当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to JVM class loading
Introduction to JVM class loading
2022-08-05 00:44:00 【xmh - sxh - 1314】
 Class loading and initialization is done only once
Class loading and initialization is done only once
1, Loading (requires the support of the class loader): In this stage, a java.lang.Class object representing this class will be generated in memory as the entry for various data of this class in the method area.Note that this does not necessarily have to be obtained from a Class file. It can be read from a ZIP package (such as from a jar package and a war package), calculated at runtime (dynamic proxy), or generated by otherFile generation (such as converting JSP files into corresponding Class classes).
2, Verification: The main purpose of this stage is to ensure whether the information contained in the byte stream of the Class file meets the requirements of the current virtual machine, and will not endanger the security of the virtual machine itself.
3, preparation (all default values): The preparation phase is the phase in which memory is formally allocated for class variables and the initial value of the class variable (usually the zero value of the data type) is set, and the memory used by these variables will beAllocate in the method area.At this time, memory allocation only includes class variables (variables modified by static), not instance variables. Instance variables will be allocated in the Java heap along with the object when the object is instantiated.
4, parsing: The parsing phase is a process in which the virtual machine replaces the symbolic references in the constant pool with direct references.
5. Initialization: The process of executing the class constructor clinit() method, which is formed by the compiler automatically collecting the assignments of all class variables in the class and combining the statements in the static statement block
The class initialization phase is the last step in the class loading process. At this stage, the Java program code (or bytecode) defined in the class is actually executed.In the preparation phase, the variable has been assigned the initial value required by the system, and in the initialization phase, class variables and other resources are initialized according to the subjective plan made by the programmer through the program.
Note the following:
1. The order in which the compiler collects is determined by the order in which the statements appear in the source file,
In the static statement block, only the variables defined before the static statement block can be accessed, and the variables defined after it can be assigned values in the previous static statement block, but cannot be accessed. The code is explained as follows:
Copy code
public class Test{
static{
i=0;//Assignment to variables can be compiled and passed
sout(i); //The compiler will prompt an illegal forward reference
} }
static int i = 1;
}
Copy code
2. The order in which the initialization methods are executed. The virtual machine ensures that the initialization method of the parent class has been executed before the initialization method of the subclass is executed.
3. The virtual machine ensures that a class's clinit() method is properly locked and synchronized in a multithreaded environment
4. When accessing a static field of a java class, only the class that actually declares this field will be initialized
Active reference to the class (initialization occurs)
new an object of a class
Calling static members (except final constants) and static methods of a class
When called by reflection
Start the class where the main method is located
The virtual machine ensures that the initialization method of the parent class has been executed before the initialization method of the subclass is executed,
Passive reference to class (no initialization occurs)
Referencing constants does not trigger class initialization: constants are stored in the constant pool of the calling class at compile time
Class references via arrays will not trigger initialization
When accessing a static field (static variable), only the class that actually declares the field will be initialized (subclass)
Classloader:
1. Function: Load the bytecode file into the memory, convert the static data into the runtime data structure of the method area, and generate a Class object in the heap as the access entry for the method of the class data in the method area
p>Hierarchy (tree structure)
2.ClassLoader related methods:
3, proxy for class loader
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
【idea】idea配置sql格式化
oracle create tablespace
面试汇总:为何大厂面试官总问 Framework 的底层原理?

leetcode: 266. All Palindromic Permutations
gorm joint table query - actual combat
![[230]连接Redis后执行命令错误 MISCONF Redis is configured to save RDB snapshots](/img/fa/5bdc81b1ebfc22d31f42da34427f3e.png)
[230]连接Redis后执行命令错误 MISCONF Redis is configured to save RDB snapshots
典型相关分析CCA计算过程
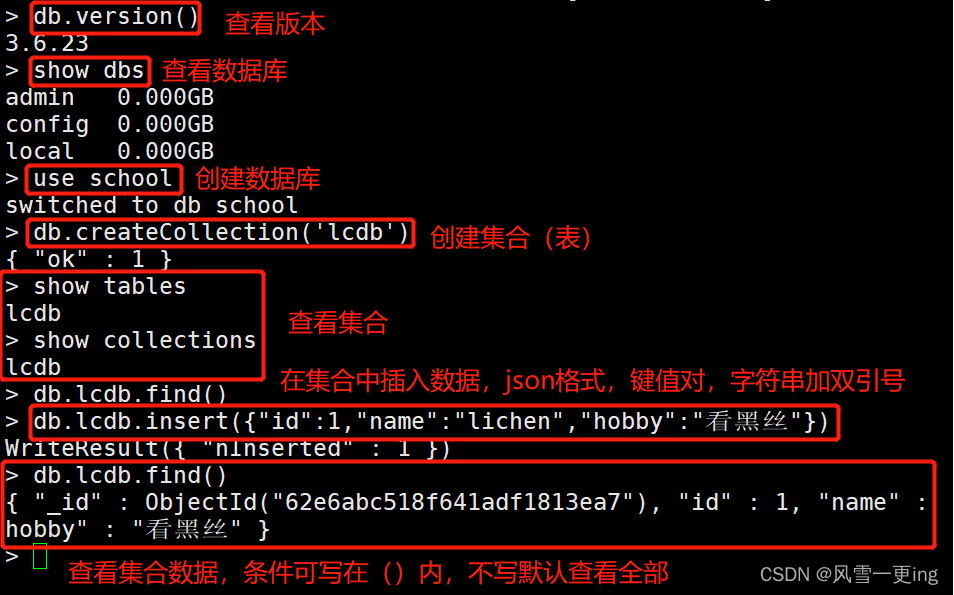
MongoDB construction and basic operations
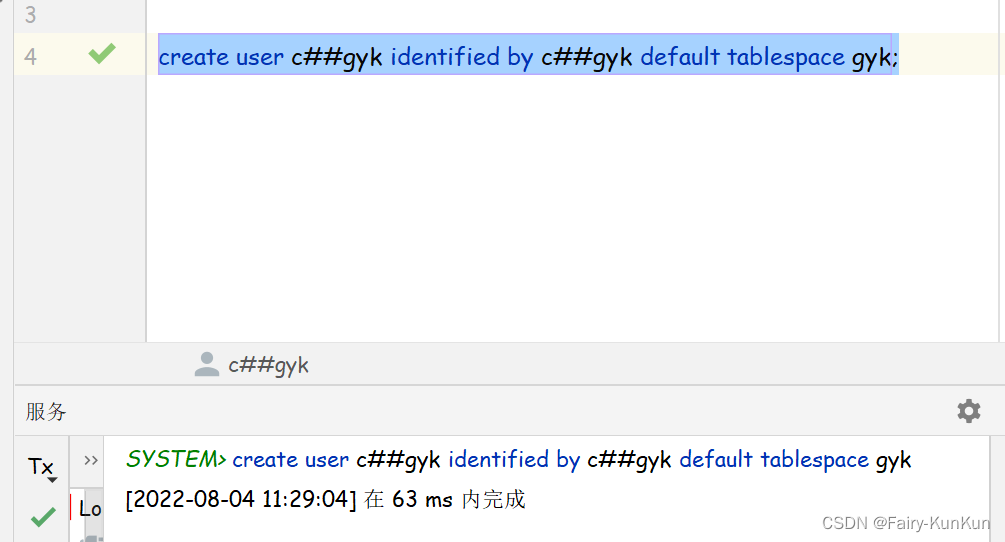
oracle create user

Will domestic websites use Hong Kong servers be blocked?
随机推荐
软件测试面试题:软件测试类型都有哪些?
《WEB安全渗透测试》(28)Burp Collaborator-dnslog外带技术
Software testing interview questions: test life cycle, the test process is divided into several stages, and the meaning of each stage and the method used?
Software testing interview questions: What stages should a complete set of tests consist of?
2022 The Third J Question Journey
tiup telemetry
活动推荐 | 快手StreamLake品牌发布会,8月10日一起见证!
NMS原理及其代码实现
tiup telemetry
2022牛客多校第三场 J题 Journey
2022 Nioke Multi-School Training Session H Question H Take the Elevator
Software Testing Interview Questions: About Automated Testing Tools?
典型相关分析CCA计算过程
[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy
CNI(Container Network Plugin)
EL定时刷新页面中的皕杰报表实例
OPENWIFI实践1:下载并编译SDRPi的HDL源码
软件测试面试题:做好测试计划的关键是什么?
tiup update
torch.autograd.grad求二阶导数