当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode - 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树;023.合并K个升序链表
LeetCode - 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树;023.合并K个升序链表
2022-08-02 19:21:00 【NPE~】
LeetCode【105、023】
一、 LeetCode - 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
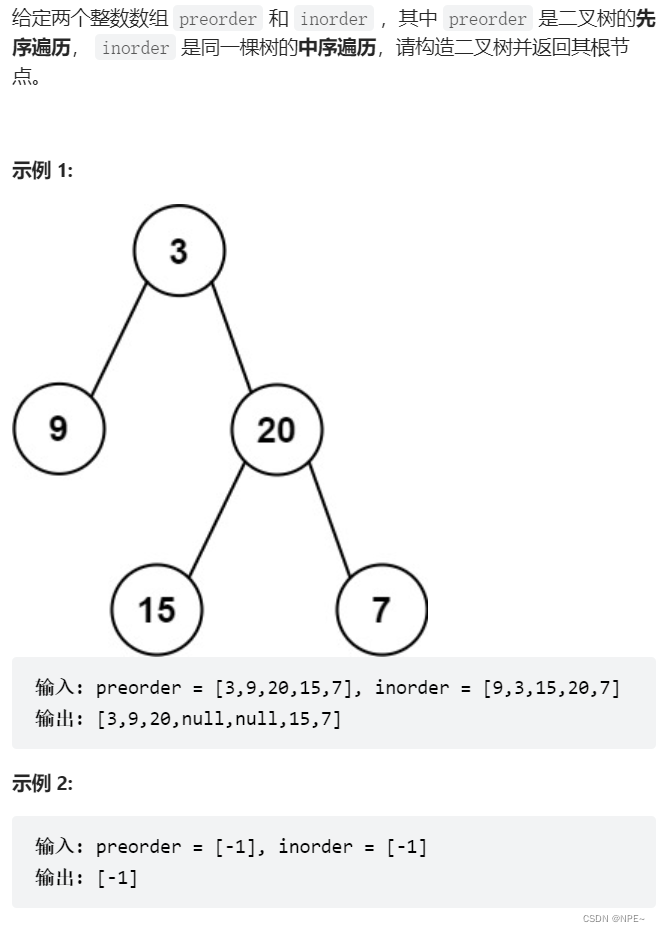
该题目让我们根据先序和中序构造出一棵二叉树,首先:
先序:根左右
中序:左右根
因此,我们可以根据先序,明确知道该树的root节点是哪个,然后根据中序的顺序,找到根节点所在位置,根节点左边的就是左子树所有元素,根节点右边的就是右子树所有的元素
1 确定先序数组及中序数组中左子树的范围
首先,找到root位置【先序数组中的第一个元素就是root,找到root元素后遍历中序数组,找到在中序数组中root的位置】
pre:先序数组
L1:先序数组的左边界
pre[L1]:root节点
L2:中序数组的左边界
find:用于标记中序数组中root节点的位置
//头节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
int find = L2;
while(in[find] != pre[L1]){
find++;
}
2 构造fun函数,用于创建node
首先判断两个数组中是否有一个为null,同时判断两个数组长度是否一致
public TreeNode fun(int[] pre, int L1, int R1, int[] in, int L2, int R2){
if(L1 > R1){
//一边子树全部为null
return null;
}
//头节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
int find = L2;
while(in[find] != pre[L1]){
find++;
}
head.left = fun(pre, L1 + 1, L1 + find - L2, in, L2, find - 1);
head.right = fun(pre, L1 + find - L2 + 1, R1, in, find + 1, R2);
return head;
}
3 全部代码
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null || preorder.length != inorder.length){
return null;
}
return fun(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode fun(int[] pre, int L1, int R1, int[] in, int L2, int R2){
if(L1 > R1){
//一边子树全部为null
return null;
}
//头节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
int find = L2;
while(in[find] != pre[L1]){
find++;
}
head.left = fun(pre, L1 + 1, L1 + find - L2, in, L2, find - 1);
head.right = fun(pre, L1 + find - L2 + 1, R1, in, find + 1, R2);
return head;
}
}
4 优化【使用hash表】
使用空间换时间的方式,将中序表in的每个值与下标对应起来,这样就可以不用每次用while循环去找中序表in里的root位置了
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; ++i){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
根据hash表,直接获取
int find = map.get(pre[L1]);
优化后代码:
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(preorder == null || inorder == null || preorder.length != inorder.length){
return null;
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < inorder.length; ++i){
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return fun(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, map);
}
public TreeNode fun(int[] pre, int L1, int R1, int[] in, int L2, int R2, HashMap<Integer, Integer> map){
if(L1 > R1){
//一边子树全部为null
return null;
}
//头节点
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(pre[L1]);
int find = map.get(pre[L1]);
// int find = L2;
// while(in[find] != pre[L1]){
// find++;
// }
head.left = fun(pre, L1 + 1, L1 + find - L2, in, L2, find - 1, map);
head.right = fun(pre, L1 + find - L2 + 1, R1, in, find + 1, R2, map);
return head;
}
}

二、 LeetCode - 023.合并K个升序链表
题目提供的ListNode结构:
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */

1 分析
该题我们的思路可以通过小根堆来实现【因为题目要求的是升序】,数组中的每一个元素都是一个链表的head,我们只需要将链表数组中的每个head入堆,然后根据小根堆特性(自动排序,最小的在堆顶),每次弹出堆顶元素,假设为head1,再将head1的next入堆,再让根堆自动排序即可
前置知识:
PriorityQueue优先级队列(底层其实就是小根堆)
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
heap.add(4);
heap.add(9);
heap.add(1);
heap.add(5);
System.out.println(heap.poll());//弹出堆顶元素 1
heap.add(8);
System.out.println(heap.poll());// 弹出堆顶元素 4
}
}
2 代码实现
2.1 MyComparator
因为基本数据类型,java已经默认规定好了排序,但是此题的ListNode并没有规定如何排序,因此需要我们自定义比较器来规定如何排序【该题规定小的在前,因此我们只需要将node的val值相减即可】
public class MyComparator implements Comparator<ListNode>{
//自定义比较器
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2){
return o1.val - o2.val;
}
}
2.2 将每个链表头head入堆
if(lists == null) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new MyComparator());
for(int i = 0; i < lists.length; ++i){
if(lists[i] != null){
//将每个链表的头入堆
heap.add(lists[i]);
}
}
2.3 查看堆是否为空,如果不为空,入堆进堆即可
如果heap为空,直接返回null;
如果不为null,我们用head接收第一个堆顶,然后用临时节点pre指向head;
只要pre.next != null表明该链表还没有结束,直接入堆
只要heap不为空,我们就一直弹出堆顶元素【用cur接收,让pre.next = cur连接上将要返回的链表; pre = cur 将要返回的链表后移;】
只要当前cur.next != null ,入堆
if(heap.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
ListNode head = heap.poll();//弹出顶点
ListNode pre = head;//临时节点
//因为前面已经弹出了一个,所以需要判断是否还有新节点要入堆
if(pre.next != null){
heap.add(pre.next);
}
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
ListNode cur = heap.poll();
pre.next = cur;
pre = cur;
if(cur.next != null){
heap.add(cur.next);
}
}
return head;
3 全部代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */
//使用优先级队列实现[小根堆]
class Solution {
public class MyComparator implements Comparator<ListNode>{
//自定义比较器
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2){
return o1.val - o2.val;
}
}
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists == null) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(new MyComparator());
for(int i = 0; i < lists.length; ++i){
if(lists[i] != null){
//将每个链表的头入堆
heap.add(lists[i]);
}
}
if(heap.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
ListNode head = heap.poll();//弹出顶点
ListNode pre = head;//临时节点
if(pre.next != null){
heap.add(pre.next);
}
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
ListNode cur = heap.poll();
pre.next = cur;
pre = cur;
if(cur.next != null){
heap.add(cur.next);
}
}
return head;
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
golang刷leetcode 经典(13) 最小高度树
腾讯云孟凡杰:我所经历的云原生降本增效最佳实践案例
技术分享 | Apache Linkis 快速集成网页IDE工具 Scriptis
栈、队列和数组
治疗 | 如何识别和处理消极想法
NC | Structure and function of soil microbiome reveal N2O release from global wetlands
geoserver+mysql+openlayers问题点
斯堪尼亚SCANIA OTL标签介绍
ALV报表学习总结
MySQL安装配置教程(超级详细、保姆级)
Kali命令ifconfig报错command not found
清除浮动与BFC
2022-08-01
7.25 - 每日一题 - 408
golang刷leetcode 动态规划(13) 最长公共子序列
MaxCompute 的SQL 引擎参数化视图具体有哪些增强功能?
Geoserver+mysql+openlayers
TPAMI2022 | TransCL:基于Transformer的压缩学习,更灵活更强大
互联网寒冬,挚友7面阿里,终获Offer
流量分析四—蓝牙