当前位置:网站首页>二叉搜索树的实现
二叉搜索树的实现
2022-08-02 20:27:00 【'派派'】
目录
1.二叉搜索树概念
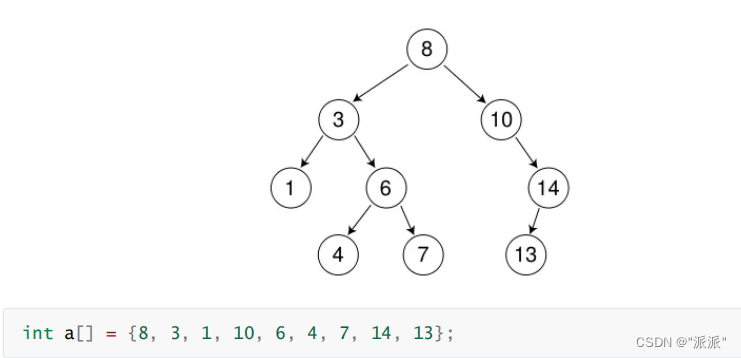
2.二叉树插入的实现
如何插入?
如果树为空,直接插入。
如果树不为空,则将要插入的值与二叉树中各结点的值比较,最后再插入例如: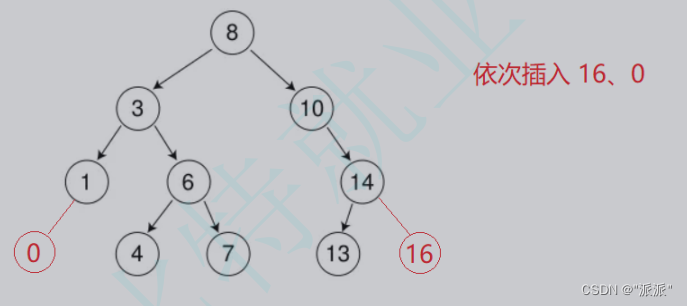
代码实现:
先创建一个结构体存储每个结点的信息:
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
bool _InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (key > root->_key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (key < root->_key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else//不允许存在相同的值
return false;
}
}root是父亲结点的左右指针的引用,修改root也就是修改父亲结点的左右指针,3. 二叉搜索树的查找
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}4.二叉树的删除
二叉树的删除可分为两种情况。
1.要删除的结点只有一个孩子或无孩子。
2.要删除的结点有两个孩子。例如:
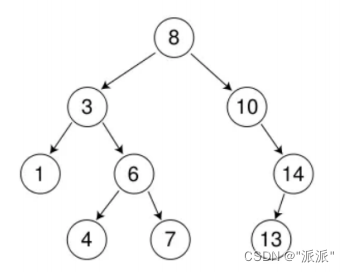
第一种情况:
1.删除4;
2.删除10;
第二种情况:
1.删除3;在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小,也就是最左结点),用它的值填补到被删除
节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题--替换法删除 bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)//root是父亲结点左右指针的引用
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else//先找到要删除的结点
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;//找到被删删除结点的右孩子,minRight
while (minRight->_left)//以minRight为根,找到最左的孩子。
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);//将被删出的结点与最左孩子值替换。
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);//此时被删除的结点在之前最左孩子的位置,它
无左孩子,转换成了第一种情况对其删除。
}
delete del;
return true;
}
} 画图分析: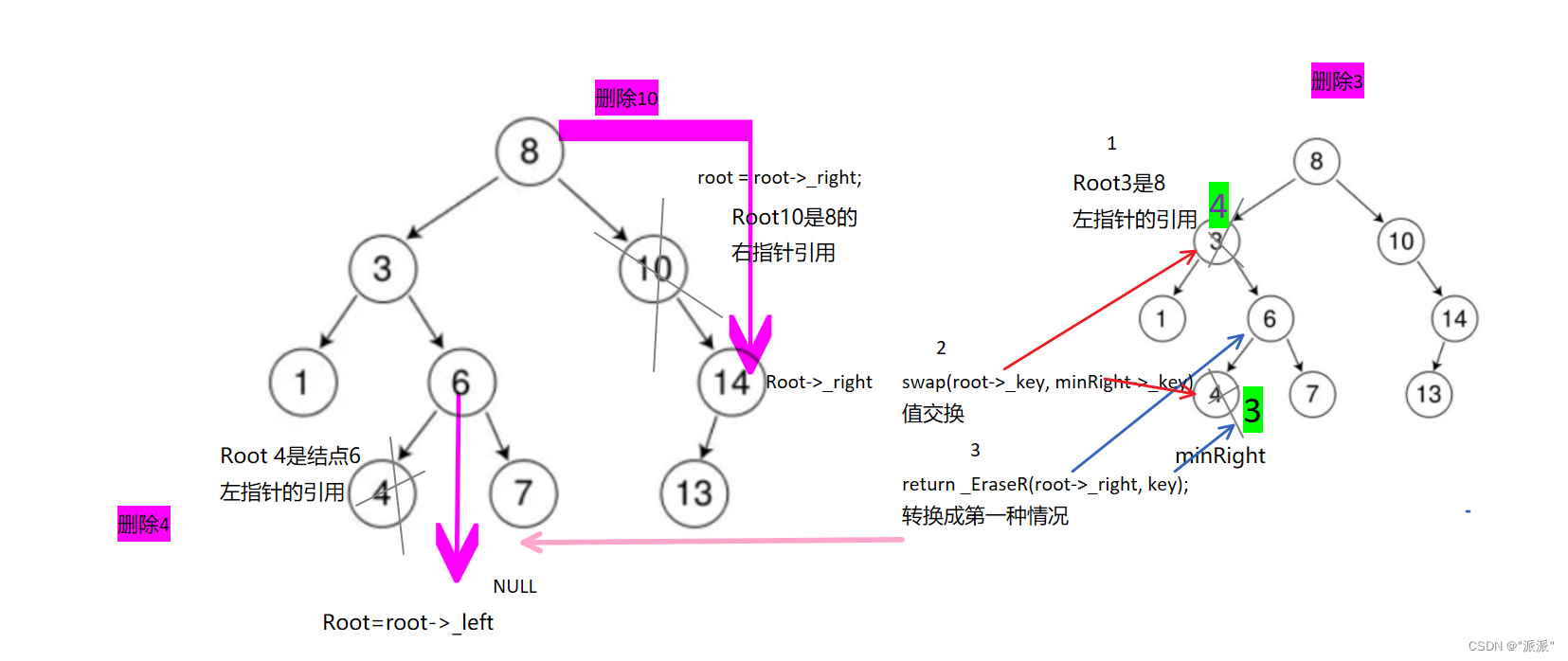
完整代码:
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
private:
void DestoryTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
DestoryTree(root->_left);
DestoryTree(root->_right);
delete root;
}
Node* CopyTree(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copyNode = new Node(root->_key);
copyNode->_left = CopyTree(root->_left);
copyNode->_right = CopyTree(root->_right);
return copyNode;
}
public:
// 强制编译器自己生成构造,C++11支持
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)//写了拷贝构造,不会默认生成构造函数
{
_root = CopyTree(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
DestoryTree(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
bool _FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool _InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool _EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
}
private:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else
{
Node* minRight = root->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
swap(root->_key, minRight->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (key > root->_key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (key < root->_key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
return false;
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};5.二叉搜索树的应用
5.1 K模型
5.2 KV模型
template<class K, class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
const K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};template<class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)//返回结点的指针,可对结点内容进行修改
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
private:
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);
else
return false;
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return root;
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};例如:
void test2()
{
string arr[] = { "香蕉","苹果","梨","桃子","梨","香蕉","黄瓜" };
BSTree<string, int> p;
for (auto ch : arr)
{
auto ret = p.FindR(ch);
if (ret==nullptr)
{
p.InsertR(ch, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
p.InOrder();
}
int main()
{
test2();
return 0;
}结果:
黄瓜:1
梨:2
苹果:1
桃子:1
香蕉:2边栏推荐
- Likou Question of the Day - Day 46 - 344. Reverse Strings
- 「 每日一练,快乐水题 」1374. 生成每种字符都是奇数个的字符串
- 特拉维夫大学 | Efficient Long-Text Understanding with Short-Text Models(使用短文本模型进行高效的长文本理解)
- C# Barrier class
- 「每周译Go」这次我们来点不一样的!--《How to Code in Go》系列上线
- How to use windbg check c # a thread stack size?
- X 2 Earn必须依靠旁氏启动?GameFi的出路在哪?(下)
- ALV concept explanation
- Qt提升自定义控件,找不到头文件
- Xcode13.1运行工程报错fatal error: ‘IFlyMSC/IFly.h‘ file not found的问题
猜你喜欢
人尽皆知的云原生,到底是大势所趋还是过度炒作?
特拉维夫大学 | Efficient Long-Text Understanding with Short-Text Models(使用短文本模型进行高效的长文本理解)

实现fashion_minst服装图像分类

基于 outline 实现头像剪裁以及预览

callback prototype __proto__

Axure9的元件用法

iframe------------frame-
9,共模抑制比一-不受输入信号中共模波动的影响。【如何分析共模CM抑制比。】
浅议.NET遗留应用改造
vscode如何能将输出从OUTPUT改为TERMINAL或者DebugConsole
随机推荐
HCIP--BGP基础实验
iframe------------frame-
Bena的生命周期
How the sensor works
【手撕AHB-APB Bridge】~ AMBA总线 之 APB
奥特学园ROS笔记--7(289-325节)
PLC工作原理动画
模板的进阶
信息学奥赛一本通(1256:献给阿尔吉侬的花束)
The time series database has been developed for 5 years. What problem does it need to solve?
Async的线程池使用的哪个?
信息学奥赛一本通(1257:Knight Moves)
华为设备配置BFD多跳检测
.NET性能优化-你应该为集合类型设置初始大小
TodoList案例
【目标检测】YOLOv5:640与1280分辨率效果对比
J9 Digital Currency Theory: Identifying Web3's New Scarcity: Open Source Developers
setup语法糖 defineProps defineEmits defineExpose
【SLAM】DM-VIO(ros版)安装和论文解读
EasyExcel dynamic parsing and save table columns