当前位置:网站首页>SVM and ANN of OpenCV neural network library_ Use of MLP
SVM and ANN of OpenCV neural network library_ Use of MLP
2022-06-10 15:29:00 【HNU_ Liu Yuan】
opencv Neural network library SVM and ANN_MLP
brief introduction
opencv It is the most commonly used library for computer vision , It integrates many functions needed for image processing , Recently, one of them has been used SVM( Support vector machine ) and ANN_MLP( Hand designed multi-layer perceptron ), Both are very classic “ neural network ”, The requirement for computing power is not so high , And it is very convenient to use , It's also faster , At the same time, it is integrated in opencv Medium , No need to install additional libraries .
SVM
In machine learning , Support vector machine ( English :support vector machine, Often referred to as SVM, Also known as support vector network ) It is a supervised learning model and related learning algorithm for analyzing data in classification and regression analysis . Give a set of training examples , Each training instance is marked as belonging to one or the other of the two categories ,SVM The training algorithm creates a model that assigns a new instance to one of two categories , Make it a non probability binary linear classifier .
SVM A model represents an instance as a point in space , In this way, the mapping makes the instances of individual categories separated by as wide and obvious intervals as possible . then , Map new instances to the same space , And based on which side of the interval they fall to predict the category .
For some low dimensional 、 Generally, linear kernel function is used for simple separable features , For complex features , Consider using nonlinear kernel functions , Mapping to linearly separable kernel functions .
The optimization formula is :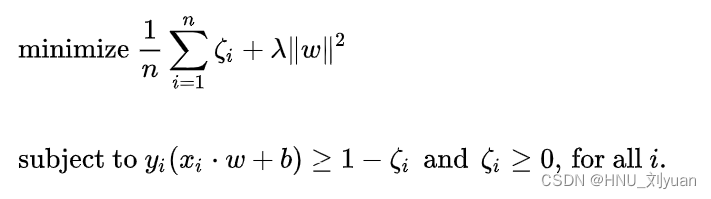
It's a convex optimization problem , There is no expansion here. For details, please refer to :SVM
MLP
Multilayer perceptron (Multilayer Perceptron, abbreviation MLP) It is an artificial neural network with forward structure , Map a set of input vectors to a set of output vectors .MLP It can be seen as a directed graph , It consists of multiple node layers , Each layer is fully connected to the next layer . In addition to the input node , Each node is a neuron with nonlinear activation function ( Or processing unit ).
MLP That is, the neural network built by the linear layer , The activation function must be nonlinear , such as ReLU、Sigmoid. The bottom layer of multi-layer perceptron is the input layer , In the middle is the hidden layer , Finally, the output layer .
MLP Has a long history , For some simple classification tasks , For example, handwritten numeral recognition , Can achieve better results . But for complex machine vision tasks , For example, testing 、 Tracking, etc , It seems that I can't do it .
MLP For a detailed introduction, please refer to : Multilayer perceptron
data fetch
SVM and MLP The required data formats are basically similar , For this kind of supervised learning , You need to enter features and labels . Features can be viewed as a form of data that can be observed , For example, for a picture, it is pixel information , For text , It can be its word vector . A tag is an attribute represented by a feature , Such as category and other information .
In common use MNIST Data sets, for example :
This is a number 3 Photos of the , Numbers 3 It corresponds to the label , The pixel value of this picture is a number 3 Show the characteristics of .
generally speaking , The number of features should be the same as the number of labels , Each feature corresponds to a label , But the dimensions of features are usually higher . Suppose the above figures 3 The photo size of is 16x16x1, Take the pixel of the photo as the feature vector , Its characteristic dimension is 256 dimension , The label dimension is generally set to 10 that will do , Corresponding 0~9 Ten figures .
Python The training and data reading under the environment are more convenient , In this paper, the general data preprocessing code is given :
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import glob
# Take two categories as an example
positive_dir = ""# Category 1 Folder path of pictures
negative_dir = ""# Category 2 Folder path of pictures
# Traverse images
positive_dir_imgs = glob.glob(positive_dir + "*.jpg")
negative_dir_imgs = glob.glob(negative_dir + "*.jpg")
img_size = 40 # Set picture size
train_mat=[] # Characteristic matrix
labels_label = np.zeros((len(positive_dir_imgs) + len(negative_dir_imgs), 2), np.float32) # Label matrix
# Category 1
for positive_dir_img in positive_dir_imgs:
pso_img=cv2.imread(positive_dir_img,0) # Read grayscale
pso_img = cv2.resize(pso_img, (img_size,img_size)) # Make it into a fixed size
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=pso_img[i][j] # Transform two-dimensional images into one-dimensional information
train_mat.append(Vect) # Add to the characteristic matrix
print(len(train_mat)) # Category 1 Number of pictures
# Category 2
for negative_dir_img in negative_dir_imgs:
nega_img=cv2.imread(negative_dir_img,0)
nega_img = cv2.resize(nega_img, (img_size,img_size))
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=nega_img[i][j]
train_mat.append(Vect)
print(len(train_mat))
train_mat = np.array(train_mat, dtype=np.float32)
# Label use one-hot code , For dichotomy , Category 1 The label of is [1,0], Category 2 yes [0,1]
for i in range(len(train_mat)):
if i <= len(positive_dir_imgs):
labels_label[i][0] = 1
labels_label[i][1] = 0
else:
labels_label[i][0] = 0
labels_label[i][1] = 1
Since then, the data processing operation has been completed , Get the characteristics (train_mat) Label corresponding to the feature (lables_label)
SVM Training and forecasting
For details, please refer to :[SVM file ]
Training
(https://docs.opencv.org/3.4.7/d1/d2d/classcv_1_1ml_1_1SVM.html)
# establish SVM
svm=cv.ml.SVM_create()
#SVM type
svm.setType(cv.ml.SVM_C_SVC)
# Linear kernel function
svm.setKernel(cv.ml.SVM_LINEAR)
svm.setC(0.01)
# Start training ( data , type , label )
result = svm.train(train_mat,cv.ml.ROW_SAMPLE,labels_num)
# Save the training model
svm.save("svm100.xml")
Open the saved xml file :
It can be seen that xml There is... In the file SVM Parameters of , Among the key information, the input feature dimension is 1600, The dimension of the output label is 2, The back is SVM Specific network parameters .
python edition SVM forecast
svm=cv.ml.SVM_load("svm100.xml")# Data saved from previous training
test_mat=train_mat[-10:]#SVM The processing methods of prediction data and training data are consistent , Take training data as an example
print(test_mat)
(P1,P2) = svm.predict(test_mat)# Output results
print(P1, P2)
C++ edition SVM forecast
To be added later ...
MLP Training and forecasting
For details, please refer to :MLP file
MLP Training
ann = cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_create()# establish MLP
ann.setLayerSizes(np.array([img_size*img_size, 64, 2])) # Set up MLP Every dimension of , The first is the input layer , In the middle is the hidden layer , The final output layer dimension
ann.setActivationFunction(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_SIGMOID_SYM, 0.6, 1.0)# Activate function settings
ann.setTrainMethod(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_BACKPROP, 0.1, 0.1)# How to train
ann.setTermCriteria((cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 1000, 0.01))
ann.train(train_mat, 0, labels_label)
ann.save("MLP")
Open the saved MLP file :
and SVM similar , It also contains dimension information of all layers , And the parameters of each neuron .
python edition MLP forecast
ann = cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_load("MLP")# load MLP Model parameters
test_mat=train_mat[-10:]#MLP Forecast data
(P1,P2) = ann.predict(test_mat)# Output results
print(P1, P2)
C++ edition MLP forecast
using namespace std;
#define RESIZE 40
int main()
{
std::string xml_path = "MLP";
cv::Ptr<cv::ml::ANN_MLP> ann = cv::ml::ANN_MLP::load(xml_path);
std::string img_path = "/";
cv::Mat frame, frame_resize;
std::vector<std::string> img_paths;
getFiles(img_path, img_paths);
cv::Mat responseMat;
for (int i = 0; i < img_paths.size(); i++)
{
frame = cv::imread(img_paths[i], 0);
cv::resize(frame, frame_resize, cv::Size(RESIZE, RESIZE));
cv::Mat testMat = frame_resize.clone().reshape(1, 1);
testMat.convertTo(testMat, CV_32F);
ann->predict(testMat, responseMat);
float* p = responseMat.ptr<float>(0);
cout << img_paths[i];
if (p[0] > p[1])
{
cout << "predict label 1" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "predict label 0" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Code summary
SVM
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import glob
positive_dir = "./crop_plane/"
negative_dir = "./random_crop/"
positive_dir_imgs = glob.glob(positive_dir + "*.jpg")
negative_dir_imgs = glob.glob(negative_dir + "*.jpg")
img_size = 100
train_mat=[]
labels_label = np.zeros((len(positive_dir_imgs) + len(negative_dir_imgs), 1), np.int32)
for positive_dir_img in positive_dir_imgs:
pso_img=cv2.imread(positive_dir_img,0)
pso_img = cv2.resize(pso_img, (img_size,img_size))
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=pso_img[i][j]
train_mat.append(Vect)
train_mat = np.array(train_mat, dtype=np.float32)
print(len(train_mat))
for negative_dir_img in negative_dir_imgs:
nega_img=cv2.imread(negative_dir_img,0)
nega_img = cv2.resize(nega_img, (img_size,img_size))
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=nega_img[i][j]
train_mat.append(Vect)
print(len(train_mat))
for i in range(len(train_mat)):
if i <= len(positive_dir_imgs):
labels_label[i][0] = 1
else:
labels_label[i][0] = -1
svm=cv2.ml.SVM_create()#SVM type
svm.setType(cv2.ml.SVM_C_SVC)# Linear kernel function
svm.setKernel(cv2.ml.SVM_LINEAR)
svm.setC(0.01)# Start training ( data , type , label )
result = svm.train(train_mat,cv2.ml.ROW_SAMPLE,labels_label)# Create a list to store test samples
svm.save("svm100.xml")
test_mat=train_mat[-10:]#SVM forecast
print(test_mat)
(P1,P2) = svm.predict(test_mat)# Output results
print(P1, P2)
MLP
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import glob
positive_dir = "./crop_plane/"
negative_dir = "./random_crop/"
positive_dir_imgs = glob.glob(positive_dir + "*.jpg")
negative_dir_imgs = glob.glob(negative_dir + "*.jpg")
img_size = 40
train_mat=[]
labels_label = np.zeros((len(positive_dir_imgs) + len(negative_dir_imgs), 2), np.float32)
for positive_dir_img in positive_dir_imgs:
pso_img=cv2.imread(positive_dir_img,0)
pso_img = cv2.resize(pso_img, (img_size,img_size))
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=pso_img[i][j]
train_mat.append(Vect)
print(len(train_mat))
for negative_dir_img in negative_dir_imgs:
nega_img=cv2.imread(negative_dir_img,0)
nega_img = cv2.resize(nega_img, (img_size,img_size))
Vect=np.zeros(img_size*img_size) # First, then
for i in range(img_size):
for j in range (img_size):
Vect[img_size*i+j]=nega_img[i][j]
train_mat.append(Vect)
print(len(train_mat))
train_mat = np.array(train_mat, dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(len(train_mat)):
if i <= len(positive_dir_imgs):
labels_label[i][0] = 1
labels_label[i][1] = 0
else:
labels_label[i][0] = 0
labels_label[i][1] = 1
ann = cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_create()
ann.setLayerSizes(np.array([img_size*img_size, 64, 2]))
ann.setActivationFunction(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_SIGMOID_SYM, 0.6, 1.0)
ann.setTrainMethod(cv2.ml.ANN_MLP_BACKPROP, 0.1, 0.1)
ann.setTermCriteria((cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS, 1000, 0.01))
print(train_mat.shape)
print(labels_label.shape)
ann.train(train_mat, 0, labels_label)
ann.save("MLP")
test_mat=train_mat[-10:]
print(test_mat)
(P1,P2) = ann.predict(test_mat)# Output results
print(P1, P2)
边栏推荐
- 企业如何提升文档管理水平
- 【奖励公示】【内容共创】第16期 五月絮升华,共创好时光!签约华为云小编,还可赢高达500元礼包!
- Problems with database creation triggers
- Explain the opencv function filter2d() in detail and remind you that the operation it does is not convolution but correlation operation
- Kubernetes 1.24: 避免为 Services 分配 IP 地址时发生冲突
- Li Kou daily question - day 18 -350 Intersection of two data Ⅱ
- 百度开源ICE-BA安装运行总结
- Summary of 5 years' experience in ERP odoo privilege management system setup
- 【高代码文件格式API】上海道宁为您提供文件格式API集——Aspose,只需几行代码即可创建转换和操作100多种文件格式
- Hessian matrix of convex function and Gauss Newton descent method
猜你喜欢

RSA a little bit of thought
CAP 6.1 版本发布通告

Development of stm8s103f single chip microcomputer (1) lighting of LED lamp

小程序网络请求Promise化

如何構建以客戶為中心的產品藍圖:來自首席技術官的建議

4. Meet panuon again UI. Title bar of silver form

AutoCAD - set text spacing and line spacing

How to build a customer-centric product blueprint: suggestions from the chief technology officer

3. Encounter the form of handycontrol again

In what scenario can we not use the arrow function?
随机推荐
MITM(中间人攻击)
企业如何提升文档管理水平
面试题详情
Tensorflow actual combat Google deep learning framework second edition learning summary tensorflow introduction
TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架第二版学习总结-TensorFlow入门
Golang uses reflection to directly copy data from one structure to another (through the same fields)
We media video Hot Ideas sharing
One-way hash function
Kubernetes 1.24: avoid conflicts when assigning IP addresses to services
C# 游戏雏形 人物地图双重移动
docket命令
cmake实战记录(一)
Technology sharing | quick intercom, global intercom
Day10/11 recursion / backtracking
在什么场景下,我们不能使用箭头函数?
详解OpenCV的函数filter2D(),并提醒大家它做的运算并不是卷积运算而是相关运算
2022第十四届南京国际人工智能产品展会
How to improve document management
Vins theory and code explanation 4 - initialization
Using GDB to quickly read the kernel code of PostgreSQL
