当前位置:网站首页>【数据挖掘】任务6:DBSCAN聚类
【数据挖掘】任务6:DBSCAN聚类
2022-07-03 01:09:00 【zstar-_】
要求
编程实现DBSCAN对下列数据的聚类
数据获取:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq1198768105/85865302
导库与全局设置
from scipy.io import loadmat
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn import datasets
import pandas as pd
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ["SimHei"]
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
DBSCAN 聚类参数说明
eps:ϵ-邻域的距离阈值,和样本距离超过ϵ的样本点不在ϵ-邻域内,默认值是0.5。
min_samples:形成高密度区域的最小点数。作为核心点的话邻域(即以其为圆心,eps为半径的圆,含圆上的点)中的最小样本数(包括点本身)。
若y=-1,则为异常点
由于DBSCAN生成的类别不确定,因此定义一个函数用来筛选出符合指定类别的最合适的参数。
合适的标准是异常点个数最少
def search_best_parameter(N_clusters, X):
min_outliners = 999
best_eps = 0
best_min_samples = 0
# 迭代不同的eps值
for eps in np.arange(0.001, 1, 0.05):
# 迭代不同的min_samples值
for min_samples in range(2, 10):
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
# 模型拟合
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 统计各参数组合下的聚类个数(-1表示异常点)
if len(np.argwhere(y == -1)) == 0:
n_clusters = len(np.unique(y))
else:
n_clusters = len(np.unique(y)) - 1
# 异常点的个数
outliners = len([i for i in y if i == -1])
if outliners < min_outliners and n_clusters == N_clusters:
min_outliners = outliners
best_eps = eps
best_min_samples = min_samples
return best_eps, best_min_samples
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red', 'blue']
smile = loadmat('data-密度聚类/smile.mat')
smile数据
X = smile['smile']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(3, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(smile['smile'])):
plt.scatter(smile['smile'][i][0], smile['smile'][i][1],
color=colors[int(smile['smile'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(smile['smile'][i][0], smile['smile'][i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")
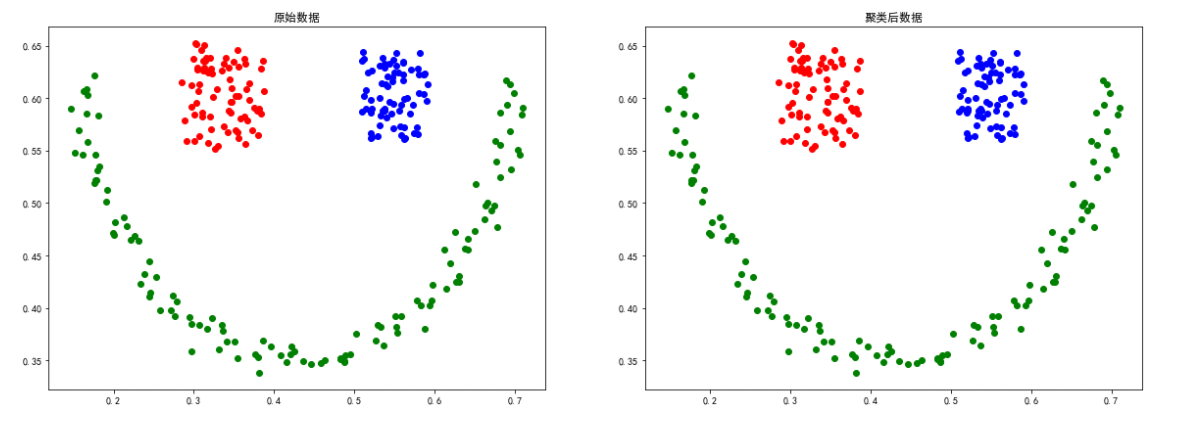
sizes5数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['blue', 'green', 'red', 'black', 'yellow']
sizes5 = loadmat('data-密度聚类/sizes5.mat')
X = sizes5['sizes5']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(4, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(sizes5['sizes5'])):
plt.scatter(sizes5['sizes5'][i][0], sizes5['sizes5']
[i][1], color=colors[int(sizes5['sizes5'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
if y[i] != -1:
plt.scatter(sizes5['sizes5'][i][0], sizes5['sizes5']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")
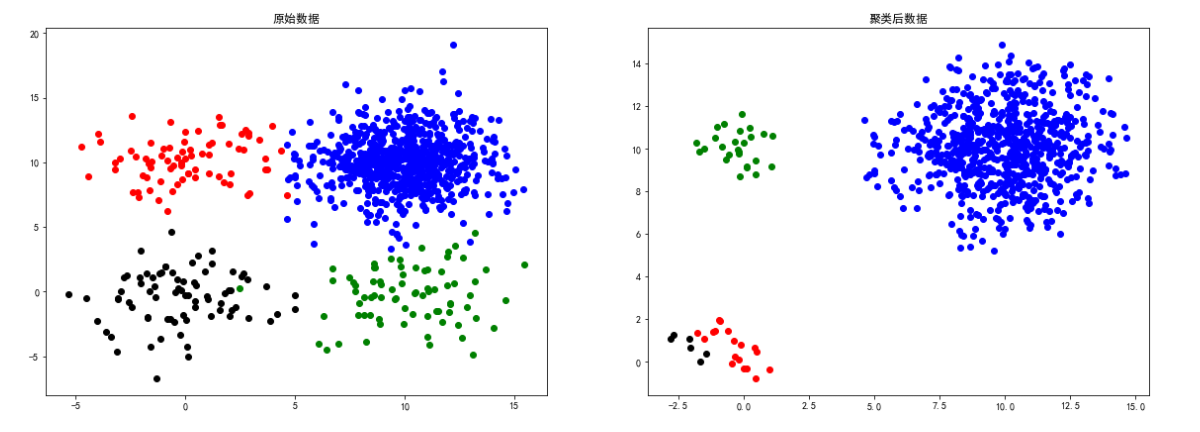
square1数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red', 'blue', 'black']
square1 = loadmat('data-密度聚类/square1.mat')
X = square1['square1']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(4, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(square1['square1'])):
plt.scatter(square1['square1'][i][0], square1['square1']
[i][1], color=colors[int(square1['square1'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(square1['square1'][i][0], square1['square1']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")

square4数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['blue', 'green', 'red', 'black',
'yellow', 'brown', 'orange', 'purple']
square4 = loadmat('data-密度聚类/square4.mat')
X = square4['b']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(5, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(square4['b'])):
plt.scatter(square4['b'][i][0], square4['b']
[i][1], color=colors[int(square4['b'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(square4['b'][i][0], square4['b']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")
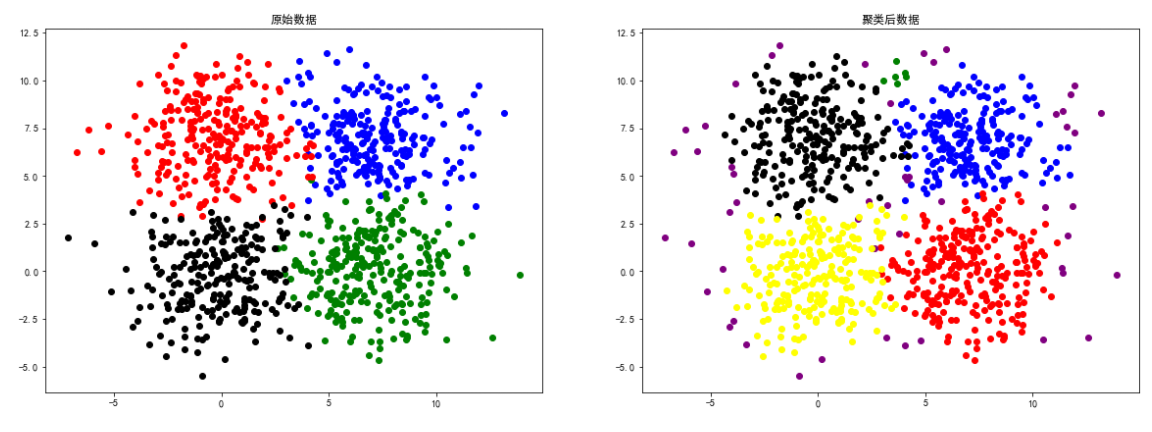
spiral数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red']
spiral = loadmat('data-密度聚类/spiral.mat')
X = spiral['spiral']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(2, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(spiral['spiral'])):
plt.scatter(spiral['spiral'][i][0], spiral['spiral']
[i][1], color=colors[int(spiral['spiral'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(spiral['spiral'][i][0], spiral['spiral']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")
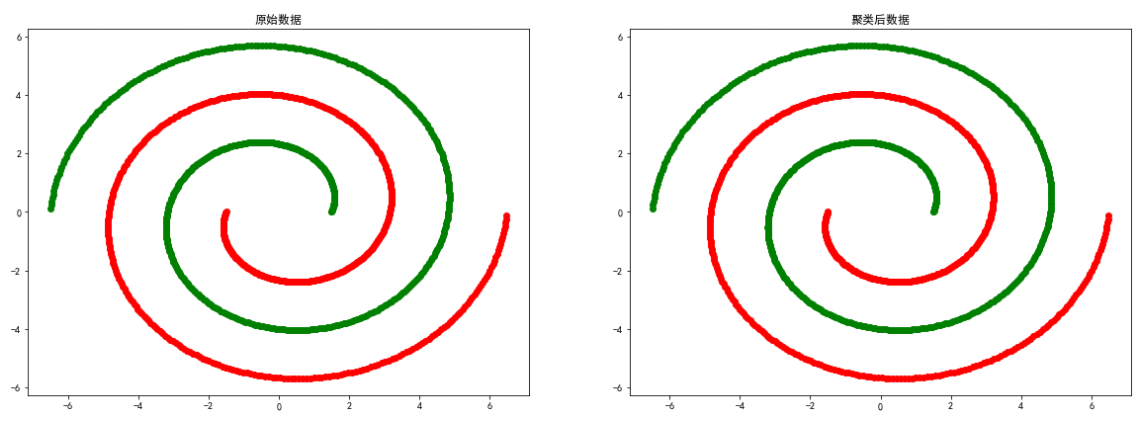
moon数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red']
moon = loadmat('data-密度聚类/moon.mat')
X = moon['a']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(2, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(moon['a'])):
plt.scatter(moon['a'][i][0], moon['a']
[i][1], color=colors[int(moon['a'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(moon['a'][i][0], moon['a']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")

long数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red']
long = loadmat('data-密度聚类/long.mat')
X = long['long1']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(2, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(long['long1'])):
plt.scatter(long['long1'][i][0], long['long1']
[i][1], color=colors[int(long['long1'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(long['long1'][i][0], long['long1']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")

2d4c数据
# 导入数据
colors = ['green', 'red', 'blue', 'black']
d4c = loadmat('data-密度聚类/2d4c.mat')
X = d4c['a']
eps, min_samples = search_best_parameter(4, X)
dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
y = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 聚类结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
for i in range(len(d4c['a'])):
plt.scatter(d4c['a'][i][0], d4c['a']
[i][1], color=colors[int(d4c['a'][i][2])])
plt.title("原始数据")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
for i in range(len(y)):
plt.scatter(d4c['a'][i][0], d4c['a']
[i][1], color=colors[y[i]])
plt.title("聚类后数据")

总结
上述实验证明了DBSCAN聚类方法比较依赖数据点位置上的关联度,对于smile、spiral等分布的数据聚类效果较好。
边栏推荐
- leetcode 2097 — 合法重新排列数对
- Machine learning terminology
- MySQL
- 【QT】自定义控件的封装
- Kivy tutorial - example of using Matplotlib in Kivy app
- Button wizard play strange learning - go back to the city to buy medicine and add blood
- Matlab Doppler effect produces vibration signal and processing
- 给你一个可能存在 重复 元素值的数组 numbers ,它原来是一个升序排列的数组,并按上述情形进行了一次旋转。请返回旋转数组的最小元素。【剑指Offer】
- Cut point of undirected graph
- MySQL --- 数据库查询 - 条件查询
猜你喜欢

【FPGA教程案例6】基于vivado核的双口RAM设计与实现
看完这篇 教你玩转渗透测试靶机Vulnhub——DriftingBlues-9

Force buckle 204 Count prime

High-Resolution Network (篇一):原理刨析
Soft exam information system project manager_ Real topic over the years_ Wrong question set in the second half of 2019_ Morning comprehensive knowledge question - Senior Information System Project Man
C application interface development foundation - form control (3) - file control

一位苦逼程序员的找工作经历
Strongly connected components of digraph
leetcode 6103 — 从树中删除边的最小分数
![[interview question] 1369 when can't I use arrow function?](/img/7f/84bba39965b4116f20b1cf8211f70a.png)
[interview question] 1369 when can't I use arrow function?
随机推荐
Excel if formula determines whether the two columns are the same
The latest analysis of tool fitter (technician) in 2022 and the test questions and analysis of tool fitter (technician)
Database SQL language 02 connection query
C#应用程序界面开发基础——窗体控制(4)——选择类控件
Key wizard play strange learning - front desk and Intranet send background verification code
【FPGA教程案例5】基于vivado核的ROM设计与实现
Mathematical knowledge: divisible number inclusion exclusion principle
MySQL foundation 04 MySQL architecture
[self management] time, energy and habit management
[Cao gongzatan] after working in goose factory for a year in 2021, some of my insights
海量数据冷热分离方案与实践
After reading this article, I will teach you to play with the penetration test target vulnhub - drivetingblues-9
leetcode 6103 — 从树中删除边的最小分数
[principles of multithreading and high concurrency: 2. Solutions to cache consistency]
The difference between tail -f, tail -f and tail
数学知识:Nim游戏—博弈论
[flutter] icons component (fluttericon Download Icon | customize SVG icon to generate TTF font file | use the downloaded TTF icon file)
Look at how clothing enterprises take advantage of the epidemic
What is tone. Diao's story
Uniapp component -uni notice bar notice bar