当前位置:网站首页>神经网络与深度学习-5- 感知机-PyTorch
神经网络与深度学习-5- 感知机-PyTorch
2022-07-08 00:16:00 【明朝百晓生】
参考文档:
《神经网络与深度学习》
前言:
感知机是1957年由Frank RoseBlatt 提出的,是一种广泛应用的线性分类器。
这是一种错误驱动的算法
Scikit-Learn (1.Sklearn提供的常用数据集 - 自带的小数据集)_Micheal超的博客-CSDN博客_体能训练数据集
一 感知机

1.1 参数学习

算法试图找到一组参数w,使得对于每个样本 有
有

1.1 损失函数

采用随机梯度下降

1.2 算法流程

1.3 算法的收敛性
1963年 Novioff证明了该算法在线性可分数据集上的可收敛性
缺点:
泛化能力差,
每次迭代顺序不一致超平面也不一样。
如果线性不可分,则永远不会收敛
二 投票感知器
感知机学习的权重向量和训练样本的顺序相关。
为了提高感知器的鲁棒性和泛化能力,我们可以讲感知器学习过程中的所有K个权重向量保存起来(出错的),并赋予每个权重向量一个 一个置信系数
一个置信系数 ,最终的分类结果通过K个不同权重的感知器投票决定,这个模型也称为投票感知器
,最终的分类结果通过K个不同权重的感知器投票决定,这个模型也称为投票感知器
设
为第k次更新权重
的迭代次数(训练过的样本数量)
为下次更新迭代次数
的置信系数
设置成
到
之间间隔的迭代次数
,置信系数
越大,
说明权重
之后分类正确的样本越多,越值得信赖
这是一种集成学习的思想,用K个分类器,投票决定一个结果
三 平均感知器




T为总迭代次数,
 为T次迭代平均权重向量
为T次迭代平均权重向量


四 生成线性可分数据集
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Jul 6 12:07:09 2022
@author: chengxf2
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
import csv
def saveCsv(trainData):
with open('trainData.csv','w') as f:
wr = csv.writer(f)
wr.writerows(trainData)
'''
分类生成器
参考 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/ask/sof/1961912/answer/2665673
args
n_samples: 生成样本总数
n_features: 单样本维度 n_informative + n_redundant + n_repeated
n_classes : 类别
centers: 要生成的样本中心,默认为3
n_informative: 多信息特征维度
n_redundant: 冗余特征维度
n_repeated: 重复信息
shuffle: 打乱
n_clusters-per_calsss: 一个类别由几个cluster组成
return
data: array 样本X
feature: 样本特征
'''
def makeTrain(batch=1000):
separable = False
trainData =[]
while not separable:
samples = make_classification(n_samples=batch, n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_informative=1, n_clusters_per_class=1, flip_y=-1)
red = samples[0][samples[1] == 0]
blue = samples[0][samples[1] == 1]
separable = any([red[:, k].max() < blue[:, k].min() or red[:, k].min() > blue[:, k].max() for k in range(2)])
data = samples[0]
feature = samples[1]
#print(np.shape(data),type(data))
for i in range(batch):
item = list(data[i])
label = feature[i]
item.append(label)
trainData.append(item)
#print(label)
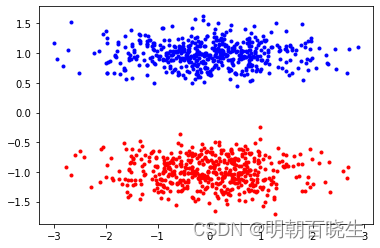
plt.plot(red[:, 0], red[:, 1], 'r.')
plt.plot(blue[:, 0], blue[:, 1], 'b.')
plt.show()
return trainData
data = makeTrain(100)
saveCsv(data)五 两类感知器的参数学习例子
以上面生成的数据集进行Train
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Jul 6 14:08:27 2022
@author: chengxf2
"""
import numpy as np
import torch
import csv
import os
#感知机(模拟大脑识别事物和差异的人工网络)
class perceptron():
'''
从csv文件里面加载数据集
args
self.fileName : 文件路径
'''
def loadData(self):
if not os.path.exists(self.fileName) :
print("\n ------文件路径不存在-----")
return None
feature =[] #样本标签Y skelearn 为0-1 要转为 -1,1
trainData =[] # 训练集X
with open(self.fileName)as f:
f_csv = csv.reader(f)
for row in f_csv:
Y = int(row[-1])*2-1 # 变成[-1,1]
X = [float(v) for v in row[0:-1]]
X.append(1) #生成增广矩阵
trainData.append(X)
feature.append(Y)
#print(data,label)
self.m,self.n = np.shape(trainData)
print("\n ----第一步 加载数据集---------")
return torch.FloatTensor(trainData),torch.IntTensor(feature)
'''
预测
'''
def forecast(self,w,x):
hatY = torch.matmul(w.T, x)
sgnY = 0
#print("\n forecast",w, x)
if hatY>0:
sgnY =1
elif hatY<0:
sgnY =-1
return hatY, sgnY
'''
预测
'''
def test(self,trainData, feature,w):
err = 0
for i in range(0,self.m):
index = torch.LongTensor([i])
#print(index, index.dtype)
i = 0
x = trainData[index].T# 列向量
y = torch.index_select(feature, -1, index) #对应的标签值
predy,sngY =self.forecast(w,x)
result = sngY*y
#print("\n sngY: ",sngY,"\t y ",y)
if result<=0:
err = err+1
print("\n 分类出错的数目 ",err)
'''
训练
'''
def train(self,trainData, feature):
w = torch.zeros((3,1)) #权重系数
k = 0 #每轮预测出错的样本个数
t = 0 #迭代次数
bLoop = True
print("\n -----step2 训练开始了---------------")
while(bLoop):
perm = torch.randperm(self.m) #打乱数据集 随机采样
k = 0 #本轮分类出错的默认为0
t =t+1 #迭代次数
for i in range(self.m):
index = perm[i] #取索引
x = trainData[index].T# 列向量
y = torch.index_select(feature, -1, index) #对应的标签值
hatY,sgnY = self.forecast(w,x) #预测
result = y*sgnY #预测是否正确
if result<=0: #预测出错了
k = k+1
a = y*x
w = w+a.view(3,1) #更新梯度
#print("\n result ",result, "\t ",y, "\t sgny ",sgnY,index)
print("\n k:%d t:%d "%(k,t),"w: ",w)
if t == self.maxIter:
print("\n ---停止训练---------")
bLoop = False
break
return w
def __init__(self):
self.m = 0 #样本个数
self.n = 0 #样本维度
self.maxIter = 10 #最大迭代次数
self.fileName = "trainData.csv"
if __name__ == "__main__":
model = perceptron()
trainData, feature = model.loadData()
w = model.train(trainData, feature)
model.test(trainData, feature, w)边栏推荐
- QML fonts use pixelsize to adapt to the interface
- Common operations of numpy on two-dimensional array
- Redux使用
- 跨模态语义关联对齐检索-图像文本匹配(Image-Text Matching)
- After modifying the background of jupyter notebook and adding jupyterthemes, enter 'JT -l' and the error 'JT' is not an internal or external command, nor a runnable program
- powerbuilder 中使用线程的方法
- 从Starfish OS持续对SFO的通缩消耗,长远看SFO的价值
- 小金额炒股,在手机上开户安全吗?
- Gnuradio transmits video and displays it in real time using VLC
- 批次管控如何实现?MES系统给您答案
猜你喜欢
![[loss function] entropy / relative entropy / cross entropy](/img/bc/574a4745336b0baf1a4ca53af41a82.jpg)
[loss function] entropy / relative entropy / cross entropy
Understanding of maximum likelihood estimation
Gnuradio transmits video and displays it in real time using VLC

The foreach map in JS cannot jump out of the loop problem and whether foreach will modify the original array

从Starfish OS持续对SFO的通缩消耗,长远看SFO的价值
The beauty of Mathematics -- the principle of fine Fourier transform
Tapdata 的 2.0 版 ,开源的 Live Data Platform 现已发布

Getting started STM32 -- how to learn stm32
About how USRP sets the sampling frequency below the minimum sampling frequency reached by the hardware

Chapter 7 behavior level modeling
随机推荐
Plot function drawing of MATLAB
QT--创建QT程序
图解网络:揭开TCP四次挥手背后的原理,结合男女朋友分手的例子,通俗易懂
DataWorks值班表
About how USRP sets the sampling frequency below the minimum sampling frequency reached by the hardware
Gnuradio 3.9 using OOT custom module problem record
Qt - - Packaging Programs - - Don't install Qt - can run directly
【SolidWorks】修改工程图格式
From starfish OS' continued deflationary consumption of SFO, the value of SFO in the long run
如何制作企业招聘二维码?
pb9.0 insert ole control 错误的修复工具
uniapp一键复制功能效果demo(整理)
break net
小金额炒股,在手机上开户安全吗?
不算不知道,花呗分期的真实利率居然这么高
How does Matplotlib generate multiple pictures in turn & only save these pictures without displaying them in the compiler
为什么更新了 DNS 记录不生效?
Redis集群
The usage of rand function in MATLAB
PB9.0 insert OLE control error repair tool
 为第k次更新权重
为第k次更新权重 为下次更新迭代次数
为下次更新迭代次数 设置成
设置成 ,置信系数
,置信系数