当前位置:网站首页>[MySQL] Table constraints
[MySQL] Table constraints
2022-06-10 22:23:00 【yuelinghou】
List of articles
One . What are constraints ?
When I introduced data types in the previous article, I introduced “ constraint ” The concept , What really constrains the field is the data type , But the data type constraint is very single , There need to be some extra constraints , Better guarantee the legitimacy of the data , This article will focus on MySQL Some of the constraints in .
The definition of constraints is given below : Constraints are essentially MySQL By limiting user actions , To achieve a set of integrity solutions to maintain its own security , That is, the ultimate goal of constraints is to ensure the correctness of data from the perspective of business logic 、 Security .
Two . Why should there be constraints ?
We know MySQL Is a set of data storage solutions , In addition to the basic data storage functions , Also ensure that the data is as secure as possible , Reduce the possibility of user misoperation .
It's like 《 Trisomy 》 Facing the wall plan in , Now that the gravitational wave deterrent system has been built , That's it , Why choose a man who faces the wall ( Swordsman ) Well ? Because people all over the world need to ensure the safety of gravitational wave deterrence system ( That is, you can't use it at will ), Therefore, it is necessary to select a unified candidate to control the system , To maintain the strategic balance between the two civilizations , The sword bearer is a restraint .
3、 ... and . How to constrain ?
1. Empty properties — not null
When we register the account or fill in the user information , Some properties are required 、 The other is optional :
Corresponding to the database level , When we define each field in the table , They have two properties :null( default ) and not null( Not empty ). The default field properties of the database are allowed to be empty , But in actual development , Try to make sure that the field is not empty , Because the data is empty .
- Create a Person surface , The field contains the name of the person 、 Gender , All allowed to be empty :

- Create a PersonNotNull surface , It also contains two fields : full name 、 Gender . However, it is not allowed to be empty :
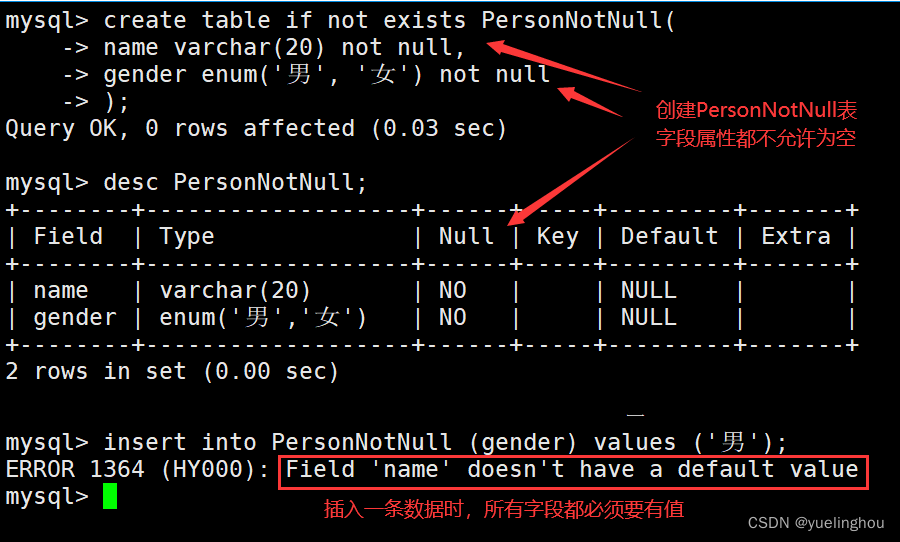
2. The default value is — default
Usually when we register a social platform account , Need to bind your phone number , Different countries have different international area codes for telephone numbers ; For example, China's international area code is +86, If this social media platform is Chinese , The default is that the Chinese use the most , So if you don't choose, the area code is +86 了 :
The default value is : A certain kind of data will often have a specific value , You can specify at the beginning , When you need real data , Users can selectively use the default value .
Usage method : When defining fields, add default The default value is .
give an example :
mysql> create table if not exists Person(
-> name varchar(20),
-> nationality varchar(20) default ' China ',
-> age tinyint unsigned default 0
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> desc Person;// The nationality and age fields use default values
+-------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| nationality | varchar(20) | YES | | China | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 0 | |
+-------------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into Person (name) values (' Zhang San ');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from Person;
+--------+-------------+------+
| name | nationality | age |
+--------+-------------+------+
| Zhang San | China | 0 |
+--------+-------------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
problem :not null and default Simultaneous setting , What will happen ?
The following code tests this problem . When we build tables , Give Way nationality The field is not null Also set the default value default; Found that when inserting data , No error will be reported even if this field is not filled in , And it is found that the default value of this field is :
mysql> create table if not exists Person(
-> nationality varchar(20) not null default ' China ',
-> age tinyint unsigned
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> insert into Person (age) values (18);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from Person;
+-------------+------+
| nationality | age |
+-------------+------+
| China | 18 |
+-------------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
summary : stay not null and default At the same time , You can still use the default value without filling in the value , No mistake. . But it is not recommended to use it together , In the fields that must be filled with data, only not null, Only use... When the default value is determined in advance default.
3. Columns. — comment
Columns. (comment), There's no real meaning , Specifically used to describe field information , The function is equivalent to annotation . It will create statements based on the table to save , For programmers or DBA To understand .
View by : Column description information is in use desc Keyword will not be displayed when viewing the table structure , Only through show When viewing the table creation statement :
mysql> create table if not exists Person(
-> name varchar(20) comment ' This is the user's name , Required ',
-> gender char(1) default ' male ' comment ' This is the gender of the user , The default is male ',
-> age tinyint unsigned default 18 comment ' This is the age of the user , The default is 18'
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
// 1、 adopt desc Unable to view comment information
mysql> desc Person;
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| gender | char(1) | YES | | male | |
| age | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | 18 | |
+--------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
// 2、 adopt show When you view the table creation statement, you can see the annotation information
mysql> show create table Person \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: Person
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `Person` (
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ' This is the user's name , Required ',
`gender` char(1) DEFAULT ' male ' COMMENT ' This is the gender of the user , The default is male ',
`age` tinyint(3) unsigned DEFAULT '18' COMMENT ' This is the age of the user , The default is 18'
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
Use advice : The class description is best written in the last position of the field , Because it's not like not null or default That will have a strong impact on the table data , In this way, it is easier for us to interpret the information of this field .
4. zerofill
up to now , We learned that the following two types can be followed by parentheses :
- Character type :char(len)、varchar(len). The number of parentheses here determines the upper limit of the number of stored characters .
- value type :int(int)、tinyint(int) etc. . The number in parentheses here determines the bit width of the displayed data , Just add
zerofillKeywords are useful .
give an example :
Let's create a table , There are two of them int Type field a and b, It is stipulated that their bit widths are 10, Only b Field added keywords zerofill, Insert a piece of data into the table , Observe the display result after insertion :
mysql> create table if not exists Number(
-> a int(10),
-> b int(10) zerofill
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec)
mysql> desc Number;
+-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| a | int(10) | YES | | NULL | |
| b | int(10) unsigned zerofill | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+---------------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into Number values (10, 20);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from Number;
+------+------------+
| a | b |
+------+------------+
| 10 | 0000000020 |
+------+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
You can see b The value of shows that the bit width is 10, and a The value of is the normal display . This is it. zerofill The function of attributes , If the width of the data itself is less than the set width ( The setting here is 10), Will be automatically filled 0 The set bit width has been reached . It should be noted that , It's just the last result , stay MySQL What is actually stored in the is 20. Why is that so ? We can use hex Function to prove , The function is based on 16 Display the value in decimal form :
mysql> select b, hex(b) from Number;
+------------+--------+
| b | hex(b) |
+------------+--------+
| 0000000020 | 14 |
+------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
It can be seen that the internal storage of the database is still digital 20,0000000020 Just set up zerofill Property is just a formatted output .
5. Primary key — primary key
Primary key (primary key) Is a field that uniquely identifies a row of data in a table . If you compare a watch to a red black tree , Each row of data in the table corresponds to each node of the red black tree ; The primary key of the table corresponds to... In the node key; The other fields of the table correspond to value.
The primary key of a table has the following three characteristics :
- A table has only one primary key field , This field uniquely identifies a row of data in the table .
- The default primary key field is not null attribute .
- The contents of the primary key field in each row of the table cannot be repeated .
give an example :
Composite main building
Create a Address surface , hold ip Fields and port Fields are combined to form a composite primary key , It is used to identify the only process in the public network :
mysql> create table if not exists Address(
-> ip varchar(20) comment ' Host's public network IP',
-> port int unsigned comment ' Unique identification of the process in the host ',
-> name varchar(20) comment ' Host username ',
-> primary key(ip, port)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc Address;
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| ip | varchar(20) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| port | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
Only when the contents of all fields in the composite primary key are identical , Primary key conflicts :
mysql> insert into Address values ('127.0.1', 8080, ' Zhang San ');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into Address values ('127.0.1', 1111, ' Zhang San ');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.17 sec)
mysql> select * from Address;
+---------+------+--------+
| ip | port | name |
+---------+------+--------+
| 127.0.1 | 1111 | Zhang San |
| 127.0.1 | 8080 | Zhang San |
+---------+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
Primary key modification
1、 Append primary key
When the table is created but there is no primary key , You can append the primary key again with the following statement , However, it is necessary to ensure the uniqueness of the data of the field appended as the primary key :
alter table Table name add primary key( Field list );
2、 Delete primary key
There is only one primary key in a table , Therefore, you do not need to specify specific fields when deleting a primary key :
alter table Table name drop primary key;
Suggestions for setting table primary key
generally speaking , We suggest that the primary key be designed as Fields unrelated to the current business , such , When the business is adjusted , We can try not to adjust the primary key too much .
6. Self growth — auto_increment
auto_increment: Fields set as self growing must be used with the primary key , As a logical primary key . This field may not be given a value , It will be automatically triggered by the system , From the self growth field of the current table The maximum value already exists Conduct +1 operation , Get a new different value .
The characteristics of self growth :
- The self growing field must be of type integer .
- The self growing field must be a field in the primary key or composite primary key .
- A table can only have one self growing field at most .
Usage method : When the table is created , Add... After the field auto_increment; If it's a composite primary key , You need to put the self growing column in the first position of the composite primary key , On the far left , As shown in the following code :
// Put the... Under the composite main construction a The field is set to self growth
// If you insert it like this , You only need to specify non self growing fields
create table t(
a int auto_increment,
b int,
primary key (a,b)
);
give an example :
Create a student table , Set the student ID as self increasing , In this way, each time you insert a row of data, you only need to specify the student name , Their student numbers are allocated according to the value given by self growth :
There is no row of data in the current table , We insert a student named “ Zhang San ”, The student ID uses the value given by self growth , It is found that the default value is a number at the beginning of the growth 1:
Continue inserting data , It is observed that the given value of self growth is based on the existing maximum value +1:
In order to verify the law of self growth again , This time we insert our own “ Student number , full name ” data , Then observe the change of self growth value :
7. The only key — unique
There are many fields in a table that need uniqueness , That is, the data of this field in a table cannot be repeated , But a table can only have one primary key , What about other fields that need to be unique ? A unique key can solve the problem that multiple fields in a table need uniqueness constraints .
Like at school , We need a student management system , There is a student list in the system , There are two fields in the student table , An ID number , One is the student number , We can choose to use the ID number as the primary key . So the student ID is just a common field ,MySQL A security constraint is not provided for it , In case you accidentally input a duplicate student ID, it will not be detected , It's very troublesome not to change until there is something wrong with the business . So when we design student numbers , Need a constraint : All student numbers cannot be repeated , We can design the student ID as the unique key when designing the table .
Unique key setting method : Add... When defining fields unique keyword .
The difference between a unique key and a primary key :
- The unique key is allowed to be empty , And more than one can be empty , That is, empty fields are not used as the basis for uniqueness .
- The main point of a primary key is that it serves as a unique identifier for a row of data ; The only key focuses on ensuring the uniqueness of the field data in the table .
give an example :
Create a learning information table , Set the student ID as the unique key and verify the unique key characteristics through a series of insertion operations :
// Create a student information sheet
mysql> create table if not exists Student(
-> name varchar(20) not null comment ' Student's name , Not allowed to be empty ',
-> st_id int unsigned unique comment ' Student's student number , Set as unique key ',
-> telephone varchar(11) primary key comment ' Student's phone number , Set as primary key '
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
// Observe the structure of the table , Unique key fields are identified UNI
mysql> desc Student;
+-----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| st_id | int(10) unsigned | YES | UNI | NULL | |
| telephone | varchar(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
+-----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
// test 1: The data of the unique key field cannot be duplicated
mysql> insert into Student (name, st_id, telephone) values (' Zhang San ', 20204912, '111xxx');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into Student (name, st_id, telephone) values (' Li Si ', 20204912, '222xxx');
ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '20204912' for key 'st_id'
// Test two : The unique key field can be repeatedly empty
mysql> insert into Student (name, telephone) values (' Zhang San ', '222xxx');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into Student (name, telephone) values (' Li Si ', '333xxx');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from Student;
+--------+----------+-----------+
| name | st_id | telephone |
+--------+----------+-----------+
| Zhang San | 20204912 | 111xxx |
| Zhang San | NULL | 222xxx |
| Li Si | NULL | 333xxx |
+--------+----------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
8. Foreign keys — foreign key
Foreign keys are used to define the relationship between the master table and the slave table : Foreign key constraints are mainly defined on the slave table , The primary table must have a primary key constraint or unique constraint . When a foreign key is defined , The foreign key field data of the secondary table must exist in the primary key of the primary table (or The only key ) The column exists or is itself NULL.
Understanding foreign keys :
Foreign key setting method :
When creating a table, a single row is used to set the foreign key :
foreign key ( From the field name in the table ) references Main table ( Field names in the main table )
give an example :
Create a student table , There are students' names and class numbers in it ; Create another class table , There are subject information corresponding to each class .
Use the foreign key to associate the class number in the student table with the class number in the class table :
// The main table must be created first
mysql> create table if not exists ClaTable(
-> id int unsigned primary key comment ' Class number ',
-> course varchar(20) not null comment ' Class courses '
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
// When creating a slave table, you can select one of your own fields and the fields of the master table for foreign key constraints
mysql> create table if not exists StuTable(
-> name varchar(20) not null comment ' The student's name ',
-> class_id int unsigned comment ' The class the students are in ',
-> foreign key(class_id) references ClaTable(id)
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
mysql> desc ClaTable;
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| course | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
// Observed from the table class_id The field key information is MUL
mysql> desc StuTable;
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| class_id | int(10) unsigned | YES | MUL | NULL | |
+----------+------------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Let's start with the main table ClaTable Insert two pieces of class related data in :
mysql> insert into ClaTable (id, course) values (401, ' Physics 、 chemical 、 Geography ');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into ClaTable (id, course) values (405, ' history 、 Politics 、 biological ');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from ClaTable;
+-----+--------------------------+
| id | course |
+-----+--------------------------+
| 401 | Physics 、 chemical 、 Geography |
| 405 | history 、 Politics 、 biological |
+-----+--------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Next, go to the slave table StuTable Insert data into to verify the characteristics of foreign keys :
- Insert a class number as 500 The students of the class , Because there is no class in the main table , So the insertion failed , At this point, the foreign key constraint is working :

- The data of the foreign key field in the table is allowed to be NULL Of . Insert class from table id by null A student of , Here comes a new student , There is no class assigned yet :

Understand foreign keys and foreign key constraints
The above example , We don't create foreign key constraints , Just set up the student list normally , And the class schedule , We have all the fields we need , Then by comparing the student table and the class table id Information can also associate two tables , here , In actual use , What could be wrong ?
Is it possible that you accidentally input the wrong class number in the inserted student information , But this class is not in the class list , At this time MySQL Not detected , The two tables are business related , But there are no constraints on the business , Then there may be problems in the later business .
The solution is to establish a foreign key constraint relationship between the two tables . The essence of establishing foreign keys is to hand over the relevance to MySQL To review , Let me know in advance MySQL Constraints between tables , So when a user inserts data that does not conform to business logic ,MySQL It will be checked out , You are not allowed to insert .
边栏推荐
- (十一)TableView
- Capacity expansion mechanism of ArrayList
- Forward slash "/", backslash "\," escape character "\" and file path separator cannot be clearly remembered
- Array union set
- 在模仿学习中进步的智能机器人
- C language to judge whether a file or folder exists
- Kdd2022 | neural network compression of depth map based on antagonistic knowledge distillation
- 数组 求并集
- Concept and use of CEPH distributed storage cluster pool resource pool
- Notes (IV) - multithreading
猜你喜欢

C语言-排序中的快速排序(简称快排)
datagrip 报错 “The specified database user/password combination is rejected...”的解决方法

Principle of gravure overprint and factors affecting overprint

ICML2022 | Sharp-MAML:锐度感知的模型无关元学习

如何激发文化创新的活力和驱动力
PHP pseudo protocol implementation command execution details

Abbexa cdan1 siRNA instruction manual

(11) Tableview

Abbexa 8-OHdG CLIA kit solution
SoC development environment and hardware development preparation
随机推荐
【MySQL】錶數據的增删查改(DML)
Super detailed tutorial for installing mysql8 in centos7 (no pit!)
ArrayList的扩容机制
解读创客空间下的教育新生态
Introduction to abbexa bacterial genome DNA Kit
系统重装以及查询系统性能
oc swift 混编
Share some information I accumulated when I was working as a dotnet9 blog site
笔记(二)
NFT copyright / royalties
Abbexa 8-OHdG CLIA kit solution
IDEA出现“XXX has broken path”报错解决方法
JS anchor positioning can extend many functions
Constructing the implementation strategy of steam education for children
AI blessing real-time interaction | analysis of zegoavatar facial expression following technology
Notes (V) - JVM
ThinkPHP v6.0. X deserialization vulnerability recurrence
【问题】解决Websocket字符串长度限制问题单包过大
Record (II)
C语言判断文件或文件夹是否存在
