当前位置:网站首页>Database design - relational data theory (ultra detailed)
Database design - relational data theory (ultra detailed)
2022-07-27 05:19:00 【New an object_】
? problem —— What is a good database logic design ?
● Logical design of relational database :
* How to construct a suitable data schema for a specific problem , That is, several relationships should be constructed , What are the attributes of each relationship
eg:
? Is this design a good design ?
Observe an instance corresponding to this table ( At some point student An actual data situation corresponding to the pattern ): If there are several students , They are all for ’ Department of Computer Science ’, The dean of the Department is ’ Zhang Ming ’, Optional ’C1’ Course , Get their own grades
*
* Relationship model STUDENT(Sno,Sdept,Mname,Cno,Grade) Problems in :*
1、 Too much data redundancy , Waste storage space
Such as : The name of the Dean reappears , The number of repetitions is the same as the number of occurrences of all course scores of all students in the Department .
2、 Update exception (Update Anomalies)
data redundancy , When updating data , Maintaining data integrity is costly
If a department changes its Dean , The system must modify every tuple related to the students of the Department .
3、 Insertion exception (Insertion Anomalies), The data to be inserted cannot be inserted
If a new software engineering department is established , No admissions yet , We can't store the information of the Department and its Dean in the database .
4、 Delete exception (Deletetion Anomalies), Data that should not be deleted has also been deleted
If all the students in a department graduate , While deleting the student information of the Department , Lose the information about the Department and its Dean .
? What is a good model ?
* A good design pattern will not cause insertion exceptions 、 Delete exception 、 Update exception 、 Data redundancy should be minimized
The cause of the problem :
Due to some in the pattern Data dependency Caused by the .
Data dependency :
◆ It is the relationship between data reflected by the equality of values between attributes in a relationship
◆ It is an abstraction of the interrelationship between real-world attributes
◆ Is the inherent nature of data
◆ Is the embodiment of semantics
The impact of data dependency on relational patterns :
Inappropriate data dependencies , Cause insertion exception 、 Delete exception 、 Update exceptions and data redundancy problems
Use a graph to represent functional dependencies 
resolvent : Separate the first mock exam. 3 A relationship model
S( Sno, Sdept, Sno→Sdept);
SC ( Sno, Cno, Grade, (Sno, Cno)→Grade);
DEPT (Sdept, Mname, Sdept→Mname)
These three modes will not cause insertion exceptions 、 Delete and other exceptions ; Data redundancy is controlled .
How to solve the problems in the relationship pattern :
Normalization theory —— Identify inappropriate data dependencies in the relational schema , Eliminate them , Insertion exceptions can be resolved to varying degrees 、 Delete exception 、 Update exceptions and data redundancy problems .
Function dependency


How to determine functional dependencies ?
◆ Functional dependency is the concept of semantic category . Can only Determine the functional dependency according to the semantics of the data .
● Such as Sname→Sno Functional dependencies only exist in “ Students are not allowed to have duplicate names ” Under the conditions of .
Trivial and nontrivial functional dependencies
●X→Y, Y⊈X, said X→Y yes Nontrivial functional dependencies .
●X→Y, Y⊆X, said X→Y yes Trivial functional dependencies .
Complete functional dependency and partial functional dependency

The transfer function depends on 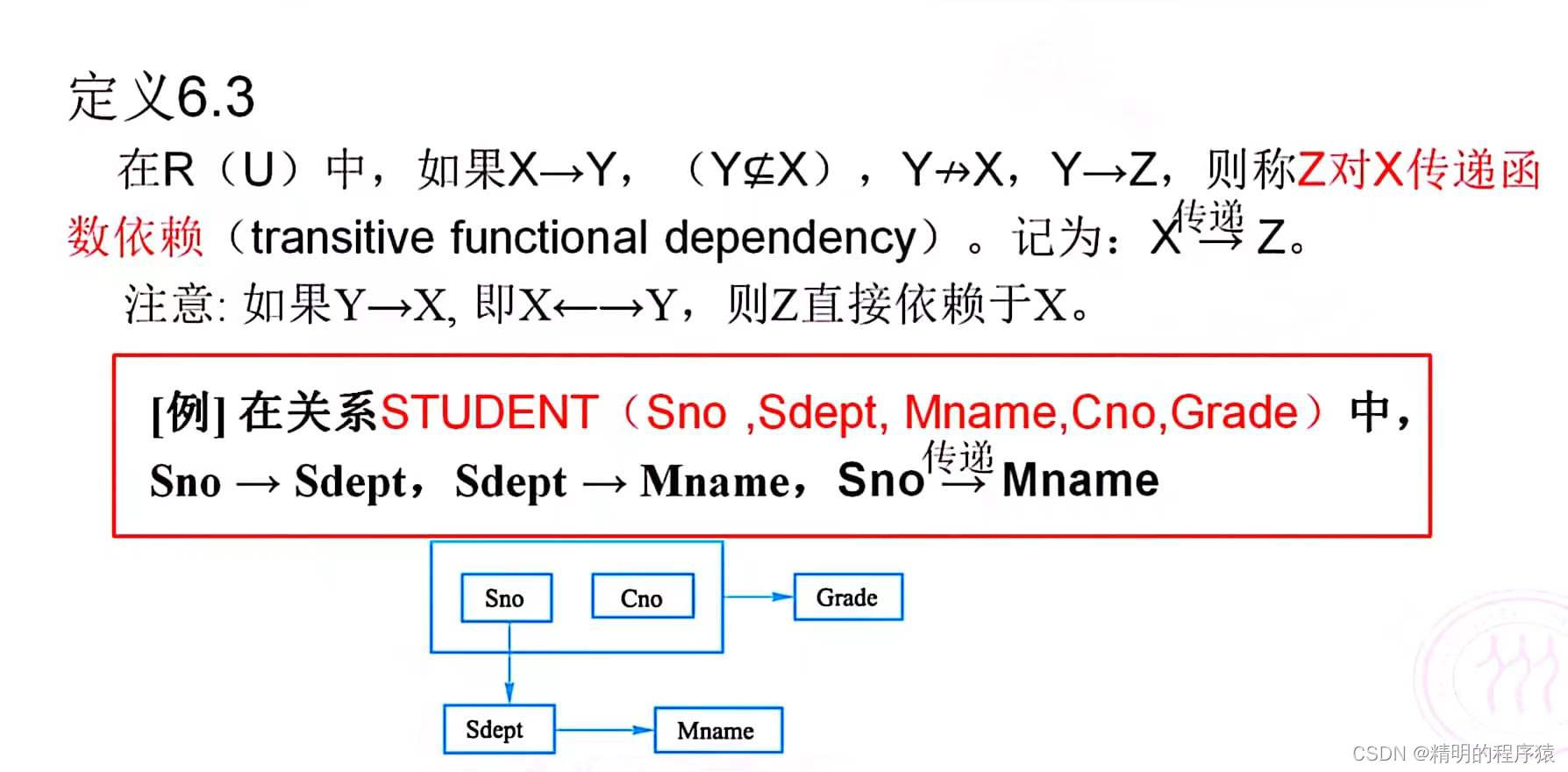
normal form
◆ A paradigm is a collection of relational patterns that conform to a certain level
◆ The relationship in relational database must meet certain requirements .
Different paradigms meet different requirements
● Types of paradigms :
* First normal form (1NF)********( Relationship model R All properties of are basic data items that cannot be separated )
* Second normal form (2NF)********( Relationship model R⊆1NF, also Each non primary attribute is completely functionally dependent on R Code of , be R⊆2NF.
* Third normal form (3NF)********( Relationship model R⊆1NF, if R There is no such code in X、 Attribute group Y And non attributes Z(Y⊉Z), bring X→Y,Y→Z,Y↛X, establish , said R<U,F>⊆3NF ◆ if R⊆3NF, be R Each non primary attribute of is neither partially functionally dependent on candidate codes nor transitive functionally dependent on candidate codes
)
*BC normal form (BCNF,Boyce and Codd Jointly proposed paradigm )******** It is also generally believed that BC Paradigm is the modified third paradigm , Sometimes called extended third paradigm , That is, in the relationship mode R<U,F> in , If every determinant contains a code , be R⊆BCNF.
◆BCNF The nature of relational patterns :
① All non main properties are completely dependent on each code .
② All main attributes are also fully functional dependent on each code that does not contain it .
③ No attribute completely depends on any set of non code attributes .
* Fourth normal form (4NF)********
* The fifth paradigm (5NF********
● There are links between various paradigms ( Low level paradigm includes high-level paradigm ):
Standardized summary
● A relational model as long as it Components are inseparable data items , It is a standardized relationship model , But this is just the most basic normalization .
● The relationship model with low standardization may not be able to describe the real world well , There may be insertion exceptions 、 Delete exception 、 Modify exception 、 Data redundancy and so on , The solution is to standardize it , Convert to high-level paradigm .
● A relational model of a lower paradigm , Through pattern decomposition, it can be transformed into a set of relational patterns of several higher-level paradigms , This process is called Normalization of relationship pattern .
● The normalization theory of relational database is a tool for database logic design .
◆ The basic steps of relational schema normalization :
边栏推荐
- Shell course summary
- How does the TCP server handle multiple client connections on one port (one-to-one or one to many)
- [untitled] I is circularly accumulated under certain conditions. The condition is usually the length of the loop array. When it exceeds the length, the loop will stop. Because the object cannot judge
- 2021 OWASP top 5: security configuration error
- Introduction to Web Framework
- I've heard the most self disciplined sentence: those I can't say are silent
- [acwing] solution to the 61st weekly match
- Differences among left join, inner join and right join
- Row, table, page, share, exclusive, pessimistic, optimistic, deadlock
- Laozi cloud and Fuxin Kunpeng achieved a major breakthrough in 3D ofd 3D format documents for the first time
猜你喜欢

Gradio quickly builds ml/dl Web Services

微淼联合创始人孙延芳:以合规为第一要义,做财商教育“正规军”

Acticiti中startProcessInstanceByKey方法在variable表中的如何存储

JVM上篇:内存与垃圾回收篇五--运行时数据区-虚拟机栈

Li Kou achieved the second largest result

String class

Installation and template setting of integrated development environment pychar

Derivation and explanation of PBR physical illumination calculation formula

35.滚动 scroll

How to sinicize the JMeter interface?
随机推荐
B1023 组个最小数
MQ message queue is used to design the high concurrency of the order placing process, the generation scenarios and solutions of message squeeze, message loss and message repetition
[CSAPP] Application of bit vectors | encoding and byte ordering
[untitled] I is circularly accumulated under certain conditions. The condition is usually the length of the loop array. When it exceeds the length, the loop will stop. Because the object cannot judge
JVM Part 1: memory and garbage collection part 7 -- runtime data area heap
集合框架的使用
A math problem cost the chip giant $500million
Invert a Binary Tree
JVM上篇:内存与垃圾回收篇八--运行时数据区-方法区
ERP system brand
Standard dialog qmessagebox
How to test the payment process?
树莓派rtmp推流本地摄像头图像
Raspberry pie RTMP streaming local camera image
Counting Nodes in a Binary Search Tree
Shell course summary
Bean的生命周期&&依赖注入*依赖自动装配
Alphabetic order problem
Deep Qt5 signal slot new syntax
Complete Binary Tree