当前位置:网站首页>Interview summary on November 7, 2020 (interview 12K)
Interview summary on November 7, 2020 (interview 12K)
2020-11-09 10:51:00 【osc_rq7kb4yf】
The reason for work , And I don't study hard ( Ha ha ha ) Try to guide the interviewer to ask ssm Framework
The article is for me This week ,5 The summary of the day's interview
First say mysql
mysql: The address of the original text
1. engine
2. Indexes
3. Isolation level
4. lock
1. Storage engine
One Innodb(mysql Default engine )
Support transactions , It's business safety , Provides row level locks and foreign key constraints , There's a buffer pool , For buffering data and indexes
Applicable scenario : For transaction processing , have ACID Things support , Used to perform a large number of insert and update Table of operations
Two MyISAM
Unsupported transaction , Foreign key constraints are not supported , Row level locks are not supported , The whole table needs to be locked during operation , However, the number of rows in the table will be saved , So when you execute select count(*) from tablename It's very fast
Applicable scenario : Used to manage non transactional tables , Provide high-speed retrieval and full-text retrieval capabilities , Apply to a large number of select Table of operations , Such as Log table
3、 ... and MEMORY
Create a table with content that exists in memory , every last memory It only corresponds to one disk file . The engine uses hash Indexes , It can be positioned at once , No need to be like B Tree like search from root node to branch node , So the access speed of precise query is very fast , But when it comes to imprecise searches , such as like, This range lookup ,hash It doesn't work .
Applicable scenario : It is mainly used for the table whose content changes infrequently , Or as an intermediate lookup table . Be careful when updating tables because the data is not written to disk , Consider the storage of data before shutting down the service
Four MERGE
MERGE Storage engine MyISAM The data table is treated as a logical unit , So we can query them at the same time . Constitute a MERGE Members of the data table structure MyISAM Data tables must have exactly the same structure . The data columns of each member data table must have the same name and type defined in the same order , Indexes must also be defined in the same order and in the same way .
Two 、 Index type
General index : Only speed up queries
unique index : Speed up queries + Column value uniqueness ( There can be null)
primary key : Speed up queries + Column value uniqueness ( There can be no null)+ There is only one in the list
Composite index : Multiple column values form an index , Dedicated to combined search , It is more efficient than index merging
When to create an index :
MySQL Only right <,<=,=,>,>=,BETWEEN,IN, And sometimes LIKE To use the index
When the index doesn't work :
1、 Use like Keyword fuzzy query , The first position is any character
3、OR When the columns in both the preceding and subsequent conditions are indexed , The index will take effect .
4、 Try to avoid where Used in clauses != or <> The operator , Otherwise the full table scan .
5、 stay where Clause to express the field , Function operation , Otherwise the full table scan .
6、order by Indexes , Problems that don't work ( Besides the primary key index ):
1、 If select Query only index fields ,order by The index field will use the index , Or it's a full table arrangement ;
2、 If there is where Conditions , such as where vtype=1 order by vtype asc . such order by Index is also used !
Composite index ? In which scenes , Composite indexes will fail :
1、 Composite index fields use indexes no matter how the order changes , The premise is that all fields are in where Conditionally
2、 If you want to use one or two fields in where Conditionally , There must be the first field in the composite index , But it's not about the order , for example a,c or c,a, This scenario can hit the index . however ,b,c or c,b This doesn't hit the index ..
3、order by Only use a, To use the index
mysql Optimization method :
What to consider when creating a table :
1、 Select the most appropriate field property
2、 Try to set the field to NOT NULL
3 Use connections (JOIN) Instead of subquery
4. Link query recommendation :inner join( Internal connection )
5. Create the appropriate index
Optimize SQL Query statement
1 Do not use subqueries
2 Avoid functional indexes
3 use IN To replace OR
4 LIKE The first position is that any character cannot be indexed
6 Avoid inconsistent data types
7 Grouping statistics can prohibit sorting
8 Prohibit unnecessary ORDER BY Sort
9 Batch INSERT Insert
Why subqueries are better than join queries (LEFT JOIN) Low efficiency :
When executing a subquery ,MYSQL You need to create a temporary table , Delete these temporary tables after query , therefore , The speed of subqueries will be affected , Here's an extra process to create and destroy the temporary table
Business :
Atomicity : One thing (transaction) All operations in , Or it's all done , Or not at all , It doesn't end in the middle . An error occurred during the execution of the transaction , Will be rolled back (Rollback) To the state where the transaction begins , It's like this transaction has never been executed .
Uniformity : Before the transaction starts and after the transaction ends , The integrity of the database is not compromised . This means that the data written must fully comply with all the default rules , This includes the accuracy of the data 、 Serialization and subsequent databases can spontaneously accomplish the scheduled work .
Isolation, : The ability of a database to allow multiple transactions to read, write, and modify its data at the same time , Isolation can prevent data inconsistency caused by cross execution when multiple transactions are executed concurrently . Transaction isolation is divided into different levels , Include read uncommitted (Read uncommitted)、 Read submitted (Read committed)、 Repeatable (repeateable read) And serialization (Serializable).
persistence : After transaction ends , Changes to data are permanent , Even if the system fails, it will not be lost .
Transaction isolation level
Read uncommitted
Read submitted
Repeatable
Serialization
The problems that arise :
1、 Dirty reading : Business A Read transaction B Updated data , then B Rollback operation , that A The data read is dirty data
2、 It can't be read repeatedly : Business A Read the same thing many times , Business B In the transaction A During multiple reads , Update the data and submit , Cause transaction A When reading the same data multiple times , Inconsistent results .
3、 Fantasy reading : System administrator A Change the scores of all students in the database from specific scores to ABCDE Grade , But the system administrator B At this time, a specific score record was inserted , When the system administrator A After the change, I found that there is another record that hasn't been changed , It's like an illusion , This is called Unreal reading .
lock
InnoDB The row lock of is the lock added for the index , It's not a lock on records . And the index cannot be invalidated , Otherwise, it will be upgraded from row lock to table lock
Row lock
The disadvantage of row lock : Spending big ; Lock the slow ; A deadlock occurs
The advantages of row locks : The granularity of the lock is small , The probability of lock conflict is low ; The ability to handle concurrency is strong
The way to lock : Automatic locking . about UPDATE、DELETE and INSERT sentence ,InnoDB An exclusive lock will be automatically added to the involved data set ; For ordinary SELECT sentence ,InnoDB No locks ; Of course, we can also show the lock :
Shared lock :select * from tableName where … + lock in share more
Exclusive lock :select * from tableName where … + for update
Exclusive lock
Exclusive lock , Also known as write lock , An exclusive lock , Before the current write operation is completed , It blocks other write and read locks .
Shared lock
Shared lock , Also known as read lock , It is used to judge whether the data exists , Multiple read operations can be performed simultaneously without affecting each other . If the transaction modifies the read lock , It is likely to cause deadlock .
Analysis line locking
clear through InnoDB_row_lock State variable analysis system row lock contention situation
innodb_row_lock_current_waits: The number of currently waiting locks
innodb_row_lock_time: The total length of time from system startup to lock up ; Very important parameters ,
innodb_row_lock_time_avg: The average time it takes to wait ; Very important parameters ,
innodb_row_lock_time_max: Time spent waiting for the most frequent time from system startup to now ;
innodb_row_lock_waits: The total number of times the system has been waiting since it was started ; Very important parameters . Directly determine the direction and strategy of optimization
Row lock optimization
1 As far as possible, all data retrieval should be done through index , Avoid non index row or index invalidation leading to row lock upgrade to table lock .
2 Try to avoid performance degradation caused by clearance lock , Reduce or use a reasonable search range .
3 Reduce transaction granularity as much as possible , For example, controlling transaction size , And from reducing the amount of locked resources and the length of time , So as to reduce the lock competition and so on , Provide performance .
4 As low level transaction isolation as possible , Higher isolation level , The less concurrent processing power .
Table locks
The advantages of watch lock : Low overhead ; Locked fast ; No deadlock
The disadvantage of watch lock : Big lock size , The probability of lock conflict is high , Low concurrency
The way to lock : Automatic locking . Query operation (SELECT), Will automatically lock all tables involved , update operation (UPDATE、DELETE、INSERT), Will automatically lock the tables involved . You can also show lock :
Shared read lock :lock table tableName read;
Exclusive write lock :lock table tableName write;
Batch unlock :unlock tables;
Shared read lock
Yes MyISAM Read operation of table ( Add read lock ), It will not block other processes from reading the same table , But it blocks writes to the same table . Only when the read lock is released , In order to perform the write operation of other processes . Cannot fetch other tables until lock is released .
Exclusive write lock
Yes MyISAM Write operation of table ( Add write lock ), Will block other processes to read and write to the same table , Only when the write lock is released , Will perform read and write operations of other processes . No other tables can be written until the lock is released .
In what situation is watch lock used
InnoDB Row lock is used by default , Promote to table lock when index field query is not used .
Case one : Full table update .
The second case : Multi-table query .
summary
1 InnoDB Support table lock and row lock , Using the index as the search condition, the row lock is used to modify the data , Otherwise, watch lock is used .
2 InnoDB Automatically lock changes , Do not lock queries automatically
3 Row lock may be promoted to table lock because index is not used , So in addition to checking whether the index is created , It also needs to pass explain Whether the execution plan query index is actually used .
4 Row lock is relative to table lock , The advantage is that it performs better in high concurrency scenarios , After all, the granularity of locks is small .
5 When most of the data in the table needs to be modified , Or when multiple tables are complex associated queries , Table lock is better than row lock .
6 In order to ensure the consistent integrity of the data , There is a locking mechanism in any database . The advantages and disadvantages of locking mechanism directly affect the concurrent processing ability and performance of a database .
版权声明
本文为[osc_rq7kb4yf]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- [QT] subclass qthread to realize multithreading
- 程序人生|从网瘾少年到微软、BAT、字节offer收割机逆袭之路
- 【译】npm developer guide
- 1486. 数组异或操作
- 使用rem,做到屏幕缩放时,字体大小随之改变
- SQL第二章第三章
- A solution to the problem that color picker (palette) cannot use shortcut keys in sublime Text3 plug-in
- Windows环境下如何进行线程Dump分析
- Initial installation of linx7.5
- Natural language processing (NLP) roadmap - KDnuggets
猜你喜欢

From the practice, this paper discusses the problems caused by the inconsistent design of ruby syntax.
Biden wins the US election! Python developers in Silicon Valley make fun of Ku Wang in this way
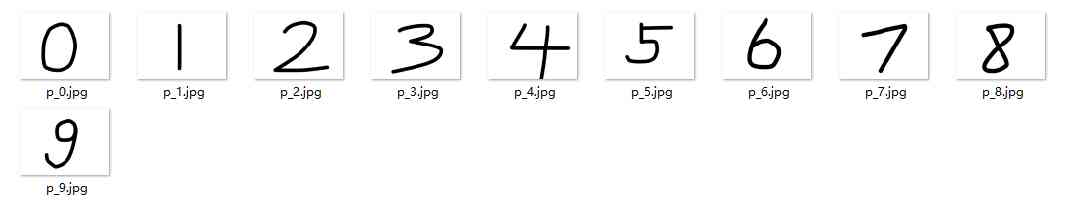
手写数字图片识别-卷积神经网络

Python零基础入门教程(01)
程序人生|从网瘾少年到微软、BAT、字节offer收割机逆袭之路

Apache Iceberg 中三种操作表的方式

20201108 programming exercise exercise 3

3.你知道计算机是如何启动的吗?
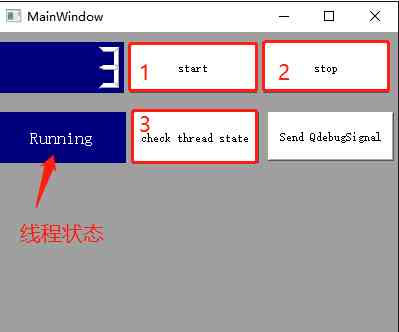
【QT】子类化QThread实现多线程

配置交换机Trunk接口流量本地优先转发(集群/堆叠)
随机推荐
1450. 在既定时间做作业的学生人数
百亿级数据分表后怎么分页查询?
开源 | HMGNN:异构小图神经网络及其在拉新裂变风控场景的应用
2 normal mode
WordPress Import 上传的文件尺寸超过php.ini中定义的upload_max_filesize值--&gt;解决方法。
你不好奇 CPU 是如何执行任务的吗?
如何保证消息不被重复消费?(如何保证消息消费的幂等性)
Natural language processing (NLP) roadmap - KDnuggets
MapStruct 解了对象映射的毒
libssl对CentOS登录的影响
20201108编程练习——练习3
Android emulator error: x86 emulation currently requires hardware acceleration的解决方案
[design pattern] Chapter 4: Builder mode is not so difficult
SQL语句实现水仙花数求取
商品管理系统——商品新增本地保存实现部分
Sublime text3 插件ColorPicker(调色板)不能使用快捷键的解决方法
In 2020, what are the best tools for Android developers to break the cold winter?
开源ERP招聘了
Finally, the python project is released as exe executable program process
Detailed analysis of OpenGL es framework (8) -- OpenGL es Design Guide