当前位置:网站首页>[C language] branch and loop statements (Part 1)
[C language] branch and loop statements (Part 1)
2022-07-03 00:58:00 【Brain melon seed Weng Feng】
List of articles
Preface
This article mainly talks about branch statements in branch and loop statements , The explanation of circular sentences will be explained in the next blog .
1. What is a sentence ?
- C Language is 【 structured 】 Control statement of

- C Sentences can be divided into the following five categories :
- Expression statement
- Function call statements
- Control statement
- Compound statement
- Empty statement
- Control statement Used to control the execution flow of the program , In order to realize the various structures of the program , They are made up of specific statement definers ,C There are nine control statements in language .
It can be divided into three categories :
- Conditional judgment statements are also called branch statements :if sentence 、switch sentence ;
- Loop statement :do while sentence 、while sentence 、for sentence ;
- Turn to statement :break sentence 、goto sentence 、continue sentence 、return sentence .
2. Branch statement ( Selection structure )
2.1 if sentence
if Sentence grammar structure
If the result of the expression is true , Then the statement executes .
stay C In language 0 Said the false , Not 0 Said really .
(1)
if( expression )
sentence ;
(2)
if( expression )
sentence 1;
else
sentence 2;
(3) Multiple branches
if( expression 1)
sentence 1;
else if( expression 2)
sentence 2;
else
sentence 3;
- Sample code 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 0;
scanf("%d", &age);
if (age < 18)
{
printf(" A minor \n");
}
return 0;
}

- Sample code 2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 0;
scanf("%d", &age);
if (age < 18)
{
printf(" A minor \n");
}
else
{
printf(" adult \n");
}
return 0;
}

- Sample code 3
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 0;
scanf("%d", &age);
if (age < 18)
{
printf(" juvenile \n");
}
else if (age >= 18 && age < 30)
{
printf(" youth \n");
}
else if (age >= 30 && age < 50)
{
printf(" middle-aged \n");
}
else if (age >= 50 && age < 80)
{
printf(" The elderly \n");
}
else
{
printf(" Old birthday star \n");
}
return 0;
}

If the condition holds , To execute multiple statements , How to use code blocks ?
if and else Can only control one statement , There are multiple statements that must use { }. A couple here { } It's just a code block
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
if ( expression )
{
Statement list 1;
}
else
{
Statement list 2;
}
return 0;
}
Code example
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int age = 10;
if (age < 18)
{
printf(" A minor \n");
printf(" Don't drink \n");
}
else
{
printf(" adult \n");
printf(" Play the game \n");
}
return 0;
}

2.1.1 In the air else
Look at the code below , Guess the printed result is hehe still haha
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
if (a == 1)
if (b == 2)
printf("hehe\n");
else
printf("haha\n");
return 0;
}

analysis :
Looking at the print results, we will find that the print results are not hehe Neither haha, It's empty , Looking back at the format of this code will make us think else Yes, and the first if matching , however else It's the one closest to him if Matching , therefore if(a==1) Conditions not established , The result is false , Do not execute statements , The result is empty. . One if…else Statement is a complete statement .
correct :
// Use properly {} It can make the logic of the code clearer .
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
if (a == 1)
{
if (b == 2)
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
}
else
{
printf("haha\n");
}
return 0;
}

2.1.2 if Contrast of writing forms
Code 1
if (condition) {
return x;
}
return y;
Code 2
if(condition)
{
return x;
}
else
{
return y;
}
Code 3
int num = 1;
if(num == 5)// If you don't write an equal sign here, the compiler won't report an error , When there is only one equal sign, it means assignment , because num Is a variable that can be re assigned , So the compiler will not warn .
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
Code 4
int num = 1;
if(5 == num)//if(num == 5), If there is only one equal sign here , The compiler will report an error , Let's put constants on the right , It is not possible to assign a variable to a constant , Even if we write the wrong compiler, it will quickly help us find problems .
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
Code 2 And code 4 Better , Logic is clearer , Not easy to make mistakes .
2.1.3 practice
1. Judge whether a number is odd
We learned here if sentence , We try to use if Statement write code .
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num = 0;
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num % 2 == 1)
printf(" Odd number \n");
else
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}

2. Output 1-100 Between the odd numbers
We need to use loop statements here , We can use while Loops can also be used for loop .
//while loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
while (i <= 100)
{
if (i % 2 == 1)
printf("%d ", i);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
//for loop
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 1)
printf("%d ", i);
}
return 0;
}

2.2 switch sentence
switch Statement is also a branch statement .
It is often used in the case of multiple branches .
such as :
Input 1, Output Monday
Input 2, Output Tuesday
Input 3, Output Wednesday
Input 4, Output Thursday
Input 5, Output Friday
Input 6, Output Saturday
Input 7, Output Sunday
I didn't write it if…else if …else if The form of is too complicated , Then we have to have different grammatical forms . This is it. switch sentence .
switch//( Shaping expression )
{
Statement item
}
What is? Statement item ?
// It's some case sentence :
// as follows :
case Integer constant expression :
sentence ;
2.2.1 stay switch Statement break
stay switch In the sentence , We can't branch directly , collocation break Use to achieve true branching .
such as :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int day = 0;
scanf("%d", &day);
switch (day)
{
case 1:
printf(" Monday \n");
break;
case 2:
printf(" Tuesday \n");
break;
case 3:
printf(" Wednesday \n");
break;
case 4:
printf(" Thursday \n");
break;
case 5:
printf(" Friday \n");
break;
case 6:
printf(" Saturday \n");
break;
case 7:
printf(" Sunday \n");
break;
}
return 0;
}

Sometimes our needs change :
- Input 1-5, The output is “weekday”;
- Input 6-7, Output “weekend”
So our code should be implemented like this :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int day = 0;
scanf("%d", &day);
switch (day)
{
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
case 4:
case 5:
printf("weekday\n");
break;
case 6:
case 7:
printf("weekend\n");
break;
}
return 0;
}

It's explained here case There is no need to add break , No, break Will continue to go down .
break sentence The actual effect of is to divide the statement list into different branches .
Programming good habits
In the last case Add a clause after the statement break sentence .
( The reason for writing this is to avoid appearing in the last one before case I forgot to add... After the statement break sentence ).
2.2.2 default Clause
default:
Write in any one case Where labels can appear .
When switch The value of the expression does not match all case The value of the tag , This default The statement following the clause will execute .
therefore , Every switch Only one... Can appear in the statement default Clause .
But it can appear anywhere in the statement list , And the statement flow will execute a case Execute as tag default Clause .
Programming good habits
At every switch Put one in every statement default Clause is a good habit , You can even add another one in the back break .
2.2.3 practice
Here we do an exercise , See if we are right switch Master , Read the following code , To calculate the m,n What's the value of ?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n = 1;
int m = 2;
switch (n)
{
case 1:
m++;
case 2:
n++;
case 3:
switch (n)
{
//switch Allow nesting
case 1:
n++;
case 2:
m++;
n++;
break;
}
case 4:
m++;
break;
default:
break;
}
printf("m = %d, n = %d\n", m, n);
return 0;
}

Be careful :
- switch Statements can be nested .
- switch In the sentence break Will only jump out of their own switch, Not a break Jump out of all switch sentence .
This chapter ends here , If there is anything bad written , Please correct me. .
If you think it's good and helpful to you, please give support to the third company !
Fighting!!!
边栏推荐
- 2022 list of manufacturers of Chinese 3D vision enterprises (guided positioning and sorting scenes)
- [introduction to AUTOSAR seven tool chain]
- KingbaseES ALTER TABLE 中 USING 子句的用法
- 2022.2.14 resumption
- Leetcode-871: minimum refueling times
- Tensorflow 2.x(keras)源码详解之第十五章:迁移学习与微调
- FPGA - 7系列 FPGA内部结构之Clocking -04- 多区域时钟
- Hdu3507 (slope DP entry)
- Leetcode-224: basic calculator
- lex && yacc && bison && flex 配置的問題
猜你喜欢
文件操作IO-Part2

【AutoSAR 四 BSW概述】
![[AUTOSAR nine c/s principle Architecture]](/img/59/ce32c0ff58ef5d8385fe950136175b.png)
[AUTOSAR nine c/s principle Architecture]
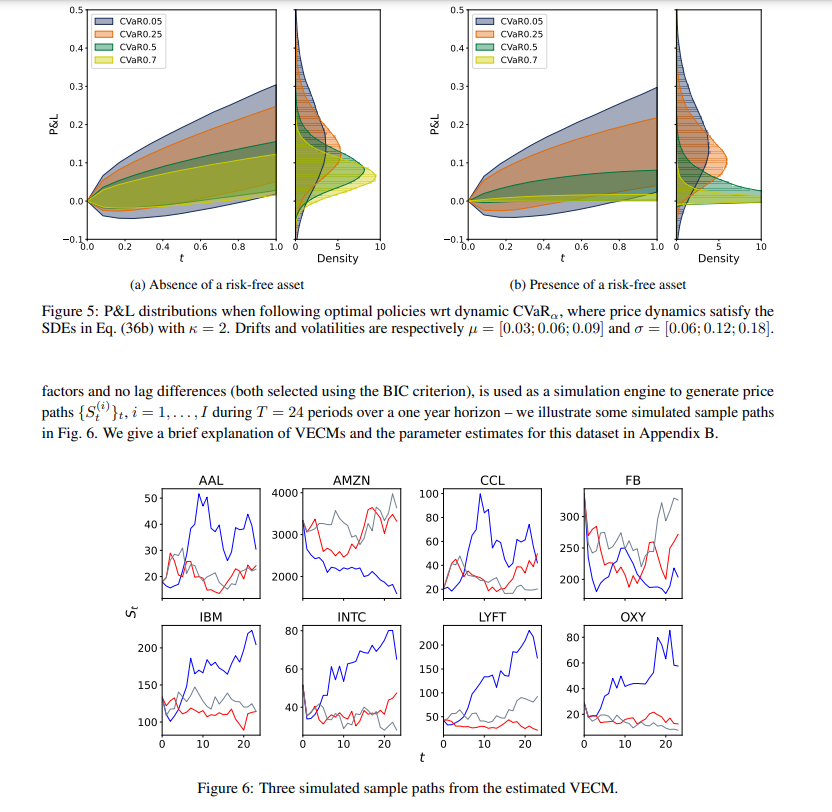
University of Toronto: Anthony coach | the conditions of deep reinforcement learning can induce dynamic risk measurement
An excellent orm in dotnet circle -- FreeSQL
![[overview of AUTOSAR four BSW]](/img/19/c2273bbedb7f8d859e5a3805ed5740.png)
[overview of AUTOSAR four BSW]
Attributeerror: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'layer' problem solving
【AutoSAR 十三 NVM】

1.12 - 指令
![[love crash] neglected details of gibaro](/img/d6/baa4b5185ddaf88f3df71a94a87ee2.jpg)
[love crash] neglected details of gibaro
随机推荐
【AutoSAR 四 BSW概述】
Extension of flutter
[AUTOSAR I overview]
Reading and writing speed of Reza rz/g2l arm development board storage and network measurement
[shutter] image component (load network pictures | load static pictures | load local pictures | path | provider plug-in)
[AUTOSAR nine c/s principle Architecture]
First hand evaluation of Reza electronics rz/g2l development board
2022中国3D视觉企业(引导定位、分拣场景)厂商名单
全志A40i/T3如何通过SPI转CAN
数学建模之线性规划(含MATLAB代码)
Thread start and priority
Array common operation methods sorting (including ES6) and detailed use
Sentry developer contribution Guide - configure pycharm
tail -f 、tail -F、tailf的区别
Lex & yacc & bison & flex configuration problems
Cordova plugin device obtains the device information plug-in, which causes Huawei to fail the audit
【AutoSAR 七 工具链简介】
Basic use of sringcloud & use of component Nacos
Attributeerror: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'layer' problem solving
KingbaseES ALTER TABLE 中 USING 子句的用法