当前位置:网站首页>Simple operation of the file system
Simple operation of the file system
2022-08-04 04:06:00 【Master_hl】
1. 文件的存储位置
文件是存储在硬盘上的!!
Simple understanding of the difference between hard disk and memory:
1.内存存储空间小,硬盘空间大.
2.内存访问速度快,硬盘访问速度慢.
3.内存成本高,硬盘便宜.
4.Memory breakpoint data is lost,The hard disk breakpoint data is still there.
Files are also managed by the operating system,There is a dedicated module in the operating system kernel,文件系统.
2. File 概述
属性
修饰符及类型 | 属性 | 说明 |
| static String | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符 '/',String 类型的表示 |
| static char | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符 '/',char 类型的表示 |
构造方法
方法 | 说明 |
File(File parent, String child) | 根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例 |
| File(String pathname) | 根据文件路径创建一个新的 File 实例,路径可以是绝对路径或者相对路径 |
File(String parent, String child) | 根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例,父目录用路径表示 |
方法
修饰符及返回值类型 | 方法 | 说明 |
| String | getParent() | 返回 File 对象的父目录文件路径 |
| String | getName() | 返回 FIle 对象的纯文件名称 |
| String | getPath() | 返回 File 对象的文件路径 |
| String | getAbsolutePath() | 返回 File 对象的绝对路径 |
String | getCanonicalPath() | 返回 File 对象的修饰过的绝对路径 |
| boolean | exists() | 判断 File 对象描述的文件是否真实存在 |
| boolean | isDirectory() | 判断 File 对象代表的文件是否是一个目录 |
| boolean | isFile() | 判断 File 对象代表的文件是否是一个普通文件 |
| boolean | createNewFile() | 根据 File 对象,自动创建一个空文件.成功创建后返回 true |
| boolean | delete() | 根据 File 对象,删除该文件.成功删除后返回 true |
| void | deleteOnExit() | 根据 File 对象,标注文件将被删除,删除动作会到 JVM 运行结束时才会进行 |
| String[] | list() | 返回 File 对象代表的目录下的所有文件名 |
| File[] | listFiles() | 返回 File 对象代表的目录下的所有文件,以 File 对象表示 |
| boolean | mkdir() | 创建 File 对象代表的目录 |
| boolean | mkdirs() | 创建 File 对象代表的目录,如果必要,会创建中间目录 |
boolean | renameTo(File dest) | 进行文件改名,也可以视为我们平时的剪切、粘贴操作 |
| boolean | canRead() | 判断用户是否对文件有可读权限 |
| boolean | canWrite() | 判断用户是否对文件有可写权限 |
绝对路径:以盘符开头的路径,称为 "绝对路径".
相对路径:以 . 或者 .. The path at the beginning is called "相对路径".
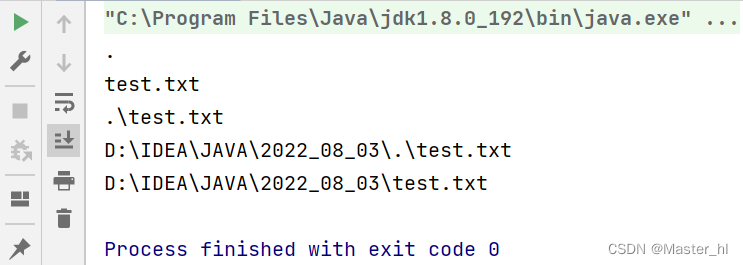
代码示例1
getA series of method demonstrations
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalFile());
}
代码示例2
普通文件的创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 前面没写 ./ ,也相当于是 ./ , ./can be ignored.
File file = new File("hello.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists()); // false
System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); // false
System.out.println(file.isFile()); // false
System.out.println("==============");
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println(file.exists()); // true
System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); // false
System.out.println(file.isFile()); // true
}代码示例3
普通文件的删除
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//file.delete();
//System.out.println(file.exists()); // false
// It is only deleted when the program exits
file.deleteOnExit(); // 用来创建临时文件
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(file.exists()); // true
}代码示例4
创建目录
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("test/aa/bb");
System.out.println(file.exists()); // false
System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); // false
System.out.println("=============");
//file.mkdir(); // 创建单级目录,Use this to create multilevel directories,The following will output two false
file.mkdirs(); // 创建多级目录
System.out.println(file.exists());
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());
}代码示例5
文件重命名
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file1 = new File("test1.txt");
File file2 = new File("test2.txt");
file1.renameTo(file2); // 把文件 file1 的名字改成 test2.txt
}边栏推荐
- How to systematically plan and learn software testing?
- new Date将字符串转化成日期格式 兼容IE,ie8如何通过new Date将字符串转化成日期格式,js中如何进行字符串替换, replace() 方法详解
- 中信证券网上开户怎么开的?安全吗?
- 如何动态添加script依赖的脚本
- Significant differences between Oracle and Postgresql in PLSQL transaction rollback
- 深度学习——以CNN服装图像分类为例,探讨怎样评价神经网络模型
- 帮助企业实现数字化转型成功的八项指导原则
- 一个属于程序员的七夕节!
- 42. 接雨水
- if,case,for,while
猜你喜欢
7. The principle description of LVS load balancing cluster

2022杭电多校联赛第五场 题解
文件内容的操作
How to systematically plan and learn software testing?
用户与用户互发红包/支付宝C2C/B2C现金红包php源码示例/H5方式/兼容苹果/安卓

2022 Hangzhou Electric Power Multi-School League Game 5 Solution
Learn iframes and use them to solve cross-domain problems
机器学习之视频学习【更新】
base address: environment variable
一文详解DHCP原理及配置
随机推荐
技术解析|如何将 Pulsar 数据快速且无缝接入 Apache Doris
2003. 每棵子树内缺失的最小基因值 DFS
7. The principle description of LVS load balancing cluster
本周四晚19:00知识赋能第4期直播丨OpenHarmony智能家居项目之设备控制实现
【MD5】采用MD5+盐的加密方式完成注册用户和登录账号
JVM笔记
解决问题遇到的问题
基于 SSE 实现服务端消息主动推送解决方案
sql语句查询String类型字段小于10的怎么查
网络工程师入门必懂华为认证体系,附系统学习路线分享
一个属于程序员的七夕节!
高效IO模型
Gigabit 2 X light 8 electricity management industrial Ethernet switches WEB management - a key Ring Ring net switch
拿捏JVM性能优化(自己笔记版本)
JVM的内存模型简介
【Ryerson情感说话/歌唱视听数据集(RAVDESS) 】
力扣(LeetCode)215. 数组中的第K个最大元素(2022.08.03)
目标检测-中篇
How to automatically export or capture abnormal login ip and logs in elastic to the database?
外卖店优先级