当前位置:网站首页>In depth anatomy of C language - key words & supplementary contents
In depth anatomy of C language - key words & supplementary contents
2022-06-12 12:28:00 【Muxixi】
Hello, I'm Mu Xixi

List of articles

Keyword classification
In ordinary books ,C Language keywords are 32 individual , But this is all C90(C89) Standards for . Actually C99 And then I added 5 Key words . however , Current mainstream compilers , Yes C99 The support is not good , according to C90 standard , The idea that 32 individual .
| keyword | explain |
|---|---|
| auto | Declare automatic variables |
| short | Declare short integer variables or functions |
| int | Declare an integer variable or function |
| long | Declare long integer variables or functions |
| float | Declare floating-point variables or functions |
| double | Declare a double precision variable or function |
| char | Declare character type variables or functions |
| struct | Declare a structural variable or function |
| union | Declare shared data type |
| enum | Declare enumeration type |
| typedef | Used to alias data types |
| const | Declare read-only variable |
| unsigned | Declare an unsigned type variable or function |
| signed | Declare a symbolic type variable or function |
| extern | Declare variables are being declared in other files |
| register | Declare register variables |
| static | Declare static variables |
| volatile | Explain that variables can be implicitly changed during program execution |
| void | Declares that the function returns no value or takes no arguments , Declare no type pointer |
| if | Conditional statements |
| else | Conditional statement negates Branch ( And if Continuous use ) |
| switch | For switch statements |
| case | Switch statement Branch |
| for | A circular statement |
| do | The body of a loop statement |
| while | The loop condition of a loop statement |
| goto | Jump statements without conditions |
| continue | End the current cycle , Start next cycle |
| break | Jump out of current loop |
| default | In the switch statement “ other ” Branch |
| sizeof | Calculate the data type length |
| return | Subroutine return statement ( With parameters , Or without parameters ) The loop condition |
Supplementary content
first C Program
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>//windows.h System header file , Just to stop the screen
int main()
{
printf("hello world!\n");
system("pause");//pause Stop screen
return 0;
}
The file code is converted into an executable program after generating the solution ( Binary .exe)
You can empty the executable by emptying the solution 
- stay windows in , Double click the essence of the program to run it , Load the program into memory .
- Any program must be loaded into memory before it can be run .
- Load into memory , Fast .
Von Neumann 
Definitions and statements
Variable
stay Memory Open up a specific size of space in , To hold data
Definition of variables
type Variable name = The default value is
int a = 10;
char c = 'c';
Define the reason for the variable : Because there is data that needs to be saved temporarily , Waiting for further processing .
The nature of variables
- The essence of all variables is to open up space somewhere in memory .
- The program runs , It needs to be loaded into memory
- Program calculation , You need to use variables
Define the nature of variables : Open up a space in memory , To hold data .( Why must it be memory : Because defining variables , It's also part of program logic , The program has been loaded into memory )
Definition : Open up space , There can only be one time .
Statement : inform , Many times .
int a = 10;//a The definition of
a = 20;// assignment
a = 100;// assignment
Classification of variables
Variables are divided into : Local and global variables
local variable : The variables contained in the code block are called local variables . Local variables are temporary . Enter code block , Automatically form local variables , The exit code block is automatically released .[ Many on the Internet say that the variables in the function are local variables , You can't say wrong , But the statement is inaccurate ]( Defined in a code block )
Global variables : Variables defined outside all functions , It's called a global variable . Global variables are global .( Defined outside the code block )
Code block : use {} The enclosed area , It's called a code block
#include<stdio.h>
int g_val = 100;// Global variables
int main()
{
int a = 10;// local variable ,main Functions are also functions , There are also code blocks {}
if(a == 10)
{
int b = 10;// local variable
}
printf("a=%d\n", a);
return 0;
}
Scope of variable
Scope : It refers to the code area of the variable that can be accessed normally .
local variable : Valid only within this code block .
Global variables : During the whole program running , Are effective .
Where global variables :
- Can be accessed in any code block
- Can be accessed in any code block , Even modified .
- When a global variable has the same name as a local variable , Local variables take precedence .
#include<stdio.h>
int g_vax = 10;// Global variables
void test()
{
int g_val = 100;// Of a local variable g_val Can only be accessed in this code
printf("%d\n", g_val);// In global variables g_val Any code block can be accessed , Even modified
// The output is local , That is, when part and all have the same name , Preferential local .
}
int main()
{
test();
printf("%d\n", g_vax);// Can be accessed in any code block
return 0;
}

Life cycle of variable
Life cycle concept : It refers to the time range from the definition of the variable to its release , The so-called release , It refers to the space once opened up ” Be released “.
local variable : Enter code block , Form local variables [ Open up space ], Exit code block ," Release " local variable .
Global variables : After definition , Throughout the life cycle of the program , This variable is always valid .
Scope vs Life cycle
Scope : Measure the extent of the variable's impact , The valid scope of this variable .
Life cycle : Describes the length of a variable's lifetime . The concept of time : When was it opened up , When is it released .

The most generous keyword - auto
How to use : Variables typically defined in code blocks , Local variable , The default is auto Embellished , But generally omit .
By default, all variables are auto Do you ? No , Generally used to modify local variables
Local variables include automatic variables , Temporary and local variables .
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) // local variable i Can also be auto modification
{
printf("i=%d\n", i);
if (1)
{
auto int j = 0;// Automatic variable
printf("before: j=%d\n", j);
j += 1;
printf("after : j=%d\n", j);
}
}
return 0;
}
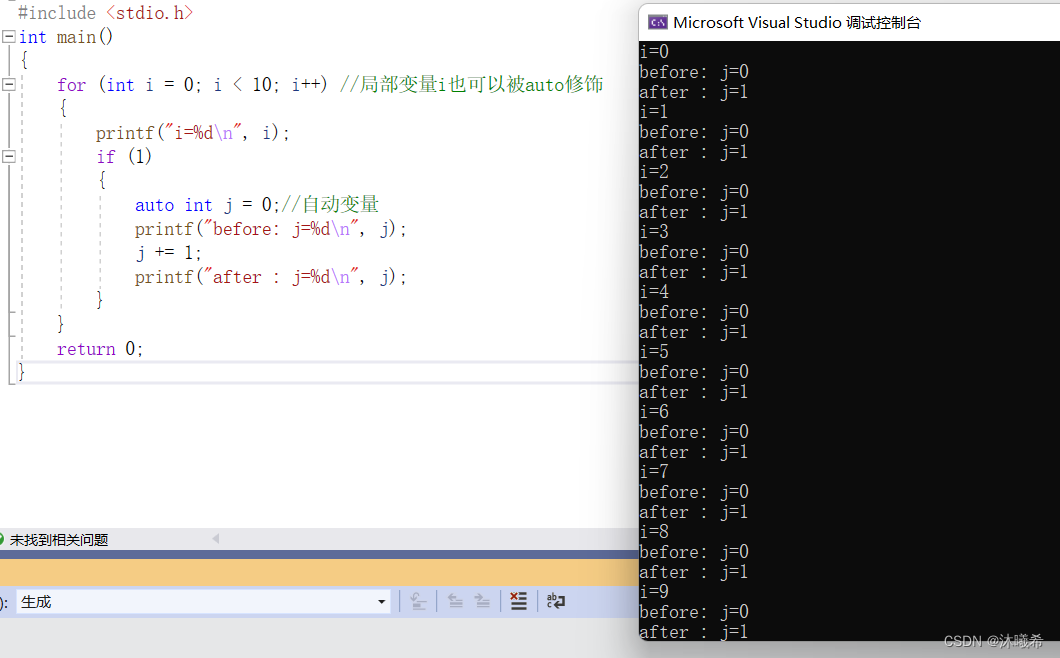
auto Already very old , Basically not used .
The fastest keyword - register
CPU It is mainly the hardware unit responsible for calculation , But for ease of calculation , Generally, the first step is to read the data from memory to CPU Inside , Then you need CPU It has certain temporary data storage capacity . Be careful :CPU It's not the time to calculate , To read specific data to CPU Inside , That's too slow .
So modern CPU Inside , Are integrated with a set of hardware called registers , Used to save temporary data .
Storage pyramid

distance CPU The closer the storage hardware , The faster the speed. .
Understanding of register
CPU A set of storage hardware is integrated into the , This set of hardware is called registers .
The essence of register existence
On the hardware level , Improve the computing efficiency of the computer . Because you don't need to read data from memory .
register Modifying variables
As far as possible The modified variable , Put in CPU In the deposit area , So as to achieve the purpose of improving efficiency
So what kind of variables , May adopt register Well ?
1. Local ( The overall situation will lead to CPU The register is occupied for a long time )
2. Will not be written ( Writing requires writing back to memory , If you need to read the test later , It doesn't make sense )
3. High frequency read ( Improving efficiency lies in )
4. If you want to use , Please don't use a lot of , Because the number of registers is limited
5.register Decorated variable , Address not available ( Because it's already in the deposit area , Address is a memory related concept )
register –cache– Memory –SSD/flash/ Hard disk – Compact disc – disk
Hard disk is converted into memory through cache technology , Memory is converted into registers through cache technology .
distance CPU The nearer the storage unit , The more efficient , The higher the unit price cost .
distance CPU The farther away the storage unit , The less efficient , The cheaper the unit price .
For any kind of hardware , Act as a cache for upstream hardware .
example : Memory can be regarded as a large cache of hard disk ;cache And registers are equivalent to some kind of cache in memory .
CPU When accessing data , Achieve the highest efficiency at the lowest cost .
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
register int a = 10;
printf("%p\n", &a);
return 0;
}

At the end
Friends who think it's good can pay attention to , Like or collect ! Thank you for your support .
Yours ️ Praise is the source of my creative power
Your collection is the direction of my struggle
Your attention is my greatest support
Yours ️ Comments are a bright light for me to move forward
It's not easy to create , I hope you can support Xiaomu
边栏推荐
- In navigation, the solution of adding borders to affect the layout
- TRON-api-波场转账查询接口-PHP版本-基于ThinkPHP5封装-附带接口文档-20220602版本-接口部署好适用于任何开发语言
- Win7 registers out of process components, services, and COM component debugging
- 服务端渲染与客户端渲染的区别(优缺点)
- Advantages and disadvantages of single page development and multi page development
- object.defineProperty 基本使用
- 无重复字符的最长字符串(LeetCode 3)
- Records of gdcpc Guangdong Provincial Games in 22 years
- What can LDAP and SSO integration achieve?
- 从小白入手,从已经训练好的模型中取出weight权重参数绘制柱状图
猜你喜欢

寻找两个有序数组的中位数(LeetCode 4)

元宇宙是短炒,还是未来趋势?

Is yuancosmos a short-term speculation or a future trend?
![[JS] some handwriting functions: deep copy, bind, debounce, etc](/img/f8/cf51a24450a88abb9e68c78e0e3aa8.jpg)
[JS] some handwriting functions: deep copy, bind, debounce, etc

You can't just use console Log ()?

DOM+JS+轮播图+无时间
promise的理解已经利用promise实现图片的预加载(顺序加载)

Rust语言学习

Reprint --win10 open the task manager to solve the blue screen problem

【Leetcode】79. Word search
随机推荐
Pytoch notes
Create servlet project
AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.12)
Quic wire layout specification - packet types and formats | quic protocol standard Chinese translation (2) package type and format
【Leetcode】416. Split equal sum subset
JS how to convert a string into an array object
Video speed doubling in PC browser
【Leetcode】637. Layer average of binary tree
[JS] some handwriting functions: deep copy, bind, debounce, etc
Invalid date of moment conversion timestamp
Lightweight ---project
promise的理解已经利用promise实现图片的预加载(顺序加载)
Linear model of machine learning
mysql复习
Take the web page animation effects that can be used. Don't you come and have a look?
Problems encountered in generating MP3 from text to speech through iFLYTEK voice API
Decision tree of machine learning
Shielding does not display vs warning
Principle of master-slave replication of redis
Find the median of two ordered arrays (leetcode 4)