当前位置:网站首页>[C language] string function and Simulation Implementation strlen & strcpy & strcat & StrCmp
[C language] string function and Simulation Implementation strlen & strcpy & strcat & StrCmp
2022-07-05 19:42:00 【Ordinary person 1】
author :@ Ordinary person 1
special column :《C Language from 0 To 1》
In a word : In the past , All is prologue
explain : The past is irreparable , The future can change
List of articles
Preface
We know , stay C The processing of characters and strings in languages is very frequent , however C The language itself has no string type ( Unlike other languages, direct String Can solve ), stay C Strings in languages are usually placed in constant strings or character arrays .
String constants apply to string functions that do not modify it .
We mainly introduce some string functions this time .
- About learning some strange functions : We can go through cplusplus.com Learn to understand , Know the meaning represented by the parameters and the functions realized are the above , This can make us get twice the result with half the effort ! If you don't understand English , We can translate it into Chinese that we are familiar with .
- Be sure to implement the code yourself , Don't eat fat in one breath
* Find the string length ——strlen()
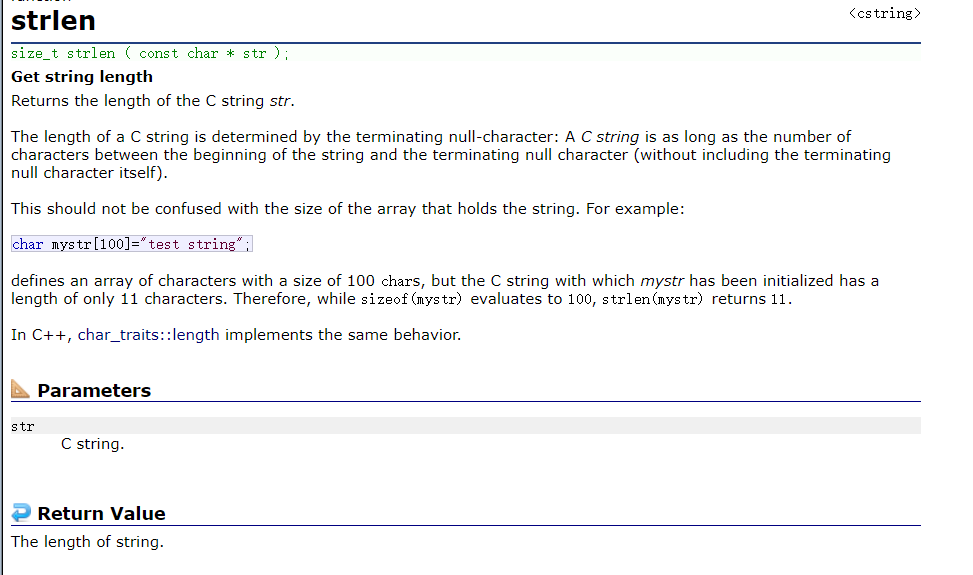
About **strlen()** We need to know a few points :
size_t strlen ( const char * str );// Returns an unsigned integer
- The string has ‘\0’ As an end sign ,strlen Function returns in a string ‘\0’ The number of characters that appear before ( No package contain ‘\0’ ).
- The string that the argument points to must be in ‘\0’ end .
- Note that the return value of the function is size_t, It's unsigned ( Fallible )
- Learn to strlen Simulation Implementation of function
For the first 3 How can we understand it? We can take an example :
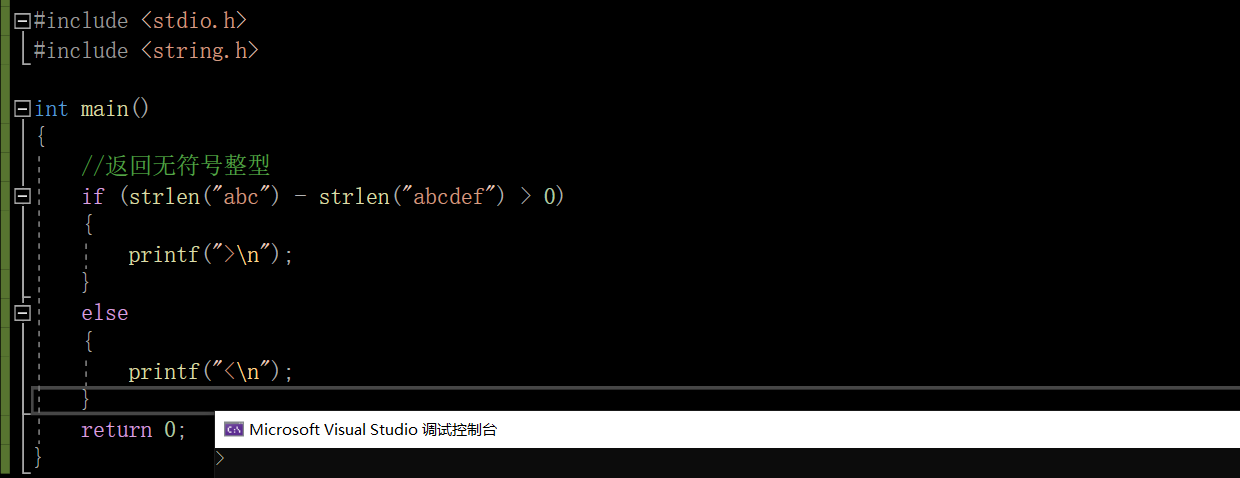
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
// Returns an unsigned integer
if (strlen("abc") - strlen("abcdef") > 0)
{
printf(">\n");
}
else
{
printf("<\n");
}
return 0;
}
What is the output result
yes :>
because strlen() Returns an unsigned integer , although 3-6<0, But for unsigned numbers , How can there be negative numbers ? So the result must be > Number
We can test and run the results :
The main content of this blog is the simulation and implementation of functions 
So let's talk about strlen() Three simulation implementation methods of :
1. Counter method
Directly define a variable to count the length of the string :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
// Counter method
size_t my_strlen(const char*str)
{
int count = 0;
assert(str);
while (*str != '\0')
{
count++;
str++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
size_t n = my_strlen(arr);
printf("%u\n", n);
return 0;
}
meanwhile , We need to be more rigorous , Pay attention to some details :
- The first one is const modification , We just need to visit , No modification is required
- The second one is assert Assertion , What if it's empty ? This is it. assert It's no longer useful
- The third is the return value size_t Unsigned
2. The pointer - Pointer method
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
size_t my_strlen(const char* str)
{
assert(str);
char* ret = str;
while (*str != '\0')
{
str++;
}
return str - ret;
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
size_t n = my_strlen(arr);
printf("%u\n", n);
return 0;
}
Pointer minus pointer is the number of elements , So we record the initial address , The length can be obtained by subtracting the pointer address just recorded from the last pointer address !
3. recursive
Finding out the recursive conditions can perfectly simulate the implementation strlen(). The following code implementation :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
size_t my_strlen(const char* str)
{
assert(str);
if (*str == '\0')
{
return 0;
}
return 1 + my_strlen(str + 1);
}
int main()
{
char arr[] = "abcdef";
size_t n = my_strlen(arr);
printf("%u\n", n);
return 0;
}
test run :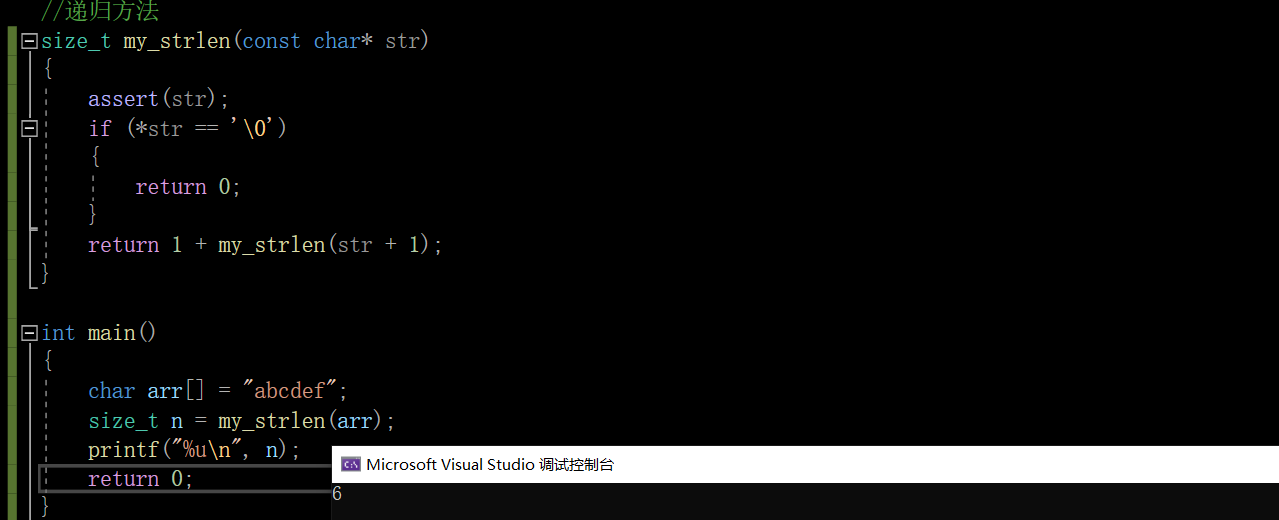

* Unlimited length string function
strcpy
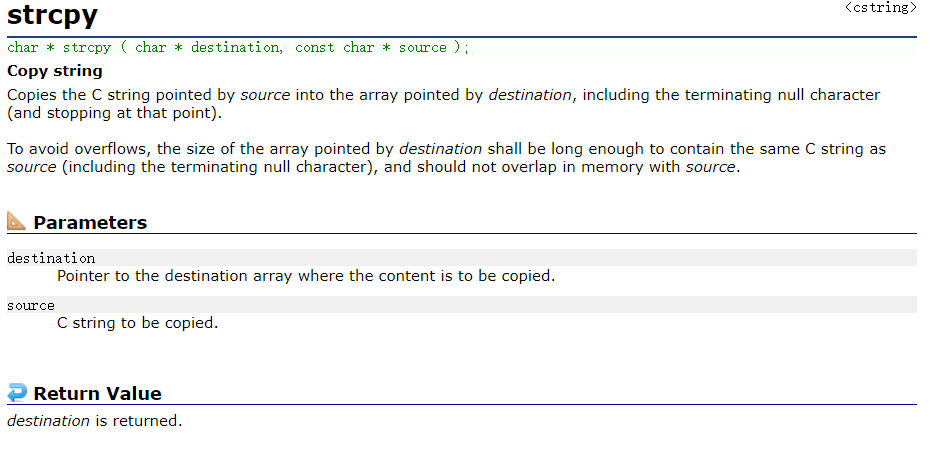
about strcpy(), We need to know a few points :
char* strcpy(char * destination, const char * source );
- Copies the C string pointed by source into the array pointed by destination, including the terminating null character (and stopping at that point). A simple understanding is a copy of a string , However, the following points should be paid attention to in copying :
- The source string must be in ‘\0’ end .
- In the source string ‘\0’ Copy to target space .
- The target space has to be large enough , To ensure that the source string can be stored .
- The target space has to be variable . Learn to simulate .
I think the most important thing about this function is : The first parameter is the destination string , The second parameter is the string from the source . The second parameter is unchangeable , It can be used const To modify . This is more important .
Now let's simulate it :
// Simulation Implementation
#include <stdio.h>
char* my_strcpy(char* dest, const char* src)
{
assert(dest);
assert(src);
char* ret = dest;
while (*src)
{
*dest++ = *src++;
}
*dest = *src;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
char arr1[] = "abcdef";
char arr2[20] = {
0 };
my_strcpy(arr2, arr1);
printf("%s\n", arr2);
return 0;
}
For this simulation implementation, we can optimize , Make it look simpler
#include <stdio.h>
char* my_strcpy(char* dest, char* src)
{
assert(dest && src);
char* ret = dest;
while (*dest++ = *src++)
{
;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
char arr1[] = "abcdef";
char arr2[20] = {
0 };
my_strcpy(arr2, arr1);
printf("%s\n", arr2);
return 0;
}
Test run results :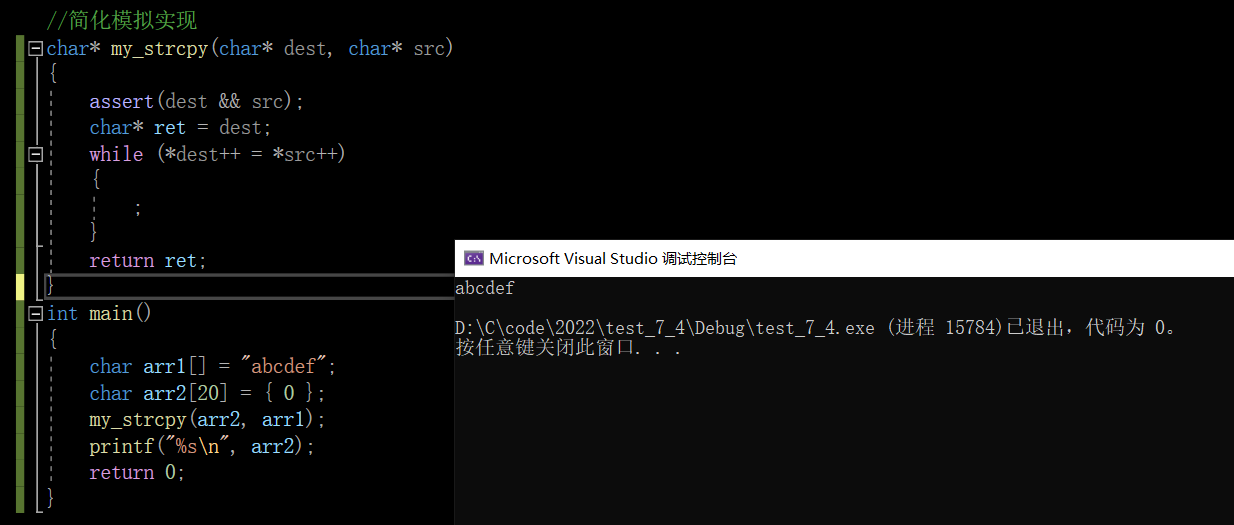
strcat
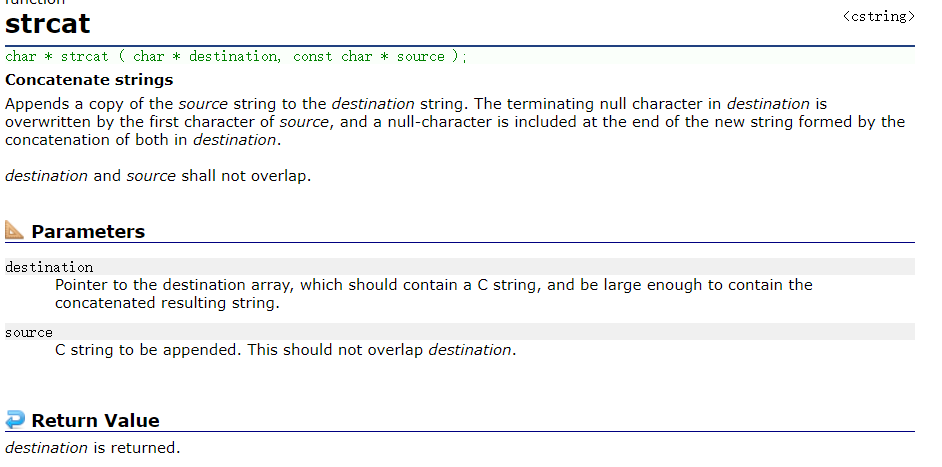
char * strcat ( char * destination, const char * source );
- Appends a copy of the source string to the destination string. The terminating null character in destination is overwritten by the first character of source, and a null-character is included at the end of the new string formed by the concatenation of both in destination. Simple understanding , It is the addition of string .
- The source string must be in ‘\0’ end .
- The target space must be large enough , It can hold the contents of the source string .
- The target space must be modifiable . The string appends itself , how ?
With the above knowledge points , about strcat We have a good understanding , Next, let's simulate the implementation :
#include <stdio.h>
// String append
// String append
char* my_strcat(char* dest, const char* src)
{
assert(dest && src);
int ret = dest;
while (*dest != '\0')
{
dest++;
}
while (*dest++ = *src++)
{
;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
char arr1[20] = "hello ";
strcat(arr1, "world");
//my_strcat(arr1, "world");
// Add to yourself ?
//my_strcat(arr1, arr1);// This is wrong , Destroy yourself .\0 Be missing
printf("%s\n", arr1);
return 0;
}
test run :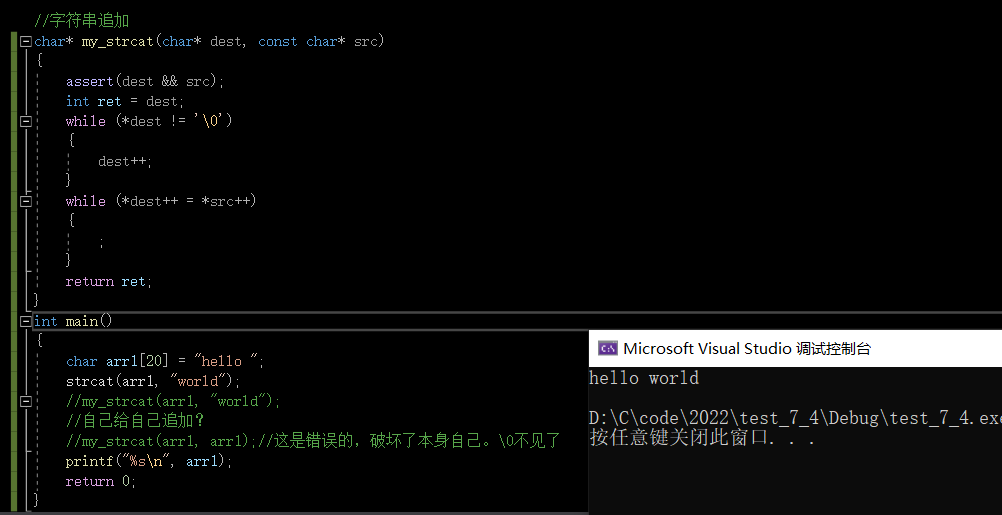
Someone here will ask : Add it to yourself ? think about it , This is the wrong way , Because you will find , The process of adding yourself has changed itself ,'\0’ It is covered. , It's impossible to achieve . Whether it is our own simulation or library function , I can't add myself .
strcmp
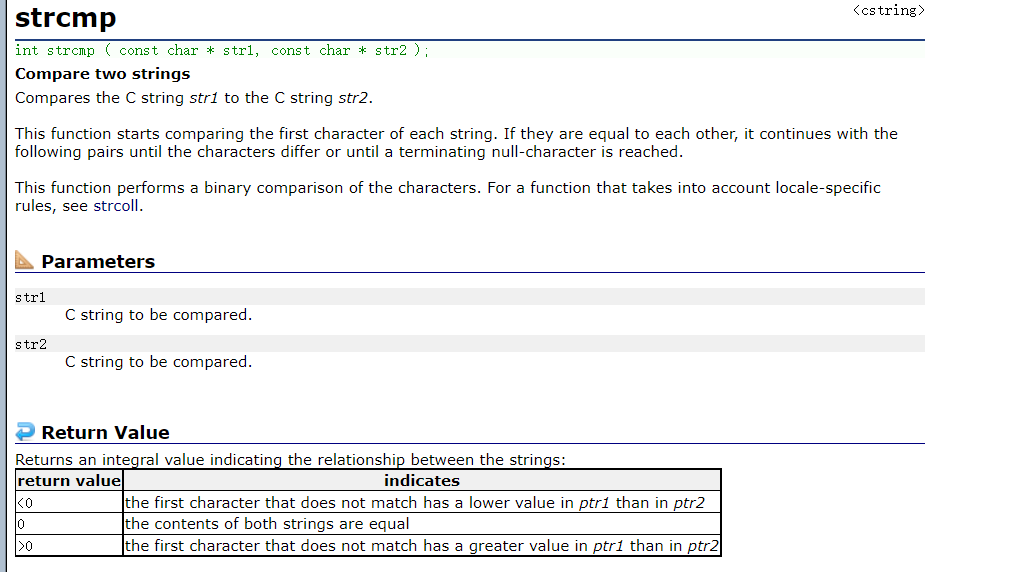
int strcmp ( const char * str1, const char * str2 );
- This function starts comparing the first character of each string. If they are equal to each other, it continues with the following pairs until the characters differ or until a terminating null-character is reached. Simply speaking , Is to compare strings .
- The standard stipulates : The first string is larger than the second string , Return greater than 0 The number of
- The first string is equal to the second string , Then return to 0
- The first string is less than the second string , Then return less than 0 The number of
- So how to judge two strings ? The comparison is the corresponding ASCII Code value
First, let's briefly understand the library function :
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int ret = strcmp("abbb", "abq");
printf("%d", ret);
return 0;
}
Will get :
Because third b Less than q Of ASCII Code value , Natural return -1. This is it. strcmp The basic principle of .
But here we need to simulate it , How to simulate the implementation
#include <stdio.h>
int my_strcmp(const char* s1, const char* s2)
{
while (*s1 == *s2)
{
if (*s1 == '\0')
{
return 0;
}
s1++;
s2++;
}
if (*s1 > *s2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
int main()
{
char* p = "abcdef";
char* q = "abbb";
int ret = my_strcmp(p, q);
if (ret>0)
{
printf("p>q");
}
else if(ret <0)
{
printf("p<q");
}
else
{
printf("p=q");
}
return 0;
}
Test run results :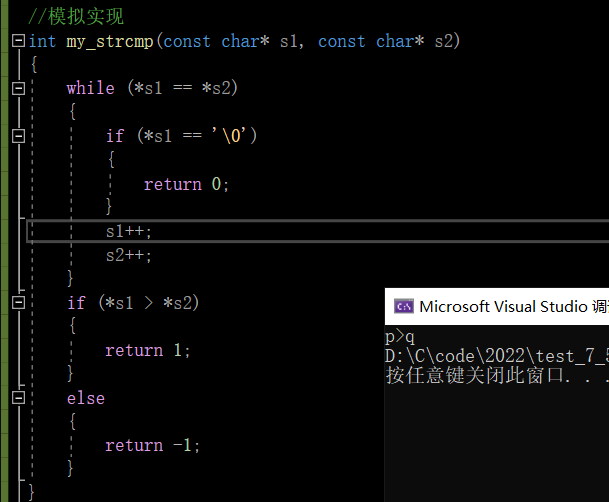
Is that over ? did not , We can optimize the code of simulation implementation and make it simpler :
did not , We can optimize the code of simulation implementation and make it simpler :
// Optimize simulation implementation
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
int my_strcmp(const char* s1, const char* s2)
{
assert(s1 && s2);
while (*s1 == *s2)
{
if (*s1 == '\0')
{
return 0;
}
s1++;
s2++;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}
int main()
{
char* p = "abcdef";
char* q = "abbb";
int ret = my_strcmp(p, q);
if (ret>0)
{
printf("p>q");
}
else if(ret <0)
{
printf("p<q");
}
else
{
printf("p=q");
}
return 0;
}
be aware :
No specific requirements <0 What's the number of , Or say >0 What's the number of , Let's just subtract .
Test and run the code :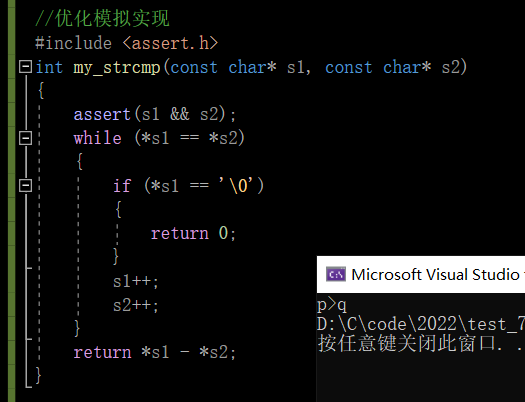
* summary
This is the end of the introduction and Simulation of string length calculation and string function with unlimited length , Then consider the actual situation , If we learn too many library functions at one time, it is not conducive to the formation of memory , Not proficient in functions , This blog first introduces this 4 Implementation of a function , The rest will be left next time !
At the same time, remember to summarize more , Knock the code with more hands , Don't think you can understand it , The actual operation is different from your own idea , I hope you can practice more !

边栏推荐
- 【C语言】字符串函数及模拟实现strlen&&strcpy&&strcat&&strcmp
- C application interface development foundation - form control (6) - menu bar, toolbar and status bar controls
- Force buckle 1200 Minimum absolute difference
- 国海证券在网上开户安全吗?
- Common interview questions in Android, 2022 golden nine silver ten Android factory interview questions hit
- MySQL中字段类型为longtext的值导出后显示二进制串方式
- okcc呼叫中心有什么作用
- Mysql如何对json数据进行查询及修改
- 众昂矿业:2022年全球萤石行业市场供给现状分析
- 软件测试是干什么的?学习有啥要求?
猜你喜欢

如何在2022年更明智地应用智能合约?
Hiengine: comparable to the local cloud native memory database engine

How to choose the notion productivity tools? Comparison and evaluation of notion, flowus and WOLAI
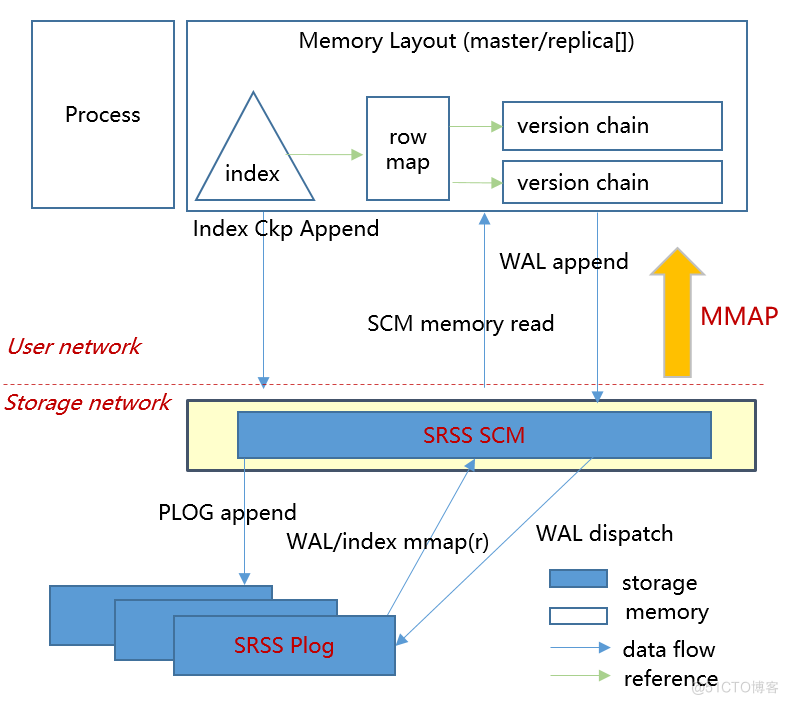
Hiengine: comparable to the local cloud native memory database engine

测试外包公司怎么样?
Using repositoryprovider to simplify the value passing of parent-child components
redis集群模拟消息队列
微波雷达感应模块技术,实时智能检测人体存在,静止微小动静感知
MMO項目學習一:預熱
力扣 729. 我的日程安排表 I
随机推荐
MySQL中字段类型为longtext的值导出后显示二进制串方式
软件测试是干什么的?学习有啥要求?
What is the function of okcc call center
That's awesome. It's enough to read this article
UWB ultra wideband positioning technology, real-time centimeter level high-precision positioning application, ultra wideband transmission technology
强化学习-学习笔记4 | Actor-Critic
IFD-x 微型红外成像仪(模块)关于温度测量和成像精度的关系
成功入职百度月薪35K,2022Android开发面试解答
力扣 1200. 最小绝对差
Common - Hero Minesweeper
完爆面试官,一线互联网企业高级Android工程师面试题大全
常用运算符与运算符优先级
acm入门day1
Explain in detail the functions and underlying implementation logic of the groups sets statement in SQL
Successful entry into Baidu, 35K monthly salary, 2022 Android development interview answer
【obs】libobs-winrt :CreateDispatcherQueueController
How about testing outsourcing companies?
Realizing deep learning framework from zero -- LSTM from theory to practice [practice]
Information / data
Summer Challenge database Xueba notes, quick review of exams / interviews~