当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode每日一练 —— 225. 用队列实现栈
LeetCode每日一练 —— 225. 用队列实现栈
2022-08-02 10:31:00 【飞向星的客机】
前言
Wassup guys!我是Edison
今天是 LeetCode 上的 leetcode 225. 用队列实现栈
Let’s get it!

1. 题目描述
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(
push、top、pop和empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例:
输入:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
2. 思路解析
首先我们知道,队列是先进先出,栈是后进先出。
那么我们可以使用两个队列,始终保持一个队列为空。
当我们需要进行 压栈 操作时,将数据压入 不为空的队列中(若两个都为空,则随便压入一个队列)。如图所示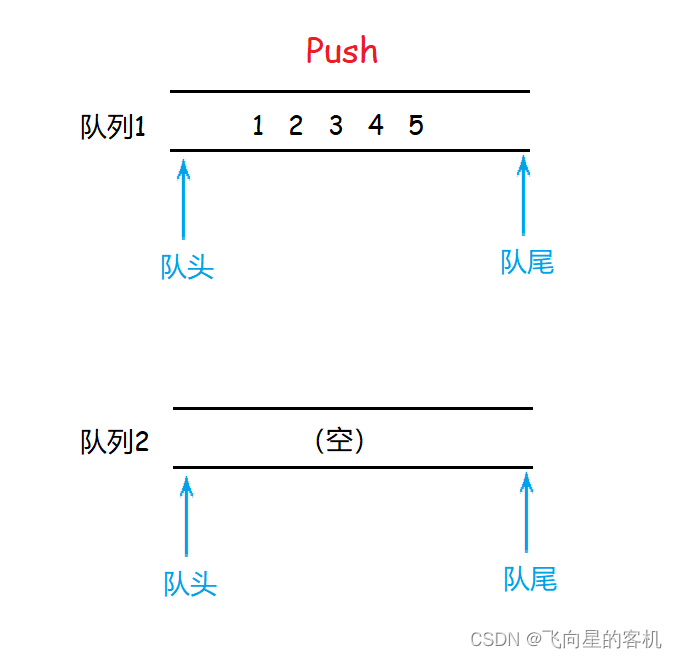
当需要进行 出栈 操作时,将 不为空的队列 中的数据导入 空队列 中,仅留下一个数据,这时将这个数据返回并且删除即可。
判断栈是否为空,即判断两个队列是否同时为空。
流程如图所示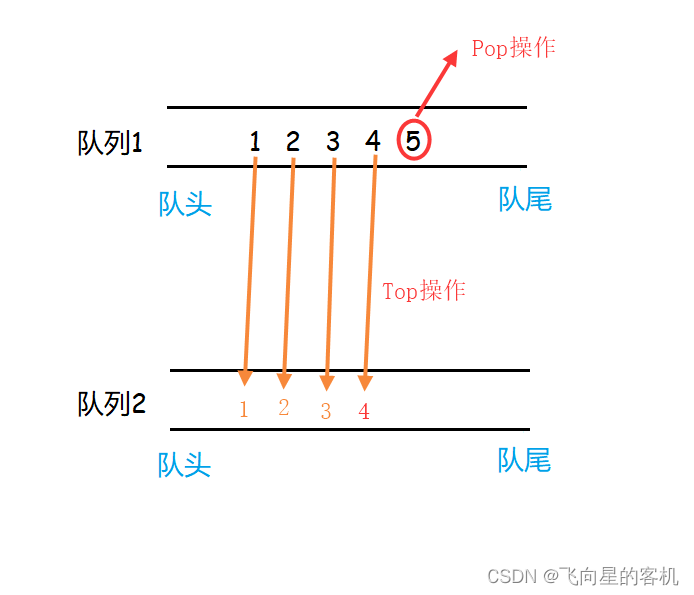
3. 代码实现
队列的实现
typedef int QDataType;
// 链式结构:表示队列(记录每个结点)
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
// 队列的结构 (找到队列的头和尾的)
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head; // 队列的头指针
QNode* tail; // 队列的尾指针
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q) {
assert(q); //队列可以为空,但是管理队列的头指针和尾指针不能为空
q->head = NULL;
q->tail = NULL;
}
// 队尾入队列(尾插)
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType x) {
assert(q);
/*开辟一个新结点*/
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL) {
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x; //把x赋给newnode的数据域
newnode->next = NULL; //因为是尾插,所以尾部的结点的next要指向NULL
/*如果头、尾都为空,那么说明队列还是空的,还没有结点*/
if (q->head == NULL && q->tail == NULL) {
assert(q);
q->head = q->tail = newnode;
}
else {
//说明队列已经有结点了,直接到插入到尾部即可
q->tail->next = newnode; //把newnode链接到tail的next
q->tail = newnode; //然后让tail指向newnode
}
}
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
assert(q->head && q->tail); //队列的head和tail不能为空,不然怎么头删呢?
//如果head的next为空,那么说明只有一个结点
if (q->head->next == NULL) {
free(q->head); //直接释放掉head
q->head = q->tail = NULL; //然后把head和tail 置为空
}
else {
QNode* next = q->head->next; //保存头结点的下一个结点地址
free(q->head); //释放掉head
q->head = next;
}
}
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
assert(q->head); //取队头的数据,那么head肯定不能为空
return q->head->data;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
assert(q->tail); //取队尾的数据,那么tail肯定不能为空
return q->tail->data;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
// 这个函数是队列里面最慢的函数,时间复杂度为O(N)
int QueueSize(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->head; //使用cur遍历整个队列
int count = 0; //统计队列元素个数
while (cur) {
//当cur不为空,就进入循环
count++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return count;
}
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
//如果head或者tail等于空,说队列为空
return q->head == NULL && q->tail == NULL;
}
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q) {
assert(q);
QNode* cur = q->head; //使用cur遍历整个队列
while (cur) {
//如果cur不为空
QNode* next = cur->next; //存储cur的下一个结点
free(cur); //释放掉cur
cur = next; //把cur的下一个结点赋给cur
}
q->head = q->tail = NULL;
}
接口代码
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
}MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
assert(pst);
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
/*判断q1和q2谁为空,谁为空就往谁里面去push*/
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) {
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else {
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1; //假设q1为空
Queue* nonEmptyQ = &obj->q2; //假设q2不为空
/*如果假设错误,那么就重新交换*/
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) {
emptyQ = &obj->q2;
nonEmptyQ = &obj->q1;
}
/*把非空队列的前N个数据,导入空队列里面去,剩下一个删掉,就实现了后进先出*/
while (QueueSize(nonEmptyQ) > 1) {
int front = QueueFront(nonEmptyQ);
QueuePush(emptyQ, front); //把非空队列里面的队头的数据放到空里面去
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ); //删除队头的元素
}
// 此时还剩下一个,把他删掉
int top = QueueFront(nonEmptyQ);
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
/**/
if (!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) {
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else {
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
/*先销毁q1和q2*/
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
/** * Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack* obj = myStackCreate(); * myStackPush(obj, x); * int param_2 = myStackPop(obj); * int param_3 = myStackTop(obj); * bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj); * myStackFree(obj); */
提交结果
边栏推荐
- The R language uses the ggtexttable function of the ggpubr package to visualize the table data (draw the table directly or add the table data to the image), set the theme parameter to customize the fi
- 关于#oracle#的问题,如何解决?
- After 21 years of graduation, I switched to software testing. From 0 income to a monthly salary of over 10,000, I am really lucky...
- Event object, do you know it well?
- Shell脚本实现多选DNS同时批量解析域名IP地址(新更新)
- wireshark的安装教程(暖气片安装方法图解)
- 为什么要使用BGP?
- MySql千万级分页优化,快速插入千万数据方法
- Event 对象,你很了解吗?
- LayaBox---TypeScript---命名空间和模块
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
LayaBox---TypeScript---Symbols
4年手工测试被应届生取代了,用血与泪的教训给xdm一个忠告,该学自动化了...
R语言ggplot2可视化:使用ggpubr包的ggtexttable函数可视化表格数据(直接绘制表格图或者在图像中添加表格数据)、使用tbody_add_border为表格中的表头添加外侧框线
qq邮箱日发5万邮件群发技术(qq邮箱怎样定时发送邮件)
太帅了!我用炫酷大屏展示爬虫数据!
LayaBox---TypeScript---命名空间和模块
Geoffery Hinton:深度学习的下一个大事件
神通数据库,批量插入数据的时候失败
yolov7 innovation point
情景剧《重走长征路》上演
转转反爬攻防战
循环结构--do-while循环
后管实现面包屑功能
从零开始Blazor Server(5)--权限验证
Linux system uninstall, install, upgrade, migrate clickHouse database
R language ggplot2 visualization: use the ggtexttable function of the ggpubr package to visualize tabular data (directly draw tabular graphs or add tabular data to images), use tbody_add_border to add
全新荣威RX5,27寸大屏吸引人,安全、舒适一个不落
R语言ggplot2可视化:基于aes函数中的fill参数和shape参数自定义绘制分组折线图并添加数据点(散点)、使用theme函数的legend.position函数配置图例到图像右侧
一款优秀的中文识别库——ocr
List-based queuing and calling system