当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to program ape (XII) -- data storage
Introduction to program ape (XII) -- data storage
2022-07-02 19:34:00 【Yuan_ o_】
1、 Data type introduction
C Basic built-in types in languages :
char // Character data type Size of bytes occupied –>1
short // Short Size of bytes occupied –>2
int // plastic Size of bytes occupied –>4
long // Long integer Size of bytes occupied –>4(32 position )/8(64 position )
long long // Longer plastic surgery (C99) Size of bytes occupied –>8
float // Single-precision floating-point Size of bytes occupied –>4
double // Double precision floating point Size of bytes occupied –>8
The meaning of type :
- Use this type to exploit the size of memory space ( Size determines the range of use ).
- How to look at the perspective of memory space .

1.1 The basic classification of types
Plastic surgery Family :
char( The essence of characters is ASCII Code value , Integer. )
unsigned char
signed charshort
unsigned short [int]
signed short [int]int
unsigned int
signed intlong
unsigned long [int]
signed long [int]long long
unsigned long long [int]
signed long long [int]
tip: among char What is the signed char still unsigned char Standards are undefined , Depends on the implementation of the compiler .
Floating point family :
float
double
Construction type :( Custom type --> We can create new types by ourselves )
An array type
Type of structure struct
Enumeration type enum
Joint type union
tip: An array type :
Pointer types :
int *pi;
char *pc;
float *pf;
void *pv;
Empty type :
void Indicates empty type ( No type ).
Usually applied to the return type of a function 、 The parameters of the function 、 Pointer types .
// first void Indicates that the function will not return any value
// the second void It means that the function does not need to pass any parameters
void test(void)
{
}
int main()
{
test(1);
return 0;
}
2、 Shaping storage in memory
The creation of a variable is to open up space in memory .
The size of space is determined according to different types .
2.1 Original code 、 Inverse code 、 Complement code
There are three ways to represent integers in a computer , The original code 、 Inverse and complement .
There are three ways of expression Sign bit and Value bits Two parts , The sign bits are all used 0 Express “ just ”, use “1” Express “ negative ”, And the number bit The three representations of negative integers are different .
Original code
Directly translate binary into binary in the form of positive and negative numbers .
Inverse code
Change the sign bit of the original code , The other bits can be inverted in turn .
Complement code
Inverse code +1 You get the complement .
A positive number 、 back 、 The complement is the same .
For plastic surgery : Data stored in memory is actually stored in the complement .
In computer system , All values are represented and stored by complements .
The reason lies in , Use complement , Symbol bit and value bit can be treated in a unified way .
meanwhile , Addition and subtraction can also be handled in a unified way (CPU Only adders ) Besides , Complement code and original code are converted to each other , Its operation process is the same , No need for additional hardware circuits .(tip: The complement is reversed +1 You can get the original code )
ep:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 20;
//20
// Original code :00000000 00000000 00000000 00010100
//16 Base number :0x 00 00 00 14
// Inverse code :00000000 00000000 00000000 00010100
// Complement code :00000000 00000000 00000000 00010100
int b = -10;
//-10
// Original code :10000000 00000000 00000000 00001010
//16 Base number :0x 80 00 00 0a
// Inverse code :11111111 11111111 11111111 11110101
//16 Base number :0x ff ff ff f5
// Complement code :11111111 11111111 11111111 11110110
//16 Base number :0x ff ff ff f6
return 0;
}
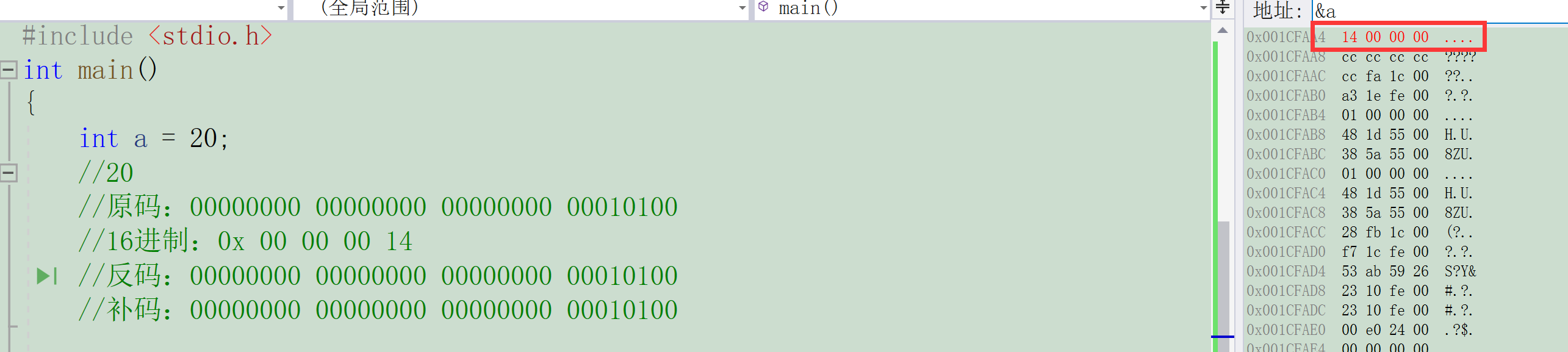
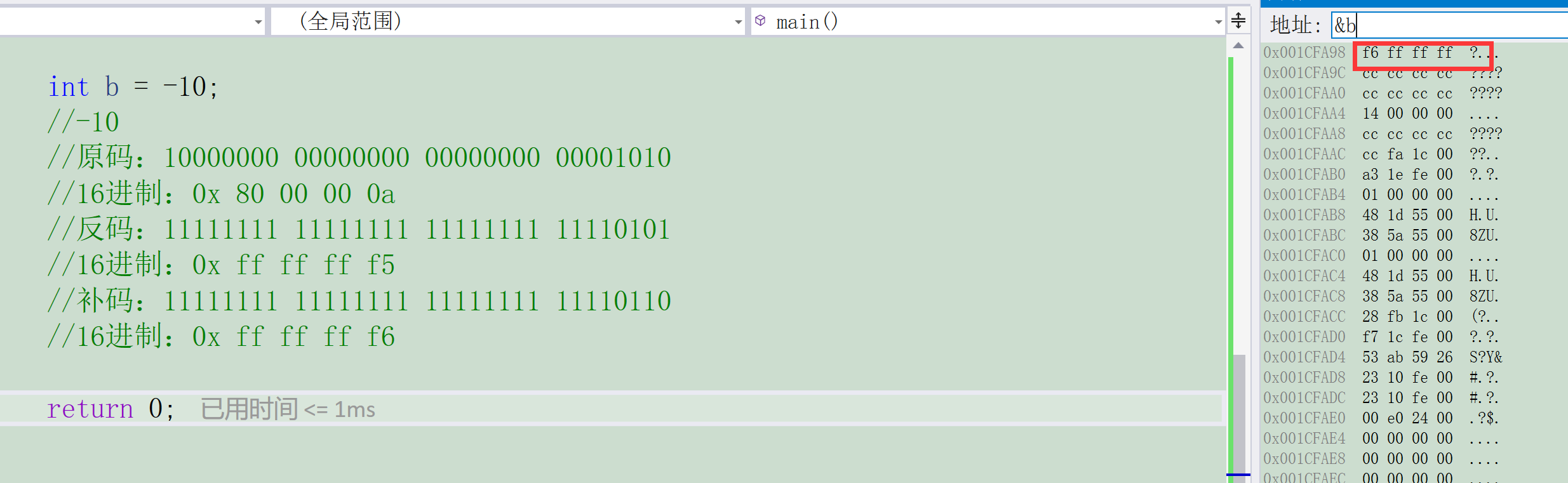
The above example shows that the integer data stored in memory is a complement .
2.2 Introduction to big and small end
What is the big and small end :
Big end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the high address of memory , And the high end of the data , Stored in a low address in memory ;( Big end byte order storage )
The small end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the low address of memory , And the high end of the data , Stored in a high address in memory .( Small end byte order storage )
Why are there big and small ends :
This is because in a computer system , We are in bytes , Each address corresponds to a byte , A byte is 8 bit. But in C In language, except 8 bit Of char outside , also 16 bit Of short type ,32 bit Of long type ( It depends on the specific compiler ), in addition , For digits greater than 8 Bit processor , for example 16 Bits or 32 Bit processor , Because the register width is larger than one byte , Then there must be a problem of how to sort multiple bytes . So it leads to big end storage mode and small end storage mode .
for example : One16 bitOfshorttypex, The address in memory is0x0010,xThe value of is0x1122, that0x11High high byte ,0x22Is low byte .
For big end mode , will0x11Put it in the low address , namely0x0010in ,0x22Put it in a high address , namely0x0011in . The small end mode is just the opposite .
That we use a lotx86The structure is small end mode , andKEIL C51It's the big end mode . quite a lot ARM,DSP It's all small end mode . There are some ARM The processor can also choose the big end mode or the small end mode by the hardware .
Baidu 2015 System Engineer written test questions :
Please briefly describe the concepts of big end byte order and small end byte order , Design a small program to determine the current machine byte order .(10 branch )

// Method 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 1;
if (*(char*)&a == 1)
{
printf(" The small end \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Big end \n");
}
return 0;
}
// Method 2
#include <stdio.h>
int check_sys()
{
int a = 1;
return *(char*)&a;
}
int main()
{
int ret = check_sys();
if (ret == 1)
{
printf(" The small end \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Big end \n");
}
return 0;
}
ep:
The meaning of the existence of pointer types : When we want to access a byte , We will convert the pointer type to char*, When we want to access two bytes , Turn into short*, When we access four bytes and are of floating-point type , Turn into float*.
2.3 practice
1、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = -1;
signed char b = -1;
unsigned char c = -1;
printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
What does the above code output ?
analysis : First, let's understand the memory signed char and unsigned char The storage range of , Signed number signed char Occupy a byte in memory ,8 individual bit position , The first bit is the sign bit ,0 It means a positive number ,1 A negative number , As shown in the figure below ,signed char The value range of is -128~127; An unsigned number unsigned char There is no sign bit , Here's the picture , His value range is 0~255.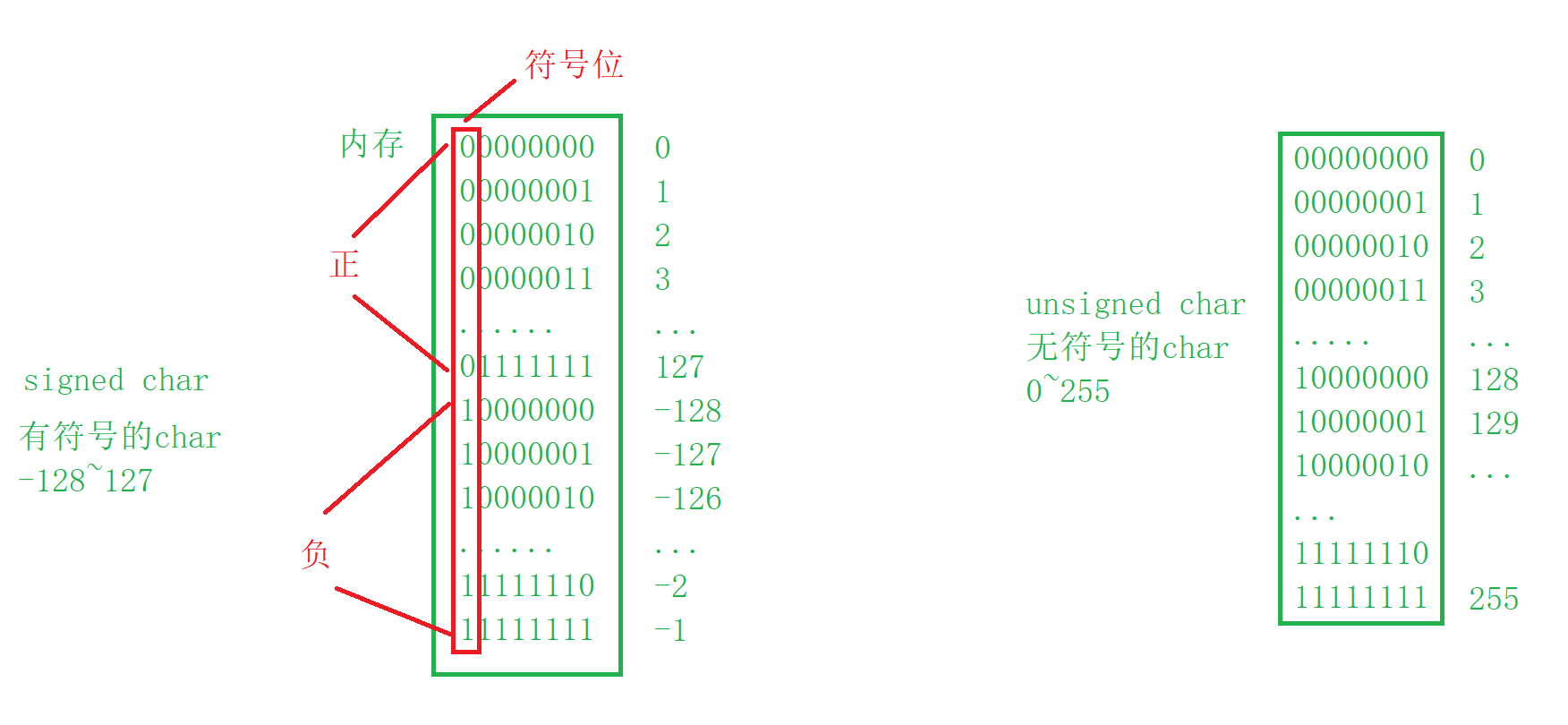
Then there is the specific conversion process of the code in memory :( In this process, you need to pay attention to storing integer data in char Truncation occurs in , And print in integer char a Integer lift occurs )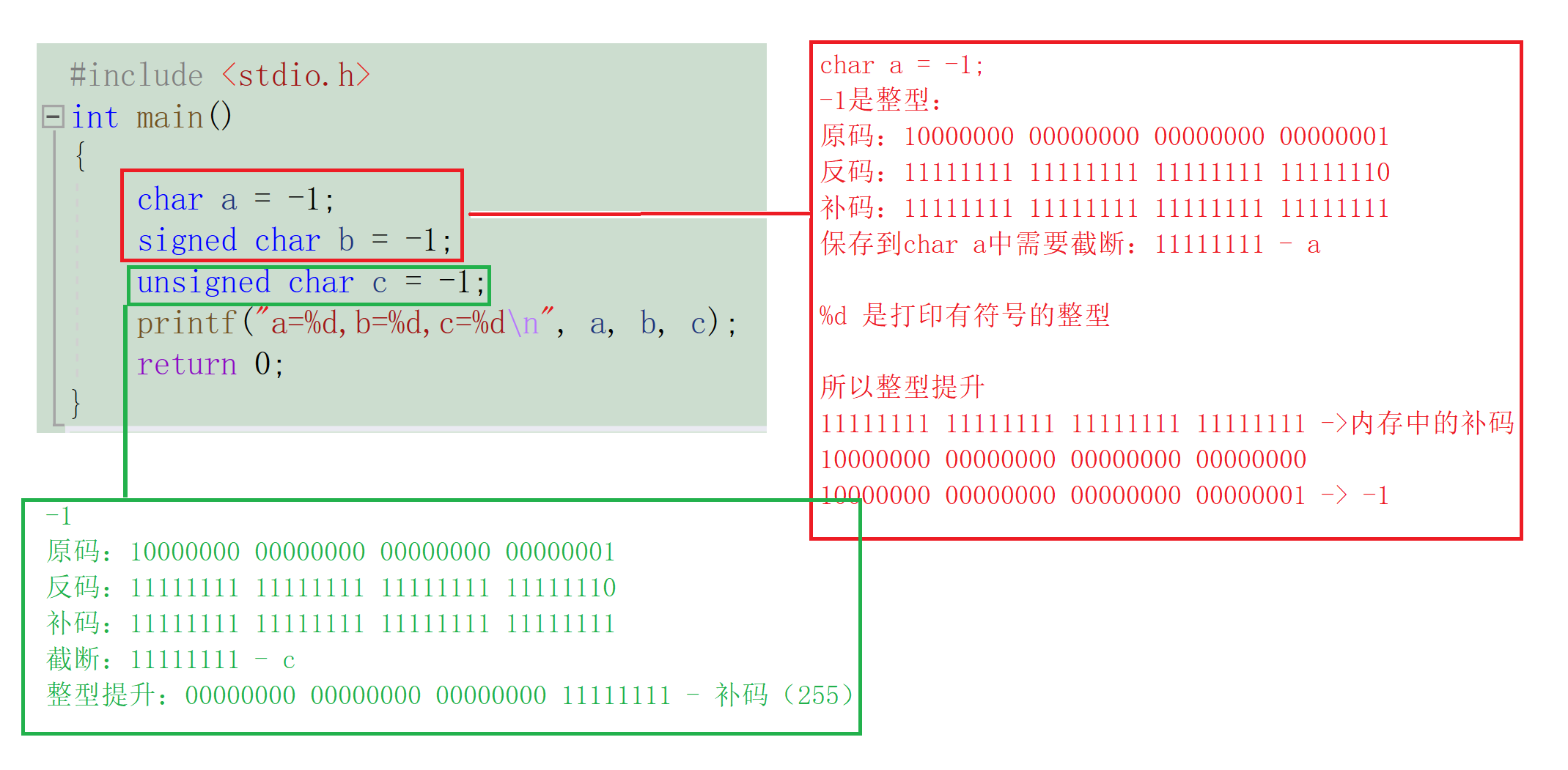
Print the results :
tip:
When an integer raises a signed number , Fill in the sign before .
When an integer raises an unsigned number , Front complement 0.
2、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = -128;
printf("%u\n", a);
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}

Print the results :
3、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char a = 128;
printf("%u\n", a);
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
Same as the second question : When printing unsigned integer and promoting signed number , The sign bit is raised .
Print the results :
4、
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = -20;
unsigned int j = 10;
printf("%d\n", i + j);
return 0;
}
// Operate in the form of complement , Finally, it is formatted as a signed integer

5、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int i;
for (i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
{
printf("%u\n", i);
Sleep(1000);// For convenience of observation , Sleep 1000 millisecond
}
return 0;
}
Output results :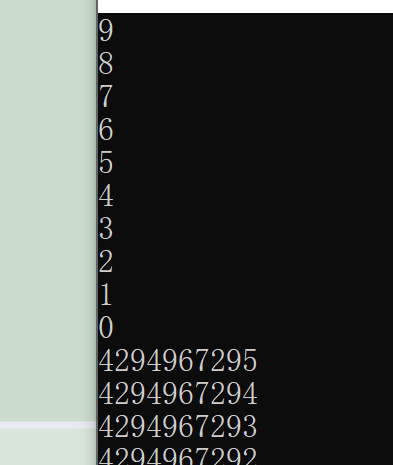
Because of the definition i Is an unsigned number , So when i=0, One more time , There is no sign bit by default , Become a big number , Create a dead cycle .
6、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char a[1000];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
a[i] = -1 - i;
}
printf("%d", strlen(a));
return 0;
}

a[1000]yes char type , Value range :-128~127strlenIs to find the length of the string , Focus on... In the string ’\0’(ASCII The code value is 0) How many characters have appeared before .
When the program circulates as shown in the above figure-1,-2...-128,127,126,125...3,2,1,0meet 0 It stopped. .
here a[1000] The length of is 128+127=255
7、
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned char i = 0;
int main()
{
for (i = 0; i <= 255; i++)
{
printf("hello world\n");
}
return 0;
}
because unsigned char i The value range of is 0~255
therefore i <= 255 Hang up , Program loop
8、
// The wrong sample :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
if (strlen("abc") - strlen("abcdef") >= 0)
printf(">\n");
else
printf("<\n");
return 0;
}
// Modify one
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
if (strlen("abc") > strlen("abcdef"))
printf(">\n");
else
printf("<\n");
return 0;
}
// Amendment two
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
if ((int)strlen("abc") - (int)strlen("abcdef") >= 0)
printf(">\n");
else
printf("<\n");
return 0;
}
because strlen The return value of size_t type , and size_t Namely unsigned int type , So the running result of the program is always greater than ( An unsigned number - An unsigned number = An unsigned number )
3、 Floating point storage in memory
Common floating point numbers :
3.14159
1E10( Scientific notation means )
The family of floating-point numbers includes :float、double、long doubletype
The range represented by floating point numbers :float.h Definition ( integer :limits.h Definition )
3.1 An example
Examples of floating point storage :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 9;
float* pFloat = (float*)&n;
printf("n The value of is :%d\n", n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%d\n", *pFloat);
*pFloat = 9.0;
printf("n The value of is :%d\n", n);
printf("pFloat The value of is :%f\n", *pFloat);
return 0;
}
Output results :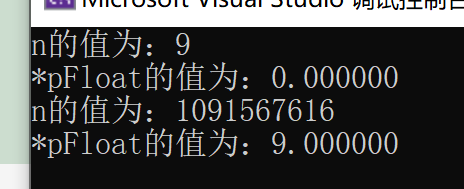
thus it can be seen , In memory , Integer and floating-point types are stored in different ways .
3.2 Floating point storage rules
num and *pFloat It's the same number in memory , Why is there such a big difference between the interpretation results of floating-point numbers and integers ?
To understand this result , Be sure to understand the representation of floating-point numbers in the computer .
According to international standards IEEE( Institute of electrical and Electronic Engineering )745, Any binary floating point number V It can be expressed in the following form :
- (-1)^S * M * 2^E(-1 Of S Power multiplication M ride 2 Of E Power )
- (-1)^S The sign bit , When S=0,V Is a positive number ; When S=1,V It's a negative number .
- M Represents a significant number , Greater than or equal to 1, Less than 2.
- 2^E Indicates the index bit .
ep: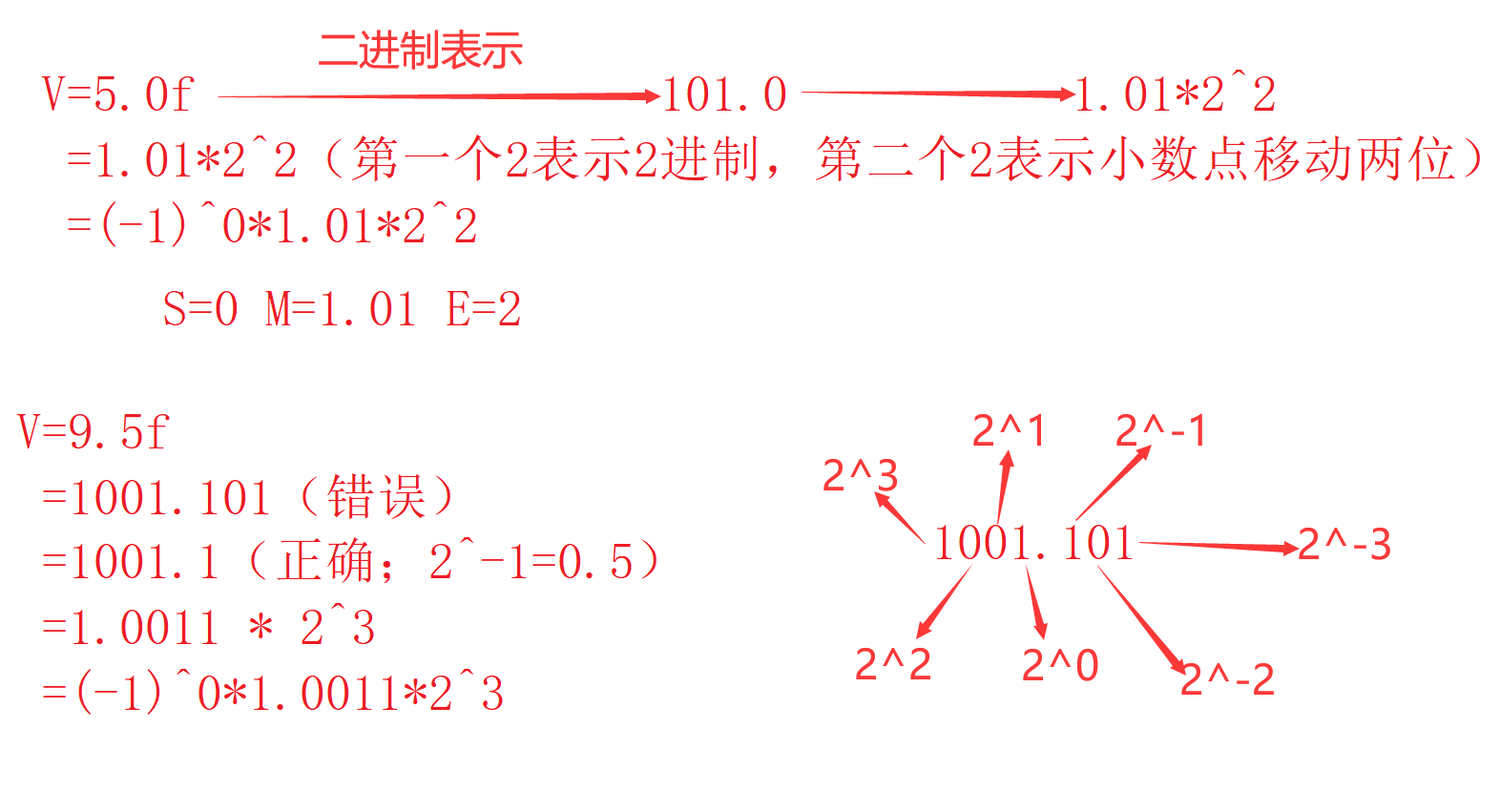

Thus we can see that , Floating point numbers cannot be accurately stored in memory .
ep2:
Decimal -5.0, Written as binary is -101.0, amount to -1.01*2^2. that ,S=1,M=1.01,E=2.
IEEE 754 Regulations :
about 32 Floating point number for , The highest 1 Bits are sign bits S, And then 8 The number of digits is an index E, The rest 23 Significant digits M.
about 64 Floating point number of bits , The highest 1 Bits are sign bits S, And then 11 Bits are exponents E, The rest 52 Bits are significant numbers M.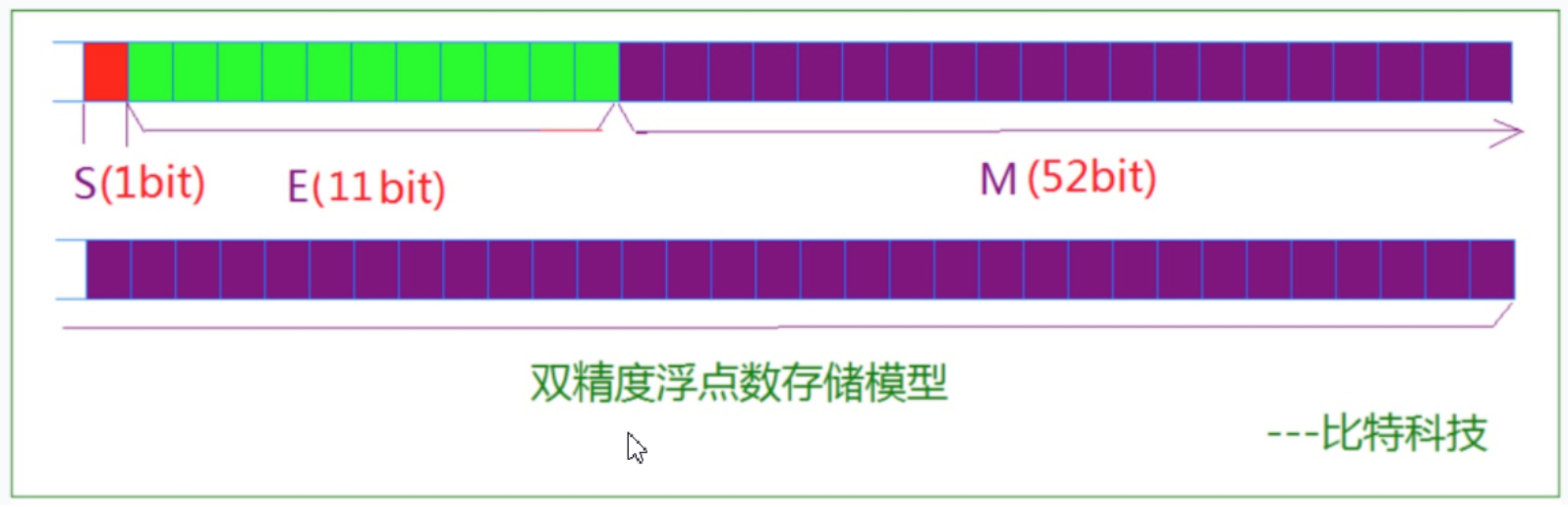
IEEE 745 For significant figures M And the index E, There are some special rules .
As I said before , Keep it in the computer M when , By default, the first digit of this number is always 1, So it can be discarded , Save only the back xxxxxx part . For example preservation 1.01 When , Save only 01, Wait until you read , Put the first 1 Add . The purpose of this , It's saving 1 Significant digits . With 32 For example, a floating-point number , Leave to M Only 23 position , Will come first 1 After giving up , It's equivalent to being able to save 24 Significant digits .
As for the index E, The situation is more complicated .
First ,E It's an unsigned integer (unsigned int)
It means , If E by 8 position , Its value range is 0255; If E by 11 position , Its value range is 02047. however , We know , In scientific counting E You can have negative numbers , therefore IEEE 745 Regulations , In memory E The true value of must be added with an intermediate number , about 8 Bit E, This number is 127; about 11 Bit E, The middle number is 1023. such as ,2^10 Of E yes 10, So save it as 32 When floating-point numbers are in place , Must be saved as 10+127=137, namely 10001001.
then , Index E Fetching from memory can be further divided into three cases :
E Not all for 0 Or not all of them 1
At this time , Floating point numbers are represented by the following rules , The index E The calculated value of minus 127( or 1023), Get the real value , And then the significant number M Add the first 1.
such as :
0.5(1/2) The binary form of is 0.1, Since it is stipulated that the positive part must be 1, That is to move the decimal point to the right 1 position , Then for 1.0*2^(-1), Its order code is -1+127=126, Expressed as 01111110, And the mantissa 1.0 Remove the integer part and make it 0, A filling 0 To 23 position 00000000000000000000000, Then its binary representation is :
0 01111110 0000000000000000000000
E All for 0
At this time , The exponent of a floating point number E be equal to 1-127( perhaps 1-1023) That's the true value , Significant figures M No more first 1, It's reduced to 0.xxxxxx Decimals of . This is to show that ±0, And close to 0 A very small number of .
E All for 1
At this time , If the significant number M All for 0, Express ± infinity ( It depends on the sign bit s);
Add :
Explain the initial topic :
Why? 0x00000009 Restore to floating point number , became 0.000000?
First , take 0x00000009 Split , Get the first sign bit S=0, Back 8 Bit index E=00000000, Last 23 A significant number of bits M=00000000 00000000 00001001
9 -> 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001001
Because the index E All for 0, So in line with E The second case of fetching from memory , therefore , Floating point numbers V The just :
V=(-1)^0 * 0.000000000000000000001001 * 2(-126)=1.001*2(-146)
obviously ,V It's a very small one, close to 0 Positive number of , So the decimal number is 0.000000
Look at the second part of the example :
First , Floating point numbers 9.0 Equal to binary 1001.0, namely 1.001 *2^3
9.0 -> 1001.0 -> (-1)^0 * 1.001 * 2^3 -> S=0,M=1.001,E=3+127 = 130
that , The first sign bit S=0, Significant figures M be equal to 001 Back plus 20 individual 0, Cramming 23 position , Index E4 be equal to 3+127=130, namely 10000010
therefore , Written in binary form , Should be S+E+M, namely
0 10000010 0010000 00000000 00000000
This 32 The binary number of bits , Restore to decimal , It is 1091567616
边栏推荐
- Reduce -- traverse element calculation. The specific calculation formula needs to be passed in and combined with BigDecimal
- 思考变量引起的巨大变化
- Tutorial (5.0) 10 Troubleshooting * fortiedr * Fortinet network security expert NSE 5
- Golang并发编程——goroutine、channel、sync
- 移动机器人路径规划:人工势场法[通俗易懂]
- AcWing 1129. 热浪 题解(最短路—spfa)
- How to print mybats log plug-in using XML file
- Chapter 7 - class foundation
- [pytorch learning notes] tensor
- PHP asymmetric encryption method private key and public key encryption and decryption method
猜你喜欢

Why should we build an enterprise fixed asset management system and how can enterprises strengthen fixed asset management

Chic Lang: completely solve the problem of markdown pictures - no need to upload pictures - no need to network - there is no lack of pictures forwarded to others
《重构:改善既有代码的设计》读书笔记(下)
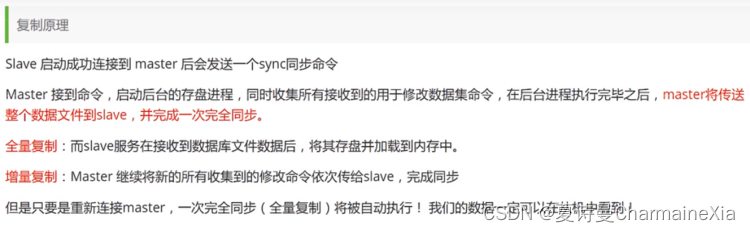
搭建主从模式集群redis

Web2.0 giants have deployed VC, and tiger Dao VC may become a shortcut to Web3
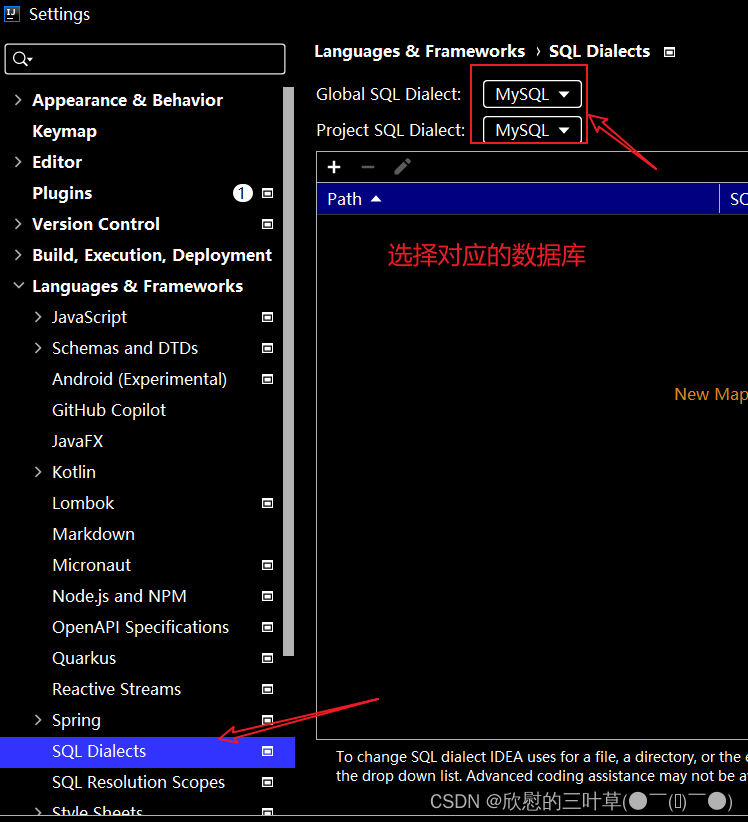
IDEA编辑器去掉sql语句背景颜色SQL语句警告No data sources are configured to run this SQL...和SQL Dialect is Not Config

Develop fixed asset management system, what voice is used to develop fixed asset management system

守望先锋世界观架构 ——(一款好的游戏是怎么来的)

Yunna | why use the fixed asset management system and how to enable it

SQLite 3.39.0 发布,支持右外连接和全外连接
随机推荐
【pytorch学习笔记】Tensor
mysql备份后缀是什么_mysql备份还原
开发固定资产管理系统,开发固定资产管理系统用什么语音
PHP非对称加密方法私钥及公钥加密解密的方法
NPOI导出Excel2007
AcWing 1125. 牛的旅行 题解(最短路、直径)
Golang concurrent programming goroutine, channel, sync
mybatiesHelperPro工具必须的可以生成到对应项目文件夹下
《代码整洁之道》读书笔记
Gamefi chain game system development (NFT chain game development function) NFT chain game system development (gamefi chain game development source code)
高级性能测试系列《24. 通过jdbc执行sql脚本》
电脑使用哪个录制视频软件比较好
A4988 drive stepper motor "recommended collection"
教程篇(5.0) 10. 故障排除 * FortiEDR * Fortinet 網絡安全專家 NSE 5
Chapter 7 - class foundation
Reduce -- traverse element calculation. The specific calculation formula needs to be passed in and combined with BigDecimal
IDEA编辑器去掉sql语句背景颜色SQL语句警告No data sources are configured to run this SQL...和SQL Dialect is Not Config
安装单机redis详细教程
Registration opportunity of autowiredannotationbeanpostprocessor under annotation development mode
4274. 后缀表达式-二叉表达式树