当前位置:网站首页>[200 opencv routines] 101 adaptive median filter
[200 opencv routines] 101 adaptive median filter
2022-06-29 00:02:00 【Xiaobai youcans】
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】101. Adaptive median filter
Welcome to your attention 『OpenCV routine 200 piece 100 piece 』 series , Ongoing update
Welcome to your attention 『Python Small white OpenCV Learning lessons 』 series , Ongoing update
3.8 Adaptive median filter (Adaptive median filter)
The window size of median filter is fixed , We can't take into account both denoising and protecting the details of the image at the same time , The performance is better when the noise density is small , When the noise probability is high, the performance will deteriorate .
Adaptive median filter according to preset conditions , In the process of filtering, the window size of the filter is changed dynamically ; Further , Judge whether the current pixel is noisy according to the conditions , This determines whether to replace the current pixel with the neighborhood median .
Adaptive median filter can deal with impulse noise with high probability , Smooth non impulsive noise , Protect image details as much as possible , Avoid thinning or coarsening of image edges .
Make S x y Sxy Sxy Indicates that the center is at the point ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y) 、 The size is m ∗ n m*n m∗n Rectangular sub window ( Neighborhood ), The filter is controlled by S x y Sxy Sxy Defined neighborhood operations .
Z m i n 、 Z m a x 、 Z m e d Zmin、Zmax、Zmed Zmin、Zmax、Zmed Express S x y Sxy Sxy Minimum gray value in 、 The maximum gray value and the median value of the gray value , Z x y Zxy Zxy Yes. ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y) Gray value , S m a x Smax Smax Is the maximum window size allowed .
Adaptive median filter is divided into two processes :
Step A:
- A1 = Zmed - Zmin
- A2 = Zmed - Zmax
- If A1>0 And A2<0, The jump to Step B; otherwise , Increase the window size
- If the increased size ≤ Smax, Then repeat A; otherwise , Output Zmed
Step B:
- B1 = Zxy - Zmin
- B2 = Zxy - Zmax
- If B1>0 And B2<0, The output Zxy; otherwise , Output Zmed
StepA The purpose of is to determine the median value obtained in the current window Zmed Is it noise . If Zmin<Zmed<Zmax, Then the median Zmed It's not noise , go to StepB. If Zmin<Zxy<Zmax, be Zxy It's not noise , Filter output Zxy. If the above conditions are not met , Then judge Zxy It's noise , Output median Zmed.
If in StepA in ,Zmed Not meeting the conditions Zmin<Zmed<Zmax, Then we can judge the median value Zmed It's noise . At this time, increase the window size of the filter , Find the median value of a non noise point in a larger range .
therefore , If the probability of noise in the image is low , The adaptive median filter can use a smaller window size , In order to improve the calculation speed ; conversely , If the probability of noise is high , We need to increase the window size of the filter , To improve the filtering effect .
routine 9.15: Adaptive median filter
# # 9.15: Adaptive median filter (Adaptive median filter)
img = cv2.imread("../images/Fig0514a.tif", 0) # flags=0 Read as grayscale image
hImg = img.shape[0]
wImg = img.shape[1]
smax = 7 # Maximum window size allowed
m, n = smax, smax
imgAriMean = cv2.boxFilter(img, -1, (m, n)) # Arithmetic average filtering
# Edge fill
hPad = int((m-1) / 2)
wPad = int((n-1) / 2)
imgPad = np.pad(img.copy(), ((hPad, m-hPad-1), (wPad, n-wPad-1)), mode="edge")
imgMedianFilter = np.zeros(img.shape) # Median filter
imgAdaMedFilter = np.zeros(img.shape) # Adaptive median filter
for i in range(hPad, hPad+hImg):
for j in range(wPad, wPad+wImg):
# 1. Median filter (Median filter)
ksize = 3
k = int(ksize/2)
pad = imgPad[i-k:i+k+1, j-k:j+k+1] # Neighborhood Sxy, m*n
imgMedianFilter[i-hPad, j-wPad] = np.median(pad)
# 2. Adaptive median filter (Adaptive median filter)
ksize = 3
k = int(ksize/2)
pad = imgPad[i-k:i+k+1, j-k:j+k+1]
zxy = img[i-hPad][j-wPad]
zmin = np.min(pad)
zmed = np.median(pad)
zmax = np.max(pad)
if zmin < zmed < zmax:
if zmin < zxy < zmax:
imgAdaMedFilter[i-hPad, j-wPad] = zxy
else:
imgAdaMedFilter[i-hPad, j-wPad] = zmed
else:
while True:
ksize = ksize + 2
if zmin < zmed < zmax or ksize > smax:
break
k = int(ksize / 2)
pad = imgPad[i-k:i+k+1, j-k:j+k+1]
zmed = np.median(pad)
zmin = np.min(pad)
zmax = np.max(pad)
if zmin < zmed < zmax or ksize > smax:
if zmin < zxy < zmax:
imgAdaMedFilter[i-hPad, j-wPad] = zxy
else:
imgAdaMedFilter[i-hPad, j-wPad] = zmed
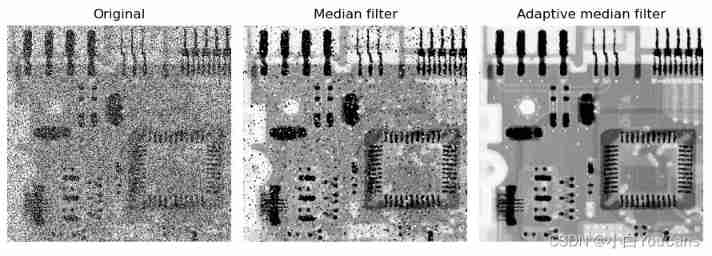
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.subplot(131), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Original")
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(132), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Median filter")
plt.imshow(imgMedianFilter, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.subplot(133), plt.axis('off'), plt.title("Adaptive median filter")
plt.imshow(imgAdaMedFilter, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=255)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
( At the end of this section )
Copyright notice :
[email protected] Original works , Reprint must be marked with the original link
reference :《Python digital image processing (DIP) - Image restoration and reconstruction 11 》
Copyright 2021 youcans, XUPT
Crated:2022-2-1
Welcome to your attention 『OpenCV routine 200 piece 100 piece 』 series , Ongoing update
Welcome to your attention 『Python Small white OpenCV Learning lessons 』 series , Ongoing update【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】01. Image reading (cv2.imread)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】02. Image saving (cv2.imwrite)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】03. Image display (cv2.imshow)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】04. use matplotlib Display images (plt.imshow)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】05. The properties of the image (np.shape)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】06. Pixel editing (img.itemset)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】07. Image creation (np.zeros)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】08. Copy of image (np.copy)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】09. Image clipping (cv2.selectROI)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】10. Image stitching (np.hstack)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】11. Split of image channel (cv2.split)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】12. Merging of image channels (cv2.merge)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】13. The addition of images (cv2.add)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】14. The image is added to the scalar (cv2.add)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】15. Weighted addition of images (cv2.addWeight)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】16. Addition of images of different sizes
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】17. Gradient switching between two images
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】18. Mask addition of images
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】19. The circular mask of the image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】20. Bitwise operation of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】21. Image overlay
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】22. Add non Chinese text to the image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】23. Add Chinese text to the image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】23. Add Chinese text to the image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】24. Affine transformation of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】25. Translation of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】26. The rotation of the image ( Centered on the origin )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】27. The rotation of the image ( Centered on any point )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】28. The rotation of the image ( Right angle rotation )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】29. Image flipping (cv2.flip)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】30. Image zooming (cv2.resize)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】31. Image pyramid (cv2.pyrDown)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】32. Image distortion ( Crosscutting )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】33. Composite transformation of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】34. Projection transformation of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】35. Projection transformation of image ( Border filling )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】36. Conversion of rectangular coordinates and polar coordinates
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】37. Gray processing and binary processing of image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】38. Inverse color transformation of image ( Image reversal )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】39. Linear transformation of image gray
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】40. Image piecewise linear gray scale transformation
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】41. Gray scale transformation of image ( Grayscale stratification )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】42. Gray scale transformation of image ( Bit plane layering )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】43. Gray scale transformation of image ( Logarithmic transformation )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】44. Gray scale transformation of image ( Gamma transform )
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】45. Gray histogram of the image
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】46. Histogram equalization
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】47. Image enhancement — Histogram matching
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】48. Image enhancement — Color histogram matching
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】49. Image enhancement — Local histogram processing
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】50. Image enhancement — Histogram statistics image enhancement
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】51. Image enhancement — Histogram back tracking
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】52. Image correlation and convolution
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】53. Scipy Realize image two-dimensional convolution
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】54. OpenCV Realize image two-dimensional convolution
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】55. Separable convolution kernel
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】56. Low pass cartridge filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】57. Low pass Gaussian filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】58. Nonlinear filtering — median filtering
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】59. Nonlinear filtering — Bilateral filtering
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】60. Nonlinear filtering — Joint bilateral filtering
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】61. Guided filtering (Guided filter)
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】62. Sharpen the image —— Passivation masking
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】63. Sharpen the image ——Laplacian operator
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】64. Sharpen the image ——Sobel operator
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】65. Sharpen the image ——Scharr operator
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】66. Low pass of image filtering / qualcomm / Band stop / Bandpass
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】67. Comprehensive application of image enhancement in spatial domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】68. Comprehensive application of image enhancement in spatial domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】69. Discontinuous Fourier coefficients
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】70. Fourier transform of one-dimensional continuous function
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】71. Sampling of continuous functions
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】72. One dimensional discrete Fourier transform
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】73. Two dimensional continuous Fourier transform
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】74. Anti aliasing of images
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】75. Numpy Realize image Fourier transform
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】76. OpenCV Realize image Fourier transform
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】77. OpenCV Realize fast Fourier transform
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】78. Fundamentals of image filtering in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】79. The basic steps of image filtering in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】80. Detailed steps of image filtering in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】81. Gaussian low pass filter in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】82. Butterworth low pass filter in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】83. Low pass filtering in frequency domain : Printed text character repair
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】84. The high pass filter is obtained from the low pass filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】85. Application of high pass filter in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】86. Frequency domain filtering applications : Fingerprint image processing
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】87. Frequency domain passivation masking
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】88. Laplace high pass filter in frequency domain
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】89. Transfer function of band stop filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】90. Frequency domain notch filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】91. Gaussian noise 、 rayleigh noise 、 Irish noise
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】92. Exponential noise 、 Uniform noise 、 Salt and pepper noise
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】93. Histogram of noise model
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】94. Arithmetic average filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】95. Geometric mean filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】96. Harmonic averaging filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】97. Anti harmonic averaging filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】98. Statistical sorting filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】99. Modified alpha mean filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】100. Adaptive local noise reduction filter
【OpenCV routine 200 piece 】101. Adaptive median filter
边栏推荐
- Stm32f407 ------ running lamp and buzzer
- 三个pwn题
- 一条update语句到底加了多少锁?带你深入理解底层原理
- Test experience: how testers evolve from 0 to 1
- 随笔记:重新认识 else if
- The second session of question swiping and clock out activity -- solving the switching problem with recursion as the background (2)
- TypeScript --第三节:接口
- Typescript -- Section 5: classes
- Typescript -- Section 1: basic types
- stm32F407-------通用定时器
猜你喜欢

随笔记:插入排序 --from wcc

oracle 去掉html标签
Summary of software testing cognition

Haskell 配置 VS code 开发环境 (2022年6月)
Technology sharing | software development process that you must understand if you want to get started with testing

每日一题:移除元素

ctfshow XSS

stm32F407-------时钟系统(SystemInit时钟初始化、Systick滴答定时器)

Typescript -- Section 2: variable declaration

Implementation of dynamic timer for quartz
随机推荐
Edge extraction based on Halcon learning [2] circles Hdev routine
Blue Bridge Cup top ten common heaven level skill - breath of water The type of one recursion
stm32F407-------LCD
【C Primer Plus第二章课后编程题】
Be on the list again! Know that Chuangyu was selected as one of the top 50 competitive enterprises in China's network security industry in 2022
How many locks are added to an update statement? Take you to understand the underlying principles
MySQL connection query is easy to understand
11.目标分割
Reading notes of English grammar new thinking Basic Edition 2 (I)
PHP函数file_get_contents与操作系统的内存映射
10. Yolo series
This thing is called a jump watch?
[SSM] an error is reported that the user name of the access denied for user 'WYF' @ 'localhost' (using password: yes) data becomes the user name of the computer
mysql 高可用双主同步
Stm32f407-------- NVIC interrupt priority management
一条update语句到底加了多少锁?带你深入理解底层原理
Is it reliable and safe to avoid five in case of stock trading account opening
Typescript -- Section 5: classes
Mobile heterogeneous computing technology - GPU OpenCL programming (basic)
Implementation of dynamic timer for quartz