当前位置:网站首页>SQL interview Questions
SQL interview Questions
2022-08-04 03:37:00 【梦想家DBA】

SQL Cheat Sheet
What is SQL
Data
a collection of facts related to some object
Database
a collection of small units of data arranged in a systematic manner.
RDBMS
a collection of tools that allows the users to manipulate,organize and visualize the contents of a database while following some standard rules that facilate fast response between the database and the user side.
SQL
Structured Query Language
SQL Features
SQL allows us to interact with the databases and bring out/manipulate data within them. Using SQL, we can create our own databases and then add data into these databases in the form of tables.
The following functionalities can be performed on a database using SQL
Create or Delete a Database
Create or Alter or Delete some tables in a Database
Select data from tables
INSERT data into tables
Update data in tables
Delete data from tables
Create Views in the database
Execute various aggregate functions
SQL Advanced Concepts
Create Table:CREATE TABLE student( ID INT NOT NULL, Name varchar(25), Phone varchar(12), Class INT);
Delete Table:To delete a table from a database, we use the DROP command.DROP TABLE student;
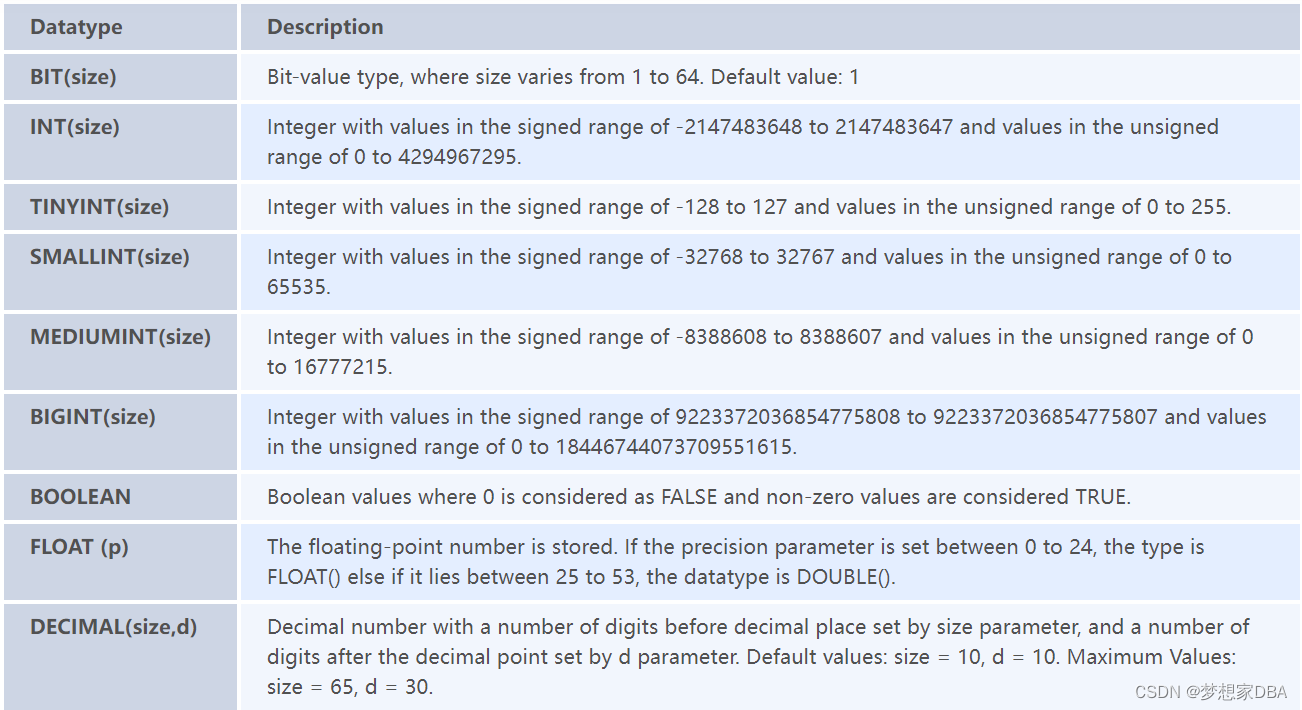
SQL DataTypes:
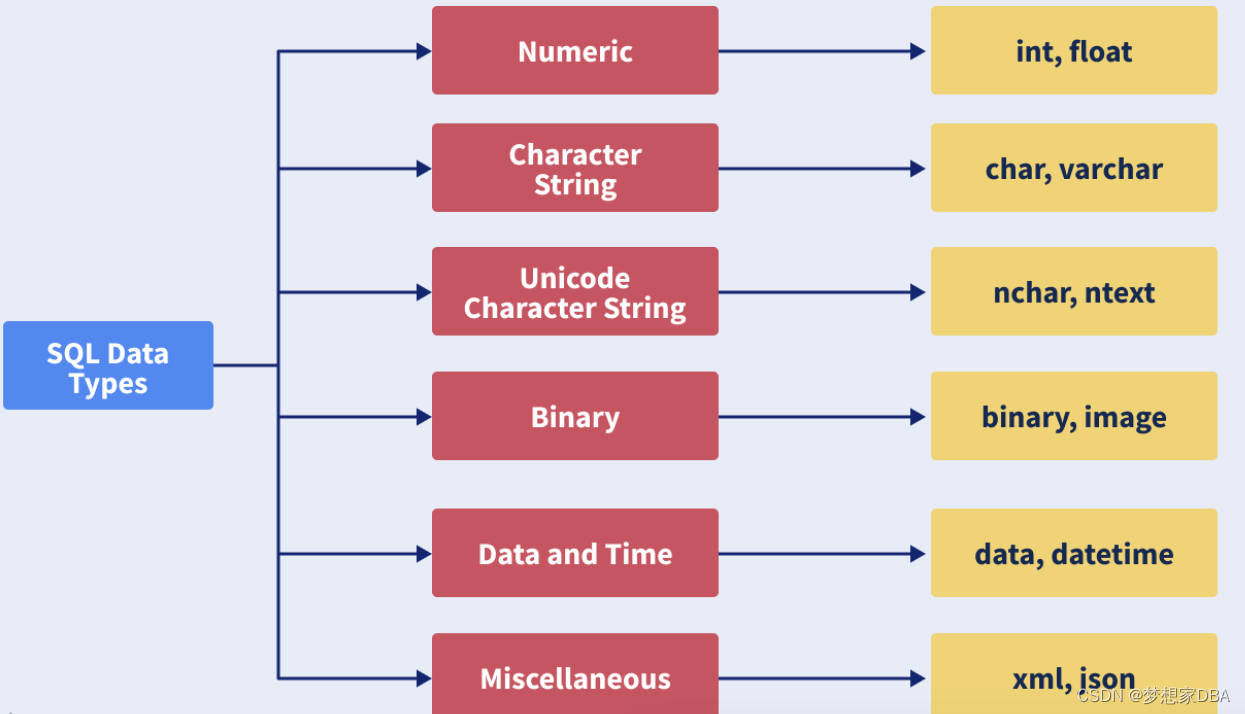
String Datatypes:

Numeric Datatypes:
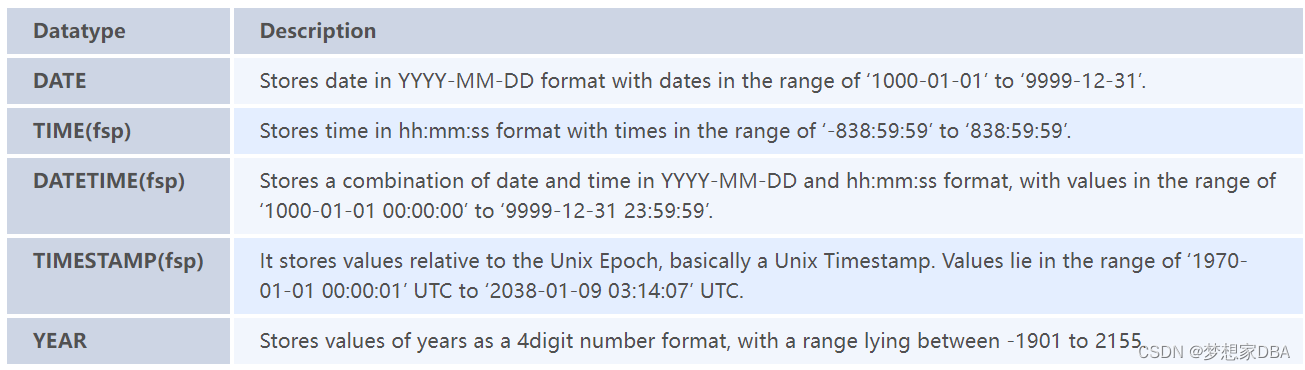
Date/Time Datatypes:
SQL Commands:
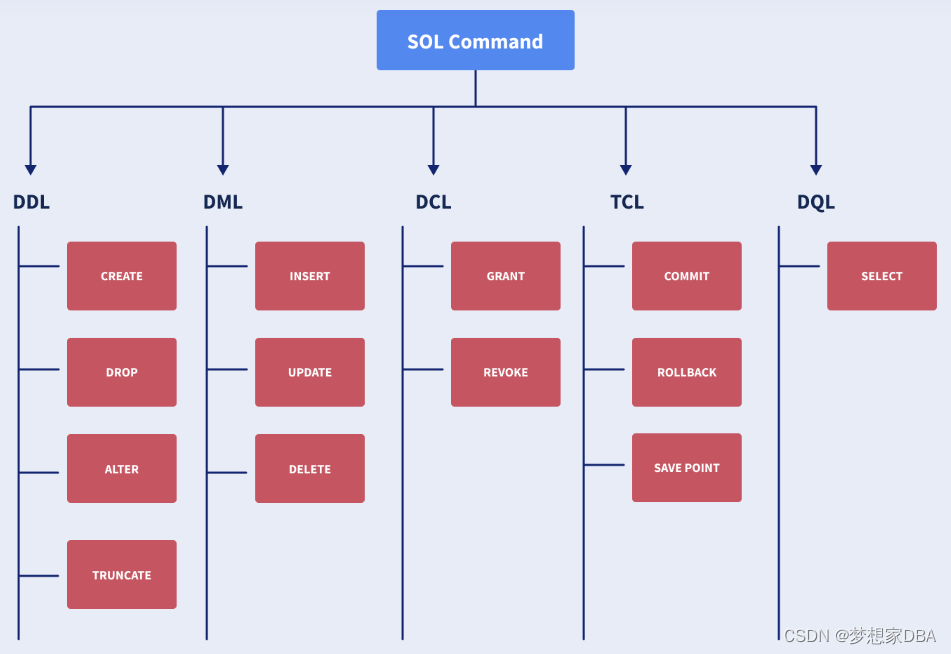
Data Definition Language(DDL): It changes a table’s structure by adding, deleting and altering its contents. Its changes are auto-committed(all changes are automatically permanently saved in the database).
- CREATE: Used to create a new table in the database.
• CREATE TABLE STUDENT(Name VARCHAR2(20), Email VARCHAR2(100), DOB DATE);
- ALTER: Used to alter contents of a table by adding some new column or attribute, or changing some existing attribute.
• ALTER TABLE STUDENT ADD(ADDRESS VARCHAR2(20)); ALTER TABLE STUDENT MODIFY (ADDRESS VARCHAR2(20));
- DROP: Used to delete the structure and record stored in the table.
• DROP TABLE STUDENT;
- TRUNCATE: Used to delete all the rows from the table, and free up the space in the table.
• TRUNCATE TABLE STUDENT;
Data Manipulation Language(DML): It is used for modifying a database, and is responsible for any form of change in a database. These commands are not auto-committed, i.e all changes are not automatically saved in the database.
- INSERT: Used to insert data in the row of a table.
• INSERT INTO STUDENT (Name, Subject) VALUES ("Scaler", "DSA");
- UPDATE: Used to update value of a table’s column.
• UPDATE STUDENT SET User_Name = 'Interviewbit' WHERE Student_Id = '2'
- DELETE: Used to delete one or more rows in a table.
• DELETE FROM STUDENT WHERE Name = "Scaler";
Data Control Language(DCL): These commands are used to grant and take back access/authority (revoke) from any database user.
- Grant: Used to grant a user access privileges to a database.
• GRANT SELECT, UPDATE ON TABLE_1 TO USER_1, USER_2;
- Revoke: Used to revoke the permissions from an user.
• REVOKE SELECT, UPDATE ON TABLE_1 FROM USER_1, USER_2;
Transaction Control Language: These commands can be used only with DML commands in conjunction and belong to the category of auto-committed commands.
- COMMIT: Saves all the transactions made on a database.
• DELETE FROM STUDENTSWHERE AGE = 16; COMMIT;
- ROLLBACK: It is used to undo transactions which are not yet been saved.
• DELETE FROM STUDENTS WHERE AGE = 16; ROLLBACK;
- SAVEPOINT: Used to roll transaction back to a certain point without having to roll back the entirity of the transaction.
• SAVEPOINT SAVED;DELETE FROM STUDENTS WHERE AGE = 16; ROLLBACK TO SAVED;
Data Query Language: It is used to fetch some data from a database.
- SELECT: It is used to retrieve selected data based on some conditions which are described using the WHERE clause. It is to be noted that the WHERE clause is also optional to be used here and can be used depending on the user’s needs.
• SELECT Name FROM Student WHERE age >= 18;
SQL Constraints
NOT NULL: Specifies that this column cannot store a NULL value.
- CREATE TABLE Student( ID int(8) NOT NULL, NAME varchar(30) NOT NULL, ADDRESS varchar(50));
UNIQUE: Specifies that this column can have only Unique values, i.e the values cannot be repeated in the column.
- CREATE TABLE Student( ID int(8) UNIQUE, NAME varchar(10) NOT NULL, ADDRESS varchar(20));
Primary Key: It is a field using which it is possible to uniquely identify each row in a table. We will get to know about this in detail in the upcoming section.
Foreign Key: It is a field using which it is possible to uniquely identify each row in some other table. We will get to know about this in detail in the upcoming section.
CHECK: It validates if all values in a column satisfy some particular condition or not.
- CREATE TABLE Student( ID int(6) NOT NULL, NAME varchar(10), AGE int CHECK (AGE < 20));
DEFAULT: It specifies a default value for a column when no value is specified for that field.
- CREATE TABLE Student( ID int(8) NOT NULL, NAME varchar(50) NOT NULL, CLASS int DEFAULT 2);
Crud Operations in SQL
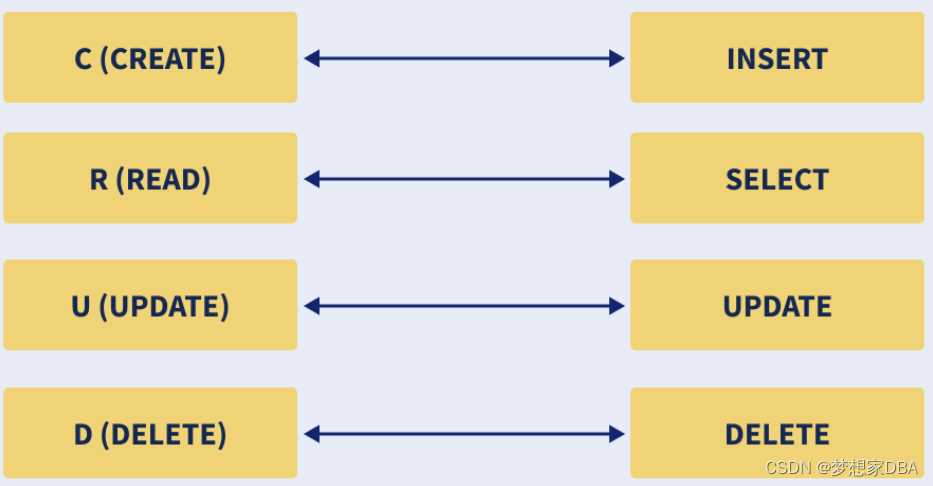
CRUD is an abbreviation for Create, Read, Update and Delete. These 4 operations comprise the most basic database operations.
INSERT: To insert any new data ( create operation - C ) into a database, we use the INSERT INTO statement.
- INSERT INTO name_of_table(column1, column2, ....) VALUES(value1, value2, ....)
- INSERT INTO name_of_table(column1, column2, ....) VALUES(value1, value2, ....), (new_value1, new_value2, ...), (....), ... ;
SELECT: We use the select statement to perform the Read ( R ) operation of CRUD.
- SELECT column1,column2,.. FROM name_of_table;
UPDATE: Update is the ‘U’ component of CRUD. The Update command is used to update the contents of specific columns of specific rows.
- UPDATE name_of_tableSET column1=value1,column2=value2,...WHERE conditions...;
DELETE:The Delete command is used to delete or remove some rows from a table. It is the ‘D’ component of CRUD.
- DELETE FROM name_of_tableWHERE condition1, condition2, ...;
Important SQL Keywords
ADDWill add a new column to an existing table.
- ALTER TABLE student ADD email_address VARCHAR(255);
ALTER TABLEAdds edits or deletes columns in a table
- ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN email_address;
ALTER COLUMNCan change the datatype of a table's column
- ALTER TABLE student ALTER COLUMN phone VARCHAR(15);
ASRenames a table/column with an alias existing only for the query duration
- SELECT name as student_name,phone FROM student;
ASCUsed in conjunction with order by to sort data in ascending order.
- SELECT column1,column2,...FROM table_name ORDER BY column1,column2,...ASC;
DESCUsed in conjunction with order by to sort data in descending order
- SELECT column1,column2,...FROM table_name ORDER BY column1,column2,...DESC;
CHECKConstraints the value which can be added to a column.
- CREATE TABLE student(fullName varchar(255),age INT,CHECK(age >= 18));
CREATE DATABASECreates a new database
- CREATE DATABASE student;
DEFAULTSets the default value for a given column
- CREATE TABLE products(ID int,name varchar(255) DEFAULT 'Username', from date DEFAULT GETDATE());
DELETEDelete values from a table
- DELETE FROM users WHERE user_id=674;
DROP COLUMNDeletes/Drops a column from a table
- ALTER TABLE student DROP COLUMN name;
DROP DATABASECompletely deletes a database with all its content within
- DROP DATABASE student;
DROP DEFAULTRemoves a default value for a column.
- ALTER TABLE student ALTER COLUMN age DROP DEFAULT;
DROP TABLEDeletes a table from a database
- DROP TABLE students;
FROMDetermines which table to read or delete data from
- SELECT * FROM student;
INUsed with WHERE clause for multiple OR conditionals.
- SELECT * FROM students WHERE name IN ('Scaler','Interview','Academy');
ORDER BYUsed to sort given data in Ascending or Descending order.
- SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY age ASC;
SELECT DISTINCTWorks in the same war as SELECT ,except that only unique values are included in the results.
- SELECT DISTINCT age from student;
TOPUsed in conjunction with SELECT to select a fixed number of records
- SELECT TOP 5 * FROM student;
VALUESUsed along with the INSERT INTO keyword to add new values to a table.
- INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerName, City, Country) VALUES (‘Cardinal’, ‘Stavanger’, ‘Norway’);
WHERE Filters given data based on some given condition.
- SELECT * FROM students WHERE age >= 18;
UNIQUEEnsures that all values in a column are different.
- UNIQUE (ID)
UNIONUsed to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements.
- SELECT column_name(s) FROM Table1 UNION SELECT column_name(s) FROM Table2;
UNION ALLCombines the result set of two or more SELECT statements(if allows duplicate values)
- SELECT City FROM table1 UNION ALL SELECT City FROM table2 ORDER BY City;
SELECT TOPUsed to specify the number of records to return.
- SELECT TOP 3 * FROM Students;
LIMITPuts a restriction on how many rows are returned from a query.
- SELECT * FROM table1 LIMIT 3;
UPDATEModifies the existing records in a table
- UPDATE Customers SET ContactName = 'Scaler',City='India' WHERE CustomerID = 1;
SETUsed with UPDATE to specify which columns and values should be updated in a table.
- UPDATE Customers SET ContactName = 'Scaler',City='India' WHERE CustomerID =1;
IS NULLColumn values are tested for NULL values using this operator.
- SELECT CustomerName,ContactName,Address FROM Customers WHERE Address IS NULL;
LIKE Used to search for a specified pattern in a column.
- SELECT * FROM Students WHERE Name LIKE 'a%';
ROWNUMReturns a number indicating the order in which Oracle select row from a table or set of join rows.
- SELECT * FROM Employees where ROWNUM < 10;
GROUP BYGroups rows that have the same values into summary rows.
- SELECT COUNT(StudentID),State FROM Students GROUP BY State;
HAVINGEnables the user to specify conditions that filterwhich group results appear in the results.
- HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5;
Clauses in SQL
WHEREUsed to select data from the database based on some conditions.
- SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE age >= 18;
ANDUsed to combine 2 or more conditions and returns true if all the conditions are True.
- SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE age >= 18 AND salary >= 45000;
ORSimilar to AND but returns true if any of the conditions are True.
- SELECT * from Employee where salary >= 45000 OR age >= 18;
LIKEUsed to search for a specified pattern in a column
- SELECT * FROM Students WHERE Name Like 'a%';
LIMITPuts a restriction on how many rows are returned from a query.
- SELECT * FROM table1 LIMIT 3;
ORDER BYUsed to sort given data in Ascending or Descending from a query.
- SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY age ASC;
GROUP BYGroups rows that have the same values into summary rows.
- SELECT COUNT(StudentID),State FROM Students GROUP BY State;
HAVINGIt performs the same as the WHERE clause but can also be used with aggregate functions
- SELECT COUNT(ID),AGE FROM Students GROUP BY AGE HAVING COUNT(ID) > 5;
Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns any records which have matching values in both tables.
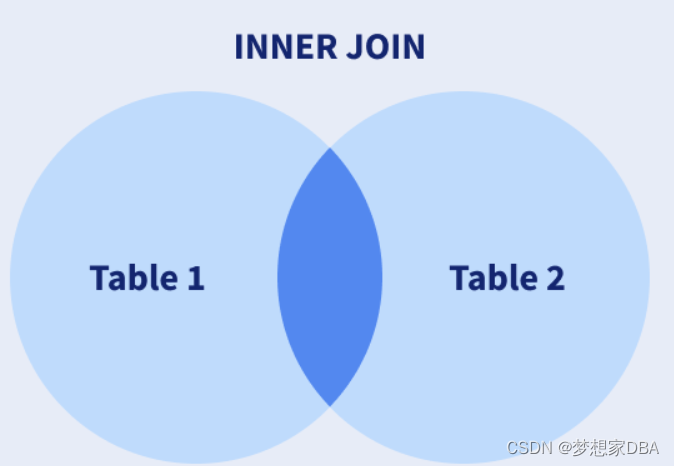
- SELECT orders.order_id, products.product_name,customers.customer_name,products.priceFROM ordersINNER JOIN products ON products.product_id = order.product_idINNER JOIN customers on customers.customer_id = order.customer_id;
NATURAL JOIN: It is a special type of inner join based on the fact that the column names and datatypes are the same on both tables.
- Select * from table1 Natural JOIN table2;
RIGHT JOIN: Returns all of the records from the second table, along with any matching records from the first.
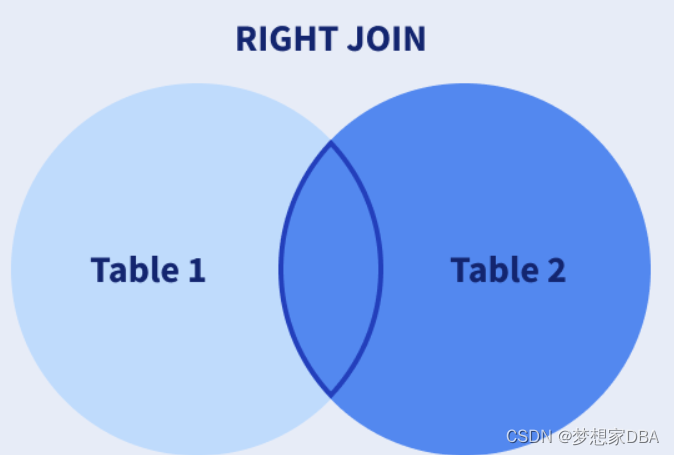
- SELECT Orders.OrderID, Employees.LastName, Employees.FirstNameFROM OrdersRIGHT JOIN EmployeesON Orders.EmployeeID = Employees.EmployeeIDORDER BY Orders.OrderID;
LEFT JOIN: Returns all of the records from the first table, along with any matching records from the second table.
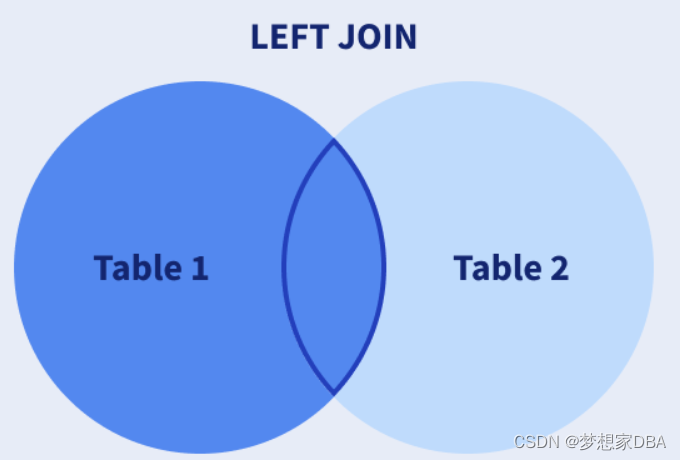
- SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderIDFROM CustomersLEFT JOIN OrdersON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerIDORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
FULL JOIN: Returns all records from both tables when there is a match.
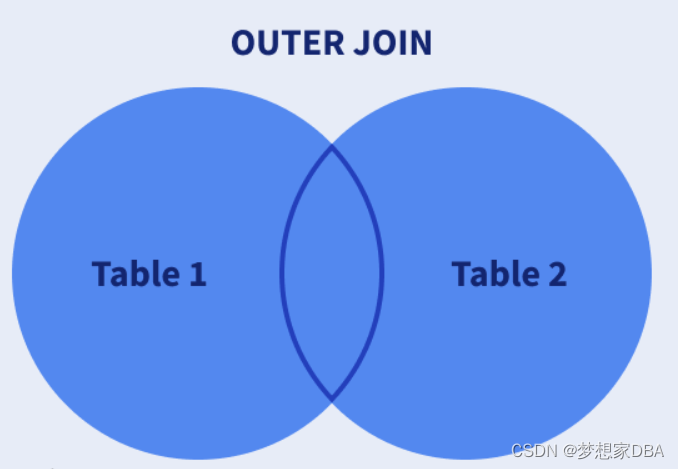
- SELECT ID, NAME, AMOUNT, DATE FROM CUSTOMERS FULL JOIN ORDERS ON CUSTOMERS.ID = ORDERS.CUSTOMER_ID;
Triggers in SQL
SQL codes automatically executed in response to a certain event occurring in a table of a database are called triggers. There cannot be more than 1 trigger with a similar action time and event for one table.
Create Trigger Trigger_Name(Before | After) [ Insert | Update | Delete]on [Table_Name][ for each row | for each column ][ trigger_body ]
- CREATE TRIGGER trigger1before INSERTON StudentFOR EACH ROWSET new.total = (new.marks/ 10) * 100;
DROP: This operation will drop an already existing trigger from the table
- DROP TRIGGER trigger name;
SHOW: This will display all the triggers that are currently present in the table.
- SHOW TRIGGERS IN database_name;
SQL Stored Procedures
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name AS sql_statementGO;
- CREATE PROCEDURE SelectAllCustomers AS SELECT * FROM Customers;GO;
EXEC procedure_name;
SQL Injection
Insertion or ‘Injection’ of some SQL Query from the input data of the client to the application is called SQL Injection. They can perform CRUD operations on the database and can read to vulnerabilities and loss of data.
Data is used to dynamically construct an SQL Query.Unintended data from an untrusted source enters the application.
Here the hacker is injecting SQL code - :UNION SELECT studentName, rollNo FROM students
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
docker+网桥+redis主从+哨兵模式
Polygon zkEVM网络节点

2022 Hangzhou Electric Power Multi-School League Game 5 Solution
Deep Learning (3) Classification Theory Part
The general SQL injection flow (sample attached)

Hey, I had another fight with HR in the small group!
pnpm 是凭什么对 npm 和 yarn 降维打击的
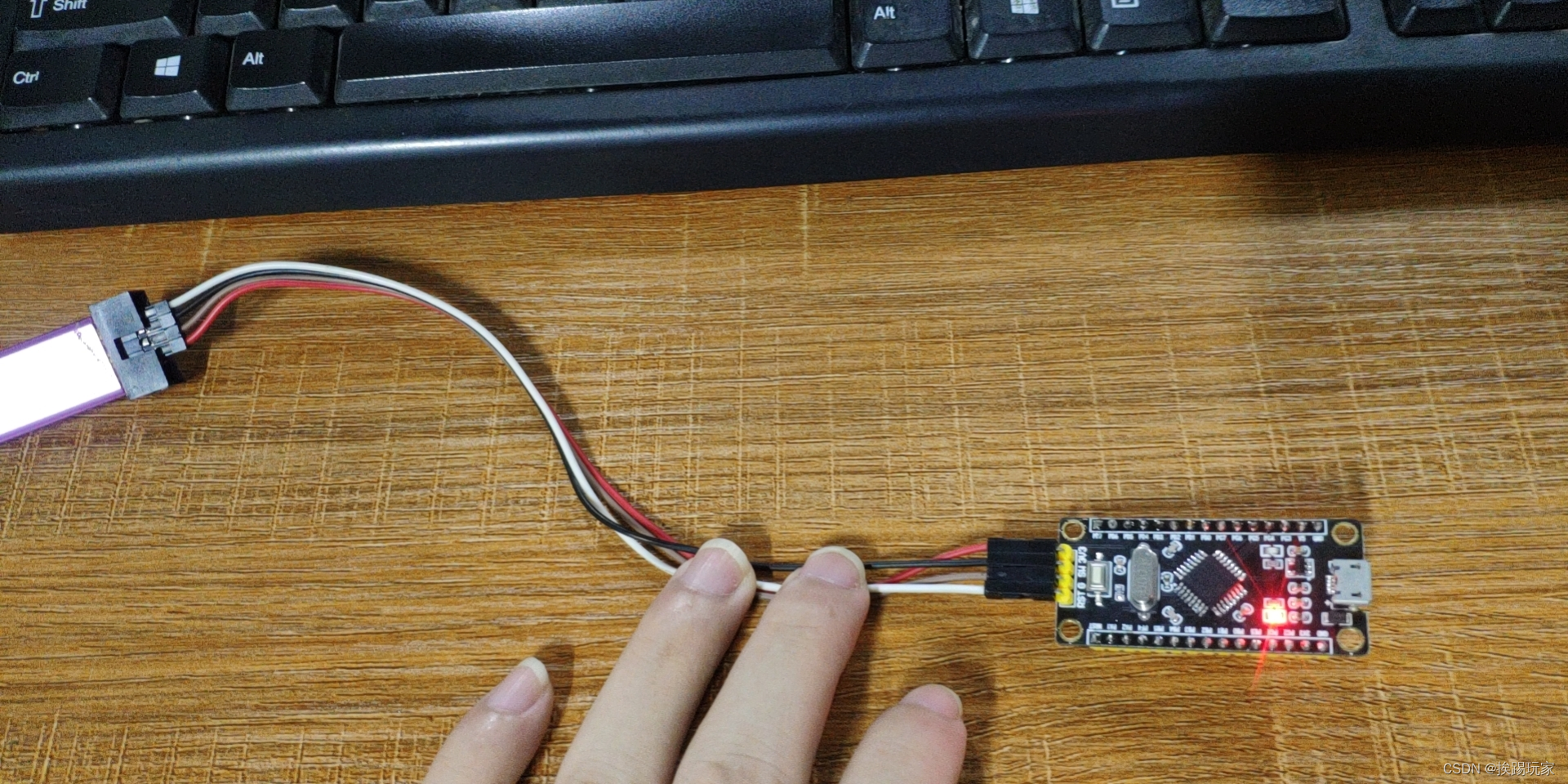

STM8S105k4t6c---------------Light up LED
A Preliminary Study of RSS Subscription to WeChat Official Account-feed43

Why use Selenium for automated testing
随机推荐
DIY电工维修如何拆卸和安装开关面板插座
STM8S project creation (STVD creation) --- use COSMIC to create a C language project
Postgresql源码(66)insert on conflict语法介绍与内核执行流程解析
复制带随机指针的链表
typescript type 和 interface 的区别
4-way two-way HDMI integrated business high-definition video optical transceiver 8-way HDMI high-definition video optical transceiver
MySQL query optimization and tuning
Metaverse "Drummer" Unity: Crazy expansion, suspense still exists
The keytool command
【观察】超聚变:首提“算网九阶”评估模型,共建开放繁荣的算力网络
外卖店优先级
使用serve搭建本地服务器
自定义通用分页标签02
MySQL Query Exercise (1)
Enterprise live broadcast is on the rise: Witnessing focused products, micro-like embracing ecology
FPGA parsing B code----serial 3
[Study Notes Dish Dog Learning C] Dynamic Memory Management
How to read the resources files in the directory path?
机器学习之视频学习【更新】
pnpm 是凭什么对 npm 和 yarn 降维打击的
