda= 3 or 4 respectively
2. people return cars the probability for people returning n cars in first location and
second location is lambda^n * e^(-lambda)/n! lambda= 3 or 2 respectively
'''
gamma=0.9; # discounting factor is 0.9
dsize=20; # maximum of cars at one location is 20 (changeable)
# set probability of n cars requested
def pr_required(lamb,num):
return math.pow(lamb,num)*math.exp(-lamb)/math.factorial(num);
# set probability of n cars returned
def pr_returned(lamb,num):
return math.pow(lamb,num)*math.exp(-lamb)/math.factorial(num);
# obtain updated value function
def v_s_a(i,j,action,v,gamma):
val=0.;
# half reward
reward_night = -2*abs(action);
# state_next in the evening
state_next = (min(i-action,dsize), min(j+action,dsize));
for k in range(0,dsize+1):
for l in range(0,dsize+1):
# s' = (k,l) get p(s',r|s,action)
for x in range(0, int (min(i-action+1,k+1))):
for y in range(0,int (min(j+action+1,l+1))):
# number of car required is i-action-x , j+action-y,
# number of car returned is k-x,l-y
val+= pr_required(3,i-action-x)*pr_required(4,j+action-y)\
*pr_returned(3,k-x)*pr_returned(2,l-y)*( reward_night + \
10* (i-action-x + j+action-y)+ gamma* v[k,l]);
return val;
# initial values
v=numpy.zeros((dsize+1,dsize+1),dtype = numpy.float); # x is first (0-20) , y is second (0-20)
# better policy (tabular) pi(s) = a default is 0, which represent no car moved
policy = numpy.zeros((dsize+1,dsize+1));
judge2=True;
while(judge2):
# policy evaluation
judge1=True;
while(judge1):
judge1=False;
# update every state
for i in range(0,dsize+1):
for j in range(0,dsize+1):
action=policy[i][j];
v_temp=v_s_a(i,j,action,v,gamma);
# judge if value functions of this policy converge
if math.fabs(v_temp-v[i,j])>5:
judge1=True;
v[i,j]=v_temp;
# policy improvement
judge2=False;
for i in range(0,dsize+1):
for j in range(0,dsize+1):
action_max=policy[i,j];
for act in range( -min(j,5),min(i,5)+1 ):
if v_s_a(i,j,act,v,gamma)>v_s_a(i,j,action_max,v,gamma):
action_max=act;
# judge if policy improvement converges
judge2=True;
policy[i,j]=action_max;
print(policy);
Second Edition ( with visualization )
### Settings
import math
import numpy
import random
# visualization
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#import seaborn as sns
gamma=0.9; # discounting factor is 0.9
dsize=6; # maximum of cars at one location is 20 (changeable)
### for policy evaluation
# set probability of n cars requested
def pr_required(lamb,num):
return math.pow(lamb,num)*math.exp(-lamb)/math.factorial(num);
# set probability of n cars returned
def pr_returned(lamb,num):
return math.pow(lamb,num)*math.exp(-lamb)/math.factorial(num);
# obtain updated value function
def v_s_a(i,j,action,v,gamma):
val=0.;
# half reward
reward_night = -2*abs(action);
# state_next in the evening
state_next = (min(i-action,dsize), min(j+action,dsize));
for k in range(0,dsize+1):
for l in range(0,dsize+1):
# s' = (k,l) get p(s',r|s,action)
for x in range(0, int (min(i-action+1,k+1))):
for y in range(0,int (min(j+action+1,l+1))):
# number of car required is i-action-x , j+action-y,
# number of car returned is k-x,l-y
val+= pr_required(3,i-action-x)*pr_required(4,j+action-y)\
*pr_returned(3,k-x)*pr_returned(2,l-y)*( reward_night + \
10* (i-action-x + j+action-y)+ gamma* v[k,l]);
return val;### visualization
def visualization(policies):
num_pic = len(policies) ;
# number of rows of figures
num_columns = 3 ;
num_rows = math.ceil(num_pic/num_columns) ;
# establish the canvas
fig, axes = plt.subplots( num_rows ,num_columns, figsize=(num_columns*2*10,num_rows*1.5*10));
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.2, hspace=0.2)
axes = axes.flatten()
for i in range(0,num_pic):
# show policy in cmap
im = axes[i].imshow( policies[i] ,cmap=plt.cm.cool,vmin=-5, vmax=5)
# settings
axes[i].set_ylabel('# cars at first location',fontsize=10)
axes.flat[i].invert_yaxis()
axes[i].set_xlabel('# cars at second location', fontsize=10)
axes[i].set_title('policy {}'.format(i), fontsize=10)
#axes[i].xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
#fig.colorbar(im,ax=axes[i])
# hide unused axes
for j in range(num_pic,num_columns*num_rows):
axes[j].axis('off')
fig.colorbar(im, ax=axes.ravel().tolist()) # it can just show one colorbar
plt.show()
### main programming
# initial values
v=numpy.zeros((dsize+1,dsize+1),dtype = numpy.float); # x is first (0-20) , y is second (0-20)
# better policy (tabular) pi(s) = a default is 0, which represent no car moved
policy = numpy.zeros((dsize+1,dsize+1));
policies_set=[];
judge2=True;
while(judge2):
# policy evaluation
judge1=True;
while(judge1):
judge1=False;
# update every state
for i in range(0,dsize+1):
for j in range(0,dsize+1):
action=policy[i][j];
v_temp=v_s_a(i,j,action,v,gamma);
# judge if value functions of this policy converge
if math.fabs(v_temp-v[i,j])>5:
judge1=True;
v[i,j]=v_temp;
# we could not use policies_set.append(policy), because it will only copy the address of policy
policies_set.append(policy.copy())
# policy improvement
judge2=False;
for i in range(0,dsize+1):
for j in range(0,dsize+1):
action_max=policy[i,j];
for act in range( -min(j,5),min(i,5)+1 ):
if v_s_a(i,j,act,v,gamma)>v_s_a(i,j,action_max,v,gamma):
action_max=act;
# judge if policy improvement converges
judge2=True;
policy[i,j]=action_max;
print(policy)
# visualization from policies_set
visualization( policies_set )
Result
For dsize = 15:
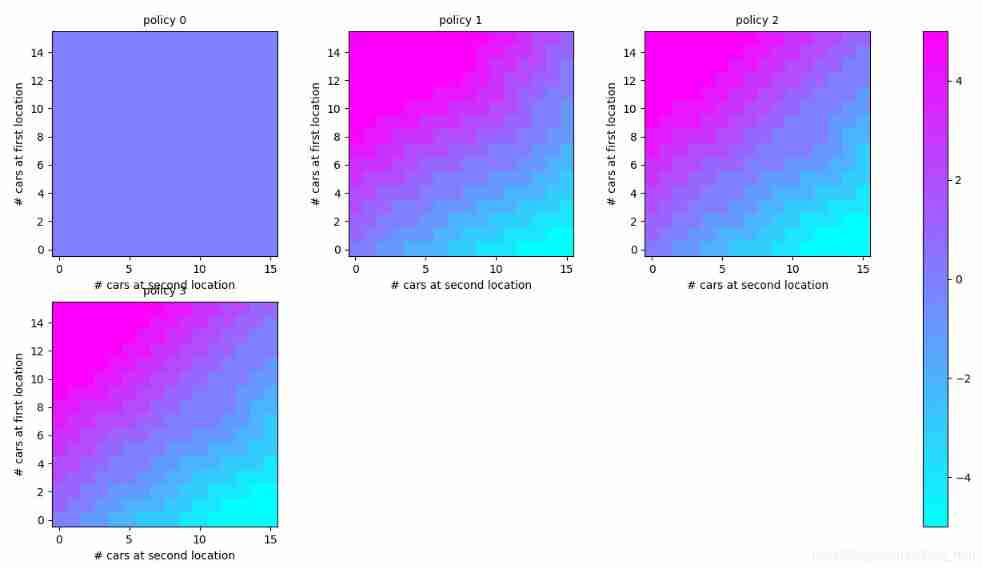
For dsize = 12:
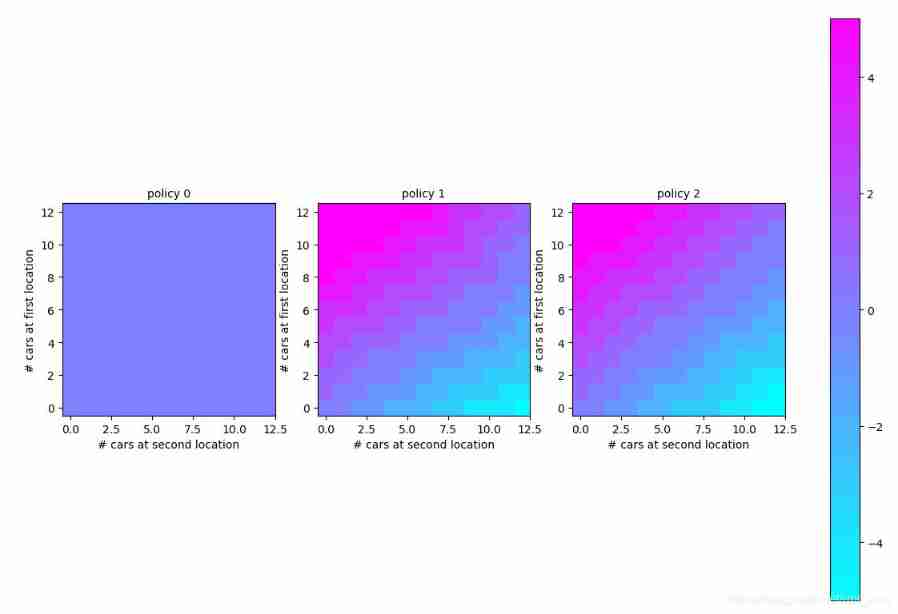
For dsize = 6:
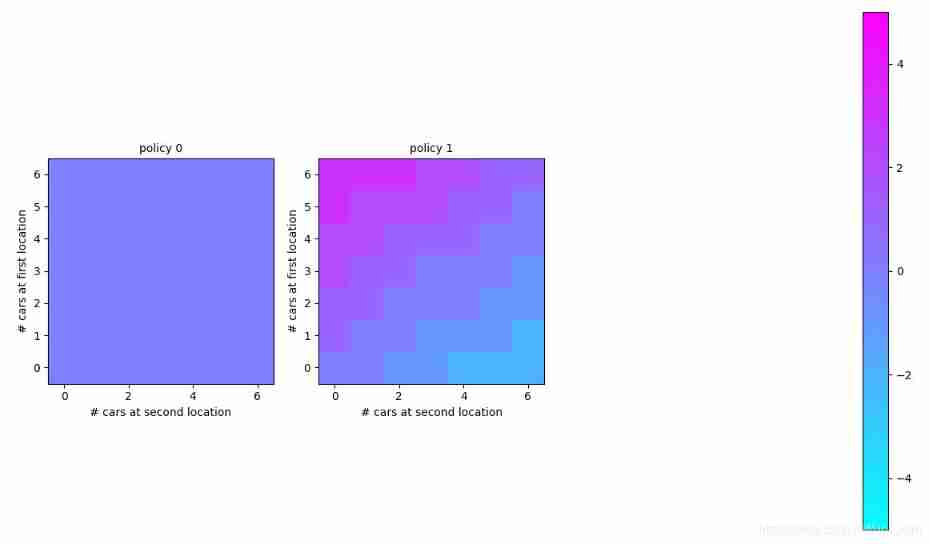
Reference resources : RL(Chapter 4): Jack’s Car Rental_ Lian Li o The blog of -CSDN Blog
边栏推荐
- MySQL root user needs sudo login
- LeetCode - 705 设计哈希集合(设计)
- Opencv Harris corner detection
- QT self drawing button with bubbles
- LeetCode - 673. 最长递增子序列的个数
- 4G module at command communication package interface designed by charging pile
- 2.Elment Ui 日期选择器 格式化问题
- Basic use and actual combat sharing of crash tool
- 2021-01-03
- Leetcode 300 最长上升子序列
猜你喜欢

For new students, if you have no contact with single-chip microcomputer, it is recommended to get started with 51 single-chip microcomputer
LeetCode - 673. 最长递增子序列的个数

MySQL root user needs sudo login

Not many people can finally bring their interests to college graduation

LeetCode - 5 最长回文子串

CV learning notes - scale invariant feature transformation (SIFT)

Windows下MySQL的安装和删除

LeetCode - 508. Sum of subtree elements with the most occurrences (traversal of binary tree)

Leetcode - 460 LFU cache (Design - hash table + bidirectional linked hash table + balanced binary tree (TreeSet))*

CV learning notes - Stereo Vision (point cloud model, spin image, 3D reconstruction)
随机推荐
When the reference is assigned to auto
SCM is now overwhelming, a wide variety, so that developers are overwhelmed
Opencv notes 17 template matching
Installation and removal of MySQL under Windows
Vscode markdown export PDF error
My openwrt learning notes (V): choice of openwrt development hardware platform - mt7688
Do you understand automatic packing and unpacking? What is the principle?
The 4G module designed by the charging pile obtains NTP time through mqtt based on 4G network
Google browser plug-in recommendation
STM32 running lantern experiment - library function version
LeetCode - 919. Full binary tree inserter (array)
Window maximum and minimum settings
CV learning notes - image filter
QT detection card reader analog keyboard input
(2)接口中新增的方法
[combinatorics] combinatorial existence theorem (three combinatorial existence theorems | finite poset decomposition theorem | Ramsey theorem | existence theorem of different representative systems |
2312、卖木头块 | 面试官与狂徒张三的那些事(leetcode,附思维导图 + 全部解法)
On the problem of reference assignment to reference
is_ power_ of_ 2 judge whether it is a multiple of 2
Leetcode 300 longest ascending subsequence
 : Current state is the number of current cars at two locationsin the evening after cars requested and car returned.
: Current state is the number of current cars at two locationsin the evening after cars requested and car returned.  : Action is the number of car movd from the first location to the second location. And negative number means moving cars from second location to the first location. ( limitation: -5~5 )
: Action is the number of car movd from the first location to the second location. And negative number means moving cars from second location to the first location. ( limitation: -5~5 ) : Next state is the number of cars at two locations after cars requested and cars returned in the second day. ( car requested or returned: p(n|s,a) =
: Next state is the number of cars at two locations after cars requested and cars returned in the second day. ( car requested or returned: p(n|s,a) =  ,
,  is 3 and 4 for rental requests, and 3 and 2 for returns )
is 3 and 4 for rental requests, and 3 and 2 for returns ) : Reward is the cost of moving cars and rewards of renting cars out. ( cost of moving per car is $2, rewards of renting per car is $10.
: Reward is the cost of moving cars and rewards of renting cars out. ( cost of moving per car is $2, rewards of renting per car is $10.