当前位置:网站首页>Template: globally balanced binary tree
Template: globally balanced binary tree
2022-07-01 01:52:00 【wind__ whisper】
The so-called globally balanced binary tree , It is a binary tree that is very balanced in the overall situation .
( flee
Preface
This quote is true ( Fog
You can cut some trees into two log The problem is in the list log Time complexity resolution .
Generally speaking, modification can only support Single point modification .
It is more convenient to query and solve chain problems or global problems ( But the subtree seems to be OK )
The constant is relatively large , But it's better than LCT strong .
analysis
Tree sectioning can actually be seen as maintaining a segment tree for each node on the heavy chain , Nodes in the same heavy chain enjoy the same query complexity .
But we found this “ Seemingly balanced ” The data structure of is actually not balanced , Because some nodes may have many light sons , And some nodes may not have light sons at all , The former will be more accessible in most data .
So it leads to Globally balanced binary tree Thought .
Define the weight of a node v a l x val_x valx by All its light sons are sub tree size +1.
Globally balanced binary tree structure and LCT Very similar . First, the original tree is divided into heavy chains , Then maintain a binary search tree for each heavy chain , The interval breakpoint selected here is not the midpoint ( That is the segment tree ), But according to v a l val val Found Weighted center of gravity , And set the father of the root node of the binary search tree as the father of the heavy chain head of the original tree .
( On LCT The difference is , Here the structure of binary search tree is static state Of .)
In my writing, the non leaf nodes of the binary search tree are imaginary points .
For a single point of modification , After modifying its information, you can constantly skip the father update .
For a chain query , It corresponds to the prefix of several heavy chains and the interval of one heavy chain , From the definition of the former, it is not difficult to find that the complexity of each consumption is inevitable siz Double , So it is log n \log n logn Of , The latter is due to the height of the tree log, So it is log n \log n logn Of .
The subtree can find the required node information on the binary search tree of the root node of the subtree and merge it .
Code
P4751 【 Templates 】“ dynamic DP”& Dynamic tree divide and conquer ( Enhanced Edition )
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr,__VA_ARGS__)
#define ok debug("ok\n")
inline ll read(){
ll x(0),f(1);char c=getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}
while(isdigit(c)) {
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+c-'0';c=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
const int N=2e6+100;
const int inf=1e9+100;
const bool Flag=0;
int n,m;
int tot;
struct matrix{
int x,y;
int a[3][3];
matrix(int X=0,int Y=0,int u=-inf,int v=-inf,int p=-inf,int q=-inf):x(X),y(Y){
a[1][1]=u;a[1][2]=v;a[2][1]=p;a[2][2]=q;
}
};
matrix operator * (const matrix &u,const matrix &v){
matrix res(u.x,v.y);
for(int k=1;k<=u.y;k++){
for(int i=1;i<=u.x;i++){
int tmp=u.a[i][k];
for(int j=1;j<=v.y;j++) res.a[i][j]=max(res.a[i][j],tmp+v.a[k][j]);
}
}
return res;
}
vector<int>e[N];
int a[N],fa[N],siz[N],val[N],hson[N];
int s0[N],s1[N];
void dfs1(int x,int f){
siz[x]=1;fa[x]=f;
for(int to:e[x]){
if(to==f) continue;
dfs1(to,x);
siz[x]+=siz[to];
if(siz[to]>siz[hson[x]]) hson[x]=to;
}
val[x]=siz[x]-siz[hson[x]];
return;
}
struct node{
matrix ans;
int fa,ls,rs;
}tr[N];
int nod[N];
inline void pushup(int x){
tr[x].ans=tr[tr[x].rs].ans*tr[tr[x].ls].ans;
}
int build(int l,int r,int f){
if(l==r){
int x=nod[l];
matrix o(2,2,s0[x],s1[x],s0[x],-inf);
tr[x].ans=o;
tr[x].fa=f;
return x;
}
int cur(0),sum(0),now(0);
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) sum+=val[nod[i]];
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){
cur+=val[nod[i]];
if(cur*2<sum) continue;
if(i==r) --i;
now=++tot;
tr[now].fa=f;
tr[now].ls=build(l,i,now);
tr[now].rs=build(i+1,r,now);
break;
}
pushup(now);
return now;
}
inline void ins(int rt,int op){
int f=tr[rt].fa;
if(f){
s0[f]+=op*max(tr[rt].ans.a[1][1],max(tr[rt].ans.a[1][2],max(tr[rt].ans.a[2][1],tr[rt].ans.a[2][2])));
s1[f]+=op*max(tr[rt].ans.a[1][1],tr[rt].ans.a[2][1]);
matrix o(2,2,s0[f],s1[f],s0[f],-inf);
tr[f].ans=o;
}
}
int dfs2(int x,int f){
int top(0);
for(int p=x;p;p=hson[p]){
for(int to:e[p]){
if(to==hson[p]||to==fa[p]) continue;
dfs2(to,p);
}
}
for(int p=x;p;p=hson[p]){
nod[++top]=p;
}
int rt=build(1,top,f);
if(f) ins(rt,1);
return rt;
}
inline void upd(int x,int y){
if(!x) return;
s1[x]=y;
for(int p=x;p;p=tr[p].fa){
if(tr[p].fa&&tr[tr[p].fa].ls!=p&&tr[tr[p].fa].rs!=p) ins(p,-1);
if(p==x) tr[p].ans.a[1][2]=y;
if(p>n) pushup(p);
if(tr[p].fa&&tr[tr[p].fa].ls!=p&&tr[tr[p].fa].rs!=p) ins(p,1),p=tr[p].fa;
}
return;
}
signed main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n=read();m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) s1[i]=a[i]=read();
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int x=read(),y=read();
e[x].push_back(y);
e[y].push_back(x);
}
tot=n;
dfs1(1,0);
int rt=dfs2(1,0),lst(0);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x=read()^lst,y=read();
upd(x,s1[x]+y-a[x]);
a[x]=y;
printf("%d\n",lst=max(tr[rt].ans.a[1][1],max(tr[rt].ans.a[1][2],max(tr[rt].ans.a[2][1],tr[rt].ans.a[2][2]))));
}
return 0;
}
practice
SP2666 QTREE4 - Query on a tree IV
The difficulty of this problem is that if a heap is opened for each point to store the maximum distance between all young sons and their fathers , The heap operation is required when modifying , The complexity is just two log 了 .
A magical and small and fresh optimization method is to put the whole tree Third degree , So there is only one young son , No need to open the stack .
Code implementation reference @hehezhou The blog of .
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr,__VA_ARGS__)
#define ok debug("ok\n")
inline ll read(){
ll x(0),f(1);char c=getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) {
if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}
while(isdigit(c)) {
x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+c-'0';c=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
const int N=4e5+100;
const int inf=1e9;
const bool Flag=0;
int n,m;
#define pr pair<int,int>
#define mkp make_pair
vector<pr>e[N];
int dep[N],tot;
int lson[N],wson[N],siz[N],val[N];
inline void link(int x,int y){
//debug("link: %d %d\n",x,y);
if(!lson[x]) lson[x]=y;
else wson[x]=y;
}
void dfs0(int x,int f){
link(x+n,x);
for(int i=0;i<(int)e[x].size();i++){
if(e[x][i].first==f){
e[x].erase(e[x].begin()+i);
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<(int)e[x].size();i++){
dep[e[x][i].first+n]=dep[x];
dep[e[x][i].first]=dep[x]+e[x][i].second;
dfs0(e[x][i].first,x);
}
for(int i=1;i<(int)e[x].size();i++) link(e[x][i-1].first+n,e[x][i].first+n);
if(!e[x].empty()) link(x,e[x][0].first+n);
}
struct node{
int l,r,ls,rs,lmax,rmax,ans,pre,suf,fa;
}tr[N];
void dfs1(int x){
siz[x]=1;
if(wson[x]){
dfs1(wson[x]);
siz[x]+=siz[wson[x]];
}
if(lson[x]){
dfs1(lson[x]);
siz[x]+=siz[lson[x]];
}
if(siz[wson[x]]<siz[lson[x]]) swap(lson[x],wson[x]);
val[x]=siz[x]-siz[wson[x]];
return;
}
int zhan[N];
int build(int l,int r,int f){
if(l==r){
tr[zhan[l]].pre=tr[zhan[l]].suf=zhan[l];
tr[zhan[l]].l=tr[zhan[l]].r=l;
tr[zhan[l]].fa=f;
return zhan[l];
}
int sum(0),cur(0),now(0);
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) sum+=val[zhan[i]];
for(int i=l;i<=r;i++){
cur+=val[zhan[i]];
if(cur*2<sum) continue;
if(i==r) --i;
now=++tot;
tr[now].ls=build(l,i,now);
tr[now].rs=build(i+1,r,now);
break;
}
tr[now].l=l;tr[now].r=r;
tr[now].pre=zhan[l];tr[now].suf=zhan[r];
tr[now].fa=f;
if(Flag) printf("now=%d (%d %d)\n",now,l,r);
return now;
}
int dfs2(int x,int f){
int top=0;
for(int p=x;p;p=wson[p]) zhan[++top]=p;
if(Flag) for(int i=1;i<=top;i++) printf("%d ",zhan[i]);
if(Flag) puts("\n");
int rt=build(1,top,f);
for(int p=x;p;p=wson[p]){
if(lson[p]) tr[p].ls=dfs2(lson[p],p);
}
return rt;
}
bool ban[N];
#define ls(x) tr[x].ls
#define rs(x) tr[x].rs
inline void pushup(int x){
if(tr[x].l==tr[x].r){
int d=tr[ls(x)].lmax+dep[tr[ls(x)].pre]-dep[x];
if(!ban[x]){
tr[x].lmax=tr[x].rmax=max(d,0);
tr[x].ans=max(tr[ls(x)].ans,0);
}
else{
tr[x].lmax=tr[x].rmax=d;
tr[x].ans=tr[ls(x)].ans;
}
return;
}
else{
tr[x].lmax=max(tr[ls(x)].lmax,tr[rs(x)].lmax+(dep[tr[rs(x)].pre]-dep[tr[ls(x)].pre]));
tr[x].rmax=max(tr[rs(x)].rmax,tr[ls(x)].rmax+(dep[tr[rs(x)].suf]-dep[tr[ls(x)].suf]));
tr[x].ans=max(max(tr[ls(x)].ans,tr[rs(x)].ans),tr[ls(x)].rmax+tr[rs(x)].lmax+dep[tr[rs(x)].pre]-dep[tr[ls(x)].suf]);
return;
}
}
void init(int x){
if(!x) return;
if(tr[x].l==tr[x].r){
init(tr[x].ls);
}
else{
init(tr[x].ls);
init(tr[x].rs);
}
pushup(x);
if(Flag) printf("x=%d lmax=%d rmax=%d ans=%d\n",x,tr[x].lmax,tr[x].rmax,tr[x].ans);
return;
}
signed main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
#endif
tr[0].lmax=tr[0].rmax=tr[0].ans=-inf;
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int x=read(),y=read(),w=read();
e[x].push_back(mkp(y,w));
e[y].push_back(mkp(x,w));
}
tot=n+n;
dfs0(1,0);
dfs1(1);
int rt=dfs2(1,0);
for(int i=n+1;i<=tot;i++) ban[i]=1;
init(rt);
if(Flag) for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++) printf("i=%d dep=%d\n",i,dep[i]);
m=read();
char c;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf(" %c",&c);
if(c=='A'){
if(tr[rt].ans<0) puts("They have disappeared.");
else printf("%d\n",tr[rt].ans);
}
else{
int x=read();
ban[x]^=1;
for(;x;x=tr[x].fa) pushup(x);
}
if(Flag) init(rt);
if(Flag) puts("");
}
return 0;
}
/* 5 1 2 -8 2 3 -5 1 4 -7 4 5 -6 */
边栏推荐
- After working for 6 years, let's take stock of the golden rule of the workplace where workers mix up
- 数学知识:满足条件的01序列—求组合数
- 7-2 拼题A打卡奖励 dp
- Laravel event & subscription
- [无线通信基础-15]:图解移动通信技术与应用发展-3- 数字通信2G GSM、CDMA、3G WDCMA/CDMA200/TD-SCDMA、4G LTE、5G NR概述
- Institute of Microbiology, commonly used biochemical reactions in microbiological testing
- Sitge joined the opengauss open source community to jointly promote the ecological development of the database industry
- FL Studio20.9水果软件高级中文版电音编曲
- 【JS】【掘金】获取关注了里不在关注者里的人
- 亲测有效,快速创建JMeter桌面快捷方式
猜你喜欢

For the sustainable development of software testing, we must learn to knock code?

Necessary tools for testing - postman practical tutorial
3500 word summary: a complete set of skills that a qualified software testing engineer needs to master

机器学习9-通用逼近器径向基函数神经网络,在新观点下审视PDA和SVM
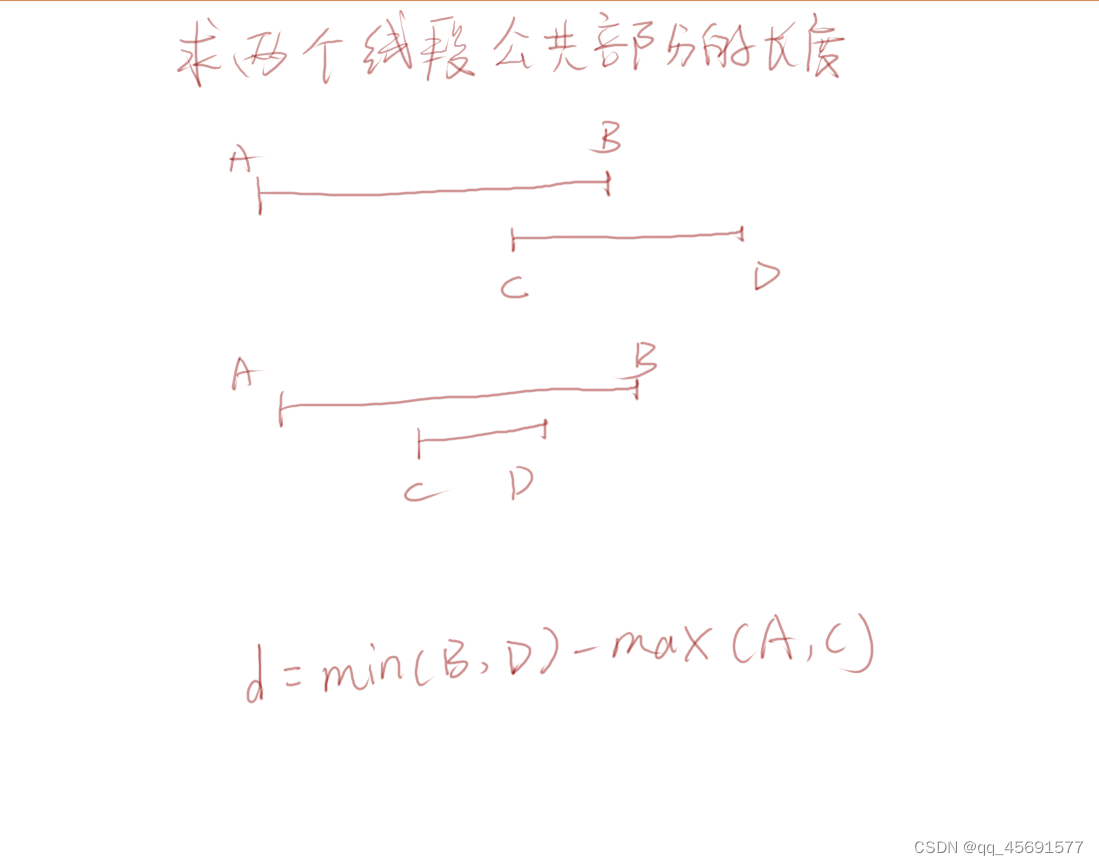
求两个线段公共部分的长度

int和位数组互转

Compile and install oh my Zsh

1500w播放下还藏着什么热点?B站2个未来趋势你不得错过

3dsmax plug-in development traversal node object and object acquisition and inode transformation matrix description

【JS】【掘金】获取关注了里不在关注者里的人
随机推荐
Mysql database foundation: process control
[Qt5 basics] random number display
[fundamentals of wireless communication-15]: illustrated mobile communication technology and application development-3-overview of digital communication 2G GSM, CDMA, 3G wdcma/cdma200/td-scdma, 4G LTE
Draw some interesting figures with flutter's canvas
2022年最新csdn涨薪技术栈-app自动化测试概述
Video tutorial | Chang'an chain launched a series of video tutorial collections (Introduction)
修复表中的名字(首字符大写,其他小写)
小程序中实现excel数据的批量导入
zabbix如何配置告警短信?(预警短信通知设置流程)
Lecun, a Turing Award winner, pointed out that the future of AI lies in self-learning, and the company has embarked on the journey
【2022年】江西省研究生数学建模方案、代码
What other hot spots are hidden under 1500W playback? Station B 2 future trends you can't miss
Use of laravel carbon time processing class
工厂+策略模式
What are the preferential activities for stock account opening? In addition, is it safe to open a mobile account?
工作八年的程序员,却拿着毕业三年的工资,再不开窍就真晚了...
Opencv -- Notes
For the sustainable development of software testing, we must learn to knock code?
Sitge joined the opengauss open source community to jointly promote the ecological development of the database industry
More pragmatic in business