当前位置:网站首页>In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (II) concurrency theory
In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (II) concurrency theory
2022-07-02 06:14:00 【I think starfish_ ninety-eight】
List of articles
Concurrency theory
Java Memory model (JMM)
First , What mechanism is used to exchange information between threads , There are two main types : Shared memory and messaging .Java The memory model is Shared memory Concurrent model of , Threads mainly pass through read - Write shared variables To complete implicit communication
Concept
The above said Shared memory Model refers to Java Memory model ( abbreviation JMM):
- Java The memory model determines when a thread's write to a shared variable is visible to another thread
- Shared variables between threads are stored in Main memory (main memory) in , Each thread has one Private local memory (local memory), The thread is stored in local memory to read / Write a copy of the shared variable
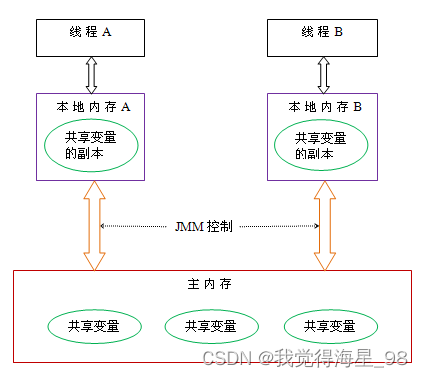
The picture shows , Threads A With threads B If you want to communicate with each other , Must go through the following 2 A step :
- First , Threads A Put the local memory A The shared variables updated in are refreshed to main memory
- then , Threads B Read threads into main memory A Previously updated shared variables
JVM Yes Java Implementation of memory model
Java The memory model divides memory into two parts : Thread stack area and heap area , The following figure shows Java The memory model is JVM Logical view in :
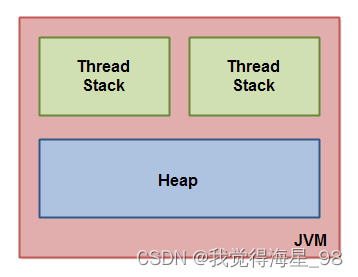
Stack area and heap area
JVM Each thread running in has its own thread stack , The thread stack contains information about the method calls executed by the current thread , We also call it call stack . As the code continues to execute , The call stack changes constantly
Thread stack :
- All local variable information of the current method
- All primitive types (boolean,byte,short,char,int,long,float,double) The local variables of are directly saved in the online process stack
Heap area : Contains Java Application created All object information , No matter which thread created the object

Reordering and data dependency
Reorder
When executing the program , To improve performance , Compilers and processors reorder instructions
- Compiler optimization reorder : Compiler without changing the semantics of single thread program , Sure Rearrange the execution order of statements .
- Instruction level parallel reordering : If there is no data dependency , The processor can Change the execution order of the machine instructions corresponding to the statements .
- Reordering of memory system : The processor uses cache and read / write buffer , This makes loading and storage operations appear to be out of order .
Memory barrier (Memory Barrier)
The compiler and CPU Ability to reorder instructions , Guarantee the same result in the end , Try to optimize performance . But insert one Memory barrier Tell the compiler and CPU: No matter what the order is, it can't be with this Memory barrier Reorder
use volatile Realization : Memory barrier Another thing to do is to force all kinds of CPU cache , Like a Write barrier All data previously written to the cache will be flushed , therefore , whatever CPU All threads on can read the latest version of these data ( That is to say volatile, Keep up to date )
Data dependency
- If two operations access the same variable , One of them is write operation , At this time, there is Data dependency
- Compilers and processors do not change the existence Data dependency The execution order of the two operations of the relationship , It doesn't reorder
as-if-serial and happens-before The rules
as-if-serial
No matter how reorder , The execution result under single thread cannot be changed , compiler 、runtime And the processor must comply as-if-serial semantics
happens-before
If the execution result of one operation needs to be visible to another operation , Then there must be... Between these two operations happens-before Relationship , The two operations of this can be performed on the same thread , It can also be in two different threads
happens-before The rules
- Rules of procedure sequence : Every operation in a thread ,happens-before Any subsequent operation in this thread
- Monitor lock rules : Unlocking a lock ,happens-before In the subsequent locking operation of this lock
- volatile Domain rules : To a volatile Write operation of domain ,happens-before Apply to any subsequent thread on this volatile Domain reading
- Transitive rules : If A happens-before B, And B happens-before C, that A happens-before C
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

VLAN experiment of switching technology

Frequently asked questions about jetpack compose and material you

Invalid operation: Load into table ‘sources_orderdata‘ failed. Check ‘stl_load_errors‘ system table

Linear DP (split)

神机百炼3.54-染色法判定二分图
如何使用MITMPROXy
Contest3147 - game 38 of 2021 Freshmen's personal training match_ G: Flower bed
数据回放伴侣Rviz+plotjuggler

从设计交付到开发,轻松畅快高效率!
In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (I) what is JUC
随机推荐
Unity shader learning notes (3) URP rendering pipeline shaded PBR shader template (ASE optimized version)
Support new and old imperial CMS collection and warehousing tutorials
Servlet web XML configuration details (3.0)
Little bear sect manual query and ADC in-depth study
Talking about MySQL database
使用HBuilderX的一些常用功能
495. Timo attack
Linkage between esp8266 and stc8h8k single chip microcomputer - Weather Clock
Mock simulate the background return data with mockjs
格式校验js
Redis Key-Value数据库 【高级】
Redis Key-Value数据库 【秒杀】
Flutter hybrid development: develop a simple quick start framework | developers say · dtalk
From design delivery to development, easy and efficient!
Happy Lantern Festival | Qiming cloud invites you to guess lantern riddles
I/o multiplexing & event driven yyds dry inventory
MUI底部导航的样式修改
ROS2----LifecycleNode生命周期节点总结
来自读者们的 I/O 观后感|有奖征集获奖名单
In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (I) what is JUC