当前位置:网站首页>[deep learning theory] (7) long and short term memory network LSTM
[deep learning theory] (7) long and short term memory network LSTM
2022-06-26 11:01:00 【Vertical sir】
Hello everyone , Today, I would like to share with you the short - and long-term memory network LSTM Principle , And use Pytorch Implement from formula LSTM layer
The previous section introduced the cyclic neural network RNN, You can have a look at what you are interested in :https://blog.csdn.net/dgvv4/article/details/125424902
There are many in my column LSTM The actual combat cases of , It is convenient for everyone to consolidate their knowledge :https://blog.csdn.net/dgvv4/category_11712004.html
1. introduction
The memory function of recurrent neural network has great advantages in dealing with time series problems , But as the training continues ,RNN The network has been expanding its memory , the RNN Produce gradient disappearance and gradient explosion .
In order to solve RNN Difficult to train effectively , Having the function of selective memory LSTM The model is proposed .LSTM Is in RNN Based on the improvement , It can learn the long-term dependence in data , It can also solve the problem of gradient disappearance .LSTM It contains a memory unit and three gates , The gate structures are input gates respectively 、 Output gate and forgetting gate .
LSTM The working process is as follows :
First of all input data X_t And The output data of the previous hidden layer h_t-1 Act together on Oblivion gate , The forgetting gate filters the above information , Memorize important characteristic information in time series , Discard irrelevant information ; And then input data x_t as well as The output data of the previous hidden layer h_t-1 As Input gate Input information for , updated ; Secondly, the memory unit inputs data X_t、 The output data of the previous hidden layer h_t-1 And the state of the memory unit at the previous moment C_t-1 Update your status ; The final will be input data X_t、 The output data of the previous hidden layer h_t-1 as well as The state of the memory unit at the current time C_t Act together on Output gate , Output the hidden layer information at the current time h_t.
LSTM The structure diagram of is as follows :
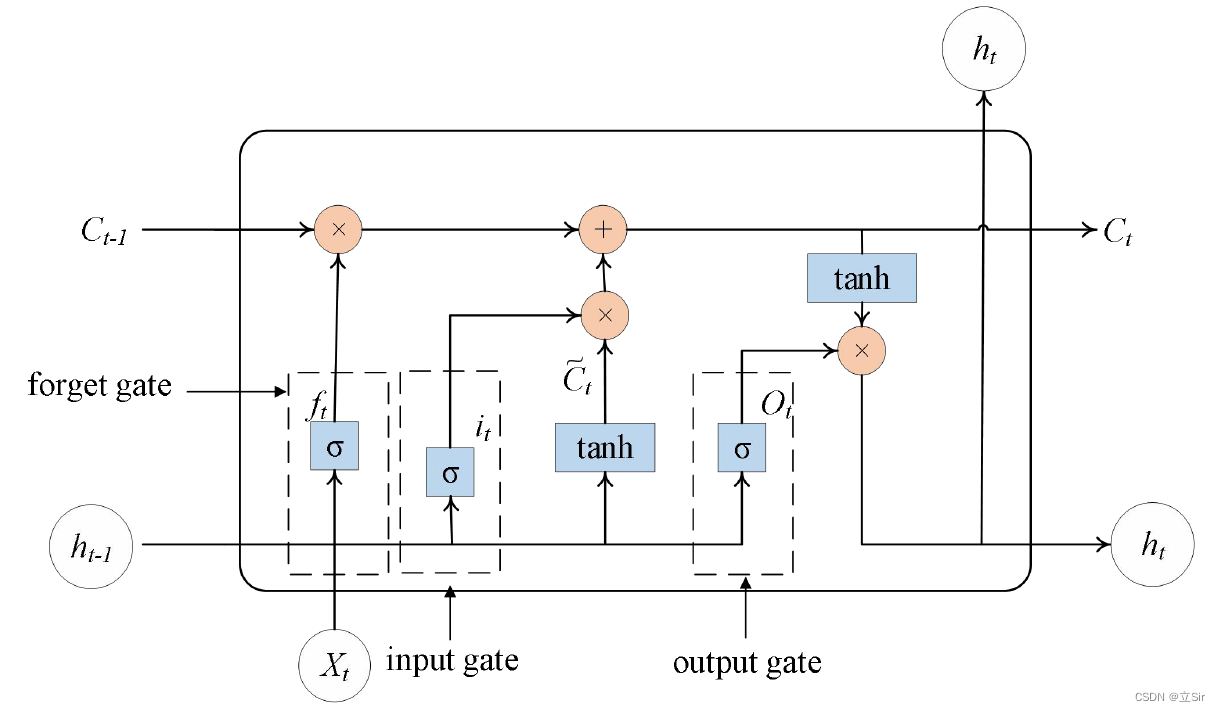
2. Principle analysis
2.1 Oblivion gate
take Last time output h_t-1 And Input of current time X_t combination , And pass Sigmoid The function calculates a threshold of [0,1] Tensor f_t, The f_t It can be regarded as right The state of the last moment C_t-1 Weight item of ,f_t be responsible for Control the extent to which the last state needs to be forgotten .
Calculation formula :
![f_t = \sigma (W_f \cdot [h_t-1, x_t] + b_f)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/26/202206260959471189_12.gif)
Expand the formula , among W_if It is the feature extraction of the input at the current time ,W_hf It is the feature extraction of the previous state ,@ For matrix multiplication .


2.2 Input gate
The input gate is the same as tanh Function to control the degree of adding new information . In the process ,tanh Function will give a new candidate vector  , The input door is
, The input door is  Each item in the results in a [0,1] Between the value of the i_t, Control how much new information is added .
Each item in the results in a [0,1] Between the value of the i_t, Control how much new information is added .
Calculation formula :
![i_t = \sigma (W_i \cdot [h_t-1, x_t] + b_i)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/26/202206260959471189_6.gif)
![\tilde{C}_t = tanh (W_c \cdot [h_t-1, x_t] + b_c)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/26/202206260959471189_7.gif)
Formula expansion , among W_i It is the feature extraction of the input at the current time ,W_h It is the feature extraction of the previous state ,@ For matrix multiplication .



thus , The model has calculated The output of the forgetting gate f_t, and The output of the input gate i_t, They are used to control the degree to which the state of the previous moment needs to be forgotten , And the scale of new information , Next, you can update... Based on these two outputs The state of the current moment C_t.
Calculation formula , among * Represents element by element multiplication between tensors .


2.3 Output gate
The output gate is used to filter some information about the current state , Let it go . Calculation process of output gate , take input data X_t、 The output data of the previous hidden layer h_t-1 after sigmoid function , Compress the value of each term to [0-1] Between , As a weight item for filtering information . Then with Updated current status C_t Multiply by element ,
Calculation formula :
![o_t = \sigma (W_o \cdot [h_t-1, x_t] + b_o)](http://img.inotgo.com/imagesLocal/202206/26/202206260959471189_9.gif)

Formula expansion :


3. Code implementation
3.1 official API
torch.nn.LSTM() The parameters are as follows :
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bias=True, batch_first=False)
'''
input_size: How many vectors are used for each word to represent
hidden_size: Hidden layer , after LSTM After the layer, each word is represented by a vector of how long
num_layers: LSTM The number of layers
bias: Whether to use the offset term , The default is True, namely [email protected]+b
batch_first: Whether the input will batch Put it in axis=0 The location of , Default False, namely [seq_len, batch, feature_len]
'''Instantiate a single layer LSTM, Do a forward propagation , View the output
import torch
from torch import nn
# Defining parameters
batch = 3 # Now there is 3 A sentence
seq_len = 10 # Each sentence has 10 Word
feature_len = 100 # Each word has a length of 100 To represent the vector of
hidden_len = 20 # after LSTM The length of each word after the layer is 20 To represent the vector of
# Input of current time [batch, seq_len, feature_len]
inputs = torch.randn(batch, seq_len, feature_len)
# The state of the last moment [batch, hidden_len]
h0 = torch.randn(batch, hidden_len)
c0 = torch.randn(batch, hidden_len)
# Instantiation LSTM layer
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=feature_len, hidden_size=hidden_len,
num_layers=1, batch_first=True)
# c: Status of the last word update ,[num_layer, batch, hidden_size]
# h: Output of the last word ,[num_layer, batch, hidden_size]
# out: Overall output results ,[batch, seq_len, hidden_size]
out, (h,c) = lstm(inputs)
print('out:', out.shape, # [3, 10, 20]
'h:', h.shape, # [1, 3, 20]
'c:', c.shape) # [1, 3, 20]
# View weight information
for k,v in lstm.named_parameters():
print(k, v.shape)
'''
weight_ih_l0 torch.Size([80, 100])
weight_hh_l0 torch.Size([80, 20])
bias_ih_l0 torch.Size([80])
bias_hh_l0 torch.Size([80])
'''3.2 Custom function
Next, according to the formula explained in the second section , In principle, a LSTM layer , Mainly 6 The calculation of a formula , Also note the tensor shape change .


The code implementation is as follows :
import torch
from torch import nn
'''
inputs: Input of current time [batch, seq_len, feature_len]
c0: The state of the last moment ,[batch, hidden_len]
h0: Last time output ,[batch, hidden_len]
w_ih, b_ih: Input the characteristic matrix and offset at the current time
w_hh, b_hh: The characteristic matrix and offset of the state at the previous time
w_ih.shape=[4*hdiien_size, feature_len]
w_hh.shape=[4*hdiien_size, hidden_len]
b.shape=[4*hidden_size]
'''
# ------------------------------------------------------------- #
#(1) Customize LSTM Model
# ------------------------------------------------------------- #
def lstm_forward(inputs, initial_states, w_ih, w_hh, b_ih, b_hh):
h0, c0 = initial_states # Get the initial state
# batch Represents the number of sequences ,seq_len Represents how many samples there are in each sequence ,feature_len Represents how many characteristics each sample has
batch, seq_len, feature_len = inputs.shape # Get the input shape
# Get the number of hidden layers , According to the formula 4 individual W Splicing into
hidden_len = w_ih.shape[0] // 4 # weight_ih_l0 torch.Size([80, 100])
# Initialize the output layer [batch, seq_len, hidden_len]
outputs = torch.zeros(batch, seq_len, hidden_len)
# stay LSTM Update the status of the previous time continuously
pre_h, pre_c = h0, c0
# expand w Dimensions ==>[b, 4*hdiien_size, feature_len]
batch_w_ih = w_ih.unsqueeze(0).tile(batch, 1, 1)
# ==>[b, 4*hdiien_size, hidden_len]
batch_w_hh = w_hh.unsqueeze(0).tile(batch, 1, 1)
# Traverse each word in each sequence
for t in range(seq_len):
# Get the input tensor at the current time
x = inputs[:, t, :] # [b, feature_len]
# Three dimensional matrix multiplication [b, 4*hdiien_size, feature_len] @ [b, feature_len, 1]
w_time_x = torch.bmm(batch_w_ih, x.unsqueeze(-1)) # [b, 4*hidden_len, 1]
w_time_x = w_time_x.squeeze(-1) # [b, 4*hidden_len]
# Matrix multiplication of states [b, 4*hdiien_size, hidden_len] @ [b, hidden_len, 1]
w_time_h_pre = torch.bmm(batch_w_hh, pre_h.unsqueeze(-1)) # [b, 4*hidden_size, 1]
w_time_h_pre = w_time_h_pre.squeeze(-1) # [b, 4*hidden_size]
# Take before 1/4 Used as input gate (i)
i_t = w_time_x[:, :hidden_len] + b_ih[:hidden_len] + w_time_h_pre[:, :hidden_len] + b_hh[:hidden_len]
i_t = torch.sigmoid(i_t)
# Oblivion gate (f)
f_t = w_time_x[:, hidden_len:hidden_len*2] + b_ih[hidden_len:hidden_len*2] + w_time_h_pre[:, hidden_len:hidden_len*2] + b_hh[hidden_len:hidden_len*2]
f_t = torch.sigmoid(f_t)
# Cell door (g)
g_t = w_time_x[:, hidden_len*2:hidden_len*3] + b_ih[hidden_len*2:hidden_len*3] + w_time_h_pre[:, hidden_len*2:hidden_len*3] + b_hh[hidden_len*2:hidden_len*3]
g_t = torch.tanh(g_t)
# Output gate (o)
o_t = w_time_x[:, hidden_len*3:] + b_ih[hidden_len*3:] + w_time_h_pre[:, hidden_len*3:] + b_hh[hidden_len*3:]
o_t = torch.tanh(o_t)
# state (c)
pre_c = f_t * pre_c + i_t * g_t
# The current moment lstm Output (h)
pre_h = o_t * torch.tanh(pre_c)
# Update output layer
outputs[:, t, :] = pre_h
# Return output 、 The output of the last moment h, state c
return outputs, (pre_h, pre_c)
# ------------------------------------------------------------- #
#(2) Forward propagation
# ------------------------------------------------------------- #
batch = 3 # 3 A sentence
seq_len = 10 # Sequence length , Each sentence has 10 Word
feature_len = 100 # The number of features , The length of a word is 100 To represent the vector of
hidden_len = 20 # Hidden layer , after LSTM The length behind the layer is 20 To represent the vector of
# Construct input layer [batch, seq_len, feature_len]
inputs = torch.randn(batch, seq_len, feature_len)
# The initial state , No training required [batch, hidden_len]
h0 = torch.randn(batch, hidden_len)
c0 = torch.randn(batch, hidden_len)
# Construction weight
w_ih = torch.randn(hidden_len*4, feature_len) # [80, 100]
w_hh = torch.randn(hidden_len*4, hidden_len) # [80, 100]
# Structural bigotry
b_ih = torch.randn(hidden_len*4) # [80]
b_hh = torch.randn(hidden_len*4) # [80]
# lstm Layer calculation results
outputs, (final_h, final_c) = lstm_forward(inputs, (h0, c0), w_ih, w_hh, b_ih, b_hh)
'''
outputs: Output of all sentences ,[batch,seq_len, hidden_len]
pre_h: Last word output ,[batch, hidden_len]
pre_c: The state of the last word ,[batch, hidden_len]
'''
print('outputs.shape:', outputs.shape, # [3, 10, 20]
'pre_h.shape:', final_h.shape, # [3, 20]
'pre_c.shape:', final_c.shape) # [3, 20]
边栏推荐
- ISO 26262之——2功能安全概念
- RDB持久化验证测试
- Fabric.js 上划线、中划线(删除线)、下划线
- Vscode environment setup: synchronous configuration
- Jasperreports - print PDF (project tool)
- Qixia housing and Urban Rural Development Bureau and fire rescue brigade carried out fire safety training
- 搜索引擎高级搜索方法记录
- 用同花顺手机炒股是安全的吗?如何用同花顺炒股
- Flutter and native communication (Part 1)
- Oracle sqlplus query result display optimization
猜你喜欢

哪些PHP开源作品值得关注

Origin of b+ tree index

Getting started with postman

【深度学习理论】(7) 长短时记忆网络 LSTM

2021 Q3-Q4 Kotlin Multiplatform 使用现状 | 调查报告

JS take the date of the previous month 【 pit filling 】

Qixia housing and Urban Rural Development Bureau and fire rescue brigade carried out fire safety training
Opencv image processing - grayscale processing

2、 Linear table

Adaptiveavgpool2d does not support onnx export. Customize a class to replace adaptiveavgpool2d
随机推荐
Server single and two-way adjustable one key mutual trust script!
MySQL 30 military regulations
Pit record_ TreeSet custom sorting results in less data loss
UDP Flood攻击防御原理
mysql性能监控和sql语句
[Beiyou orchard microprocessor design] 10 serial communication serial communication notes
Work report (3)
Query online users and forced withdrawal users based on oauth2
MySQL模糊查询详解
目前为止最全的Kubernetes最新版核心命令
wangEditor 上传本地视频修改
Grain Mall - High Availability Cluster
AIX basic operation record
nacos2.x.x启动报错信息Error creating bean with name ‘grpcClusterServer‘;
【北邮果园微处理器设计】10 Serial Communication 串口通信笔记
VS或Qt编译链接过程中出现“无法解析的外部符号”的原因:
Developers, what is the microservice architecture?
【软件项目管理】期末复习知识点整理
工作汇报(3)
哪些PHP开源作品值得关注